Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
A&P Chapter 9 Muscles and Muscle Tissue
front 1 Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. | back 1 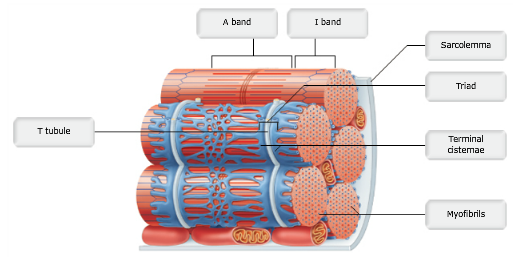 |
front 2 Action potential propagation in a skeletal muscle fiber ceases when acetylcholine is removed from the synaptic cleft. Which of the following mechanisms ensures a rapid and efficient removal of acetylcholine? | back 2 Acetylcholine is degraded by acetylcholinesterase. |
front 3 The neuromuscular junction is a well-studied example of a chemical synapse. Which of the following statements describes a critical event that occurs at the neuromuscular junction? | back 3 Acetylcholine is released by axon terminals of the motor neuron. |
front 4 Action potentials travel the length of the axons of motor neurons to the axon terminals. These motor neurons __________. | back 4 extend from the brain or spinal cord to the sarcolemma of a skeletal muscle fiber |
front 5 Calcium entry into the axon terminal triggers which of the following events? | back 5 Synaptic vesicles fuse to the plasma membrane of the axon terminal and release acetylcholine. |
front 6 Acetylcholine binds to its receptor in the sarcolemma and triggers __________. | back 6 the opening of ligand-gated cation channels |
front 7 Sodium and potassium ions do not diffuse in equal numbers through ligand-gated cation channels. Why? | back 7 The inside surface of the sarcolemma is negatively charged compared to the outside surface. Sodium ions diffuse inward along favorable chemical and electrical gradients. |
front 8 Excitation-contraction coupling is a series of events that occur after the events of the neuromuscular junction have transpired. The term excitation refers to which step in the process? | back 8 Excitation, in this case, refers to the propagation of action potentials along the sarcolemma. |
front 9 Excitation of the sarcolemma is coupled or linked to the contraction of a skeletal muscle fiber. What specific event initiates the contraction? | back 9 Calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum initiates the contraction. |
front 10 A triad is composed of a T-tubule and two adjacent terminal cisternae of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. How are these components connected? | back 10 A series of proteins that control calcium release. |
front 11 What is name given to the regularly spaced infoldings of the sarcolemma? | back 11 transverse or T tubules |
front 12 Which of the following is most directly responsible for the coupling of excitation to contraction of skeletal muscle fibers? | back 12 Calcium ions. |
front 13 What is the relationship between the number of motor neurons recruited and the number of skeletal muscle fibers innervated? | back 13 Typically, hundreds of skeletal muscle fibers are innervated by a single motor neuron. |
