Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Festival 2 (Heart and vessels)
front 1 Which of the following structures sets the pace of heart contraction? atrioventricular bundle SA node bundle branches AV node | back 1 SA node |
front 2 The layers of the heart wall from superficial to deep are: __________. epicardium, endocardium, and myocardium epicardium, myocardium, and endocardium myocardium, endocardium, and epicardium endocardium, myocardium, and epicardium | back 2 epicardium, myocardium, and endocardium |
front 3 Which of the following would increase heart rate? cold temperature low metabolic rate epinephrine parasympathetic stimulation | back 3 Epinephrine |
front 4 The P wave of a normal electrocardiogram indicates ________. ventricular repolarization ventricular depolarization atrial repolarization atrial depolarization | back 4 Atrial depolarization |
front 5 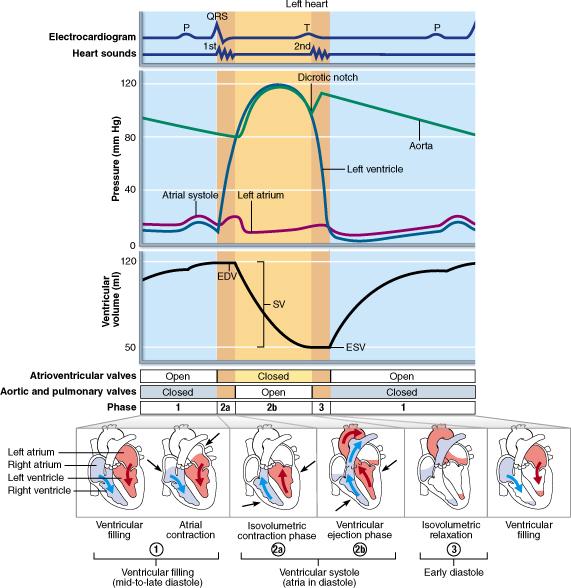 At what point in the cardiac cycle is pressure in the ventricles the highest (around 120 mm Hg)? ventricular systole mid-to-late diastole (ventricular filling) mid-to-late diastole (atrial contraction) early diastole (isovolumetric relaxation) | back 5 Ventricular systole |
front 6 The left ventricular wall of the heart is thicker than the right wall in order to ________. pump blood through a smaller valve expand the thoracic cage during diastole accommodate a greater volume of blood pump blood with greater pressure | back 6 Pump blood with greater pressure |
front 7 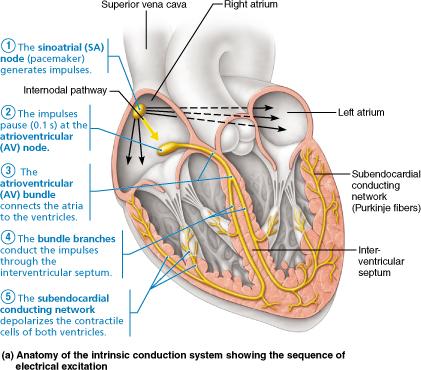 At what rate does the sinoatrial (SA) node ensure depolarization in the heart? 75 beats of the heart per minute 50 beats of the heart per minute 40 beats of the heart per minute 30 beats of the heart per minute | back 7 75 beats of the heart per minute |
front 8 The heart's pacemaker is the __________. Purkinje fibers atrioventricular node sinoatrial node atrioventricular bundle | back 8 Sinoatrial node |
front 9 The order of impulse conduction in the heart, from beginning to end, is __________. SA node, bundle of His, AV node, bundle branches, and Purkinje fibers SA node, AV node, bundle of His, bundle branches, and Purkinje fibers SA node, bundle branches, bundle of His, AV node, and Purkinje fibers SA node, bundle branches, AV node, bundle of His, and Purkinje fibers | back 9 SA node, AV node, bundle of His, and Purkinje fibers |
front 10 True or False: Auricles slightly increase blood volume in the ventricles. | back 10 False |
front 11  Into which chamber do the pulmonary veins send blood? right atrium right ventricle left atrium left ventricle | back 11 Left atrium |
front 12 Which of the following terms refers to a lack of oxygen supply to heart muscle cells? embolism functional syncytium infarction ischemia | back 12 Ischemia |
front 13 The term for pain associated with deficient blood delivery to the heart that may be caused by the transient spasm of coronary arteries is ________. angina pectoris myocardial infarct pericarditis ischemia | back 13 Angina pectoris |
front 14 Which of the following does NOT deliver blood to the right atrium? superior vena cava coronary sinus pulmonary veins inferior vena cava | back 14 Pulmonary veins |
