Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
bio 2
front 1 The structural integrity of bacteria is to peptidoglycan as the structural integrity of plant spores is to
| back 1 D |
front 2 Commonalities to both charophytes and vascular land plants include
3 chlorophyll a. 4 cellulose. 5 chlorophyll b.
| back 2 B |
front 3 According to our current knowledge of plant evolution, which group of organisms should feature mitosis most similar to that of land plants?
| back 3 C |
front 4 On a field trip, a student in a marine biology class collects an organism that has differentiated organs, cell walls of cellulose, and chloroplasts with chlorophyll a. Based on this description, the organism could be a brown alga, a red alga, a green alga, a charophyte recently washed into the ocean from a freshwater or brackish water source, or a land plant washed into the ocean. The presence of which of the following features would definitively identify this organism as a land plant?
| back 4 D |
front 5 Some green algae exhibit alternation of generations. All land plants exhibit alternation of generations. No charophytes exhibit alternation of generations. Keeping in mind the recent evidence from molecular systematics, the correct interpretation of these observations is that
| back 5 B |
front 6 Which taxon is essentially equivalent to the "embryophytes"?
| back 6 B |
front 7 The functional role of sporopollenin is primarily to
| back 7 B |
front 8 If the kingdom Plantae is someday expanded to include the charophytes, then the shared derived characteristics of the kingdom will include
| back 8 A |
front 9 Challenges for survival of the first land plants include
III. desiccation.
| back 9 D |
front 10 Adaptations in plants to life on land include
III. tracheids.
| back 10 D |
front 11 Mitotic activity by the apical meristem of a root makes which of the following more possible?
| back 11 A |
front 12 Which of the following is a true statement about plant reproduction?
| back 12 B |
front 13 The leaflike appendages of moss gametophytes may be one to two cell layers thick. Consequently, which of the following is least likely to be found associated with such appendages?
| back 13 C |
front 14 Considering that the mature sporophytes of true mosses get their nutrition from the gametophytes on which they grow, and considering these generations as individual plants, what is true of the relationship between true moss sporophytes and gametophytes?
| back 14 D |
front 15 Which of the following characteristics helped seedless plants better adapt to life on land?
| back 15 D |
front 16 Arrange the following terms from most inclusive to least inclusive.
| back 16 B |
front 17 Evidence indicates that plants increase the number of stomata in their leaves as atmospheric CO2 levels decline. Increasing the number of stomata per unit surface area should have the effect of doing which of the following?
| back 17 B |
front 18 Which of the following should have had gene sequences most similar to the charophyte that was the common ancestor of the land plants?
| back 18 B |
front 19 If intelligent extraterrestrials visited Earth 475 million years ago, and then again 300 million years ago (at the close of the Carboniferous period), what trends would they have noticed in Earth's terrestrial vegetation over this period?
| back 19 D |
front 20 In seed plants, which of the following is part of a pollen grain and has a function most like that of the seed coat?
| back 20 C |
front 21 A botanist discovers a new species of land plant with a dominant sporophyte, chlorophylls a and b, and cell walls made of cellulose. In assigning this plant to a phylum, which of the following, if present, would be least useful?
| back 21 E |
front 22 Fossil fungi date back to the origin and early evolution of plants. What combination of environmental and morphological change is similar in the evolution of both fungi and plants?
| back 22 D |
front 23 If all fungi in an environment that perform decomposition were to suddenly die, then which group of organisms should benefit most, due to the fact that their fungal competitors have been removed?
| back 23 C |
front 24 When a mycelium infiltrates an unexploited source of dead organic matter, what are most likely to appear within the food source soon thereafter?
| back 24 B |
front 25 Which of the following is a characteristic of hyphate fungi (fungi featuring hyphae)?
| back 25 D |
front 26 The vegetative (nutritionally active) bodies of most fungi are
III. usually underground.
| back 26 E |
front 27 Immediately after karyogamy occurs, which term applies?
| back 27 D |
front 28 Which description applies equally well to fungal spores produced both sexually and asexually?
III. They are produced in large numbers.
| back 28 E |
front 29 Plasmogamy can directly result in which of the following?