front 14 The cross bridge cycle is a series of molecular events that occur after excitation of the sarcolemma. What is a cross bridge? | back 14 A myosin head bound to actin |
front 15 What structure is the functional unit of contraction in a skeletal muscle fiber? | back 15 The sarcomere |
front 16 Calcium ions couple excitation of a skeletal muscle fiber to contraction of the fiber. Where are calcium ions stored within the fiber? | back 16 Calcium ions are stored in the sarcoplasmic reticulum. |
front 17 After a power stroke, the myosin head must detach from actin before another power stroke can occur. What causes cross bridge detachment? | back 17 ATP binds to the myosin head. |
front 18 How does the myosin head obtain the energy required for activation? | back 18 The energy comes from the hydrolysis of ATP. |
front 19 What specific event triggers the uncovering of the myosin binding site on actin? | back 19 Calcium ions bind to troponin and change its shape. |
front 20 When does cross bridge cycling end? | back 20 Cross bridge cycling ends when sufficient calcium has been actively transported back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum to allow calcium to unbind from troponin. |
front 21 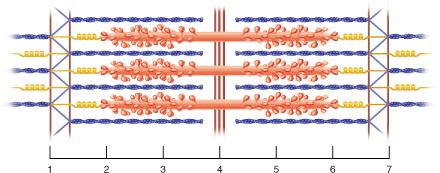 Between which two points would there be substantial amounts of both the proteins actin and myosin? | back 21 2 and 3 |
front 22 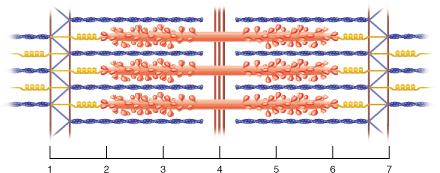 The region between which two points corresponds to the entire A band? | back 22 2 and 6 |
front 23 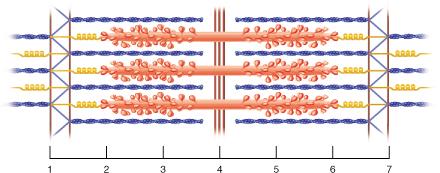 The region between which two points corresponds to the I band? 2 and 3 | back 23 None of the listed responses is correct. |
front 24 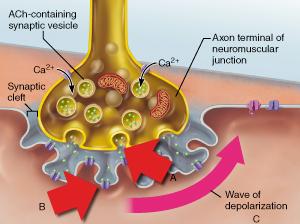 Which event is most significant in initiating the "wave of depolarization" shown in event C? | back 24 diffusion of Na+ into the muscle fiber |
front 25 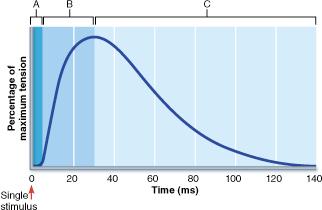 In which phase in the figure would the net movement of Ca2+ into the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) be greatest? | back 25 C |
front 26 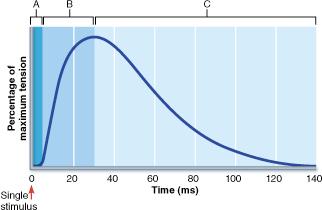 What result would be expected if an additional stimulus, equal in intensity to the first, were to be applied to the muscle at the 60 millisecond (ms) time point? | back 26 The muscle would increase in tension to a level greater than that measured at the beginning of phase C. |
front 27 Excitation-contraction coupling includes all EXCEPT which of the following events? | back 27 release of acetylcholine from axon terminals at the neuromuscular junction |
front 28 Which of the following factors influence the velocity and duration of muscle contraction? | back 28 load placed on the muscle |
front 29 The strongest muscle contractions are normally achieved by ________. | back 29 increasing the stimulation up to the maximal stimulus |
front 30 Which of the following is not a role of ionic calcium in muscle contraction? | back 30 activates epinephrine released from adrenal gland |