front 15 What causes normal heart sounds? pressure of blood in the ventricles cardiac muscle contraction opening of heart valves heart valve closure | back 15 Heart valve closure |
front 16 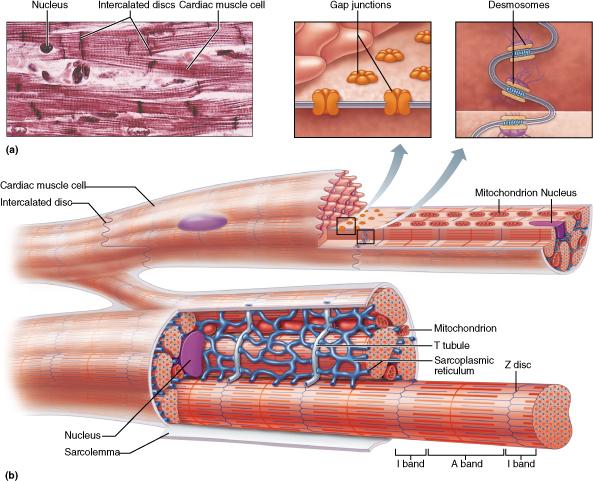 Consider the following characteristics of the cells found in muscle tissue. Which feature is shared by both cardiac muscle and skeletal muscle? branched cells triads striations intercalated discs | back 16 Striations |
front 17 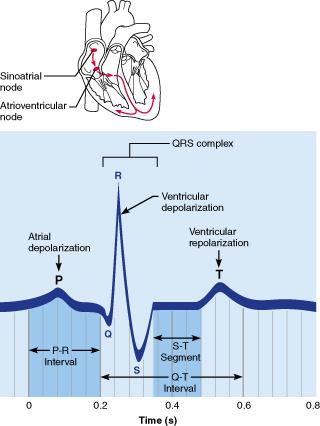 Which portion of the electrocardiogram represents the depolarization wave received from the sinoatrial (SA) node through the atria? T wave P wave QRS complex S-T segment | back 17 P wave |
front 18 The QRS complex represents __________. Check all that apply. atrial depolarization ventricular repolarization ventricular depolarization atrial repolarization | back 18 Ventricular depolarization |
front 19 Hemorrhage with a large loss of blood causes ________. no change in blood pressure but a change in respiration a lowering of blood pressure due to change in cardiac output no change in blood pressure but a slower heart rate a rise in blood pressure due to change in cardiac output | back 19 a lowering of blood pressure due to change in cardiac output |
front 20 Select the correct statement about the heart valves. The AV valves are supported by chordae tendineae so that regurgitation of blood into the atria during ventricular contraction does not occur. The tricuspid valve divides the left atrium from the left ventricle. The mitral valve separates the right atrium from the right ventricle. Aortic and pulmonary valves control the flow of blood into the heart. | back 20 The AV valves are supported by chordae tendineae so that regurgitation of blood into the atria during ventricular contraction does not occur. |
front 21 Which chamber of the heart has the highest probability of being the site of a myocardial infarction? left atrium right atrium left ventricle right ventricle | back 21 Left ventricle |
front 22 The role of the coronary arteries is to __________. direct blood to the pulmonary veins move blood from the atria to the ventricles supply blood to the heart tissue direct blood to the aorta | back 22 Supply blood to the heart tissue |
front 23 True or False: The left side of the heart pumps the same volume of blood as the right. | back 23 True |
front 24 The __________ valve is located between the right atrium and the right ventricle. pulmonary semilunar mitral aortic semilunar tricuspid | back 24 Tricuspid |
front 25 Substances absorbed in the intestines would be routed to the liver via the __________. inferior vena cava hepatic portal vein suprarenal veins abdominal aorta | back 25 Hepatic portal vein |
front 26 Which of the choices below explains why the arterioles are known as resistance vessels? Their prime function is the exchange of nutrients and wastes between the blood and tissue cells. They distribute blood to various parts of the body. The contraction and relaxation of the smooth muscle in their walls can change their diameter. They contain a large quantity of elastic tissue. | back 26 The contraction and relaxation of the smooth muscle in their walls can change their diameter. |
front 27 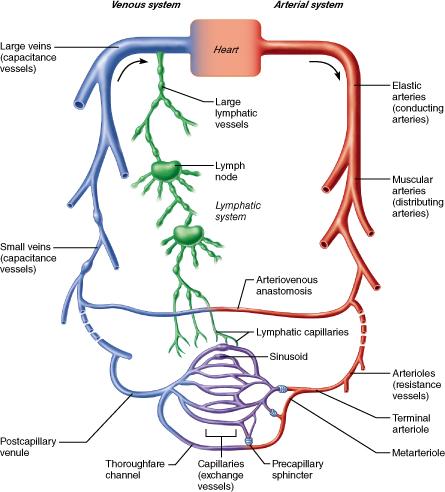 What type of vessel has relatively more smooth muscle and less elastic tissue? elastic artery arteriole muscular artery capillary | back 27 Muscular artery |