III. cells with two diploid nuclei
| back 29 B |
front 30 Which process occurs in fungi and has the opposite effect on a cell's chromosome number than does meiosis?
| back 30 E |
front 31 When pathogenic fungi are found growing on the roots of grape vines, grape farmers sometimes respond by covering the ground around their vines with plastic sheeting and pumping a gaseous fungicide into the soil. The most important concern of grape farmers who engage in this practice should be that the
| back 31 C |
front 32 Which of the following terms refers to symbiotic relationships that involve fungi living between the cells in plant leaves?
| back 32 C |
front 33 In which of the following plant groups does the mature sporophyte depend completely on the gametophyte for nutrition?
| back 33 A |
front 34 ) A botanist discovers a new species of plant in a tropical rain forest. After observing its anatomy and life cycle, he notes the following characteristics: flagellated sperm, xylem with tracheids, separate gametophyte and sporophyte generations with the sporophyte dominant, and no seeds. This plant is probably most closely related to
| back 34 C |
front 35 You are hiking in a forest and come upon a mysterious plant, which you believe to be a lycophyte or a monilophyte. Which of the following would be most helpful in determining the correct classification of the plant?
| back 35 B |
front 36 Sporophylls can be found in which of the following?
| back 36 D |
front 37 Assuming that they all belong to the same plant, arrange the following structures from largest to smallest (or from most inclusive to least inclusive).
| back 37 E |
front 38 If humans had been present to build house structures during the Carboniferous period, which plant types would have been possible building materials?
| back 38 D |
front 39 Which of the following is true of seedless vascular plants?
| back 39 B |
front 40 Which group is noted for the independence of gametophyte and sporophyte generations from each other?
| back 40 A |
front 41 Suppose that the cells of seed plants, like the skin cells of humans, produce a pigment upon increased exposure to UV radiation. Rank the following cells, from greatest to least, in terms of the likelihood of producing this pigment.
| back 41 C |
front 42 Arrange the following in the correct sequence, from earliest to most recent, in which these plant traits originated.
| back 42 E |
front 43 How have fruits contributed to the success of angiosperms?
| back 43 B |
front 44 Arrange the following structures from largest to smallest, assuming that they belong to two generations of the same angiosperm.
| back 44 E |
front 45 Which of the following flower parts develops into a seed?
| back 45 A |
front 46 Which of the following flower parts develops into the pulp of a fleshy fruit?
| back 46 D |
front 47 Angiosperms are the most successful terrestrial plants. Which of the following features is unique to them and helps account for their success?
| back 47 C |
front 48 Which of the following is a true statement about angiosperm carpels?
| back 48 D |
front 49 The generative cell of male angiosperm gametophytes is haploid. This cell divides to produce two haploid sperm cells. What type of cell division does the generative cell undergo to produce these sperm cells?
| back 49 B |
front 50 What adaptations should one expect of the seed coats of angiosperm species whose seeds are dispersed by frugivorous (fruit-eating) animals, as opposed to angiosperm species whose seeds are dispersed by other means?
| back 50 D |
front 51 Which of the following are structures of angiosperm gametophytes?
| back 51 B |
front 52 Which of the following is true concerning flowering plants?
| back 52 A |
front 53 Which of the following sex and generation combinations most directly produces the megasporangium of pine ovules?
| back 53 D |
front 54 Which of the following sex and generation combinations most directly produces the fruit?
| back 54 D |
front 55 Which of the following sex and generation combinations most directly produces the integument of a pine seed?
| back 55 D |
front 56 Which of the following sex and generation combinations most directly produces the pollen tube?
| back 56 A |
front 57 What is true of stamens, sepals, petals, and carpels?
| back 57 C |
front 58 Which structure protects seed plants' embryos from desiccation?
| back 58 E |
front 59 Arrange the following structures, which can be found on male pine trees, from the largest structure to the smallest structure (or from most inclusive to least inclusive).
| back 59 A |
front 60 hich trait(s) is (are) shared by many modern gymnosperms and angiosperms?
| back 60 D |
front 61 Which structure is common to both gymnosperms and angiosperms?
