Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Activity 1: Classification of Skeletal Muscles and Identifying Muscles of the Head and Neck
front 1 Most often, body movements result from the contraction of how many muscles? | back 1 Several muscles acting together. |
front 2 Muscles that are responsible for producing a certain movement are called what? | back 2 Agonists or prime movers |
front 3 Muscles that oppose or reverse a movement are called what? | back 3 Antagonists |
front 4 When an agonist is active, the fibers of the antagonists are affected in which two states? | back 4 1. Stretched 2. Relaxed |
front 5 How does the antagonist regulate the agonist in 2 ways? | back 5 1. Prevent overshoot of the agonist 2. Stop action of the agonist |
front 6 The biceps muscle is an agonist of what arm movement? | back 6 Flexion |
front 7 The biceps is an antagonist of what arm movement? | back 7 Extension |
front 8 The triceps is an agonist of what arm movement? | back 8 Extension |
front 9 The triceps is an antagonist of what arm movement? | back 9 Flexion |
front 10 The biceps muscle is antagonized by what muscle? | back 10 Triceps muscle |
front 11 The triceps muscle is antagonized by what muscle? | back 11 Biceps muscle |
front 12 How do synergists help the action of agonists? | back 12 1. Reduce undesirable movement |
front 13 Without synergists, contraction of a muscle crossing two or more joints would cause movement at how many joints? | back 13 All joints |
front 14 Do synergists stabilize certain joints? | back 14 Yes. |
front 15 The muscles that flex the fingers cross both the wrist and finger joints, how can you make a fist without bending at the wrist? | back 15 The synergist muscles stablize the wrist joint. |
front 16 Fixators are what type of specialized muscles? | back 16 Specialized synergists |
front 17 What is the function of fixator muscles in regard to the origin and insertion of a prime mover? | back 17 They immobilize the origin of a prime mover so that all the tension is exerted at the insertion. |
front 18 Muscles that help maintain posture are what type of skeletal muscles? | back 18 Fixators |
front 19 Muscles of the back that stabilize the scapular during arm movements are what type of skeletal muscles? | back 19 Fixators |
