Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Final Bio Exam Part 2 from Exam 2
front 1 1) You have a planar bilayer with equal amounts of saturated and
unsaturated phospholipids. After testing the permeability of this
membrane to glucose, you increase the proportion of unsaturated
phospholipids in the bilayer. What will happen to the membrane's
permeability to glucose? | back 1 B |
front 2 2) The membranes of winter wheat are able to remain fluid when it is
extremely cold by _____. | back 2 B |
front 3 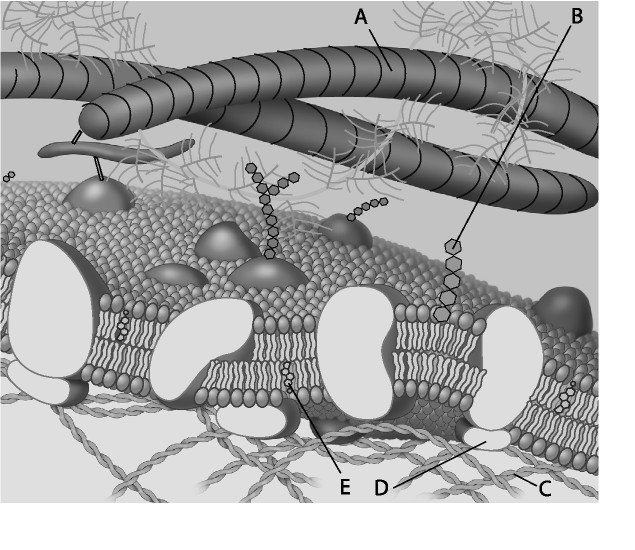 For the following questions, match the labeled component of the cell membrane in the figure with its description. 3) Which component is a peripheral protein? A) A B) B C) C D) D | back 3 D |
front 4 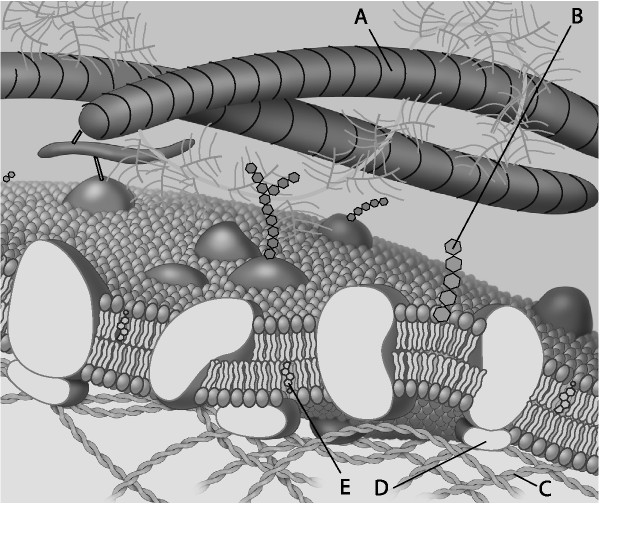 4) Which component is a protein fiber of the extracellular matrix?
| back 4 A |
front 5 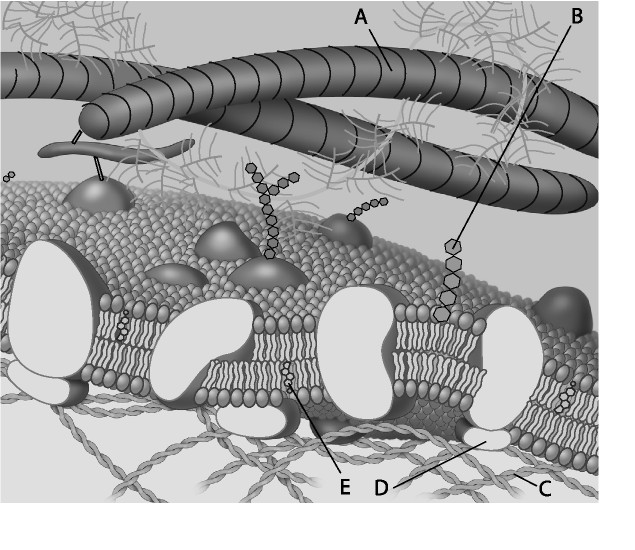 5) Which component is a microfilament (actin filament) of the cytoskeleton? A) A B) B C) C D) D | back 5 C |
front 6 6) Cell membranes are asymmetrical. Which of the following statements is the most likely explanation for the membrane's asymmetrical nature? A) Proteins only function on the cytoplasmic side of the cell
membrane, which results in the membrane's asymmetrical nature.