| back 61 C |
front 62 Which of the following can be found in gymnosperms?
| back 62 C |
front 63 Which of the following statements is true of the pine life cycle?
| back 63 D |
front 64 Within a gymnosperm megasporangium, what is the correct sequence in which the following should appear during development, assuming that fertilization occurs?
| back 64 B |
front 65 Generally, wind pollination is most likely to be found in seed plants that grow
| back 65 B |
front 66 Which of the following statements correctly describes a portion of the pine life cycle?
| back 66 A |
front 67 A researcher has developed two stains for use with seed plants. One stains sporophyte tissue blue; the other stains gametophyte tissue red. If the researcher exposes pollen grains to both stains and then rinses away the excess stain, what will occur?
| back 67 C |
front 68 Gymnosperms differ from both extinct and extant (living) ferns because they
| back 68 C |
front 69 Which of the following is most important in making the typical seed more resistant to adverse conditions than the typical spore?
| back 69 C |
front 70 Which of the following cellular structures is functionally important in cells of the gametophytes of both angiosperms and gymnosperms?
| back 70 C |
front 71 The seed coat's most important function is to provide
| back 71 E |
front 72 In addition to seeds, which of the following characteristics is unique to the seed-producing plants?
| back 72 C |
front 73 What is thought to be the correct sequence of the following events during the Carboniferous period?
| back 73 A |
front 74 The fruit of the mistletoe, a parasitic angiosperm, is a one-seeded berry. In members of the genus Viscum, the outside of the seed is viscous (sticky), which permits the seed to adhere to surfaces, such as the branches of host plants or the beaks of birds. What should be expected of the fruit if the viscosity of Viscum seeds is primarily an adaptation for dispersal rather than an adaptation for infecting host plant tissues?
| back 74 C |
front 75 What is the greatest threat to plant diversity?
| back 75 E |
front 76 The microsporidian Brachiola gambiae parasitizes the mosquito Anopheles gambiae. Adult female mosquitoes must take blood meals in order for their eggs to develop, and it is while they take blood that they transmit malarial parasites to humans. Male mosquitoes drink flower nectar. If humans are to safely and effectively use Brachiola gambiae as a biological control to reduce human deaths from malaria, then how many of the following statements should be true?
| back 76 C |
front 77 Lichens are symbiotic associations of fungi and
III. green algae.
| back 77 B |
front 78 In both lichens and mycorrhizae, what does the fungal partner provide to its photosynthetic partner?
| back 78 D |
front 79 Which of the following is a characteristic of all angiosperms?
| back 79 B |
front 80 Which of the following statements are true of monocots?
III. Monocots are most closely related to eudicots.
| back 80 D |
front 81 What do fungi and arthropods have in common?
| back 81 C |
front 82 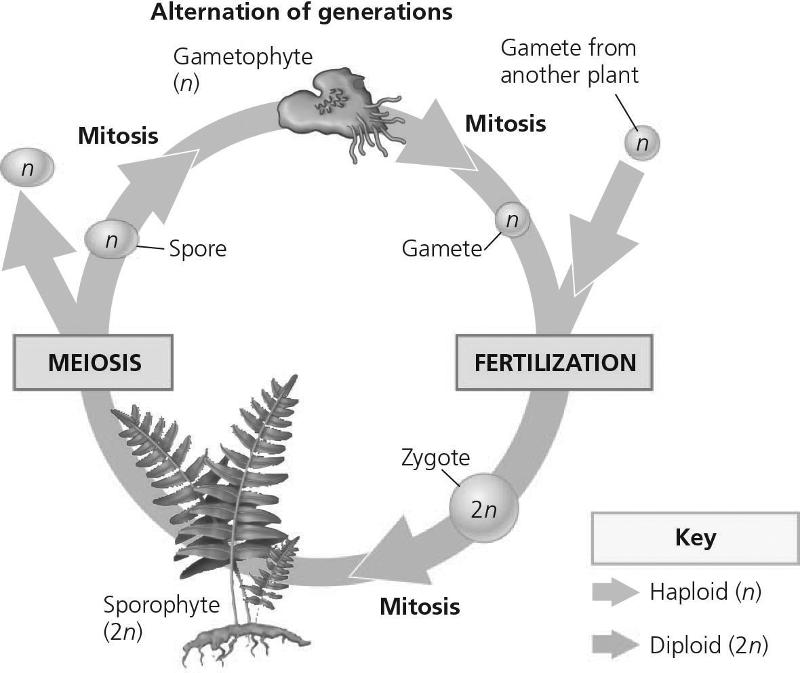 In the figure, which number produces haploid gametes by mitosis?
