Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Functional anatomy of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
front 1 Which of the following statement is incorrect regarding prokaryotic cells | back 1 they lack a plasma membrane |
front 2 Each of the following statements concerning the gram-positive cell wall is true except | back 2 it protects the cell in a hypertonic environment |
front 3 Which of the following statements best describes what happens when a bacterial cell is placed in a solution containing 5% NaCl | back 3 water will move out of the cell |
front 4 A gram-positive bacterium suddenly acquires resistance to the antibiotic methicillin. this trait most likely occurred due to acquisition of new genetic information through | back 4 conjugation |
front 5 by which of the following mechanisms can a cell transport a substance from a lower to a higher concentration | back 5 active transport |
front 6 which of the following is not a typical characteristic of most bacterial plasma membranes | back 6 contains cholesterol |
front 7 which one of the following organisms has a cell wall | back 7 fungi |
front 8 which of the following statements is true | back 8 endospores allow a cell to survive environmental changes by producing a dormant period with no growth |
front 9 which of the following pairs is mismatched | back 9 centrosomes - food storage |
front 10 which of the following organelles most likely resembles a prokaryotic cell | back 10 mitochondrion |
front 11 Which of the drawing is a tetrad | back 11 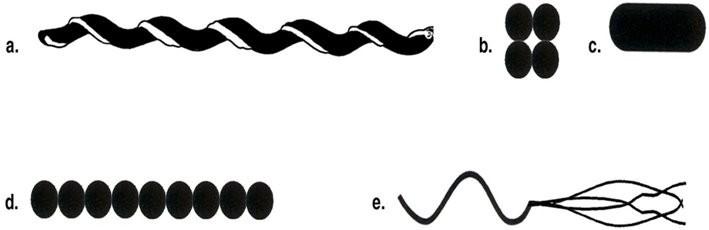 B |
front 12 which drawing in figure 4.1 posseses an axial filament | back 12 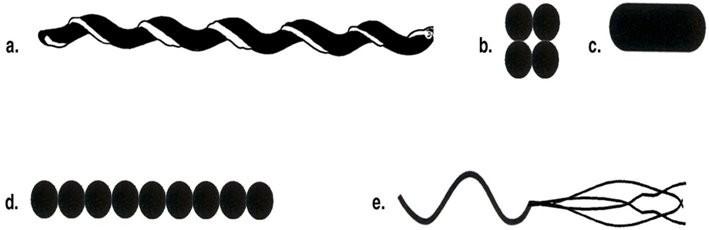 A |