| back 6 B |
front 7 Succinate dehydrogenase catalyzes the conversion of succinate to fumarate. The reaction is inhibited by malonic acid, which resembles succinate but cannot be acted upon by succinate dehydrogenase. Increasing the ratio of succinate to malonic acid reduces the inhibitory effect of malonic acid. 7) What is malonic acid's role with respect to succinate
dehydrogenase? Malonic acid _____. | back 7 B |
front 8 8) Which of the following would likely move through the lipid bilayer
of a plasma membrane most rapidly? | back 8 D |
front 9 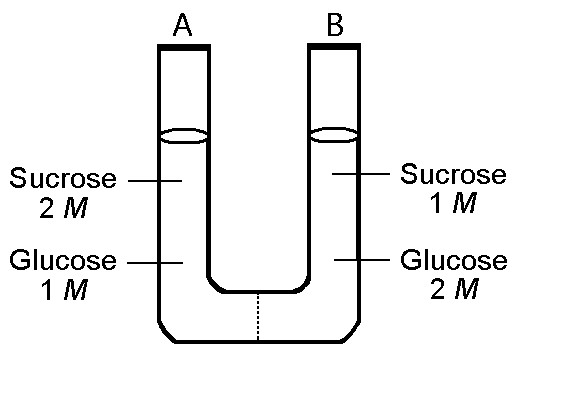 The solutions in the two arms of this U-tube are separated by a
membrane that is permeable to water and glucose but not to sucrose.
Side A is half-filled with a solution of 2 M sucrose and 1 M glucose.
Side B is half-filled with 1 M sucrose and 2 M glucose. Initially, the
liquid levels on both sides are equal. | back 9 C |
front 10 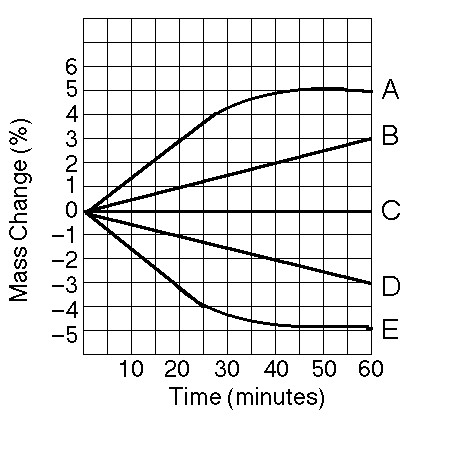 Five dialysis bags constructed of membrane, which is permeable to water and impermeable to sucrose, were filled with various concentrations of sucrose and then placed in separate beakers containing an initial concentration of 0.6 M sucrose solution. At 10-minute intervals, the bags were massed (weighed) and the percent change in mass of each bag was graphed. 