| back 82 A |
front 83 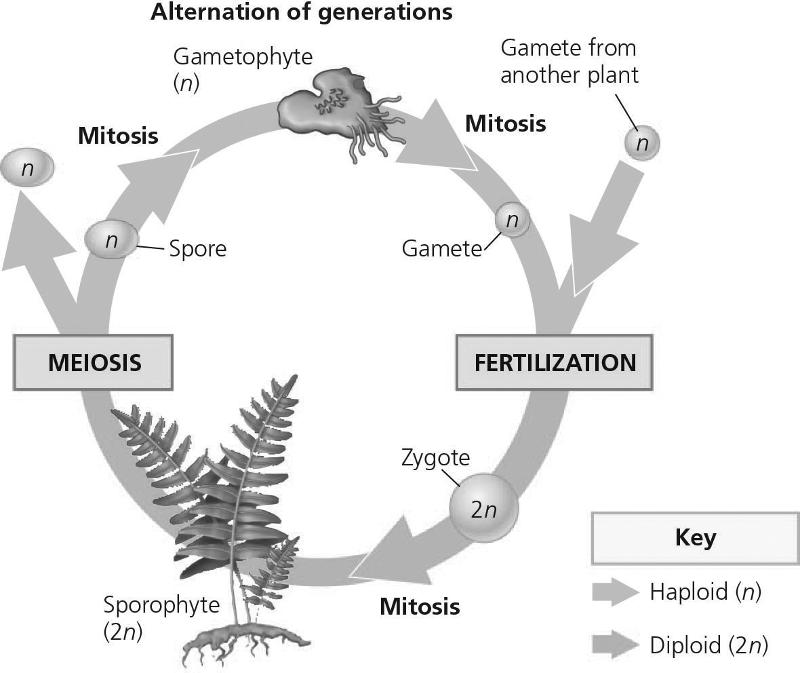 In the figure, which structure produces haploid spores by meiosis?
| back 83 C |
front 84 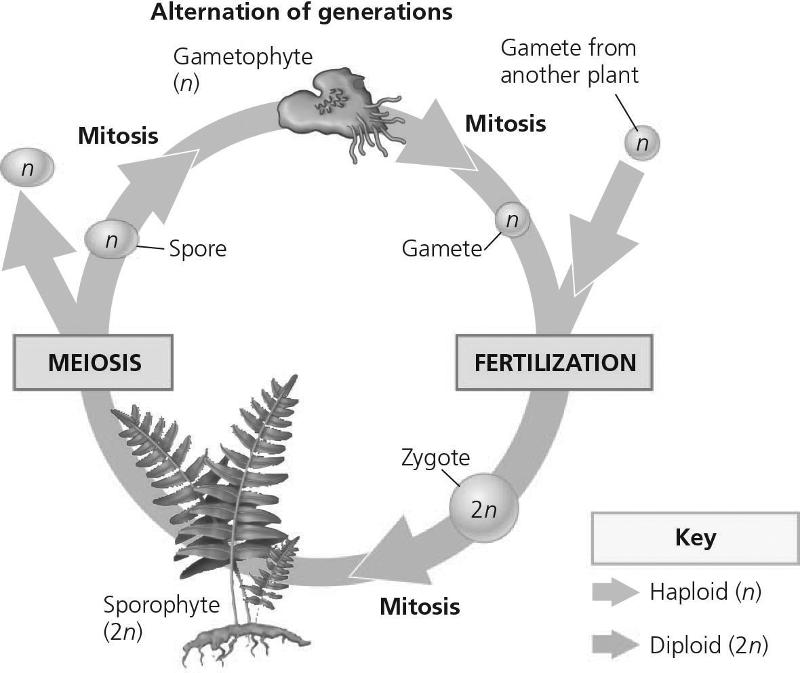 Meiosis is most likely to be represented by which number?