front 13 which drawing in figure in 4.1 is streptococci | back 13 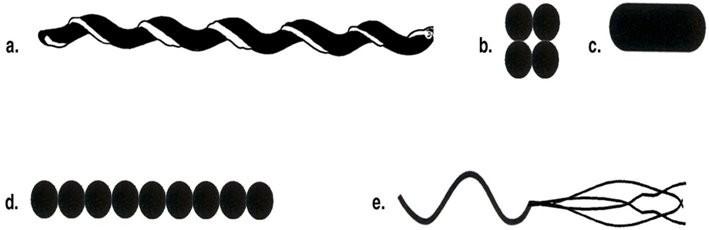 D |
front 14 antibiotics that target cell wall synthesis ultimately cause bacterial cell death as a result of | back 14 osmotic lysis |
front 15 bacteria are commonly used organism for studies of genetic material in the research laboratory. The nucleic acids must first be isolated from the cells for these studies. which of the following would most likely be used to lyse gram-positive bacterial cells for nucleic acid isolation | back 15 lysozyme |
front 16 which of the following statements about gram-negative cell walls is false | back 16 they are sensitive to penicillin |
front 17 which of the following structures is not found in some prokayotic cells | back 17 cilium |
front 18 functions of the glycocalyx include all of the following except | back 18 binary fission |
front 19 which acts like an invisibility cloak and protects bacteria from being phagocytized | back 19 capsule |
front 20 which of the following is not part of the passive transport process | back 20 ATP |
front 21 which of the following terms best describes the cell in figure 4.2 | back 21 lophotrichous flagella |
front 22 in bacteria, photosynthetic pigments are found in | back 22 chromatophores |
front 23 the difference between simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion is that facilitated diffusion | back 23 requires transporter proteins |
front 24 the term "run" and "tumble" are generally associated with | back 24 taxic movements of the cell in response to attractants or repellents |
front 25 You have isolated a motile, gram-positive cell with no visible nucleus. you can safely assume that the cell | back 25 has a cell wall |