10) Which line in the graph represents the bag with the highest initial concentration of sucrose? A) A B) B C) C D) D | back 10 A |
front 11 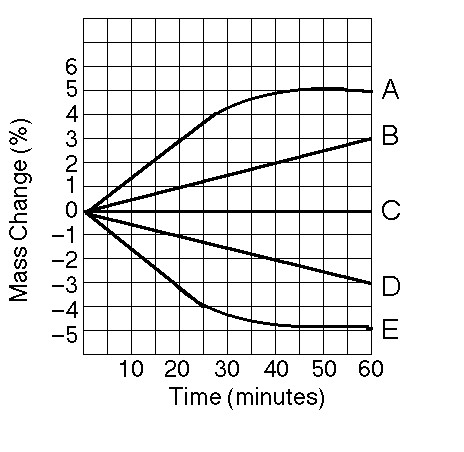 11) Which line or lines in the graph represent(s) bags that contain a
solution that is hypertonic at 50 minutes? | back 11 B |
front 12 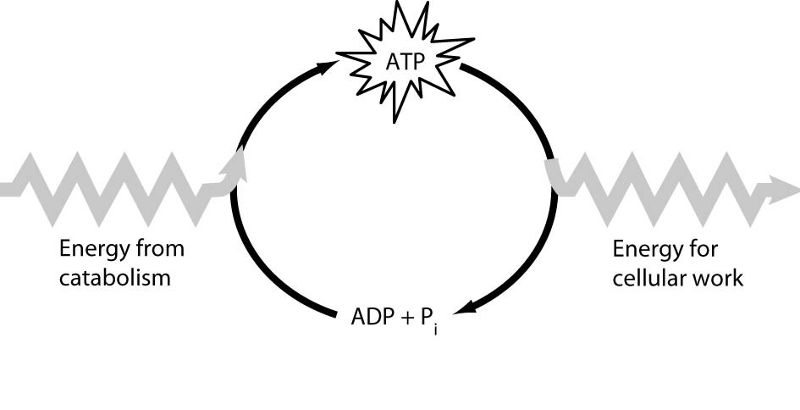 12) Which of the following is the most correct interpretation of the
figure? | back 12 A |
front 13 13) A system at chemical equilibrium _____. | back 13 A |
front 14 14) You have discovered an enzyme that can catalyze two different
chemical reactions. Which of the following is most likely to be
correct? | back 14 C |
front 15 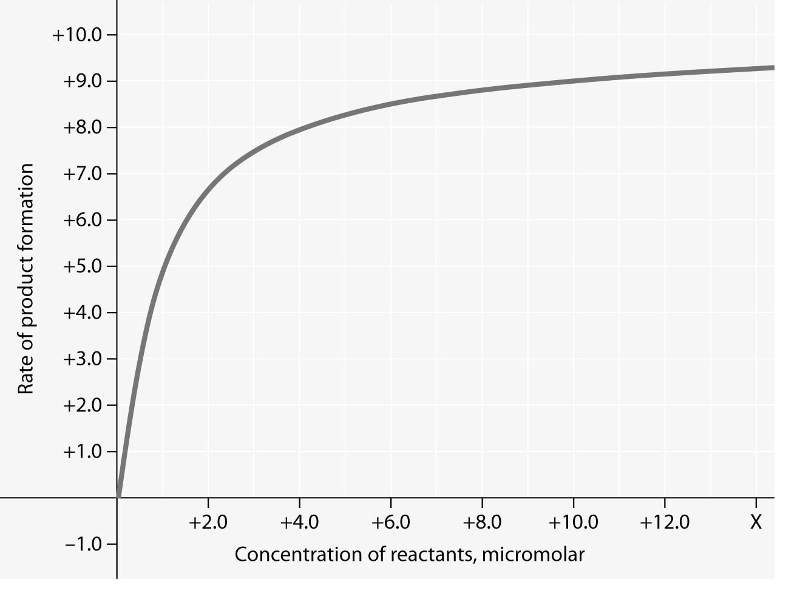 Rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction as a function of varying reactant concentration, with the concentration of enzyme constant. 15) In the figure, why does the reaction rate plateau at higher
reactant concentrations? | back 15 C |
front 16 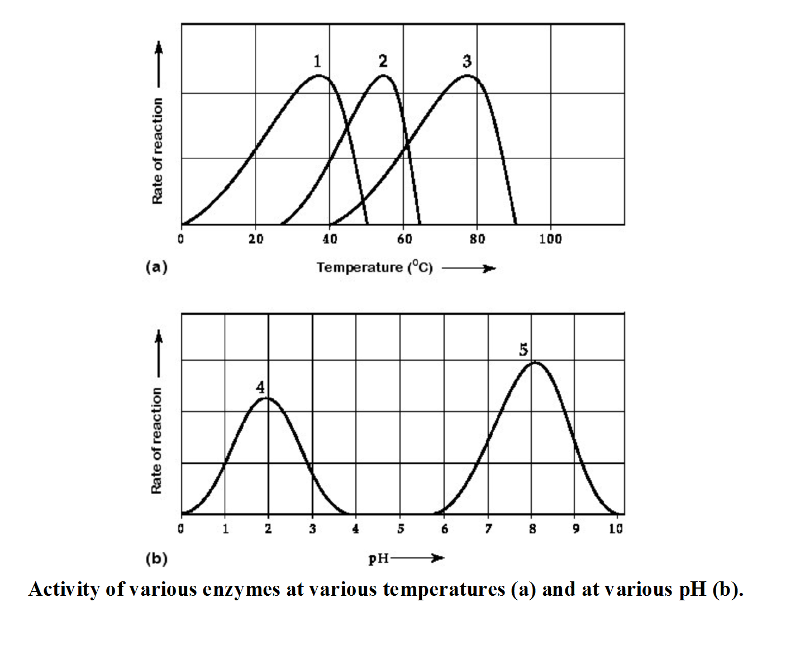 Activity of various enzymes at various temperatures (a) and at various pH (b). 16) Which curves on the graphs may represent the temperature and pH
