Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 9
front 1 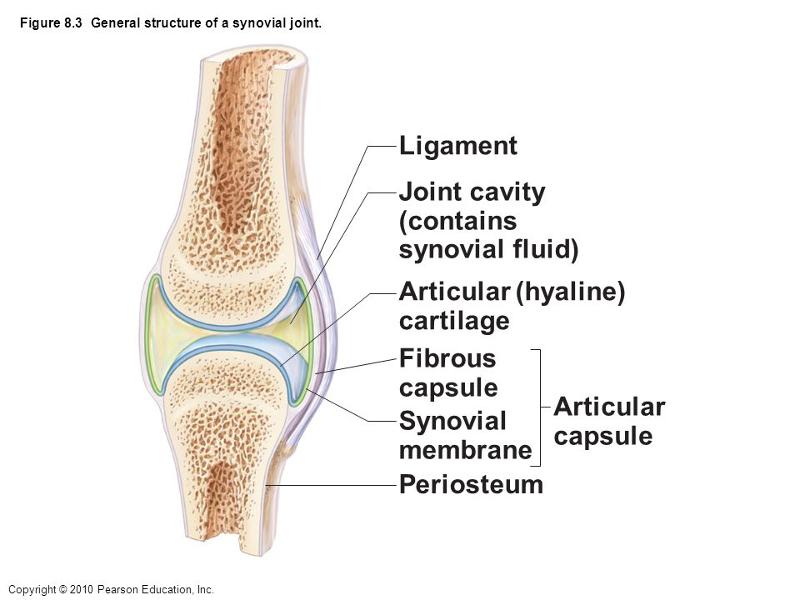 Which letter indicates the layer of the articular capsule that is the most highly vascularized? a. ligament b. joint cavity (contains synovial fluid) c. articular (hyaline) cartilage d. fibrous layer e. synovial membrane | back 1 E |
front 2 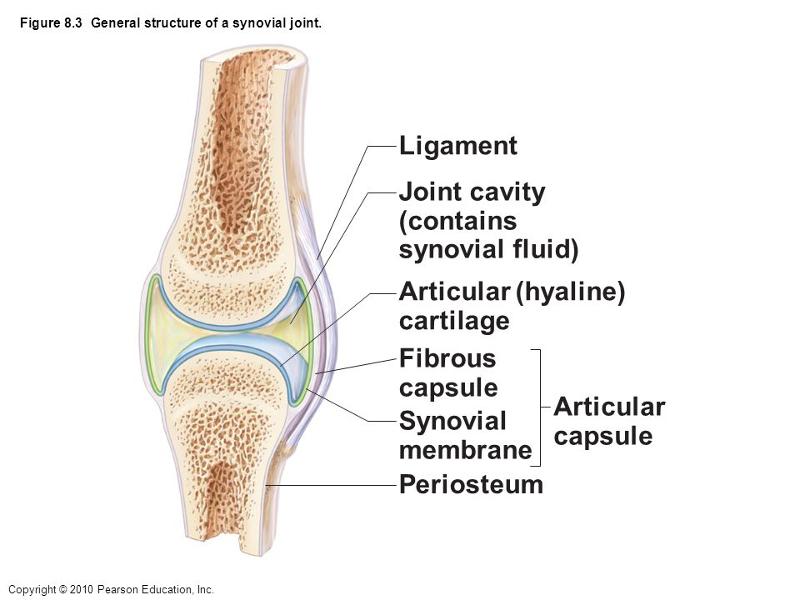 Which letter indicates the fibrous layer of the articular capsule of this synovial joint? a. ligament | back 2 D |
front 3 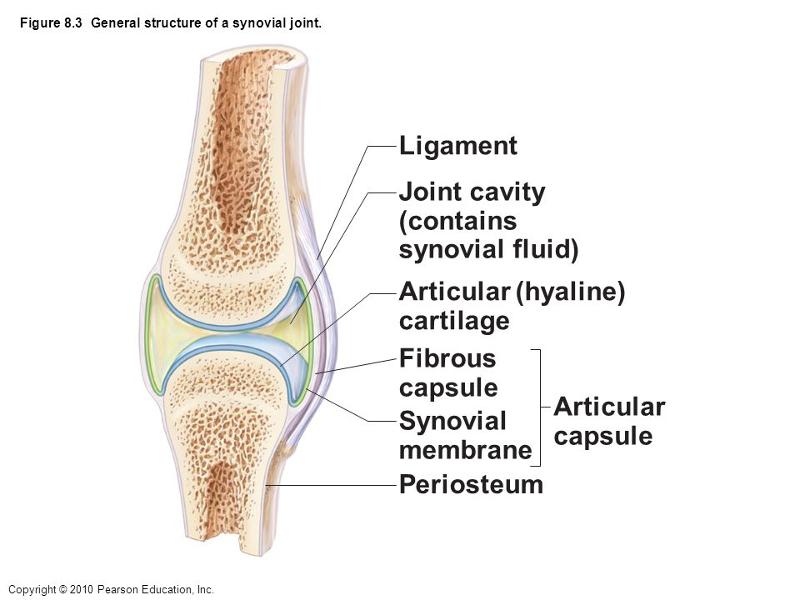 Which letter indicates a ligament that connects bone to bone and is external to the joint capsule? a. ligament | back 3 A |
front 4 When the fibrous tissue of sutures ossifies, the resulting joint is called a A) symphysis. B) synchondrosis. C) syndesmosis. D) synostosis. | back 4 D |
front 5 By plantar flexing your feet at the ankle joints, you will A) stand on your toes. B) stand back on your heels. C) stand on the medial margins of your feet. D) turn your big toes laterally. | back 5 A |