front 26 Fimbriae and pili differ in that | back 26 pili are used to transfer DNA and motility |
front 27 Which diagram of a cell wall is gram-negative cell wall | back 27 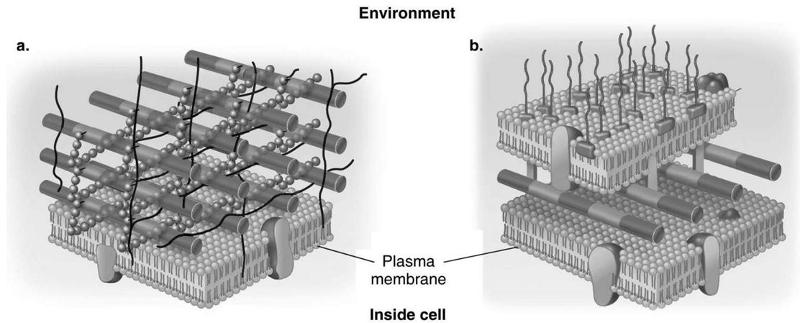 B |
front 28 which diagram of a cell wall possesses lipid A/endotoxin responsible for symptoms associated with infection | back 28 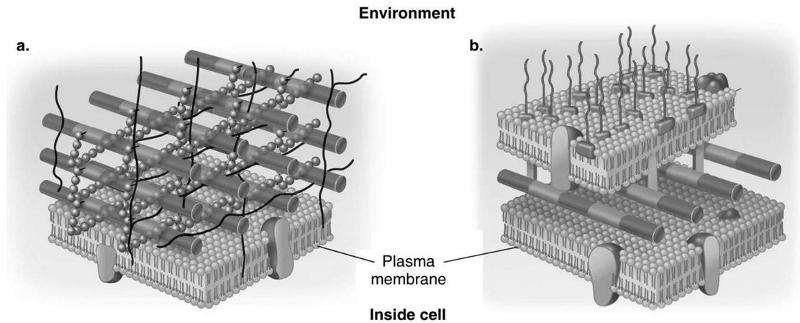 B |
front 29 which diagram of a cell wall has a structure that protects against osmotic lysis | back 29  both A and B |
front 30 which diagram of a cell wall is decolorized by alcohol | back 30 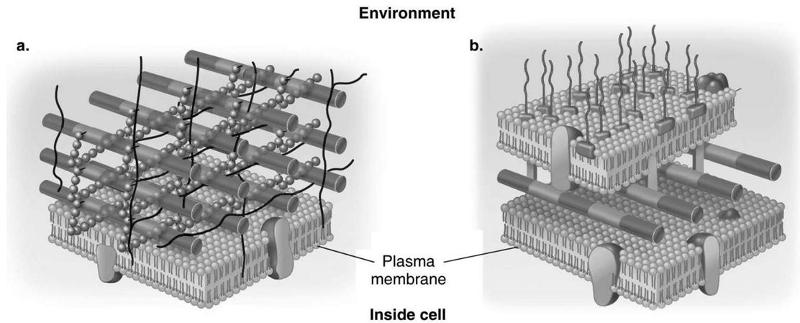 B |
front 31 which diagram of a cell wall is resistant to many antibiotics | back 31 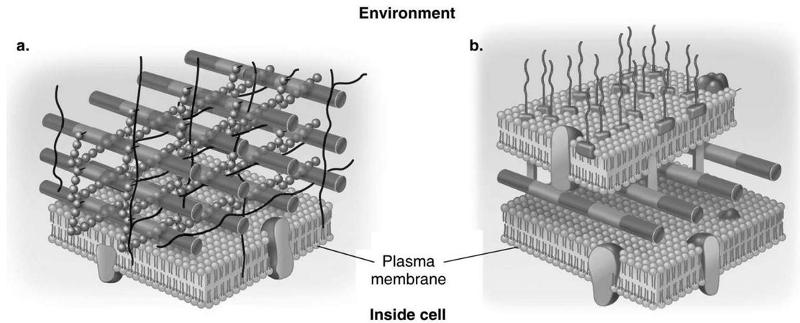 B |
front 32 which diagram of a cell wall contains teichoic acids | back 32 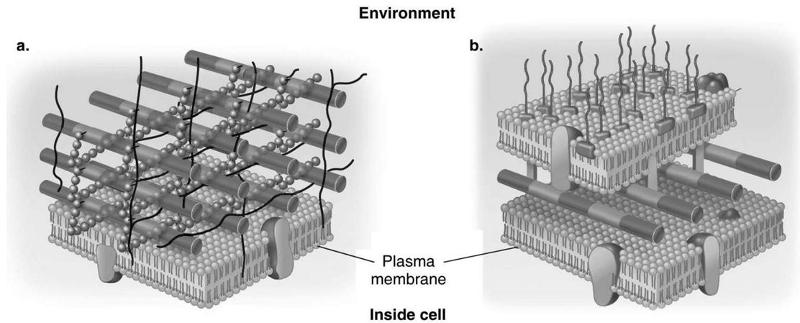 A |
front 33 which diagram of a cell wall contains porins | back 33 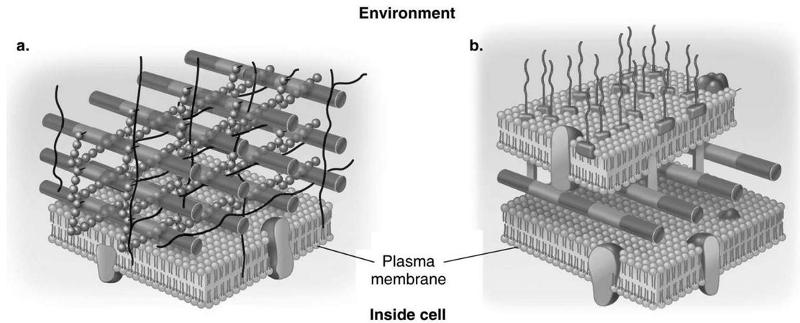 A |
front 34 where are phospholipids most likely found in a prokaryotic cell | back 34 the plasma membrane |
front 35 where are phospholipids most likely found in a eukaryotic cell | back 35 the plasma membrane, around organelles, and surrounding flagella |
front 36 which of the following is not found or observed to occur in both mitochondria and prokaryotes | back 36 cell wall |
front 37 which of the following statements is correct about passive diffusion | back 37 it involves movement of molecules down a concentration gradient and may require a transport protein |
front 38 oxygen crosses a plasma membrane | back 38 thorugh simple diffusion |
front 39 in a hypertonic solution, a bacterial cell will typically | back 39 plasmolyze |