profiles of an enzyme taken from a bacterium that lives in a mildly
alkaline hot springs at temperatures of 70°C or higher? | back 16 C |
front 17 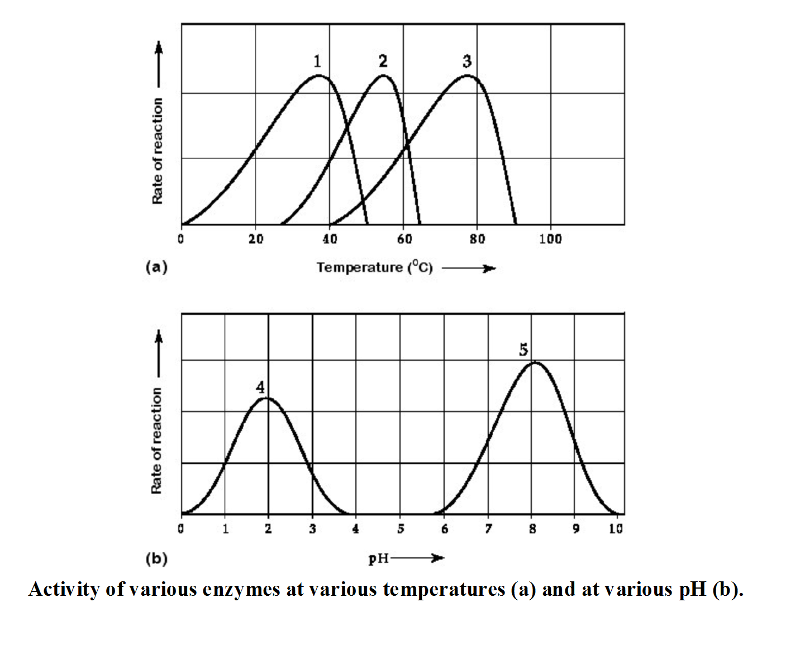 17) Which temperature and pH profile curves on the graphs were most
likely generated from analysis of an enzyme from a human stomach where
conditions are strongly acid? | back 17 C |
front 18 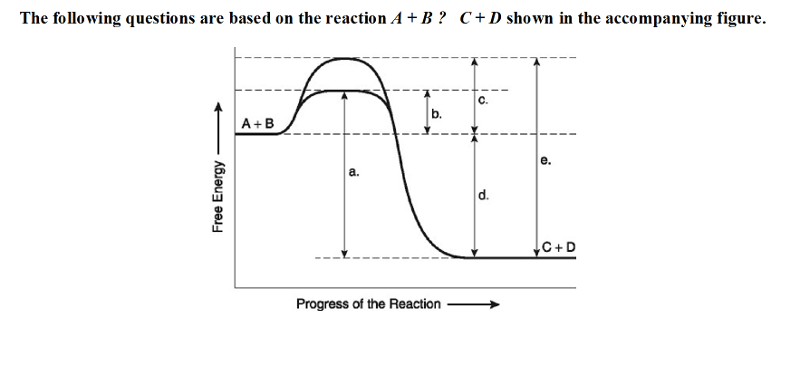 The following questions are based on the reaction A + B ↔ C + D shown in the accompanying figure. 18) Which of the following terms best describes the forward
reaction in the figure? | back 18 A |
front 19 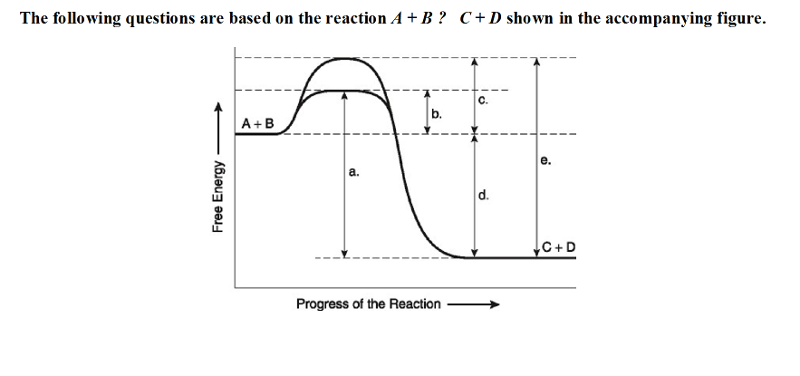 19) Which of the following in the figure would be the same in either
an enzyme-catalyzed or a noncatalyzed reaction? | back 19 D |
front 20 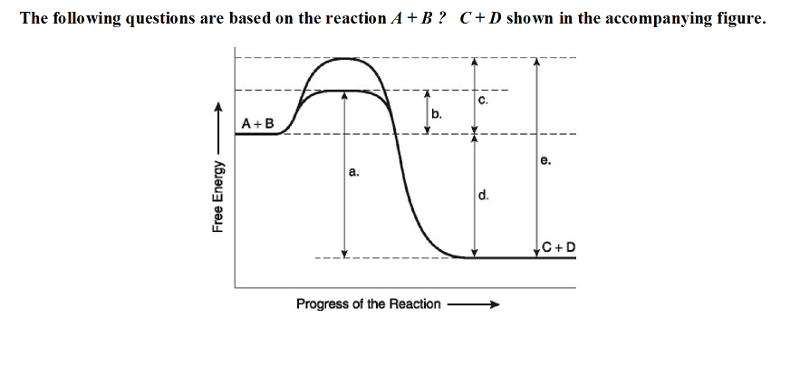 20) Which of the following represents the activation energy required
for the enzyme-catalyzed reaction in the figure? | back 20 B |
front 21 21) Substrate-level phosphorylation accounts for approximately what percentage of the ATP formed by the reactions of glycolysis? A) 100% B) 38% C) 0% D) 2% | back 21 A |
front 22 22) The chemiosmotic hypothesis is an important concept in our
