Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
MIDTERM 2 biology
front 1 2) Starting with a fertilized egg (zygote), a series of five cell
divisions would produce an early embryo with how many cells? | back 1 D)32 |
front 2 For a newly evolving protist, what would be the advantage of using
eukaryote-like cell division rather than binary fission? | back 2 B) Cell division would allow for the orderly and efficient segregation of multiple linear chromosomes. |
front 3 Suppose a biologist can separate one of a dozen pieces of chromatin
from a eukaryotic (animal) nucleus. It might consist of which of the
following? | back 3 D) two long strands of DNA plus proteins |
front 4 6) At which phase are centrioles beginning to move apart in animal
cells? | back 4 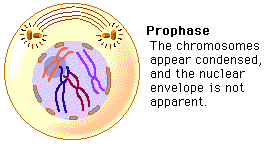 E) PROPHASE |
front 5 7) If cells in the process of dividing are subjected to colchicine, a
drug that interferes with the formation of the spindle
apparatus, at which stage will mitosis be arrested? | back 5 D) metaphase formation of the spindle apparatus |
front 6 If there are 20 centromeres in a cell at anaphase, how many
chromosomes are there in each daughter cell following cytokinesis?
| back 6 A) 10 |
front 7 Where do the microtubules of the spindle originate during mitosis in
both plant and animal cells? | back 7 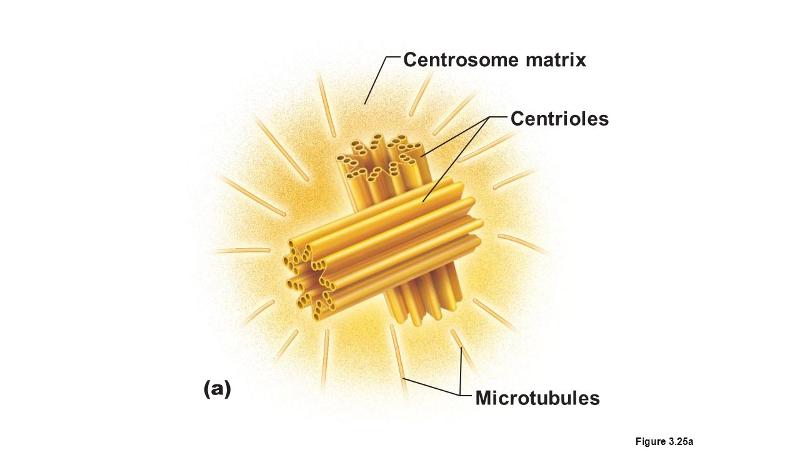 B) centrosome |
front 8 Taxol is an anticancer drug extracted from the Pacific yew tree. In
animal cells, Taxol disrupts microtubule formation by binding to
microtubules and accelerating their assembly from the protein
precursor, tubulin. Surprisingly, this stops mitosis. Specifically,
Taxol must affect | back 8 A) the formation of the mitotic spindle. |
front 9 Which of the following are primarily responsible for cytokinesis in
plant cells but not in animal cells? | back 9 B) Golgi-derived vesicles |
front 10 In which group of eukaryotic organisms does the nuclear envelope
remain intact during mitosis? | back 10 D) dinoflagellates and diatoms only research!!! |
front 11 A group of cells is assayed for DNA content immediately following