| back 84 B |
front 85 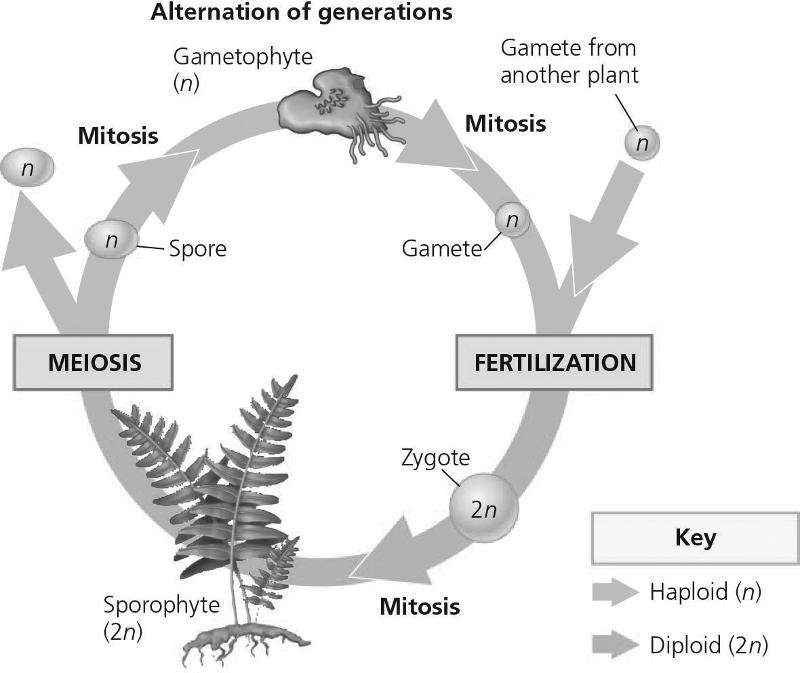 What describes the product of number 2?
| back 85 D |
front 86 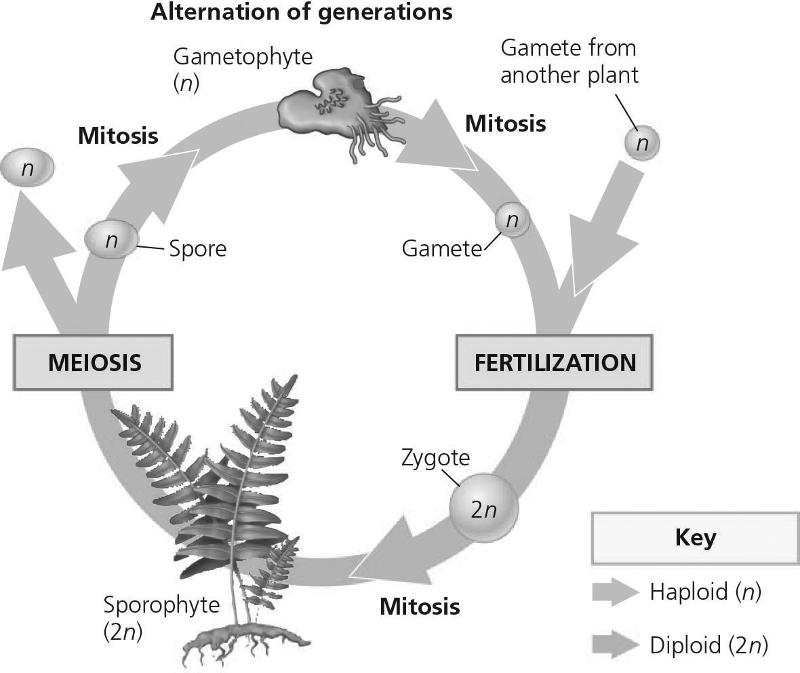 In the figure, what are the processes for numbers 4, 5, and 6, respectively?