front 31 What is the most distinguishing characteristic of muscle tissue? | back 31 the ability to transform chemical energy into mechanical energy |
front 32 Hypothetically, if a muscle were stretched to the point where thick and thin filaments no longer overlapped, ________. | back 32 no muscle tension could be generated |
front 33 The thin filaments (actin) contain a polypeptide subunit G actin that bears active sites for myosin attachment. | back 33 True |
front 34 Eccentric contractions are more forceful than concentric contractions. | back 34 True |
front 35 Muscle cells store more creatine phosphate than ATP resulting in the muscle having a reserve source of energy. | back 35 True |
front 36 Muscle tone is the small amount of tautness or tension in the muscle due to weak, involuntary contractions of its motor units. | back 36 True |
front 37 Binding of calcium to calmodulin is a step in excitation-contraction coupling of ________ cells. | back 37 smooth muscle |
front 38 A motor neuron and all the muscle cells that it stimulates are referred to as a motor end plate. | back 38 False |
front 39 Once a motor neuron has fired, all the muscle fibers in a muscle contract. | back 39 False |
front 40 Which of the following is CORRECTLY paired? | back 40 skeletal muscle: voluntary control |
front 41 In an isotonic contraction, the muscle ________. | back 41 changes in length and moves the "load" |
front 42 An increase in the calcium ion level in the sarcoplasm starts the sliding of the thin filaments. When the level of calcium ions declines, sliding stops. | back 42 True |
front 43 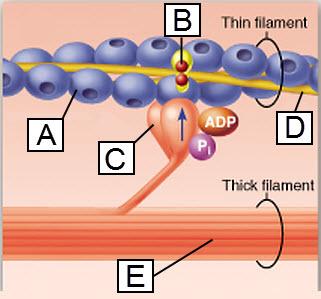 Which lettered protein functions as a motor protein? | back 43 C |
front 44 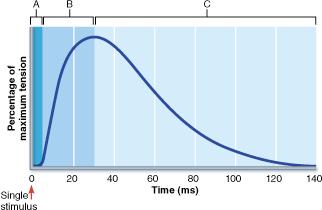 In which phase of the muscle twitch shown in the above figure would the maximum amount of ATP be consumed by myosin head groups? | back 44 B |
front 45 Peristalsis is characteristic of smooth muscle. | back 45 True |
front 46 What structure in skeletal muscle cells functions in calcium storage? | back 46 sarcoplasmic reticulum |
front 47 The distance between Z discs ________ during muscle contraction. | back 47 decreases |
front 48 Thick myofilaments are made of ________. | back 48 myosin |
front 49 Which type of muscle CANNOT contract without being stimulated by the nervous system? | back 49 skeletal |
front 50 Slow oxidative muscle fibers are best suited for ________. | back 50 running a marathon |
front 51 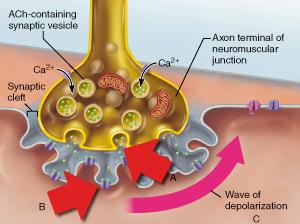 What event directly triggers the release of neurotransmitter shown in A? | back 51 diffusion of Ca2+ into the axonal terminus |
front 52 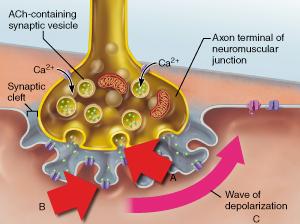 What specific neurotransmitter is released from the axonal terminus as shown in A? | back 52 acetylcholine |
front 53 Three discrete types of muscle fibers are identified on the basis of their size, speed, and endurance. Which of the following athletic endeavors best represents the use of red fibers? | back 53 a long, relaxing swim |
