Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
The Eukaryotes: Fungi, Algae, Protozoa, and Helminths
front 1 Which of the following statements regarding fungi is false | back 1 most fungi are pathogenic for humans |
front 2 Which of the following statements about helminths is false | back 2 all are parasites |
front 3 which of the following pairs is mismatched | back 3 coenocytic hyphae - hyphae with cross-walls |
front 4 which of the following statements regarding protozoa is false | back 4 nearly all protozoa causes disease |
front 5 In mid December, a woman with insulin dependent diabetes which had been in prednisone fell and received an abrasion on the dorsal side of her right hand. She was placed on penicillin. By the end of January, the ulcer had not healed, and she was referred to a plastic surgeon. On January 30, a swab of wound was cultured at 35 degrees on agar. On the same day, a smear was made for gram staining. Slid cultures set up on February 1 and incubated at 25 degrees showed septate hypae and single conidia. The most likely cause of the infection is a | back 5 dimorphic fungus |
front 6 which of the following tends to be more complex in a parasitic helminth than in a free living helminths | back 6 reproductive system |
front 7 Which of the following is false | back 7 fungal spores are highly resistant to heat and chemical agents |
front 8 helminthic diseases are usually transmitted to humans by | back 8 gastrointestinal route |
front 9 All of the following are characteristic of the platyhelminthes except that they | back 9 have highly developed digestive and nervous systems |
front 10 in the malaria parasite life cycle, humans are the ____ host, while mosquitoes are the ___ host as well as the vector | back 10 intermediate; definitive |
front 11 Three weeks after a river rafting trip, three family members experienced symptoms of coughing, fever, and chest pain. During the rafting trip, the family had consumed crayfish that they caught along the river banks. An examination of the patients' sputum revealed helminth eggs, and serum samples were positive for antibodies to Paragonimus. All of the family members recovered following treatment with praziquantel. In the Paragonimus life cycle, | back 11 Humans are the definitive host and crayfish are the intermediate host |
front 12 The encysted larva of the beef tapeworm is called | back 12 cysticercus |
front 13 Which of the following arthropods does not transmit diseases by sucking blood from human host | back 13 houseflies |
front 14 a definitive host harbors which stage of a parasite | back 14 adult |
front 15 what do tapeworms eat | back 15 intestinal contents |
front 16 Giardia and Trichomonas are unusual eukaryotes because they | back 16 lack mitochondria |
front 17 The life cycle of the fish tapeworm is similar to that of the beef tapeworm. Which of the following is the most effective preventive measure? | back 17 cooking fish before eating |
front 18 Which of the following is the most effective control for malaria | back 18 eliminate Anopheles mosquitoes |
front 19 In the microscope, you observe multinucleated amoebid cells with sporangia that form spores. This is a | back 19 plasmodial slime mold |
front 20 Which of the following pairs is mismatched | back 20 cestodes - all are free living |
front 21 which of the following is a nucleated, unicecullar organism that, if you changed the incubation temperature, would form filaments with conidiospores | back 21 ascomycete |
front 22 which of the following organisms is photoautotrophic protozoan | back 22 Euglena |
front 23 if a larva of Echinococcus granulosus is found in humans, humans are the | back 23 intermediate host |
front 24 ringworm is caused by | back 24 fungus |