| back 86 C |
front 87 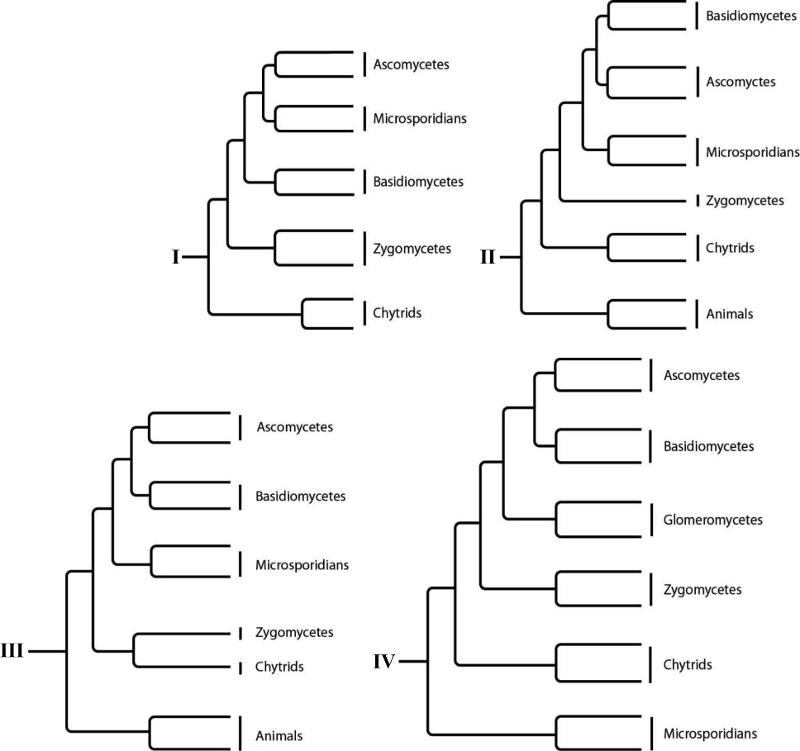 Which tree depicts all of the currently recognized major groups of fungi?
| back 87 C |
front 88 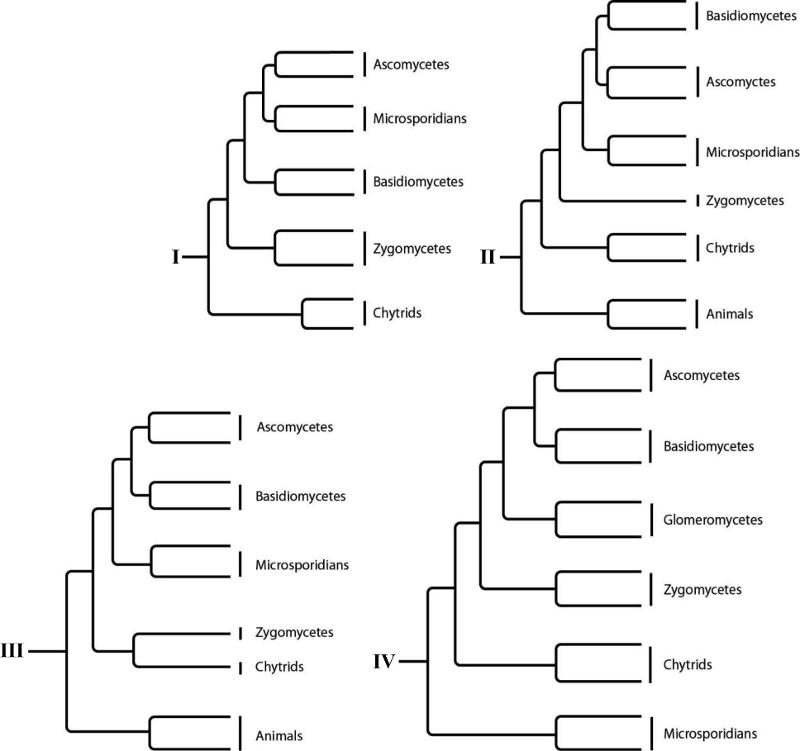 Which tree depicts the closest relationship between zygomycetes and chytrids?