front 40 what will happen if a bacteriacel is pretreated with a lysozyme solution, then placed in distilled water | back 40 the cell will undergo osmotic lysis |
front 41 how do spirochetes and spirilla differ | back 41 spirilla have an external flagella but spirochetes have axial filaments |
front 42 which one of the following pairs is mismatched | back 42 ribosomes - carbon storage |
front 43 which of the following are not energy reseves | back 43 carboxysomes |
front 44 Which of the following is not a functionally analogous pair | back 44 cilia - pilia |
front 45 the DNA found in most bacterial cells | back 45 is circular in structure |
front 46 the cell walls of bacteria are responsible for the shape of the bacteria and the difference in the gram stain reaction | back 46 true |
front 47 antibiotics that target the cell wall are an effective treatment against many pathogenic bacteria | back 47 true |
front 48 cells placed in a hypotonic solution tend to lose water due to osmotic pressure | back 48 false |
front 49 small, hydrophobic molecules pass through a cell membrane most easily by diffusion | back 49 true |
front 50 spheroplasts, protoplasts, and mycoplasms are bacterial cells without cell walls | back 50 true |
front 51 endospores are a reproductive structure | back 51 false |
front 52 the internal structure of eukaryotic cilia and flagella are the same | back 52 true |
front 53 many enzymes in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are compartmentalized within organelles | back 53 false |
front 54 the number of organelles such as chloroplasts, mitochondria, and rough endoplasmic reticulum is the same in all eukaryotic cells | back 54 true |
front 55 if you observe rod-shaped red cells after the gram stain, you can assume their cell walls contain endotoxin | back 55 true |