front 25 yeast infections are caused by | back 25 candida albicans |
front 26 plasmogamy, karyogamy, and meiosis are stages of the fungal sexual life cycle | back 26 true |
front 27 arthropod vectors are blood sucking animals such as ticks, lice and fleas that transmit microbial pathogens | back 27 true |
front 28 cercariae, metacercaria, redia, and sporocysts are all life cycle stages of trematodes | back 28 true |
front 29 the platyhelminths group includes roundworms, tapeworms, and flukes | back 29 false |
front 30 some species of dinoflagellates produce neurotoxins that cause fish kills and red tides. | back 30 true |
front 31 both the cellular slime molds and the plasmodial slime molds are members of the phylum amoebozoa | back 31 true |
front 32 In helminth life cycles, the organism that harbors the adult sexually reproductive phase of the parasite is called the intermediate host. | back 32 false |
front 33 The sporozoite, merozoite, gametocyte, and ring stages are all part of the Plasmodium life cycle. | back 33 true |
front 34 The insect vectors have six legs and include spiders, ticks, mosquitoes, and lice. | back 34 false |
front 35 Most cases of hookworm infection are acquired by ingestion of adult forms in contaminated food or water. | back 35 false |
front 36 Protozoa are unicellular, eukaryotic chemoheterotrophs | back 36 true |
front 37 organisms belonging to apicomplexa are plasmodium and cryptosporidium | back 37 true |
front 38 Parasitic flatworms belong to the Phylum Nematoda and Parasitic roundworms belong to the Phylum Platyhelminthes | back 38 false |
front 39 The adult stage of a parasitic helminth is found in the definitive host | back 39 true |
front 40 The nematodes that infect humans with their larvae include Ancylostoma duodenale and Trichinella spiralis | back 40 true |
front 41 Fungi are aerobic or facultatively anaerobic chemoheterotrophs | back 41 true |
front 42 Zygospores are produced asexually | back 42 false |
front 43 the portion of a hypha that obtains nutrient is called the aerial hypha | back 43 false |
front 44 the cestode, or tapeworm, consists of the scolex and proglottids | back 44 true |
front 45 tapeworms and flukes are similar due to their incomplete digestive system and larval stage | back 45 true |
front 46 protozoan and helminthic diseases are difficult to treat because | back 46 their cells are structurally and functionally similar to human cells |
front 47 Which of the following tends to be more complex in a parasitic helminth than in free living helminths | back 47 reproductive system |
front 48 helminthic diseases are usually transmitted to humans by | back 48 gastrointestinal route |
front 49 which of the following is not a characteristic of parasitic platyhelminths | back 49 They have a complete digestive system |
front 50 cercariae, metacercaria, miracidia, and rediae are stages in the life cycle of | back 50 nematodes |
front 51 the encysted larva of the beef tapeworm is | back 51 cysticercus |
front 52 which of the following arthropods does not transmit diseases by sucking blood from human host | back 52 houseflies |
front 53 what is common between cestodes and trematodes | back 53 cuticle |
front 54 which of the following pairs is mismatched | back 54 lice - pneumocystis |
front 55 which of the following statements is false | back 55 fungal spores are resting spores to protect the fungus from adverse environmental conditions |
front 56 which of the following pair is mismatched | back 56 sporangiospore - formed within hyphae chlamydoconidium - formed in a sac |
front 57 which of the following is not a characteristic of parasitic platyhelminths | back 57 they have a complete digestive system |
front 58 what do tapeworms eat | back 58 intestinal contents |
