Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
The control of microbial growth
front 1 Which of the following is the best method to sterilize heat-labile solutions | back 1 membrane filtration |
front 2 which of the following best describes the pattern of microbial death | back 2 the cells in a population die at a constant rate |
front 3 which of the following substances is used for surgical hand scrubs | back 3 chlorhexidine |
front 4 which of the following pairs of terms is mismatched | back 4 bateriostatic -- kills vegetative bacterial cells |
front 5 the antimicrobial activity of chlorine is due to which of the following | back 5 the formation of hypochlorous acid |
front 6 which of the following regarding antimicrobial control agents is false | back 6 alcohols effectively inactivate nonenveloped viruses by attacking lipids |
front 7 which of the following does not achieve sterilization | back 7 pasteurization |
front 8 which of the following is a limitation of the autoclave | back 8 it cannot be used with heat-labile materials |
front 9 an agent used to reduce the number of bacteria on a toilet would most accurately be called | back 9 disinfectant |
front 10 application of heat to living cells can result in all of the following except | back 10 decreased thermal death time |
front 11 which of the following disinfectant acts by disrupting the plasma membrane | back 11 bisphenols |
front 12 all of the following substances are effective against nonenveloped viruses except | back 12 alcohol |
front 13 which of the following methods is used to preserve food by slowing the metabolic processes of foodborne microbes | back 13 freezing |
front 14 which concentration of ethanol is the most effective bactericide | back 14 70% |
front 15 all of the following factors contribute to hospital-acquired infections except | back 15 all of these factors may contribute to hospital-acquired infection some bacteria metabolize disinfectants gram-negative bacteria are often resistant to disinfectant invasive procedures can provide a portal of entry for bacteria bacterial may be present in commercial products such as mouthwash `w |
front 16 which of the following treatments is the most effective for controlling microbial growth | back 16 they are equivalent treatments |
front 17 which of the following could be used to sterilize plastic petri plates in a plastic wrapper | back 17 gamma radiation |
front 18 In figure 7.1 what is the thermal death time | back 18 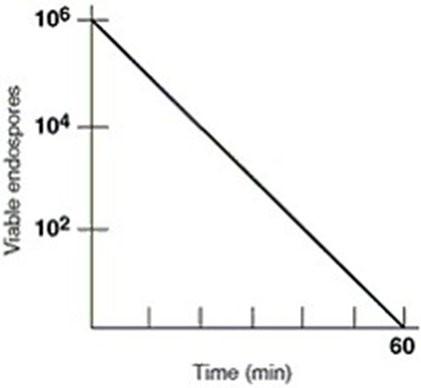 60 minutes |
front 19 In figure 7.1 the thermal death point for this culture is | back 19 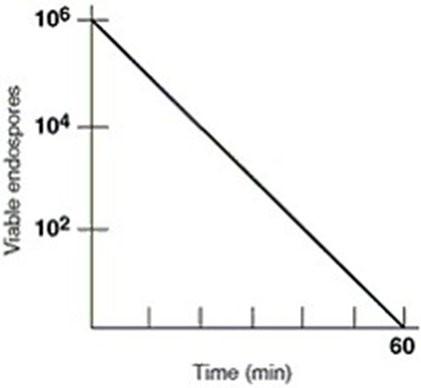 answer cannot be determined |
front 20 in figure 7.1 the decimal reduction time (D value) for the culture, which is defined as the time to reduce a population by one log, is approximately | back 20 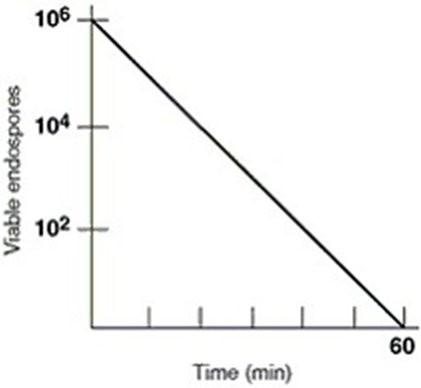 10 minutes |
front 21 which of the following results in lethal damage to nucleic acids | back 21 heat, radiation, and some chemicals |
front 22 in table 7.1 which compound was the most effective against staphylococcus | back 22 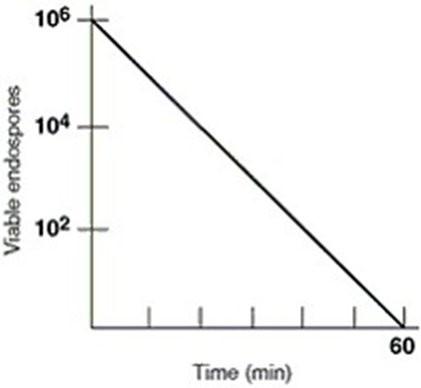 C |
front 23 in table 7.1 which compound was bactericidal | back 23 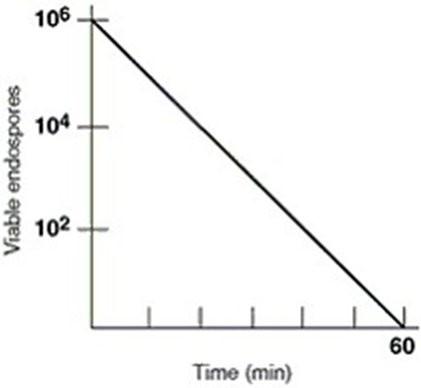 answer cannot be determined |
front 24 all of the following substances are used to preserve foods except | back 24 biguanides |
front 25 all of the following are effective for destroying prions except | back 25 boiling |
front 26 all of the following are methods of food preservation except | back 26 microwaves |
front 27 which of the following is most resistant to chemical biocides | back 27 gram-negative bacteria |
front 28 the thermal death time is the time needed to kill all the bacteria in a particular culture at a certain temperature | back 28 true |
front 29 pseudomonas has been found growing in quarternary ammonium compounds | back 29 true |
front 30 moist heat destroys organisms by denaturing proteins | back 30 true |
front 31 some antimicrobial chemicals are considered to be disinfectants and antiseptics | back 31 true |
