Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Take Home Festival Chapter 25 The Urinary System
front 1 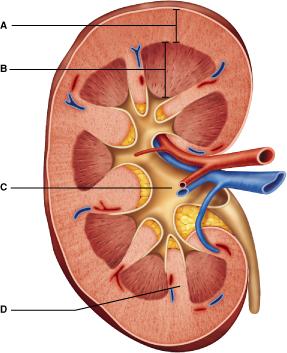 Which region of the kidney is characterized by the presence of cone-shaped pyramids? Select from letters A-D. A | back 1 B |
front 2 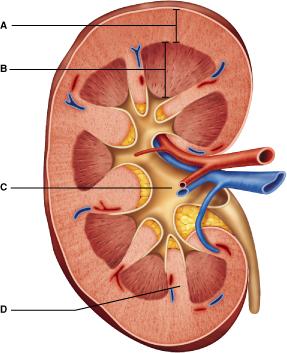 Which letter represents the most superficial region of the kidney? Select from letters A-D. A | back 2 A |
front 3 Which pressure is the chief force pushing water and solutes out of the blood and across the filtration membrane of the glomerulus? hydrostatic pressure in glomerular capillaries
(HPgc) | back 3 hydrostatic pressure in glomerular capillaries (HPgc) |
front 4 Which of the three parts of the renal tubule is formed by cuboidal epithelial cells bordered by dense microvilli? collecting duct | back 4 proximal convoluted tubule |
front 5 The __________ collect(s) urine, which drains continuously from the
papillae; the urine is then emptied into the __________. | back 5 calyces; renal pelvis |
front 6 Each nephron contains a __________, which is a tuft of capillaries,
and a __________. | back 6 glomerulus; renal tubule |
front 7 The renal corpuscle is made up of ________. | back 7 Bowman's capsule and glomerulus |
front 8 The functional and structural unit of the kidneys is the
________. | back 8 nephron |
front 9 Which cells of the kidney are chemoreceptors that respond to changes
in solute content of the filtrate? | back 9 macula densa cells |
front 10 Having a kinked ureter is called renal ptosis. | back 10 False |
front 11 In what part of the renal tubule does parathyroid hormone (PTH) promote the reabsorption of calcium ions? distal convoluted tubule (DCT) | back 11 distal convoluted tubule (DCT) |
front 12 Which statement best describes the effect diuretics have? Diuretics increase water reabsorption as a way to decrease the
osmolality of the extracellular fluids. | back 12 Diuretics increase urinary output. |
front 13 Under normal conditions, the large renal arteries deliver one-fourth
of the total cardiac output (about 1200 ml) to the kidneys each minute. | back 13 True |