front 20 Muscles are named on what 7 criteria? | back 20 1. Direction of muscle fibers 2. Relative size of the muscle 3. Location of the muscle 4. Number of origins 5. Location of the muscle's origin and insertion 6. Shape of the muscle 7. Action of the muscle |
front 21 Direction: Some muscles are named in reference to what kinda of line? | back 21 Imaginary line |
front 22 Direction: That imaginary line is usually what type of line of the body? | back 22 Midline of the body |
front 23 Direction: A muscle with fibers running parallel to that imaginary line will have what term in its name? | back 23 Rectus (straight) |
front 24 Direction: The rectus abdominis is what type of muscle of the abdomen? | back 24 Straight muscle of the abdomen |
front 25 Direction: The term transverse indicates muscles running at which type of angles relative to the imaginary line? | back 25 Right angles |
front 26 Direction: The term oblique indicates muscles running how directionally to the imaginary line? | back 26 Diagonally |
front 27 Muscle structure is determined by what type of arrangement? | back 27 Fascicle arrangement |
front 28 Relative size of the muscle: 1. Maximus means what? 2. Minimus means what? 3. Longus means what? 4. Brevis means what? | back 28 1. Largest 2. Smallest 3. Longest 4. Shortest |
front 29 Location of the muscle: Some muscles are named for the ____ with which they are associated. | back 29 bone |
front 30 The temporalis muscle overlies which bone? | back 30 Temporal bone |
front 31 Number of origins: 1. The term biceps has what number of origins or heads? 2. The term triceps has what number of origins or heads? 3. The term quadriceps has what number of origins or heads? | back 31 1. 2 2. 3 3. 4 |
front 32 Location of the muscle's origin and insertion: The sternocleidomastoid muscle has its origin in which 2 bones and inserts in which process? | back 32 Origin in the sternum (sterno) and clavicle (cleido) and inserts on the mastoid process of the temporal bone. |
front 33 Shape of the muscle: The deltoid muscle is what type of shape? | back 33 Triangular (deltoid=shape) |
front 34 Shape of the muscle: The trapezius muscle is what type of shape? | back 34 Trapezoid |
front 35 Action of the muscle: All the adductor muscles of the thigh bring about what type of movement? | back 35 Adduction |
front 36 Action of the muscle: All the extensor muscles of the wrist do what to the hand? | back 36 Extend the hand |