front 56 characteristics of a typical prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell | back 56 prokaryotic cells' DNA is not enclosed within a membrane and is usually single.they usually lack organelles and their cell walls contain peptidoglycan. Eukaryotic cells' DNA is found in the cell's nucleus, they have a number os membrane-enclosed organelles and their cell walls are chemically simple |
front 57 compare and contrast gram-positive and gram-negative cell walls | back 57 the application of alcohol dehydrates the peptidoglycan of gram positve to make it more impermeable to crystals violet iodine. in gram negative, alcohol dissolves the outer membrane and leaves small holes in the thin peptidoglycan layer through which crystal violet-iodine diffuse. Gram-positive cell walls consist of peptidoglycan while gram-negative contains a few layers of peptidoglycan and anouter membrane |
front 58 What is a biofilm and what role does biofilm play in disease | back 58 a complex aggregation of microbes. microorganisms exists as single cells that float or swim independently on a liquid or attach to each other and some solid surface. it can cause infections and its bacteria are often resistant to antibiot |
front 59 dipploccoci | back 59 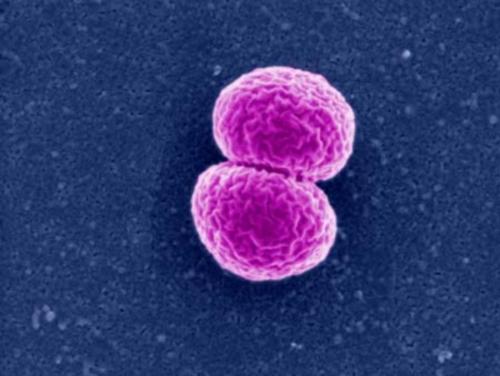 remains in pairs after dividing |
front 60 streptococci | back 60 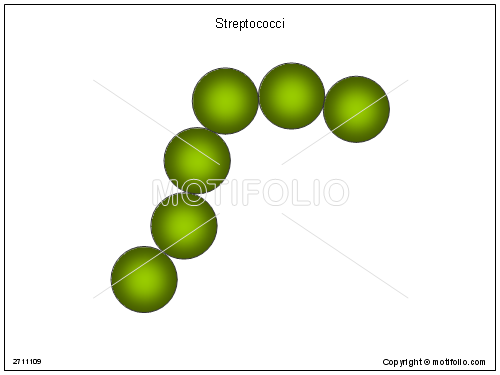 divides and remain attached in chain-like patterns |
front 61 spiral bacteria | back 61 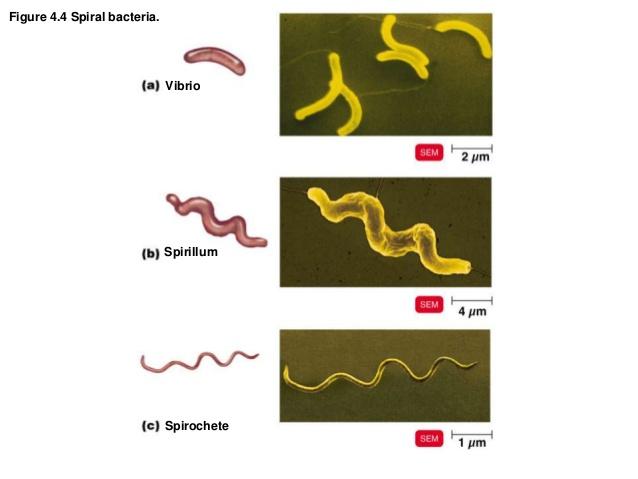 vibrios - curved rods spirillum - helical shape spirochete - helical and flexible |
