Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 8
front 1 Cardiac muscle makes most of its ATP via anaerobic pathways. | back 1 False |
front 2 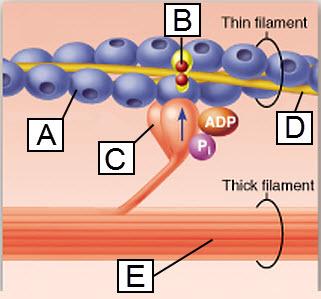 The protein actin is indicated by which letter? | back 2 A |
front 3 Peristalsis is characteristic of smooth muscle. | back 3 True |
front 4 Immediately following the arrival of the stimulus at a skeletal muscle cell there is a short period called the ________ period during which the neurotransmitter is released by exocytosis, diffuses across the synaptic cleft, and binds to its receptors. | back 4 latent |
front 5 Binding of calcium to calmodulin is a step in excitation-contraction coupling of ________ cells. | back 5 smooth muscle |
front 6 Which type of muscle CANNOT contract without being stimulated by the nervous system? | back 6 skeletal |
front 7 Muscle tissue has all of the following properties except ________. | back 7 secretion |
front 8 Once a motor neuron has fired, all the muscle fibers in a muscle contract. | back 8 False |
front 9 What structure in skeletal muscle cells functions in calcium storage? | back 9 sarcoplasmic reticulum |
front 10 Myoglobin ________. | back 10 stores oxygen in muscle cells |
front 11 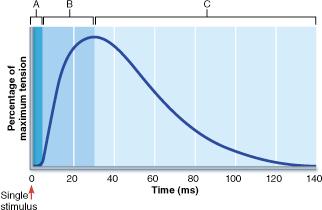 In which phase of the muscle twitch shown in the above figure would the maximum amount of ATP be consumed by myosin head groups? | back 11 B |
front 12 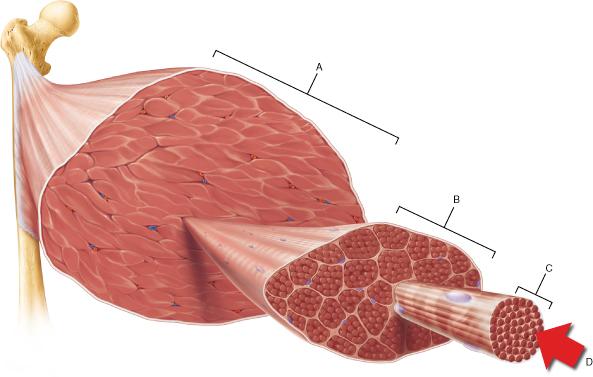 The connective tissue that covers structure A is continuous with which of the following? | back 12 tendon |
front 13 Which of the following surrounds the individual muscle cell? | back 13 endomysium |
front 14 The major role of the sarcoplasmic reticulum is to regulate ________. | back 14 intracellular levels of Ca2+ |
front 15 When a muscle is unable to respond to stimuli temporarily, it is in which of the following periods? | back 15 refractory period |
front 16 What produces the striations of a skeletal muscle cell? | back 16 the arrangement of myofilaments |
front 17 In an isotonic contraction, the muscle ________. | back 17 changes in length and moves the "load" |
front 18 The contractile units of skeletal muscles are ________. | back 18 myofibrils |
front 19 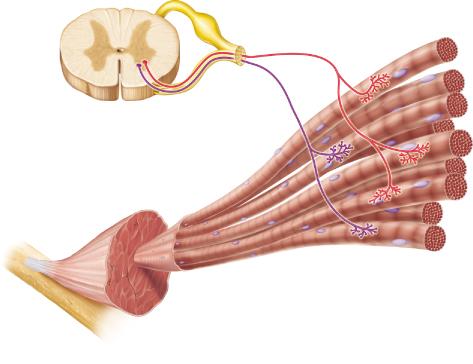 If both of the neurons in the figure were activated, more muscle fibers would contract than if either neuron alone were active. This mechanism for control of the force of muscle contraction is known as ______. | back 19 recruitment |
front 20 What is the functional unit of a skeletal muscle called? | back 20 a sarcomere |
front 21 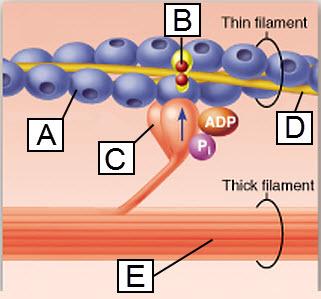 Which lettered protein functions as a motor protein? | back 21 C |
front 22 During muscle contraction, myosin cross bridges attach to which active sites? | back 22 actin filaments |
front 23 Most skeletal muscles contain ________. | back 23 a mixture of fiber types |
front 24 The smallest contractile unit of a muscle fiber is ________. | back 24 the sarcomere |
front 25 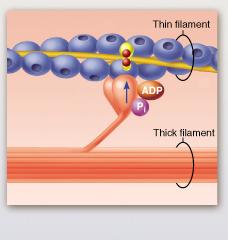 The protein troponin is shown in this figure to be bound to which substance? | back 25 calcium ion |
front 26 Although there are no sarcomeres, smooth muscle still possesses thick and thin filaments. | back 26 True |