front 37 How do the muscles of facial expression differ from most skeletal muscles? | back 37 They insert into the skin or other muscles rather than into bone. |
front 38 The muscles of facial expression move what feature of the face? | back 38 Facial skin |
front 39 The muscles of mastication move which bone? | back 39 Mandible |
front 40 The six extrinsic eye muscles do what to the eye? | back 40 Aim the eye |
front 41 Neck muscles are concerned primarily with movement of what 2 body parts? | back 41 1. Head 2. Shoulder girdle |
front 42 Raise your eyebrow to wrinkle your forehead. You are using the frontal belly of what muscle? | back 42 Epicranius muscle |
front 43 Blink your eyes. You are contracting which muscle? | back 43 Orbicularis oculi |
front 44 Close your lips and pucker up. You are contracting which muscle? | back 44 Orbicularis oris. |
front 45 Smile. You are using which muscle? | back 45 Zygomaticus muscle. |
front 46 Clench your teeth. You are using which muscle? | back 46 Temporalis. |
front 47 Primary action of the orbicularis oculi? | back 47 Close eye |
front 48 Primary action of the orbicularis oris? | back 48 Close and protrude lips |
front 49 Primary action of the zygomaticus? | back 49 Create smile |
front 50 Origin and insertion of zygomaticus? | back 50 Origin: Zygomatic bone Insertion: Skin and muscles at corners of mouth |
front 51 Primary action of buccinator? | back 51 Compress cheeks (i.e. whisle, suck) |
front 52 Primary action of platysma? | back 52 Depress mandible (aka open jaw). |
front 53 Origin and insertion of platysma? | back 53 Origin: Fascia of chest Insertion: Mandible |
front 54 Primary action of temporalis? | back 54 Close jaw |
front 55 Origin and Insertion of temporalis? | back 55 Origin: Temporal bone Insertion: Coronoid process of mandible |
front 56 Primary action of masseter? | back 56 Close jaw |
front 57 Origin and insertion of masseter? | back 57 Origin: Zygomatic arch Insertion: Angle of mandible |
front 58 Primary action of digastric? | back 58 Open mouth |
front 59 Primary action of mylohyoid? | back 59 Elevate tongue during swallowing |
front 60 Primary action of sternohyoid? | back 60 Depress larynx |
front 61 Origin and insertion of sternohyoid? | back 61 Origin: Manubrium Insertion: Hyoid |
front 62 2 primary actions of sternocleidomastoid? | back 62 1. Flex neck 2. Rotate head |