front 59 The lifestyle of the fish tapeworm is similar to that of the beef tapeworm.Which of the following is the most effective preventive measure | back 59 cooking fish before eating |
front 60 multinucleated amoebalike cells that produce funguslike spores | back 60 plasmodial slime mold |
front 61 amoebalike vegetatie structures that produce sporangia | back 61 cellular slime mold |
front 62 a multicellular organism; the digestive tract has one opening | back 62 tapeworm |
front 63 an organism that can grow photoautotrophically in the light and chemoheterotrophically in the dark | back 63 euglena |
front 64 the cells of plasmodial slime molds can grow to several centimeters in diameter because | back 64 they distribute nutrients by cytoplasmic streaming |
front 65 ringworm is caused by | back 65 ascomycete |
front 66 why are fungal colonies described as vegetative structures? | back 66 because they're composed of the cells involved in catabolism and growth. |
front 67 what is the thallus | back 67 it is the body which consist of long filaments |
front 68 hyphae | back 68 long filaments which contains septa |
front 69 septa | back 69 divides fungi into distinct, uninucleate cell-like units. |
front 70 conenocytic hyphae | back 70 long continuous cells with many nuclei |
front 71 vegetative hypha | back 71 portion of the hypha that obtains nutrient |
front 72 aerial hyphae | back 72 concerned with reproduction |
front 73 fission yeasts | back 73 divides evenly to produce two new cells. parent cell elongates, nucleus divides and 2 offspring cells are produced. capable of facultative anaerobic growth. |
front 74 dimorphic fungi | back 74 can grow either as mold or yeast |
front 75 life cycle of fungi | back 75 filamentous fungi can reproduce asexually by fragmentation of the hyphae |
front 76 spores | back 76 formation of fungi reproduction, both sexually and asexually |
front 77 asexual spores | back 77 formed by the hyphae of one organism. produced through mitoses and cell division |
front 78 condiospore | back 78 unicellular or multicellular spore that is not enclosed in a sac |
front 79 conidia/conidiophore | back 79 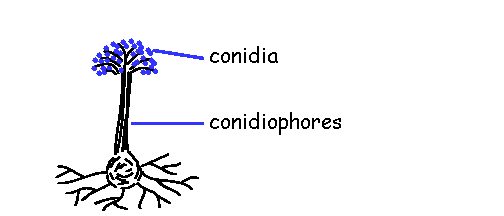 asexual spore conidia are produced in a chain at the end of conidiophore |
front 80 sporangiospore/sporangiophore | back 80 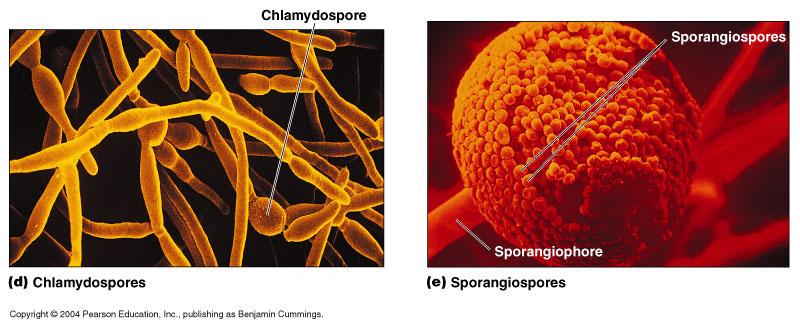 asexual spore sporangiospore is formed within a sporangium |
front 81 sexual spore | back 81 results from sexual reproduction 3 stages: phasmogamy, karyogamy, meiosis |
front 82 phasmogamy | back 82 haploid nucleus of donor cells (+) penetrates the cytoplasm of recipient (-) |
front 83 karyogamy | back 83 the (+) and (-) nuclei fuse to form a diploid zygote nucleus |
front 84 Meiosis | back 84 diploid give rise to haploid nuclei |
front 85 mycosis | back 85 fungal infection. it is classified into five groups based on degree of tissue involvement and mode of entry into the host |
front 86 systemic mycoses | back 86 fungal infection deep within the body. It is caused by fungi that live in the soil, it is spread by inhalation |
front 87 subcutaneous mycoses | back 87 fungal infections beneath the skin. It is caused by saprophytic fungi that live in soil and vegetation. Occurs by direct implantation into a wound |
front 88 cutaneous mycoses | back 88 fungi that only infect epidermis, hair, and nails. transmitted by direct contact with infected areas |
front 89 superficial mycoses | back 89 localized along hair shafts and in superficial epidermal cells |
front 90 opportunistic pathogen | back 90 generally harmless in its normal habitat but can become pathogenic in a host who is seriously traumatized. |
front 91 protozoa | back 91 unicellular eukaryotes and inhabits water and soil mostly aerobic heterotrophs and live in areas with large supply of water |