understanding of cellular metabolism in general because it explains
| back 22 C |
front 23 23) The synthesis of ATP by oxidative phosphorylation, using the energy released by movement of protons across the membrane down their electrochemical gradient, is an example of _____. A) a reaction with a positive ΔG B) allosteric regulation C) an endergonic reaction coupled to an exergonic reaction D) active transport | back 23 C |
front 24 24) You have a friend who lost 7 kg (about 15 pounds) of fat on a
regimen of strict diet and exercise. How did the fat leave his body?
| back 24 B |
front 25 25) One function of both alcohol fermentation and lactic acid fermentation is to _____. A) reduce FAD+ to FADH2 B) reduce NAD+ to NADH | back 25 C |
front 26 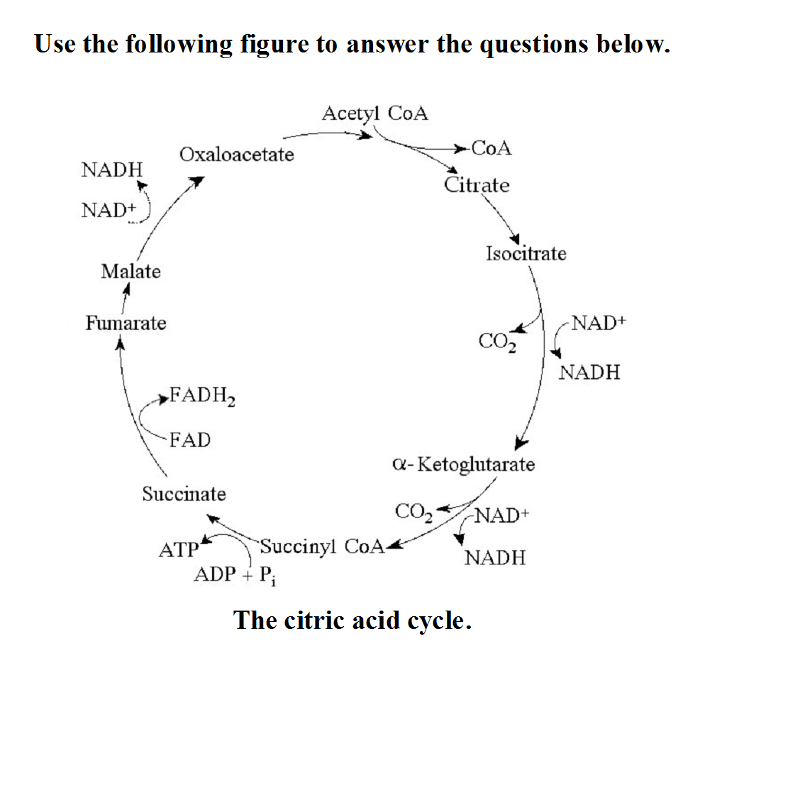 Use the following figure to answer the questions below. The citric acid cycle. | back 26 A |
front 27 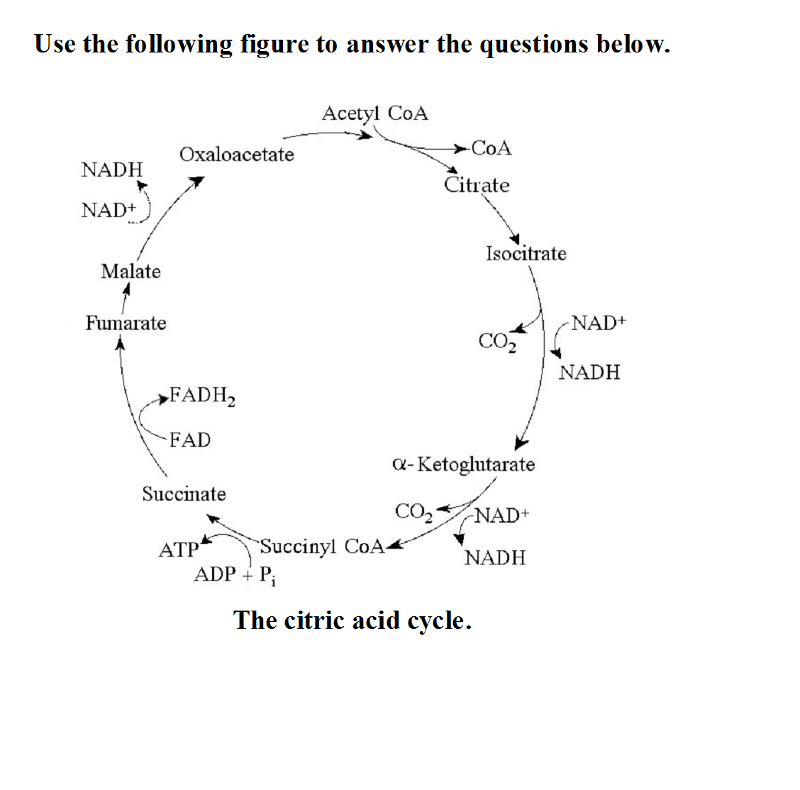 27) Starting with citrate, which of the following combinations of products would result from three acetyl CoA molecules entering the citric acid cycle (see the accompanying figure)? A) 1 ATP, 2 CO2, 3 NADH, and 1 FADH2 B) 38 ATP, 6 CO2, 3 NADH, and
12 FADH2 | back 27 D |
front 28 28) Chemiosmotic ATP synthesis (oxidative phosphorylation) occurs in