front 63 Origin and insertion of sternocleidomastoid? | back 63 Origin: manubrium and clavicle Insertion: Mastoid process of temporal bone |
front 64 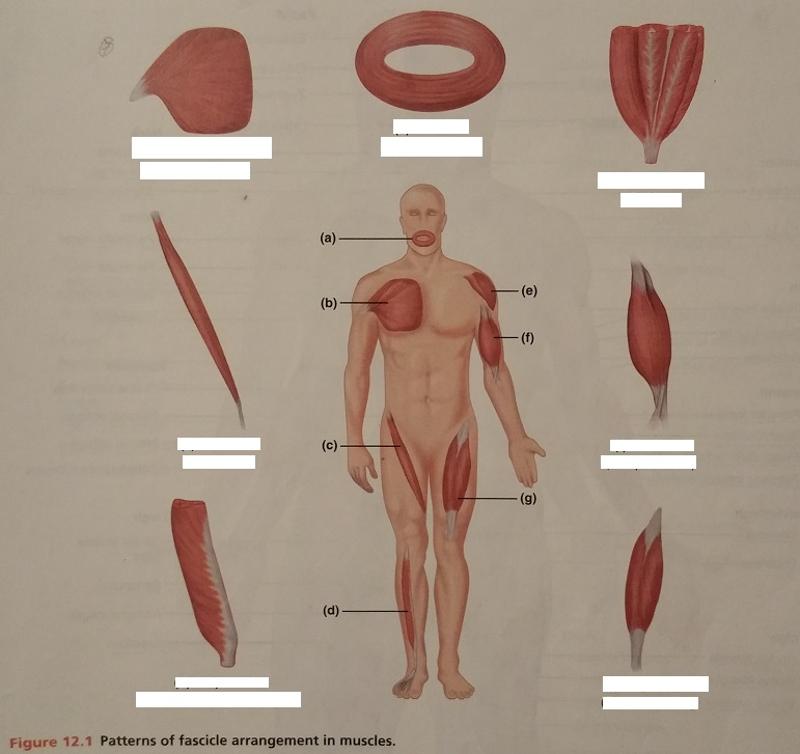 Identify the missing features. | back 64 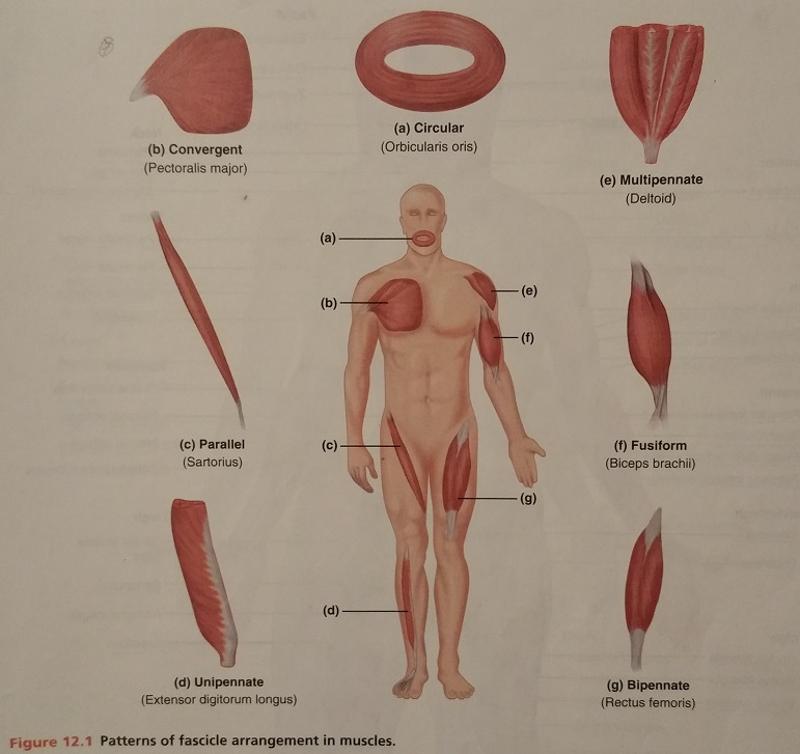 |
front 65 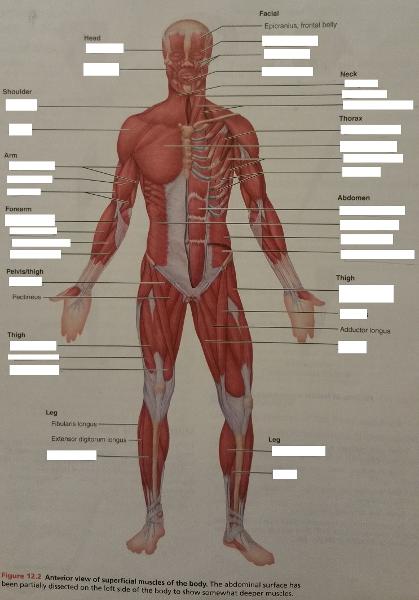 Identify the missing features. | back 65 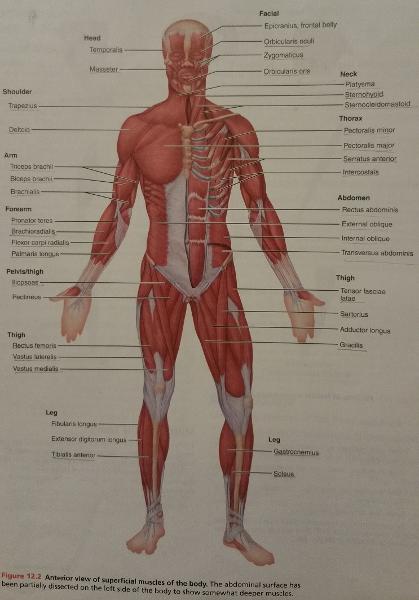 |
front 66 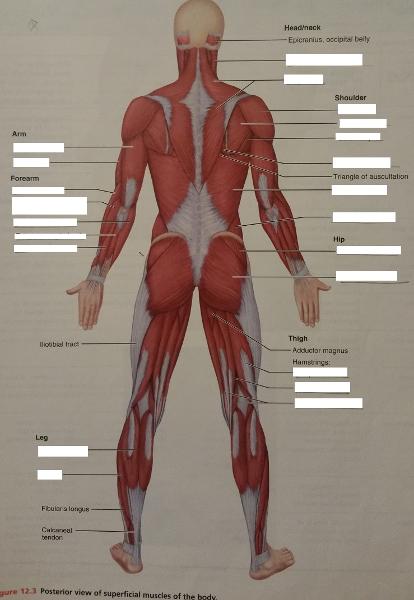 Identify the missing features. | back 66 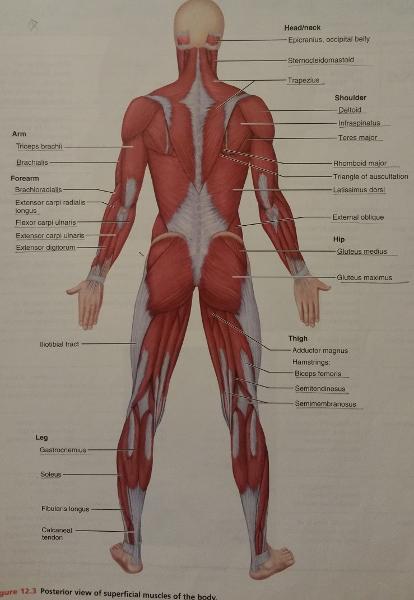 |
front 67 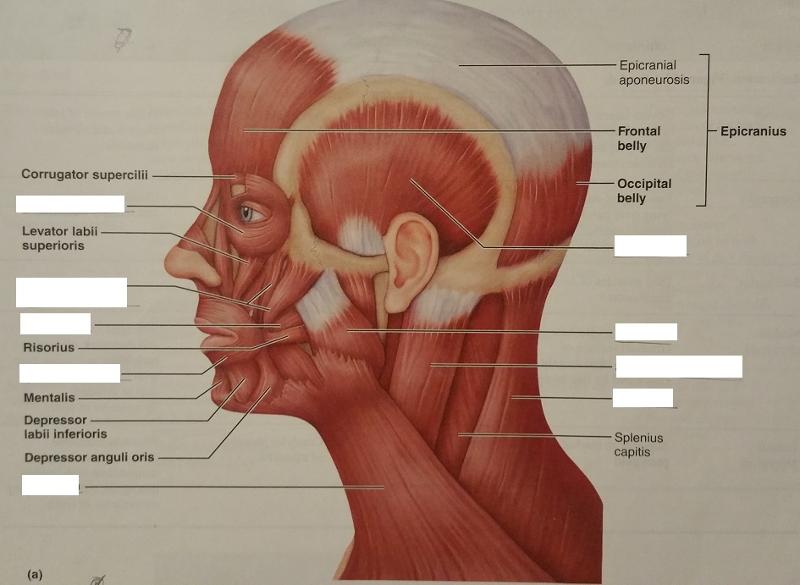 Identify the missing features. | back 67 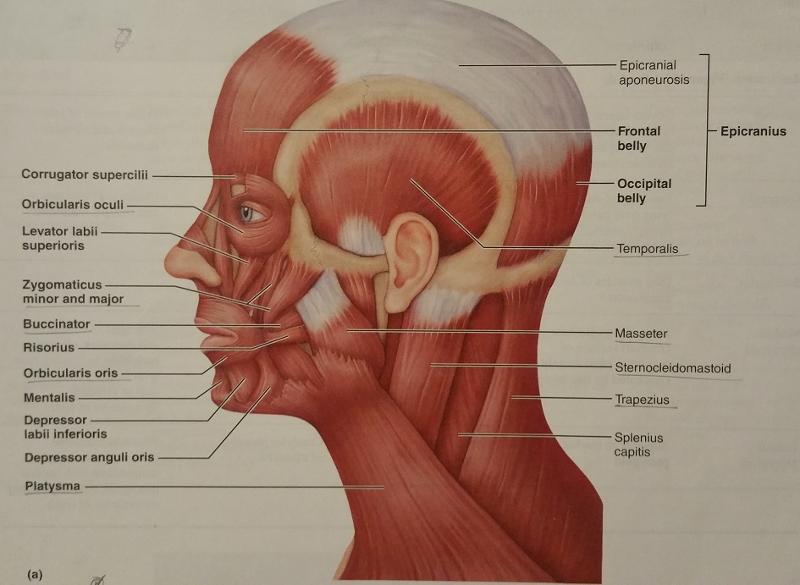 |
front 68 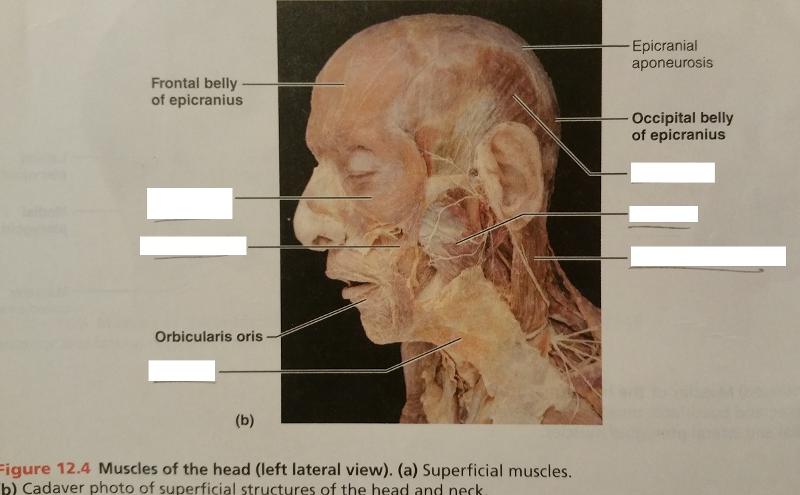 Identify the missing features. | back 68 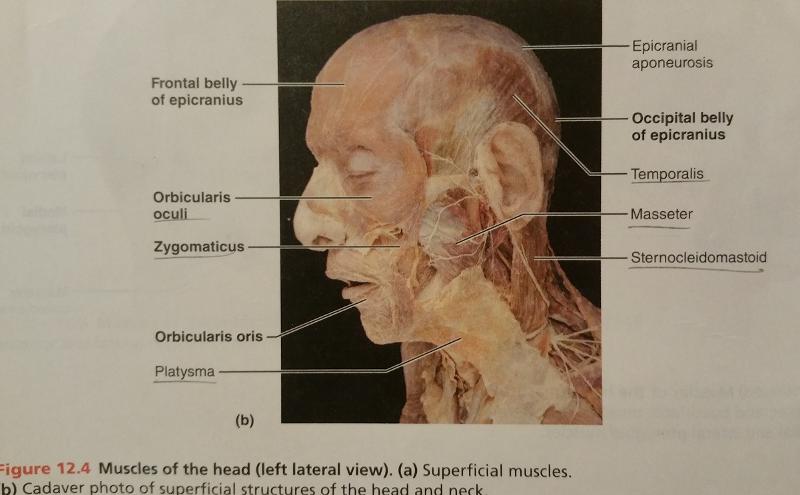 |
front 69 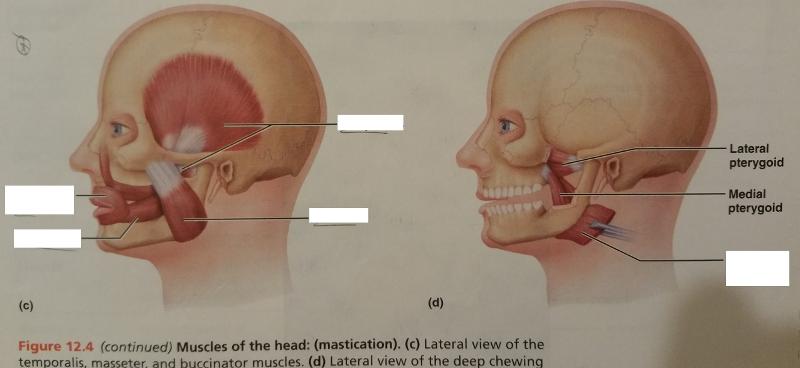 Identify the missing features. | back 69 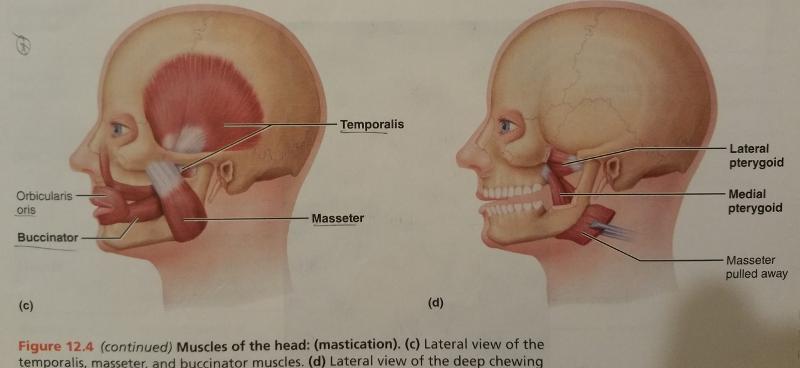 |
front 70 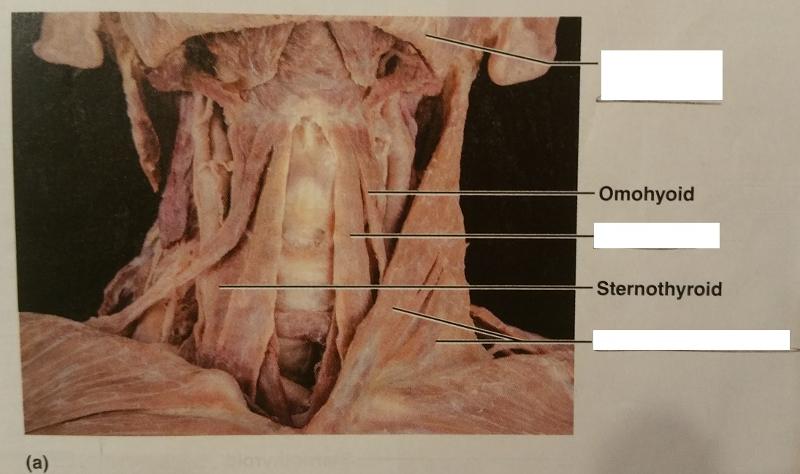 Identify the missing features. | back 70 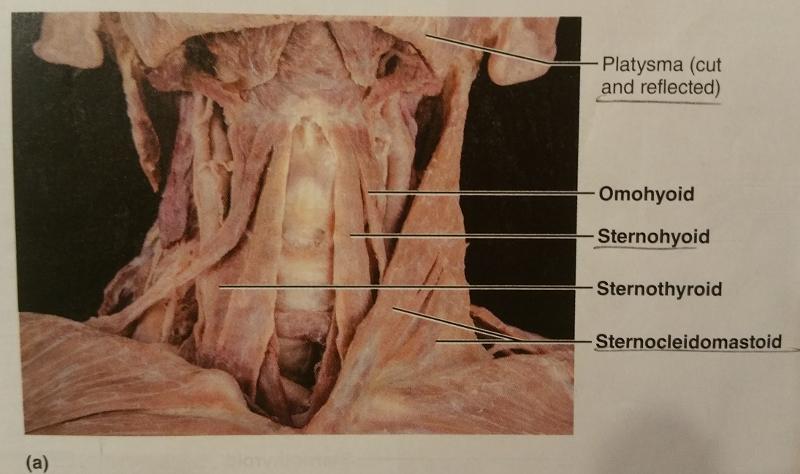 |
front 71 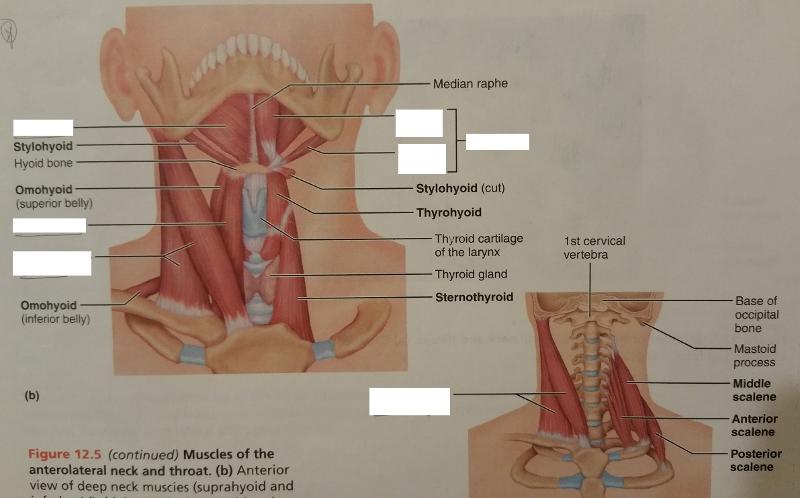 Identify the missing features. | back 71 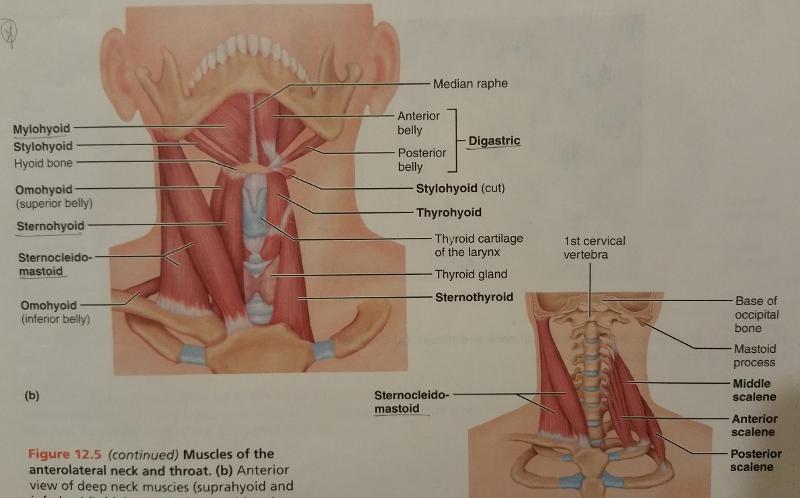 |