front 6 By hyperextending a thigh at the hip joint, you could A) hit your chin with your knee. B) perform the same movement as circumduction. C) squeeze both thighs together. D) bring your knee and leg to a position posterior to the thorax. | back 6 D |
front 7 Synovial fluid is A) identical to blood plasma. B) an extract from the bone marrow. C) a filtrate of the blood, with added glycoproteins. D) fluid from edema. | back 7 C |
front 8 All of these stabilizing structures provide structural support to the hip joint except the A) iliofemoral ligament. B) ischiofemoral ligament. C) pubofemoral ligament. D) ligament of the head of the femur. | back 8 D |
front 9 Which of these joints is one of the most freely moving joints of the body, but requires the stability provided by the rotator cuff muscles to keep it in place? A) elbow joint B) shoulder joint C) sternoclavicular joint D) hip joint E) ankle joint | back 9 B |
front 10 Which of these joints is stabilized with an annular ligament? A) elbow joint B) shoulder joint C) sternoclavicular joint D) hip joint E) ankle joint | back 10 A |
front 11 What type of excessive motion do anterior ligaments resist? A) abduction B) adduction C) extension D) flexion | back 11 C |
front 12 Which of these joints utilizes the acetabulum? A) elbow joint B) shoulder joint C) sternoclavicular joint D) hip joint E) ankle joint | back 12 D |
front 13 An example of a multiaxial joint is A) the proximal radioulnar joint. B) an intervertebral joint, between the articular processes. C) the hip. D) the pubic symphysis. | back 13 C |
front 14 Which of the response pairs listed below does not correctly pair the joint category with its functional degree of mobility? A) suture: synarthrosis B) symphysis: amphiarthrosis C) synchondrosis: amphiarthrosis D) synovial: diarthrosis | back 14 C |