| back 88 C |
front 89 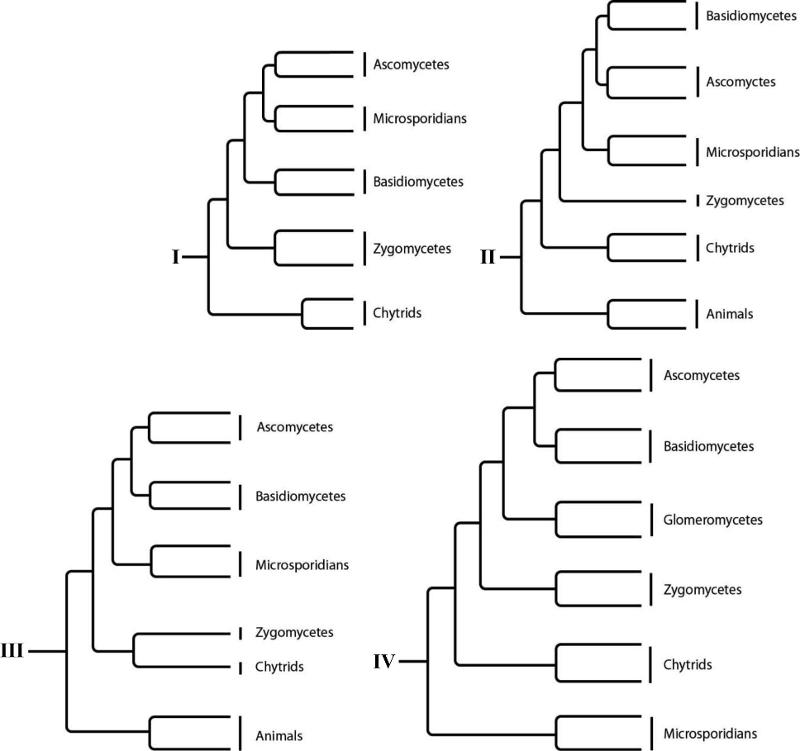 In phylogenetic tree I, which group of organisms is most directly related to the common ancestor of the tree?
| back 89 D |
front 90  What is true of the phylogenetic tree in the figure?
| back 90 B |
front 91 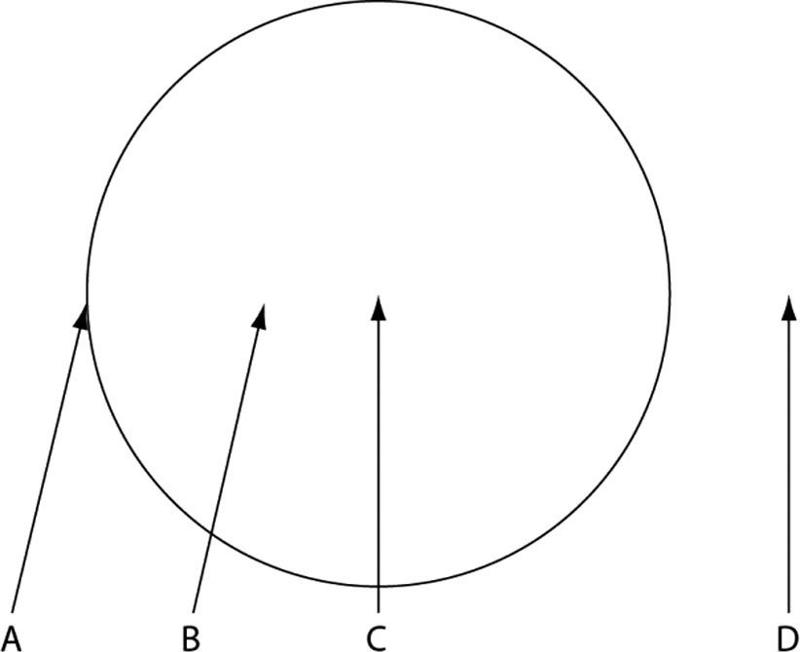 1) What is the most probable location of the oldest portion of this mycelium?
| back 91 C |