_____. | back 28 D |
front 29 29) What is the oxidizing agent in the following reaction: Pyruvate +
NADH + H+ → Lactate + NAD+ | back 29 A |
front 30 30) Glycolysis is active when cellular energy levels are _____; the regulatory enzyme, phosphofructokinase, is _____ by ATP. A) high; inhibited B) low; activated C) high; activated D) low; inhibited | back 30 D |
front 31 31) Even though plants cells photosynthesize, they still use their
mitochondria for oxidation of pyruvate. This will occur in _____.
| back 31 D |
front 32 32) Some photosynthetic organisms contain chloroplasts that lack
photosystem II, yet are able to survive. The best way to detect the
lack of photosystem II in these organisms would be to _____. | back 32 A |
front 33 33) As a research scientist, you measure the amount of ATP and NADPH
consumed by the Calvin cycle in 1 hour. You find that 30,000 molecules
of ATP were consumed, but only 20,000 molecules of NADPH were
consumed. Where did the extra ATP molecules come from? | back 33 A |
front 34 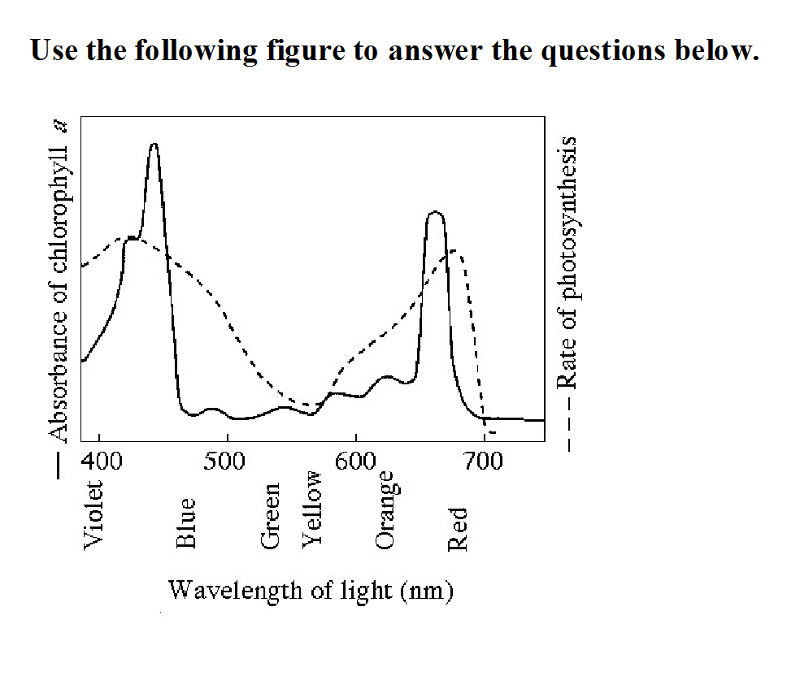 Use the following figure to answer the questions below 34) The figure shows the absorption spectrum for chlorophyll a and
the action spectrum for photosynthesis. Why are they different?