mitosis and is found to have an average of 8 picograms of DNA per
nucleus. How many picograms would be found at the end of S and the end
of G₂? | back 11 D) 16; 16 |
front 12 For anaphase to begin, which of the following must occur? | back 12 C) Cohesin must be cleaved enzymatically. |
front 13 Which of the following best describes how chromosomes move toward the
poles of the spindle during mitosis? | back 13 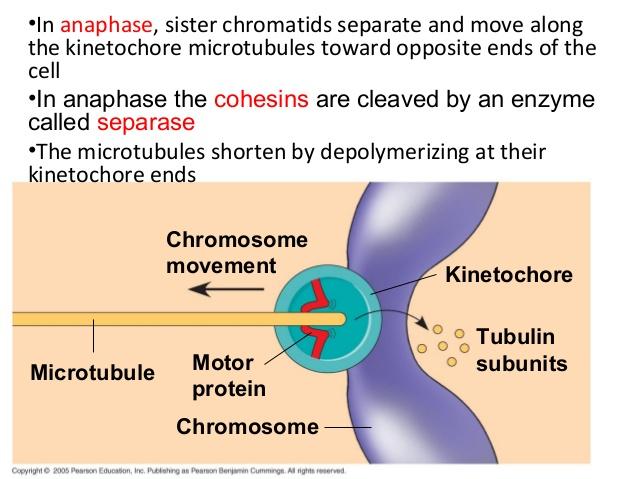 D) The chromosomes are "reeled in" by the contraction of spindle microtubules, and motor proteins of the kinetochores move the chromosomes along the spindle microtubules. |
front 14 Which of the following is a function of those spindle microtubules
that do not attach to kinetochores? | back 14 D) maintaining the region of overlap of microtubules in the cell's center |
front 15 During which phase of mitosis do the chromatids become chromosomes? A) telophase | back 15 A) telophase |
front 16 The human genome is minimally contained in which of the following? A) every human cell | back 16 A) every human cell |
front 17 In the human species, all somatic cells have 46 chromosomes. Which of the following can also be true? A) A plant species (privet shrubs) has 46 chromosomes per cell.
| back 17 A) A plant species (privet shrubs) has 46 chromosomes per cell. |
front 18 Which of the following is a true statement about sexual vs. asexual
reproduction? | back 18 B) In sexual reproduction, individuals transmit 50% of their genes to each of their offspring. |
front 19 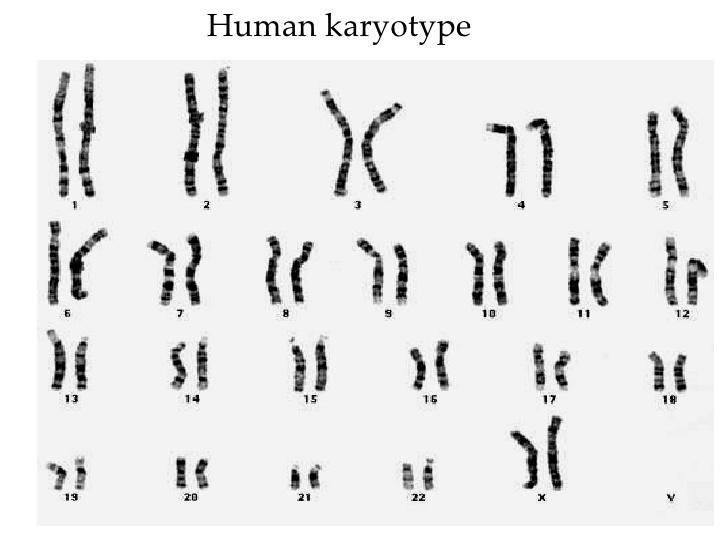 At which stage of mitosis are chromosomes usually photographed in the
preparation of a karyotype? | back 19 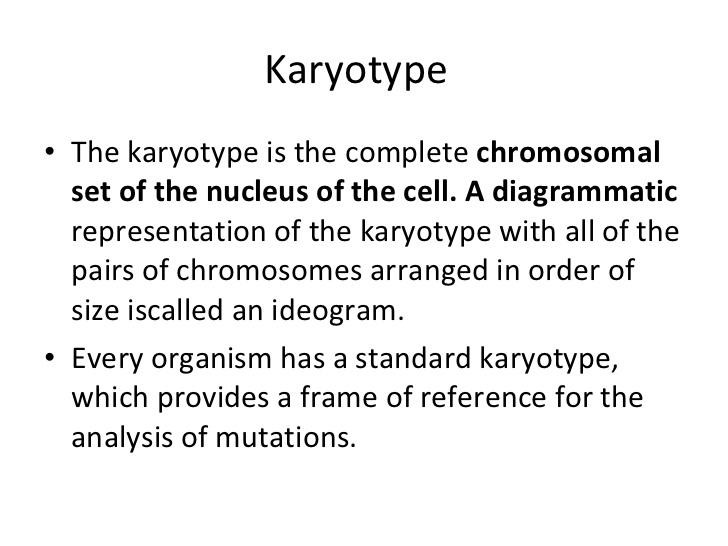 B) metaphase |
front 20 Which of the following defines a genome? | back 20 E) the complete set of an organism's genes Answer: E |
front 21 Which of the following is true of a species that has a chromosome
number of 2n = 16? | back 21 C) Each cell has eight homologous pairs. |
front 22 Eukaryotic sexual life cycles show tremendous variation. Of the
following elements, which do all sexual life cycles have in common?