front 28 Which of the following is NOT an important source of resistance to blood flow? vessel length vessel diameter total blood volume blood viscosity | back 28 Total blood volume |
front 29 Permitting the exchange of nutrients and gases between the blood and tissue cells is the primary function of ________. capillaries arteries arterioles veins | back 29 Capillaries |
front 30 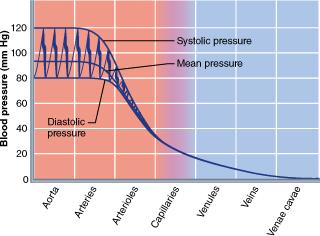 What blood vessel experiences the steepest drop in blood pressure? capillaries arterioles venules arteries | back 30 Arterioles |
front 31 The aorta is an example of a(n) __________. arteriole elastic artery vein muscular artery | back 31 Elastic artery |
front 32 What type of vessel has relatively little smooth muscle or elastin in the tunica media, a large lumen (average of 5.0 mm in diameter), and thin walls (average of 0.5 mm)? venule arteriole vein muscular artery | back 32 Vein |
front 33 Aldosterone will ________. result in a larger output of urine decrease sodium reabsorption promote an increase in blood pressure promote a decrease in blood volume | back 33 Promote an increase in blood pressure |
front 34 True or False: A precapillary sphincter is a cuff of smooth muscle that regulates the flow of blood into the capillaries. | back 34 True |
front 35 True or False: The outermost layer of a blood vessel is the tunica intima. | back 35 False |
front 36 What type of tissue is found in the walls of the arteries but not in the walls of capillaries and venules? smooth muscle collagen fibers endothelium elastic tissue | back 36 Elastic tissue |
front 37 Which of the following will lower blood pressure? atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) antidiuretic hormone (ADH) aldosterone angiotensin II | back 37 Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) |
front 38 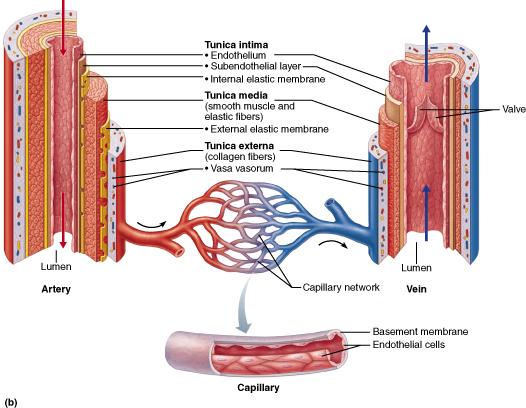 What layer can change blood vessel diameter by vasodilation and vasoconstriction? tunica intima vasa vasorum tunica externa tunica media | back 38 Tunica media |
front 39 True or False: Vasodilation is a widening of the lumen due to smooth muscle contraction. | back 39 False |
front 40 Gas and nutrient exchanges between the blood and tissues take place at the __________. veins arteries arterioles capillaries | back 40 Capillaries |
front 41 How would an attack by a mugger affect blood pressure? What is the physiological basis for your answer? Blood pressure would decrease due to sympathetic nervous system stimulation. Blood pressure would decrease due to parasympathetic nervous system stimulation. Blood pressure would increase due to parasympathetic nervous system stimulation. Blood pressure would increase due to vagal nerve stimulation. Blood pressure would increase due to sympathetic nervous system stimulation. | back 41 Blood pressure would increase due to sympathetic nervous system stimulation. |
front 42 Which statement best describes arteries? All carry oxygenated blood to the heart. All carry blood away from the heart. All contain valves to prevent the backflow of blood. Only large arteries are lined with endothelium. | back 42 All carry blood away from the heart. |