| back 34 C |
front 35 35) P680+ is said to be the strongest biological oxidizing agent. Given its function, why is this necessary? A) It obtains electrons from the oxygen atom in a water molecule,
so it must have a stronger attraction for electrons than oxygen
has. | back 35 A |
front 36 36) Which process is most directly driven by light energy? | back 36 D |
front 37 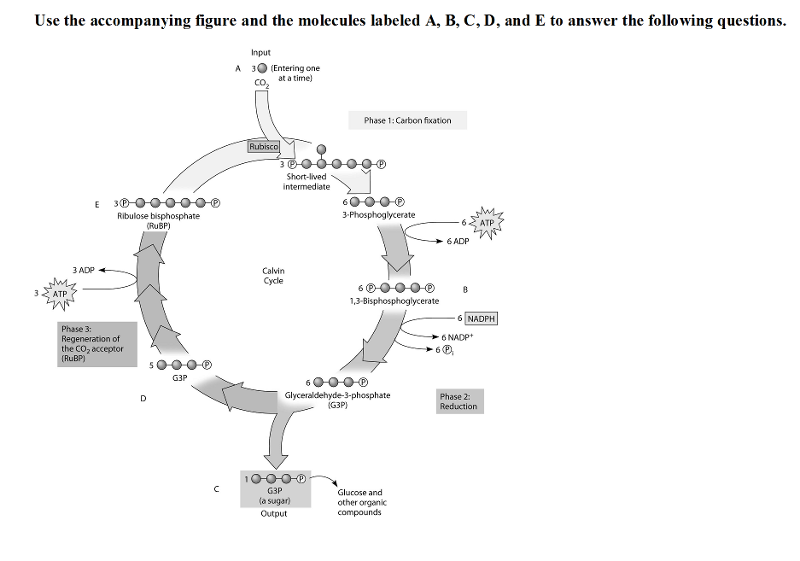 Use the accompanying figure and the molecules labeled A, B, C, D, and E to answer the following questions. 37) Refer to the figure. If the carbon atom of each of the incoming CO2 molecules is labeled with a radioactive isotope of carbon, which organic molecules will be radioactively labeled after one cycle? A) B and C only B) C, D, and E only C) C only D) B, C, D, and E | back 37 D |
front 38 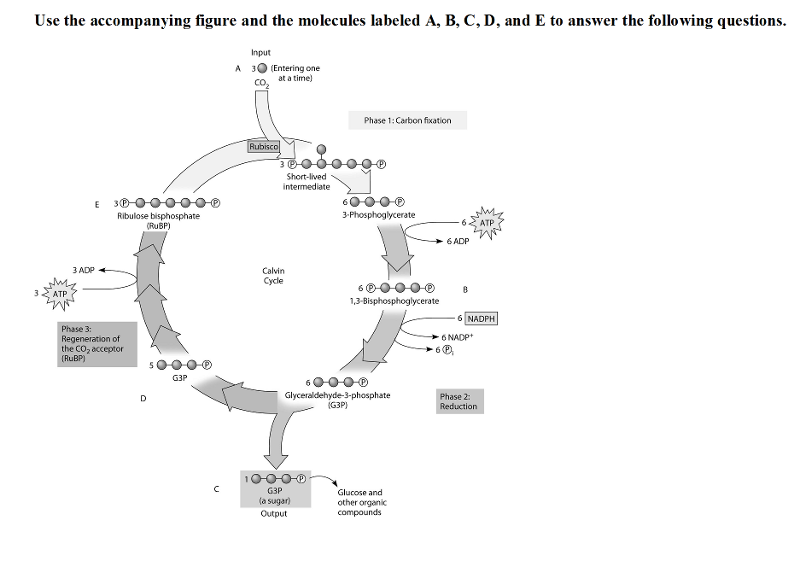 38) Refer to the figure. To identify the molecule that accepts CO2,
Calvin and Benson manipulated the carbon-fixation cycle by either
cutting off CO2 or cutting off light from cultures of photosynthetic
algae. They then measured the concentrations of various metabolites
immediately following the manipulation. How would these experiments
help identify the CO2 acceptor? | back 38 B |
front 39 39) Hormones are chemical substances produced in one organ that are
released into the bloodstream and affect the function of a target
organ. For the target organ to respond to a particular hormone, it
must _____. | back 39 B |