front 92 what is the stage of feeding of protozoa called what do they feed upon | back 92 trophozoite. They feed upon bacteria and small particle nutrients |
front 93 life cycle of protozoa | back 93 they reproduce asexually by fission, budding or schizogony |
front 94 what is schizogony | back 94 multiple fission. Nucleus undergoes multiple divisions before cell divides |
front 95 cyst | back 95 protective capsule that protozoa produce in adverse conditions. it permits the organism to survive when food, moisture or oxygen are lacking, temperature are not suitable, or when toxic chemicals are present. |
front 96 oocyst | back 96 cyst formed in members of the phylum apicomplexa. a reproductive structure in which new cells are produced asexually. |
front 97 Euglenozoa | back 97 2 groups based on rRNA sequences, disk-shaped mitochondria, and absence of sexual reproduction. Euglenoids and hemoflagellates |
front 98 Amebae | back 98 move by extending blunt, lobelike projections of pseudopods |
front 99 entamoeba histolytica | back 99 only pathogenic ameba found in human intestine. causes dysentery uses lectin to attache to galactose of plasma membrane and causes cell lysis |
front 100 aplicomplexa | back 100 not motile in their mature forms. obligate intracellular parasites |
front 101 sporozoite | back 101 an anopheles carrying the infective stage of plasmodium m |
front 102 merozoites | back 102 what is produced when sporozoites undergo schizogony |
front 103 what is the ring stage | back 103 when young trophozoite looks like a ring in which nucleus and cytoplasm are visible. |
front 104 definitve host | back 104 harbors the sexual reproducing stage of plasmodium |
front 105 intermediate host | back 105 host in which the parasite undergoes asexual reproduction |
front 106 what are the two phyla of helminths | back 106 platyhelminths (flatworms) nematodes (roundworms) |
front 107 what are some of the characteristics of helminths | back 107 they are multicellular eukaryotic animals they may lack digestive system their nervous system is reduced their means of movement is reduced or lacking reproductive system often complex |
front 108 larval | back 108 developmental stage of parasites |
front 109 dioecious | back 109 male reproductive organs are in one individual while the female reproductive organ is in another |
front 110 monoecious/hermaphroditic | back 110 one animal has both male and female reproductive organs |
front 111 trematodes (Flukes) | back 111 have flat, leaf-shaped bodies with ventral sucker and oral sucker. obtain food by absorbing it thought their cuticle |
front 112 paragonimus | back 112 lung fluke. occurs through the world |
front 113 cestodes (Tapeworm) | back 113 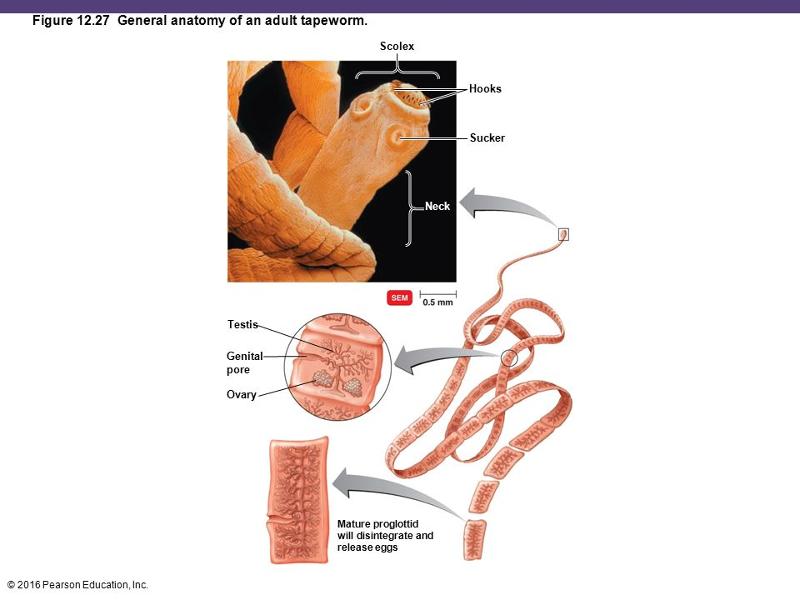 interstinal parasite. they lack a digestive system and absorb food through their cuticle |
front 114 taenia saginata | back 114 the beef tapeworm, lives in humans. |
front 115 taenia solium | back 115 pork tapeworm humans are the only definitive host |
front 116 echinococcus granulosus | back 116 humans are the intermediate hosts |
front 117 nematodes | back 117 roundworms they have complete digestive system the males are smaller than the females |
front 118 ascaris lumbricoides | back 118 a large nematode. it is dioecius with sexual diphormism |
front 119 define sexual dephormism | back 119 the male and female worms look distinctly different, the male being smaller with a curled tail |
front 120 ancylostoma duodenale | back 120 live in the small intestine of humans. eggs are excreted in feces. |
front 121 how does a larva enter its host | back 121 it penetrates the host's skin. it enters the blood or lymph vessel which carries it to the lungs. |