front 15 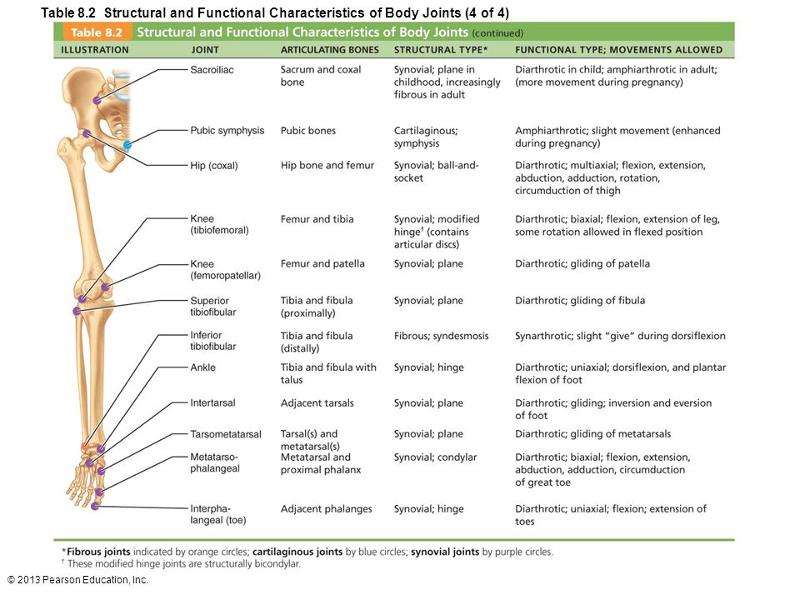 Which letter on the diagram indicates a modified hinge joint? a. sacroiliac b. pubic symphysis c. knee d. superior tibiofibular e. interphalangeal | back 15 C |
front 16 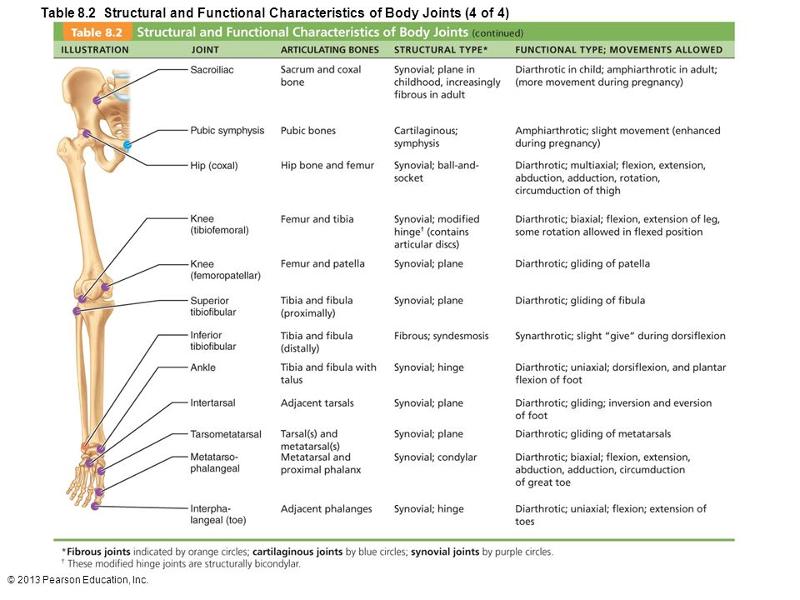 Which letter indicates an example of an interphalangeal joint? a. sacroiliac | back 16 E |
front 17 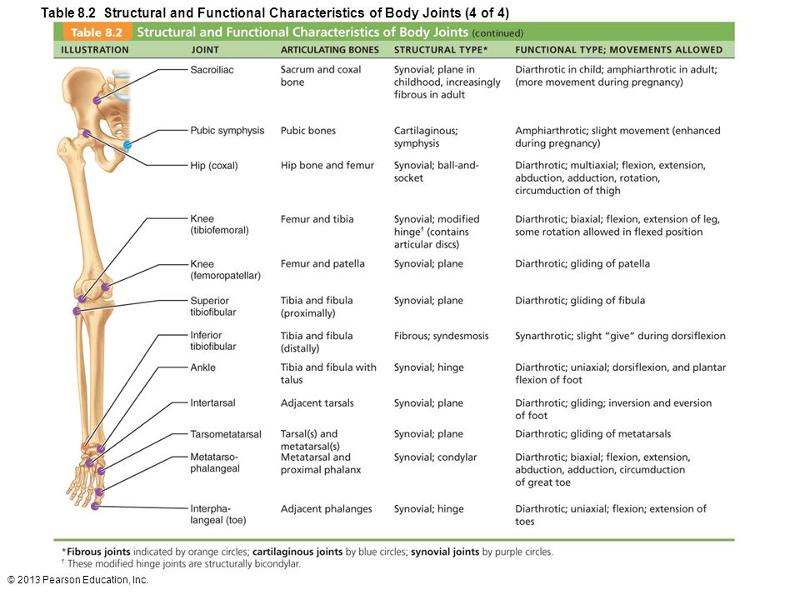 Which letter indicates a cartilaginous, amphiarthrotic, symphysis type of joint? a. sacroiliac | back 17 B |
front 18 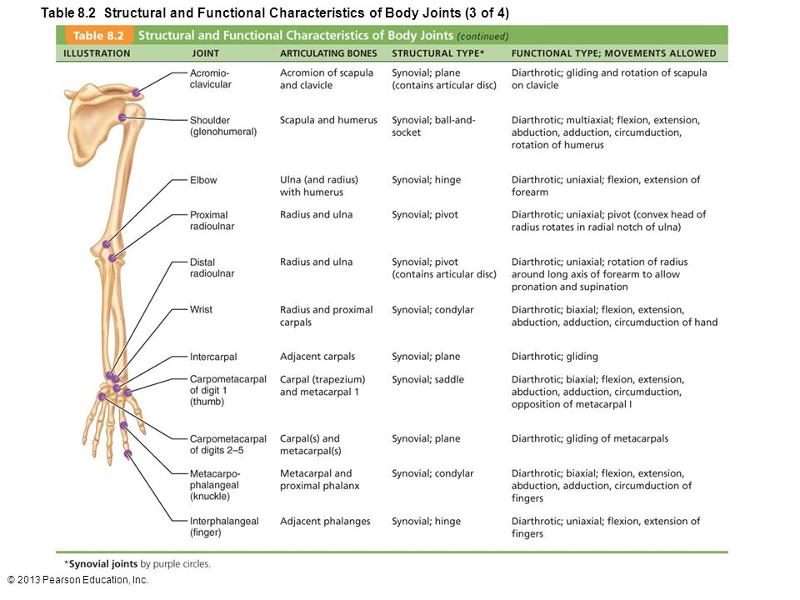 Which letter indicates the joint that is made more stable by the glenoid labrum? a. shoulder b. elbow c. distal radioulnar d. carpometacarpal of digit 1 e. metacarpo-phalangeal | back 18 A |
front 19 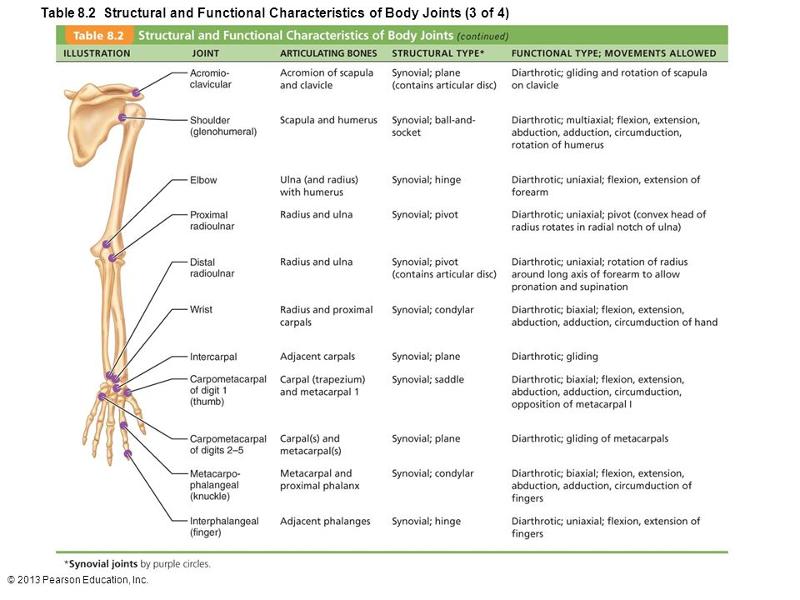 Which letter indicates a synovial, diarthrotic, saddle type of joint? a. shoulder | back 19 D |
front 20  Which letter indicates the distal articulation between the radius and ulna? a. shoulder | back 20 C |