front 43 Which of the following is a long-term mechanism for maintaining blood pressure? baroceptor-initiated reflexes hormonal control of peripheral resistance chemoreceptor-initiated reflexes renal regulation | back 43 Renal regulation |
front 44 The baroreceptors in the carotid sinus and aortic arch are sensitive to which of the following? changes in arterial pressure an increase in oxygen levels a decrease in oxygen levels a decrease in carbon dioxide | back 44 Changes in arterial pressure |
front 45 Factors that aid venous return include all except ________. urinary output activity of skeletal muscles venous valves pressure changes in the thorax | back 45 Urinary output |
front 46 True and False: Vasodilation will result in increased blood flow to a given tissue. | back 46 True |
front 47 Which tunic of an artery is most responsible for maintaining blood pressure and continuous blood circulation? tunica externa tunica intima tunica media tunica adventitia | back 47 Tunica media |
front 48 Leaky capillaries found in the bone marrow are called __________. arterioles fenestrated capillaries continuous capillaries sinusoidal capillaries | back 48 Sinusoidal capillaries |
front 49 Which of the following is true about veins? Veins carry blood away from the heart, while arteries carry blood to the heart. Veins are more muscular than arteries. Veins have valves; arteries do not. Veins have a smaller diameter lumen than arteries. | back 49 Veins have valves; arteries do not |
front 50 True or False: An increase in blood viscosity will cause an increase in peripheral resistance. | back 50 True |
front 51 Which of the following is true about veins? Up to 35% of total body blood is in venous circulation at any given time. Venous valves are formed from the tunica media. Veins have a small lumen in relation to the thickness of the vessel wall. Veins are called capacitance vessels or blood reservoirs. | back 51 Veins are called capacitance vessels or blood reservoirs. |
front 52 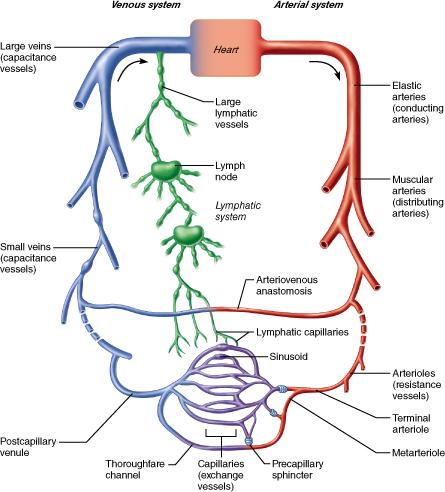 Which type of vessel contains elastin in all three tunics to allow the vessel to expand and recoil as the heart ejects blood? muscular artery arteriole distributing artery elastic artery | back 52 Elastic artery |
front 53 The arteries that directly feed into the capillary beds are called ________. venules arterioles muscular arteries elastic arteries | back 53 Arterioles |
front 54 Which of the following would experience a decreased blood flow during exercise? skeletal muscles skin brain kidneys | back 54 Kidneys |
front 55 True or False: Arteries supplying the same territory are often merged with one another, forming arterial anastomoses. | back 55 True |
front 56 __________ is the pressure that propels blood to the tissues. Mean arterial pressure Diastolic pressure Pulse pressure Systolic pressure | back 56 Mean arterial pressure |
front 57 True or False: The thick-walled arteries close to the heart are called muscular arteries. | back 57 False |
front 58 Why is it important that blood pressure drop to lower levels as it reaches the capillary beds? Because capillaries are fragile and extremely permeable. Because capillaries actually are high-pressure vessels. Because capillaries actually need a higher blood pressure for filtration activities. Because capillaries depend on the lower pressure to prevent fluid exchange between the capillaries and the tissue fluid. | back 58 Because capillaries are fragile and extremely permeable. |