front 54 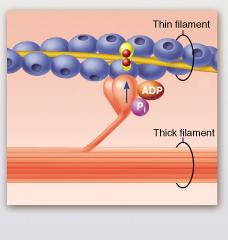 The protein troponin is shown in this figure to be bound to which substance? | back 54 calcium ion |
front 55 The smallest contractile unit of a muscle fiber is ________. | back 55 the sarcomere |
front 56 The muscle cell membrane is called the ________. | back 56 sarcolemma |
front 57 A resting potential is caused by a difference in the concentration of certain ions inside and outside the cell. | back 57 True |
front 58 What is a cross bridge cycle? | back 58 It is the cycle in which an energized myosin head binds to actin and performs a power stroke, then binds to ATP in order to detach and re-energize. |
front 59 An anaerobic metabolic pathway that results in the production of two net ATPs per glucose plus two pyruvic acid molecules is ________. | back 59 glycolysis |
front 60 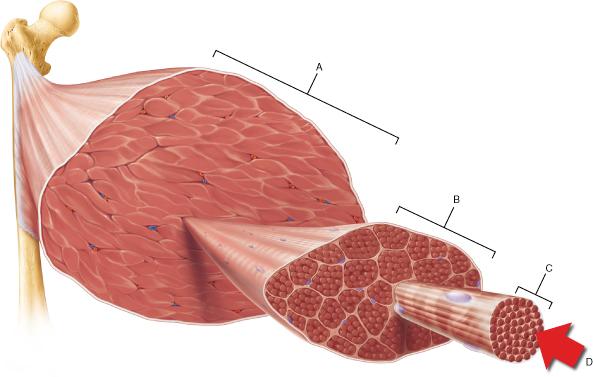 The connective tissue that covers structure A is continuous with which of the following? | back 60 tendon |
front 61 The force of a muscle contraction is NOT affected by __________. | back 61 the amount of ATP stored in the muscle cells |
front 62 Muscle tone is ________. | back 62 a state of sustained partial contraction |
front 63 The response of a motor unit to a single action potential of its motor neuron is called ________. | back 63 a muscle twitch |
front 64 The oxygen-binding protein found in muscle cells is ________. | back 64 myoglobin |
front 65 Immediately following the arrival of the stimulus at a skeletal muscle cell there is a short period called the ________ period during which the neurotransmitter is released by exocytosis, diffuses across the synaptic cleft, and binds to its receptors. | back 65 latent |
front 66 Which organelle contains the contractile elements found in skeletal muscle? | back 66 myofibril |
front 67 What is the role of tropomyosin in skeletal muscles? | back 67 Tropomyosin serves as a contraction inhibitor by blocking the myosin binding sites on the actin molecules. |
front 68 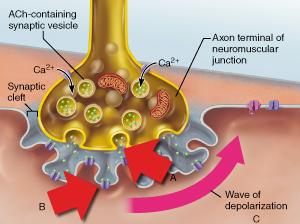 Which statement accurately describes the event indicated by B? | back 68 Binding of acetylcholine to a receptor triggers the opening of an ion channel. |
front 69 Muscle contraction will always promote movement of body parts regardless of how they are attached. | back 69 False |
front 70 What part of the sarcolemma contains acetylcholine receptors? | back 70 motor end plate |
front 71 During muscle contraction, myosin cross bridges attach to which active sites? | back 71 actin filaments |
front 72 What is the functional unit of a skeletal muscle called? | back 72 a sarcomere |
front 73 After nervous stimulation stops, what prevents ACh in the synaptic cleft from continuing to stimulate contraction? | back 73 acetylcholinesterase destroying the ACh |