front 40 40) A G-protein receptor with GTP bound to it _____. | back 40 A |
front 41 41) Testosterone functions inside a cell by _____. | back 41 D |
front 42 42) Which of the following is the best explanation for the inability
of a specific animal cell to reduce the Ca2+ concentration in its
cytosol compared with the extracellular fluid? | back 42 C |
front 43 43) Caffeine is an inhibitor of phosphodiesterase. Therefore, the
cells of a person who has recently consumed coffee would have
increased levels of _____. | back 43 D |
front 44 44) Protein kinase is an enzyme that _____. | back 44 A |
front 45 45) At puberty, an adolescent female body changes in both structure
and function of several organ systems, primarily under the influence
of changing concentrations of estrogens and other steroid hormones.
How can one hormone, such as estrogen, mediate so many effects?
| back 45 D |
front 46 46) Transcription factors _____. | back 46 B |
front 47 47) An inhibitor of which of the following could be used to block the
release of calcium from the endoplasmic reticulum? | back 47 A |
front 48 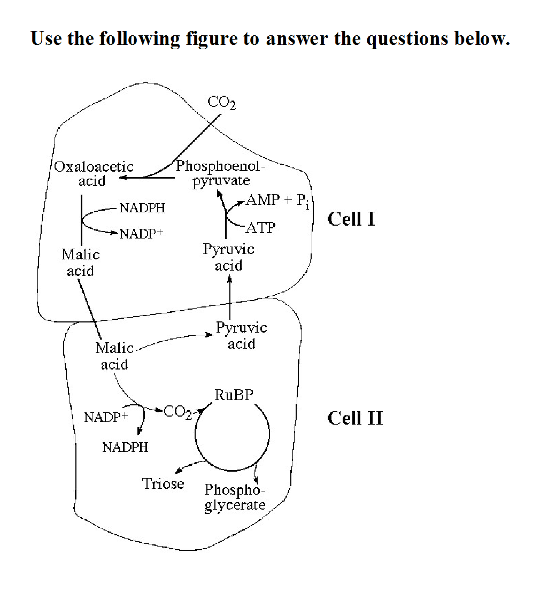 Use the following figure to answer the questions below. 48) Which of the following statements is true concerning the
accompanying figure? | back 48 B |
front 49 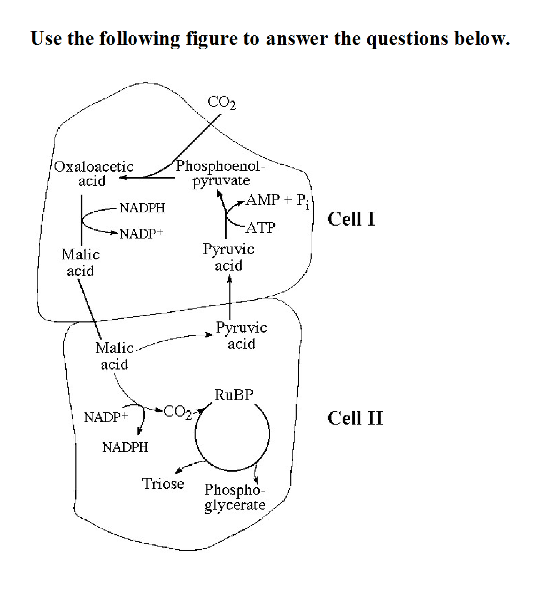 49) Referring to the accompanying figure, oxygen would inhibit the
CO2 fixation reactions in _____. | back 49 B |
front 50 50) Scaffolding proteins are _____. | back 50 A |