front 59 The inferior vena cava carries blood __________ the __________ of the heart. away from;left atrium to; right atrium away from; right atrium to: left atrium | back 59 To; right atrium |
front 60 Which of the following chemicals does not help regulate blood pressure? angiotensin II atrial natriuretic peptide nitric acid ADH | back 60 Nitric acid |
front 61 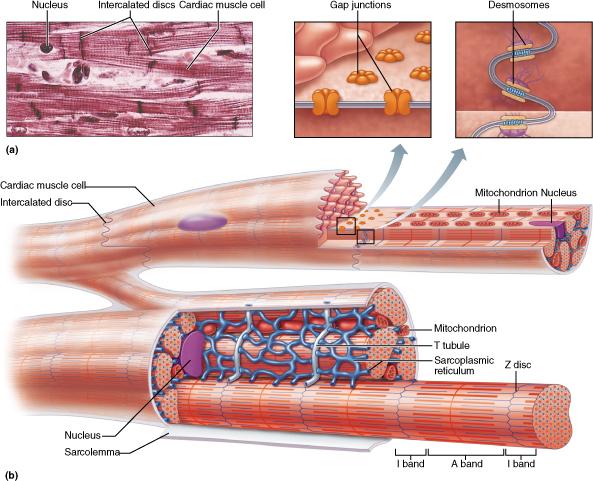 Which functional feature best describes the manner in which cardiac muscle contracts? Nerve fibers must stimulate cardiac muscle cells for them to contract. Only some motor units contract in cardiac muscle. Automaticity (autorhythmicity) promotes the spontaneous contraction of the cardiac muscle cells. Refractory periods in cardiac contractions are relatively short. | back 61 Automaticity (autorhythmicity) promotes the spontaneous contraction of the cardiac muscle cells. |
front 62 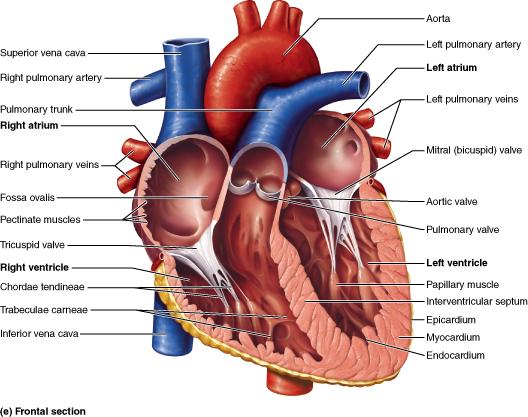 Into what vessel does the left ventricle eject blood? superior vena cava pulmonary veins aorta pulmonary trunk | back 62 Aorta |
front 63 True or False: Cardiac muscle has more mitochondria and depends less on a continual supply of oxygen than does skeletal muscle. | back 63 False |
front 64 Which heart chamber sends deoxygenated blood to the lungs? left atrium right atrium left ventricle right ventricle | back 64 Right ventricle |
front 65 True or False: The myocardium receives its blood supply from the coronary arteries. | back 65 True |
front 66 The heart has __________ chambers and __________ valves. two; two four; two two; four four; four | back 66 Four; four |
front 67 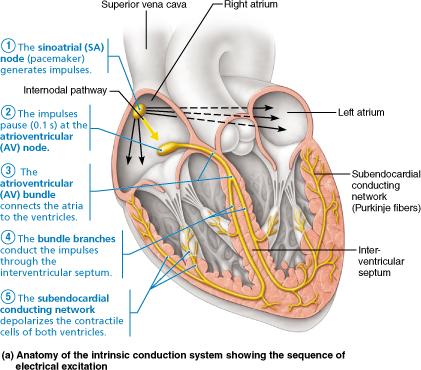 Specifically, what part of the intrinsic conduction system stimulates the atrioventricular (AV) node to conduct impulses to the atrioventricular bundle? interventricular septum subendocardial conducting network (Purkinje fibers) bundle branches sinoatrial (SA) node | back 67 Sinoatrial (SA) node |
front 68 The first heart sound (the "lub" of the "lub-dup") is caused by __________. closure of the semilunar valves closure of the atrioventricular valves opening of the semilunar valves opening of the atrioventricular valves | back 68 Closure of the atrioventricular valves |
front 69 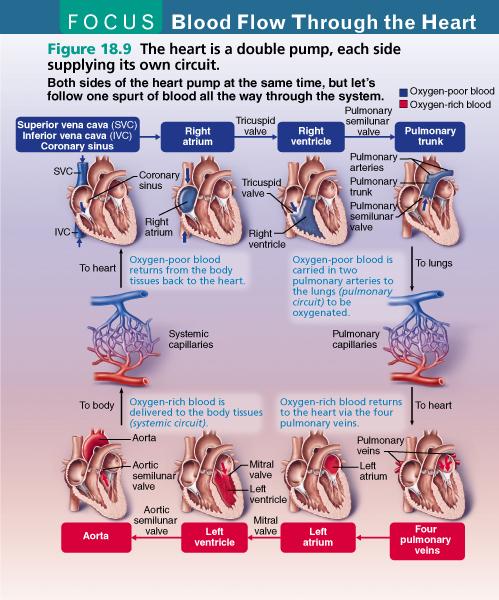 Into which chamber of the heart do the superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, and coronary sinus return deoxygenated blood? left ventricle left atrium right atrium right ventricle | back 69 Right atrium |
front 70 Compared to skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle ________. has more nuclei per cell cells are larger than skeletal muscle cells has gap junctions that allow it to act as a functional syncytium lacks striations | back 70 has gap junctions that skeletal muscle cells |
front 71 What structures connect the individual heart muscle cells? chordae tendineae trabaculae carneae intercalated discs anastomoses | back 71 intercalated discs |
front 72 In a healthy individual which of the following would be low? Afterload stroke volume contractility preload | back 72 Afterload |