front 74 During vigorous exercise, there may be insufficient oxygen available to completely break down pyruvic acid for energy. As a result, the pyruvic acid is converted to ________. | back 74 lactic acid |
front 75 Smooth muscles are able to regenerate throughout life. | back 75 True |
front 76 When muscle cells break down glucose to generate ATP under oxygen deficient conditions, they will form ________. | back 76 lactic acid |
front 77 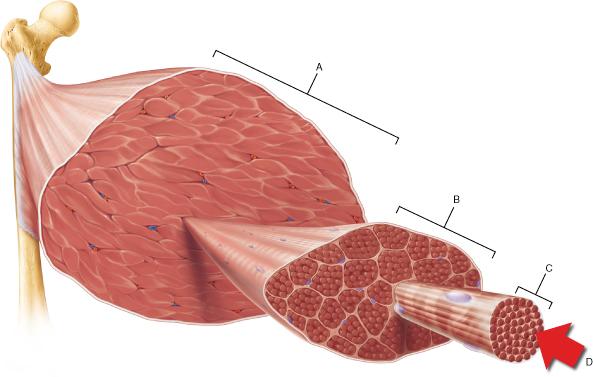 Which structure corresponds to a single fascicle? | back 77 B |
front 78 Most skeletal muscles contain ________. | back 78 a mixture of fiber types |
front 79 A muscle that is lengthening while it produces tension is performing a(an) ________ contraction. | back 79 eccentric |
front 80 The contractile units of skeletal muscles are ________. | back 80 myofibrils |
front 81 Choose the FALSE statement. | back 81 Skeletal muscle cells use creatine phosphate instead of ATP to do work. |
front 82 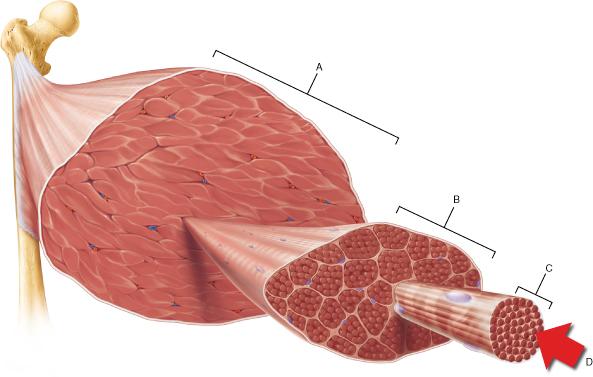 Which of the following is the smallest structural unit in which the distinctive striated bands characteristic of skeletal muscle are observed? | back 82 D |
front 83 What produces the striations of a skeletal muscle cell? | back 83 the arrangement of myofilaments |
front 84 Which protein inhibits interaction between actin and myosin to prevent skeletal muscle contraction; and which ions remove the inhibition? | back 84 tropomyosin; calcium ions |
front 85 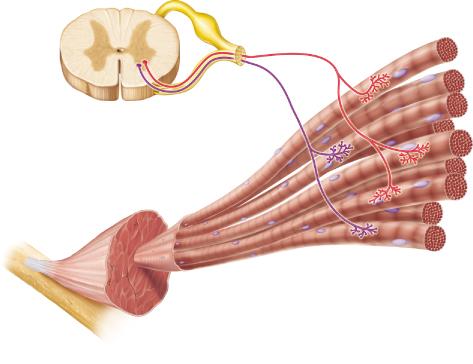 Which of the following describes the neurons shown in this figure? | back 85 somatic motor neurons |
front 86 Which of the following is TRUE? | back 86 Skeletal muscle fibers contain sarcomeres; smooth muscle fibers do not. |
front 87 Which type of muscle CANNOT contract without being stimulated by the nervous system? | back 87 skeletal |
front 88 The sliding filament model of contraction states that ________. | back 88 during contraction the thin myofilaments slide past the thick myofilaments so that the actin and myosin myofilaments overlap to a greater degree |
front 89 The major function of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in muscle contraction is to ________. | back 89 regulate intracellular calcium concentration |
front 90 The force of a muscle contraction is NOT affected by __________. | back 90 the amount of ATP stored in the muscle cells |
front 91 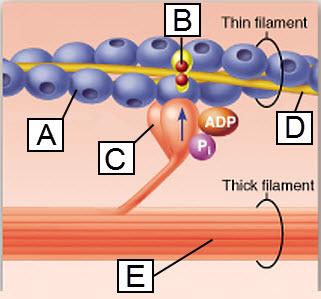 The protein actin is indicated by which letter? | back 91 A |
front 92 Muscle tissue has all of the following properties except ________. | back 92 secretion |
front 93 In an isotonic contraction, the muscle ________. | back 93 changes in length and moves the "load" |
front 94 Which of the following surrounds the individual muscle cell? | back 94 endomysium |
front 95 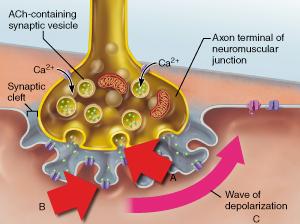 What event directly triggers the release of neurotransmitter shown in A? | back 95 diffusion of Ca2+ into the axonal terminus |