front 27 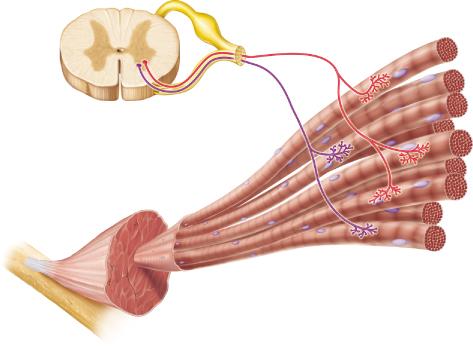 Which of the following describes the neurons shown in this figure? | back 27 somatic motor neurons |
front 28 What is the functional role of the T tubules? | back 28 enhance cellular communication during muscle contraction |
front 29 A muscle that is lengthening while it produces tension is performing a(an) ________ contraction. | back 29 eccentric |
front 30 A contraction in which the muscle does not shorten but its tension increases is called isometric contraction. | back 30 True |
front 31 Choose the FALSE statement. | back 31 Skeletal muscle cells use creatine phosphate instead of ATP to do work. |
front 32 The major function of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in muscle contraction is to ________. | back 32 regulate intracellular calcium concentration |
front 33 Three discrete types of muscle fibers are identified on the basis of their size, speed, and endurance. Which of the following athletic endeavors best represents the use of red fibers? | back 33 a long, relaxing swim |
front 34 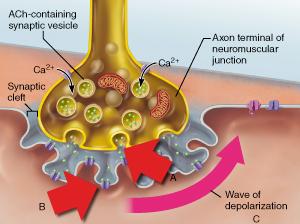 What cellular event is indicated by A? | back 34 exocytosis |
front 35 During isometric contraction, the energy used appears as movement. | back 35 False |
front 36 Isometric contraction leads to movement of a load. | back 36 False |
front 37 Which of the following is CORRECTLY paired? | back 37 skeletal muscle: voluntary control |
front 38 The distance between Z discs ________ during muscle contraction. | back 38 decreases |
front 39 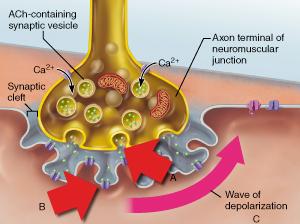 What event directly triggers the release of neurotransmitter shown in A? | back 39 diffusion of Ca2+ into the axonal terminus |
front 40 After nervous stimulation stops, what prevents ACh in the synaptic cleft from continuing to stimulate contraction | back 40 acetylcholinesterase destroying the ACh |
front 41 Which statement accurately describes the event indicated by B? | back 41 Binding of acetylcholine to a receptor triggers the opening of an ion channel. |
front 42 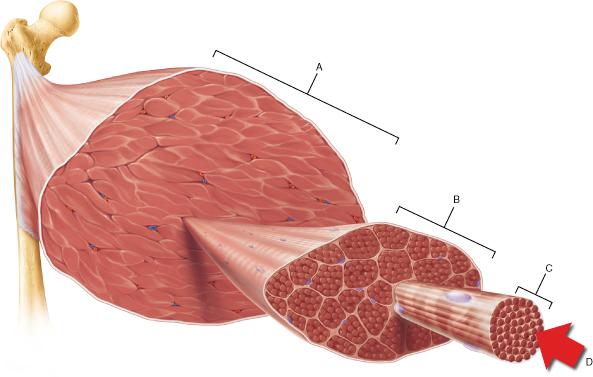 Which of the following is the smallest structural unit in which the distinctive striated bands characteristic of skeletal muscle are observed? | back 42 D |
front 43 The response of a motor unit to a single action potential of its motor neuron is called ________. | back 43 a muscle twitch |
front 44 The force of muscle contraction is controlled by multiple motor unit summation or recruitment. | back 44 True |
front 45 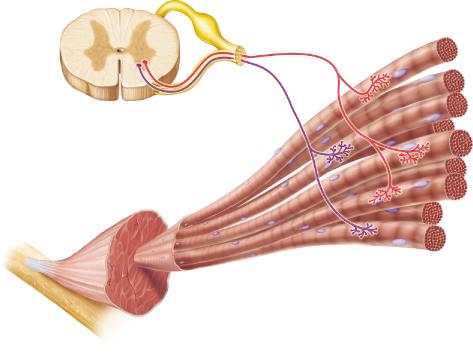 How many motor units are illustrated in the figure? | back 45 2 |
front 46 Which muscle cells have the greatest ability to regenerate? | back 46 Smooth |
front 47 An increase in the calcium ion level in the sarcoplasm starts the sliding of the thin filaments. When the level of calcium ions declines, sliding stops. | back 47 True |
front 48 The connective tissue sheaths of skeletal muscle, in order from internal to external, are the ________. | back 48 endomysium, perimysium, and epimysium |
front 49 Smooth muscles are able to regenerate throughout life. | back 49 True |
front 50 What is a cross bridge cycle? | back 50 It is the cycle in which an energized myosin head binds to actin and performs a power stroke, then binds to ATP in order to detach and re-energize. |