front 32 the pH of the medium has no effect on the activity of the disinfectant being applied | back 32 false |
front 33 autoclaving is the most effective method of moist heat sterilization | back 33 true |
front 34 microorganism placed in high concentrations of salts and sugars undergo lysis | back 34 false |
front 35 sterilization | back 35 removal or destruction of all microorganism |
front 36 sterilant | back 36 sterilizing agent |
front 37 commercial sterilization | back 37 limited heat treatment |
front 38 disinfectant | back 38 control directed at destroying harmful microorganisms |
front 39 antisepsis | back 39 when treatment is directed at living tissue |
front 40 degerming | back 40 when the skin is swabbed with alcohol before vaccination |
front 41 sanitization | back 41 intended to lower microbial counts |
front 42 biocide/gemicide | back 42 kills microorganisms |
front 43 sepsis | back 43 bacterial contamination |
front 44 what is the rate of microbial death | back 44 the number of microbes environmental influences time of exposure microbial characterisitics |
front 45 What is thermal death point | back 45 the lowest temperature at which all the microorganisms in a particular liquid suspension will be killed in 10 minutes |
front 46 What is thermal death time | back 46 the minimal length of time for all bacteria in a particular liquid culture to be killed at a given temperature |
front 47 what is decimal reduction time | back 47 time in which 90% of a population of bacteria at a given temperature will be killed |
front 48 how does moist heat kill microorganisms | back 48 by coagulating proteins |
front 49 what is an autoclave | back 49 preferred method of sterilization in health care environments |
front 50 what are retorts | back 50 large industrial autoclaves |
front 51 pressure and temperature in an autoclave | back 51 higher the temperature (121oC), the higher the pressure (150lbs/psi) |
front 52 pasteurization | back 52 elimination of pathogenic microbes |
front 53 thermoduric | back 53 heat-resistant bacteria |
front 54 high temperature short-time pasteurization | back 54 most milk pasteurization uses temperature of 72oC but for only 15 secs also lower bacterial counts |
front 55 utlra-high-temperature treatments | back 55 method of treating foods with high temperature for short times |
front 56 equivalent treatments | back 56 as temperature rises, less time is needed to kill same number of microbes |
front 57 hot air sterilization | back 57 items are placed in an oven for longer period, higher temperature is required |
front 58 filtration | back 58 passage of a liquid/gas through a screenlike material with pores small enough to retain microorganisms |
front 59 high-effeciency particulate are filters | back 59 remove almost all microorganisms larger than about 0.3um in diameter |
front 60 phenol | back 60 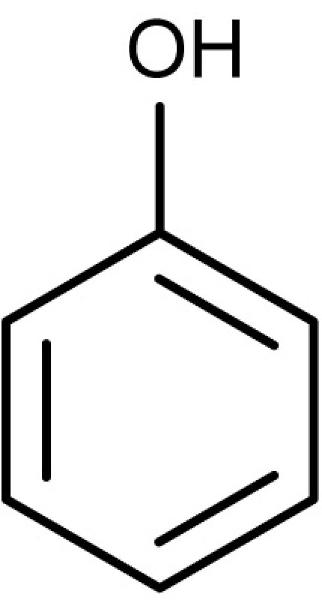 phenol was used to control surgical infections in the operation room. |
front 61 phenolics | back 61 derivative of phenol, contains a molecule of phenol that is chemically altered to reduce its irritation qualities and increase antibacterial activity |
front 62 cresols | back 62 most frequently used phenolics |
front 63 bisphenol | back 63 contain 2 phenolic groups, hexachlorophenes and triclosan |
front 64 hexachlorophenes | back 64 is an ingredient of a prescription lotion, pHisoHex, used for surgical and hospital microbial control procedure |
front 65 triclosan | back 65 is an antibacterial soap |
front 66 what forms when chlorine is combined with water | back 66 hypochlorous acid Cl2 + H2O <-> H+ + Cl- + HOCl |
front 67 quaternary ammonium compounds | back 67 most used surface active agents |
front 68 what is sodium hypochlorite used as | back 68 a household disinfectant and bleach |
front 69 what is potassium sorbate and benzoate used for | back 69 to prevent molds from growing on acidic foods |
front 70 what is calcium propionate used for | back 70 it is an effective fungistat used in bread |
front 71 evaluation of disinfectants by the disk-dilution method | back 71 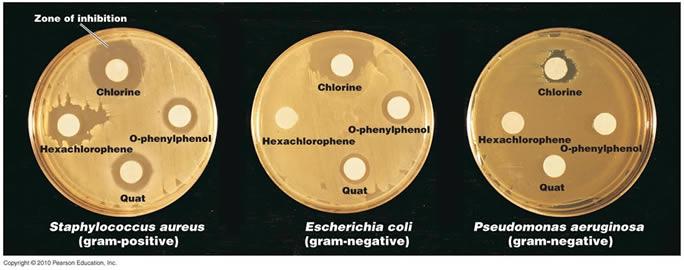 |