| back 22 C) II, III, and IV |
front 23 Which of these statements is false? | back 23 D) At sexual maturity, ovaries and testes produce diploid gametes by meiosis. |
front 24 Referring to a plant's sexual life cycle, which of the following
terms describes the process that leads directly to the formation of
gametes? | back 24 B) gametophyte mitosis |
front 25 Which of the following is an example of alternation of generations?
| back 25 B) A diploid plant (sporophyte) produces, by meiosis, a spore that gives rise to a multicellular, haploid pollen grain (gametophyte). |
front 26 The karyotype of one species of primate has 48 chromosomes. In a
particular female, cell division goes awry and she produces one of her
eggs with an extra chromosome (25). The most probable source of this
error would be a mistake in which of the following? | back 26 E) either anaphase 1 and 2 |
front 27 A given organism has 46 chromosomes in its karyotype. We can
therefore conclude which of the following? | back 27 E) Its gametes must have 23 chromosomes. |
front 28 A triploid cell contains three sets of chromosomes. If a cell of a
usually diploid species with 42 chromosomes per cell is triploid, this
cell would be expected to have which of the following? | back 28 B) 63 chromosomes in 21 sets of 3 |
front 29 A karyotype results from which of the following? | back 29 C) the ordering of human chromosome images |
front 30 Which of the following best describes a karyotype? | back 30 B) a display of each of the chromosomes of a single cell |
front 31 If a cell has completed the first meiotic division and is just
beginning meiosis II, which of the following is an appropriate
description of its contents? | back 31 A) It has half the amount of DNA as the cell that began meiosis. |
front 32 Which of the following can utilize both mitosis and meiosis in the
correct circumstances? | back 32 D) a plantlike protist |
front 33 Which of the following might result in a human zygote with 45
chromosomes? | back 33 A) an error in either egg or sperm meiotic anaphase |
front 34 Which of the following was a discovery that had to be made before
human chromosomes could be correctly counted? | back 34 A) how to use a hypotonic solution to swell nuclei |
front 35 Which of the following is (are) required for motor proteins to
function in the movement of chromosomes toward the poles of the
mitotic spindle? | back 35 D) ATP as an energy source |
front 36 Which of the following proteins are involved in binary fission as
well as eukaryotic mitotic division? | back 36 D) actin and tubulin |
front 37 Using which of the following techniques would enable your lab group
to distinguish between a cell in G₂ and a cell from the same organism
in G₁? | back 37 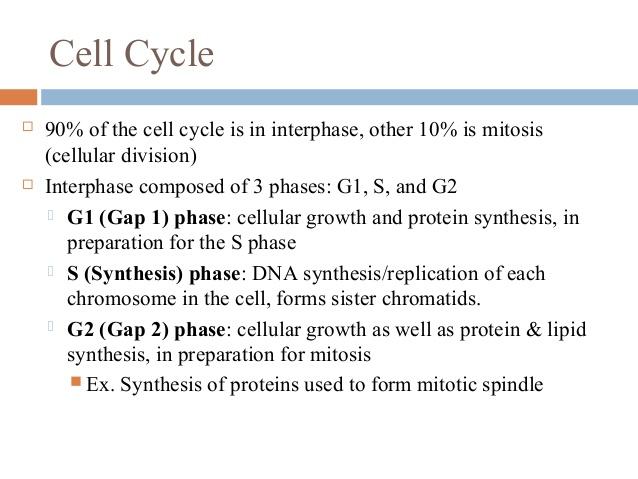 D) radioactive-labeled nucleotides |
front 38 You have the technology necessary to measure each of the following in
a sample of animal cells: chlorophylls, organelle density, picograms
of DNA, cell wall components, and enzymatic activity. Which would you
expect to increase significantly from M to G₁? | back 38 A) organelle density and enzymatic activity |