front 62 the structure of a prokaryotic cell capsule fimbriae chromosome pilus flagella | back 62 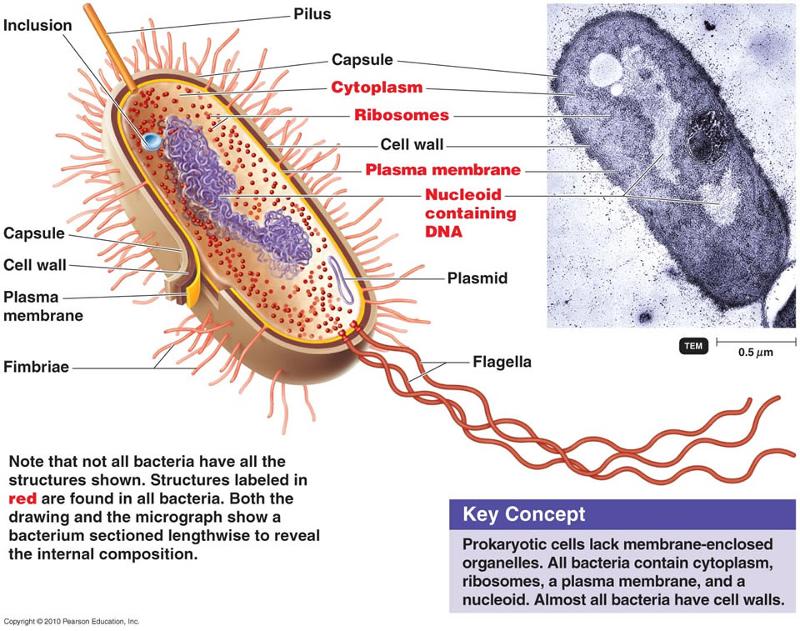 |
front 63 arrangements of bacterial flagella | back 63 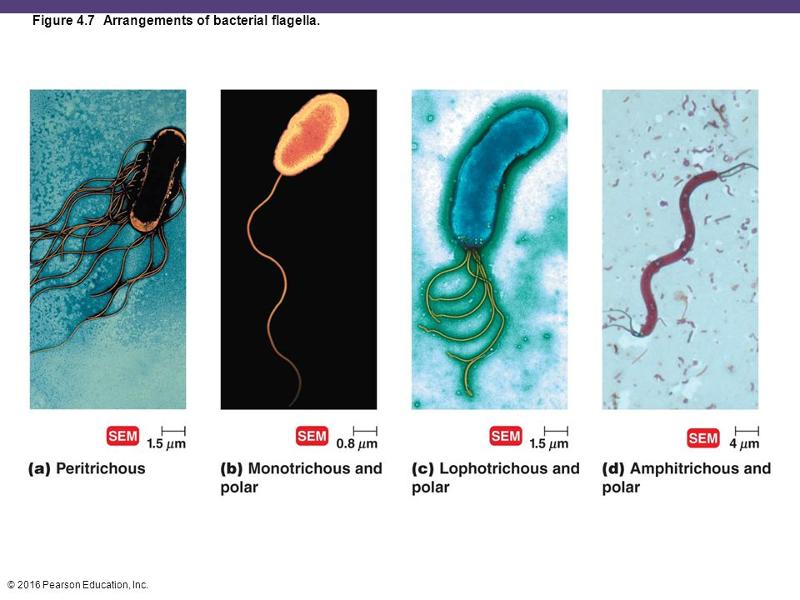 |
front 64 gram positive bacterium | back 64 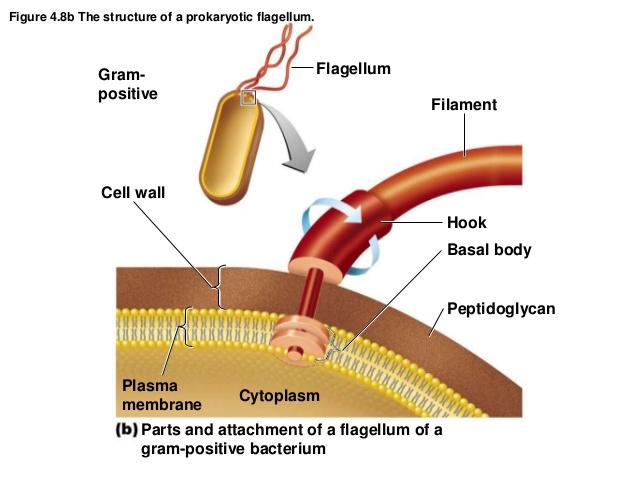 2 basal body |
front 65 gram negative bacterium | back 65 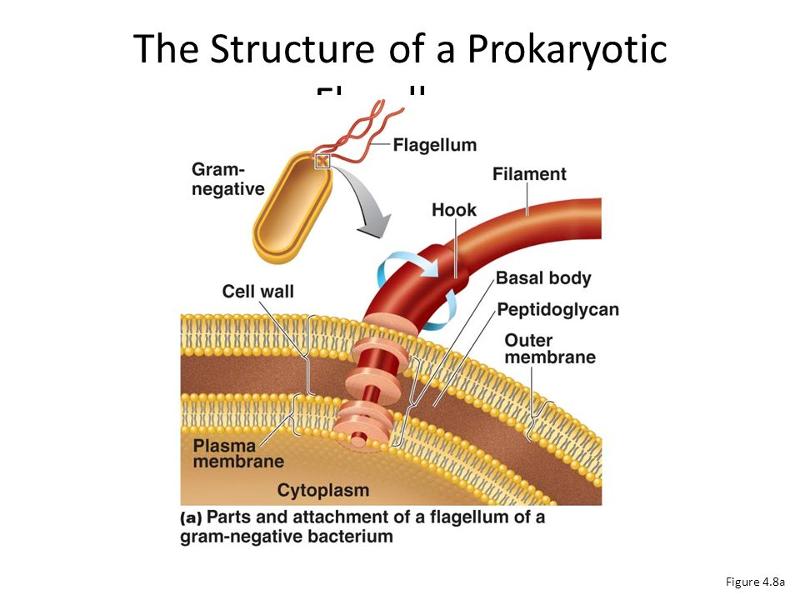 4 basal bodies |
front 66 gram positive cell wall | back 66 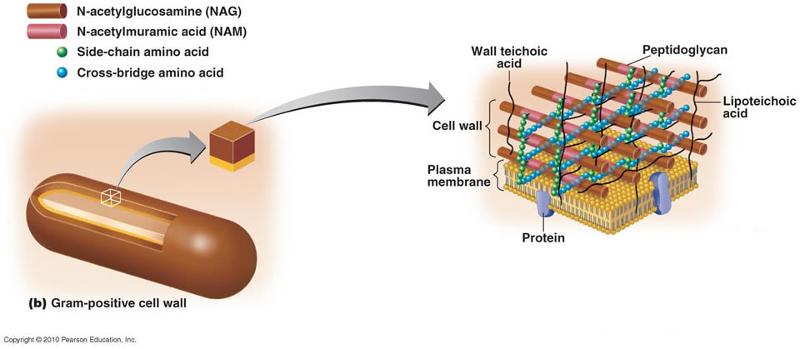 |
front 67 gram negative cell wall | back 67 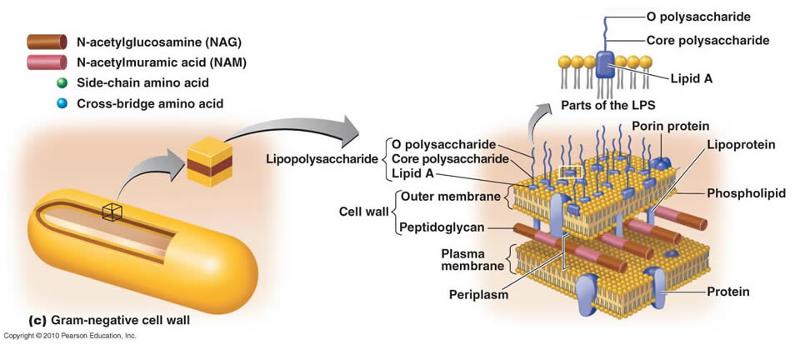 |
front 68 prokaryotes | back 68 DNA is not enclosed withing a membrane, it is inside the cell DNA is not associated with histones Lack organelles cell walls contain peptidoglycan divide by binary fission |
front 69 eukaryotes | back 69 DNA found in cell's nucleus DNA consistently associated with histones and non histones Have membrane -enclosed organelles cell walls are chemically simple cell division involves mitosis |
front 70 arrangement of cells | back 70 cocci - round shape bacilli -rod-like spiral |
front 71 monomorphic | back 71 maintains a single shape |
front 72 pleomorphic | back 72 can have many shapes |
front 73 glycocalyx | back 73 viscous, gelatinous sugar |
front 74 extracellular polymeric substance | back 74 a glycocalyx that helps cells in a biofilm attach to their target environment and to each other |
front 75 what is the difference between capsule and slime | back 75 capsule is neatly organized and firmly attached while slime is unorganized and loose |
front 76 axial filament/endoflagella | back 76 bundles of fibrils that arise at the ends of the cell. |
front 77 spirochete move by the means of | back 77 axial filaments |
front 78 fimbriae | back 78 helps bacterias attach to the wall can occur at the poles of the bacterial cell or can be evenly distributed over the entire surface of the cell |
front 79 pili | back 79 longer than fimbriae and only one or two per cell. use to transfer plasmid |
front 80 crystal violet | back 80 primary stain. Stains both gram positive/negative purple |
front 81 Iodine | back 81 forms large crystals with the dye that are too large to escape through the cell wall |
front 82 what happens to gram positive when alcohol is applied | back 82 it makes gram positive more impermeable to crystal violet-iodine |
front 83 what happens to gram negative when alcohol is applied | back 83 alcohol dissolves the outermembrane and leaves holes for crystal violet to diffuse |
front 84 what color does gram positive turn when safranin is applied | back 84 purple |
front 85 what color does gram negative turn when safranin is applied | back 85 red |
front 86 atypical cell walls | back 86 plasma membrane have sterols (lipids). protects them from lysis (rupture) |
front 87 acid- fast cell walls | back 87 used to identify mycobacterium and norcardia bacteria contain mycolic acid in their cell wall can be stained with carbolfuchsin |
front 88 protoplast | back 88 wall-less cell |
front 89 spheroplast | back 89 remaining outer wall layer |
front 90 Nucleoid | back 90 contains bacterial chromosome the cell's genetic information which carries all the information required for the cell's structures and functions. |
front 91 plasmid | back 91 double stranded DNA molecules. replicate independently of chromosomal DNA |
front 92 ribosomes | back 92 protein synthesis take place prokaryotic ribosome - 70s ribosomes eukaryotic ribosome - 80s 50s, 30s |