front 39 A plant-derived protein known as colchicine can be used to poison
cells by blocking the formation of the spindle. Which of the following
would result if colchicine is added to a sample of cells in G₂? | back 39 C) The chromosomes would coil and shorten but have no spindle to which to attach. |
front 40 What causes the decrease in the amount of cyclin at a specific point
in the cell cycle? | back 40 D) its destruction by a process initiated by the activity of its complex with a cyclin |
front 41 Which of the following is released by platelets in the vicinity of an
injury? | back 41 A) PDGF Тромбоцитарный фактор роста Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) is one of the numerous growth factors or proteins that regulate cell growth and division. In particular, it plays a significant role in blood vessel formation (angiogenesis), the growth of blood vessels from already-existing blood vessel tissue |
front 42 Which of the following is a protein synthesized at specific times
during the cell cycle that associates with a kinase to form a
catalytically active complex? | back 42 D) cyclin |
front 43 Proteins that are involved in the regulation of the cell cycle, and
that show fluctuations in concentration during the cell cycle, are
called | back 43 E) cyclins |
front 44 A mutation results in a cell that no longer produces a normal protein
kinase for the M phase checkpoint. Which of the following would likely
be the immediate result of this mutation? | back 44 E) The cell would undergo normal mitosis, but fail to enter the next G₁ phase. |
front 45 Which of the following is true concerning cancer cells? | back 45 E) When they stop dividing, they do so at random points in the cell cycle; they are not subject to cell cycle controls; and they do not exhibit density-dependent inhibition when growing in culture |
front 46 Besides the ability of some cancer cells to overproliferate, what
else could logically result in a tumor? | back 46 C) lack of appropriate cell death |
front 47 After which checkpoint is the cell first committed to continue the
cell cycle through M? | back 47 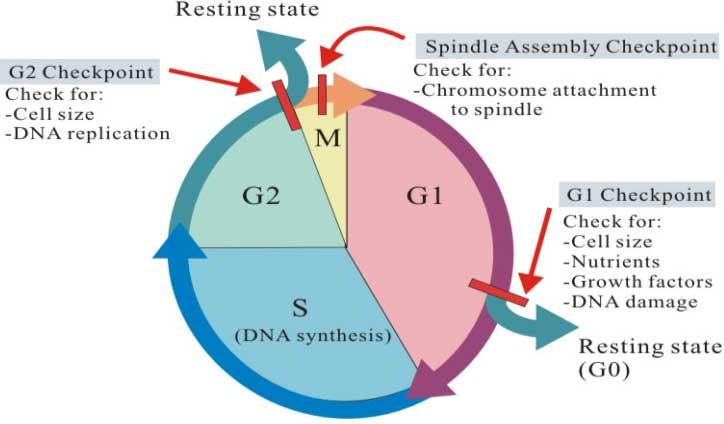 B) G₁ |
front 48 Why do neurons and some other specialized cells divide infrequently? A) They no longer have active nuclei. | back 48 C) They have been shunted into G₀. |
front 49 All cell cycle checkpoints are similar in which way? A) They respond to the same cyclins. | back 49 E) They activate or inactivate other proteins |
front 50 At the M phase checkpoint, the complex allows for what to occur? A) Separase enzyme cleaves cohesins and allows chromatids to
separate. | back 50 A) Separase enzyme cleaves cohesins and allows chromatids to separate. |
front 51 For the following question, match the key event of meiosis with the
stages listed below. Tetrads of chromosomes are aligned at the equator of the spindle;
alignment determines independent assortment. | back 51 B) II |
front 52 Which of the following best describes the frequency of crossing over
in mammals? | back 52 C) at least 1-2 per chromosome pair |