front 96 What is the functional unit of a skeletal muscle called? | back 96 a sarcomere |
front 97 The contractile units of skeletal muscles are ________. | back 97 myofibrils |
front 98 The smallest contractile unit of a muscle fiber is ________. | back 98 the sarcomere |
front 99 The first step toward generating a skeletal muscle contraction is ________. | back 99 stimulation of the muscle by a nerve ending |
front 100 Which organelle contains the contractile elements found in skeletal muscle? | back 100 myofibril |
front 101 Most skeletal muscles contain ________. | back 101 a mixture of fiber types |
front 102 The term aponeurosis refers to ________. | back 102 a sheetlike indirect attachment to a skeletal element |
front 103 Muscle tissue does NOT ________. | back 103 produce blood cells |
front 104 What special feature of smooth muscle allows it to stretch without immediately resulting in a strong contraction? | back 104 stress-relaxation response |
front 105 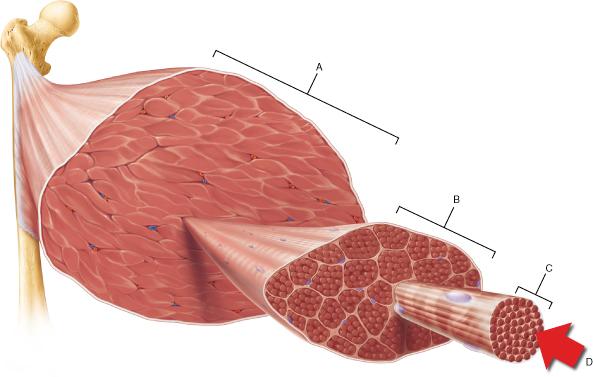 In the figure above, which structure corresponds to a single skeletal muscle cell? | back 105 C |
front 106 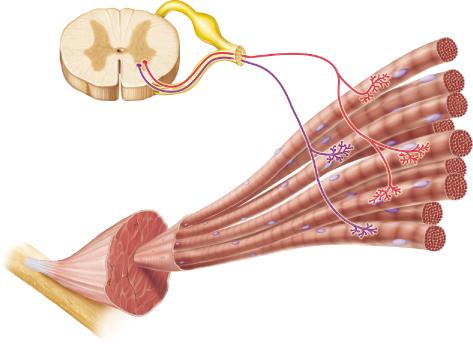 If both of the neurons in the figure were activated, more muscle fibers would contract than if either neuron alone were active. This mechanism for control of the force of muscle contraction is known as ______. | back 106 recruitment |
front 107 The sliding filament model of contraction involves ________. | back 107 actin and myosin sliding past each other and partially overlapping |
front 108 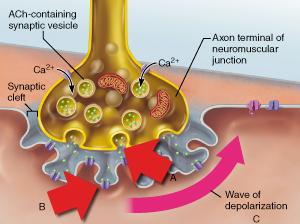 Which statement accurately describes the event indicated by B? | back 108 Binding of acetylcholine to a receptor triggers the opening of an ion channel. |
front 109 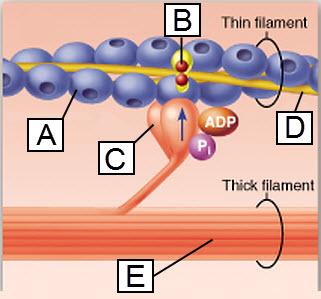 Which lettered protein functions as a motor protein? | back 109 C |
front 110 Immediately following the arrival of the stimulus at a skeletal muscle cell there is a short period called the ________ period during which the neurotransmitter is released by exocytosis, diffuses across the synaptic cleft, and binds to its receptors. | back 110 latent |
front 111 A muscle that is lengthening while it produces tension is performing a(an) ________ contraction. | back 111 eccentric |
front 112 Choose the FALSE statement. | back 112 Skeletal muscle cells use creatine phosphate instead of ATP to do work. |
front 113 Which protein inhibits interaction between actin and myosin to prevent skeletal muscle contraction; and which ions remove the inhibition? | back 113 tropomyosin; calcium ions |
front 114 Which muscle characteristic describes the ability of muscle to respond to a stimulus? | back 114 excitability |
front 115 Binding of calcium to calmodulin is a step in excitation-contraction coupling of ________ cells. | back 115 smooth muscle |
front 116 The oxygen-binding protein found in muscle cells is ________. | back 116 myoglobin |
front 117 One of the important functions of skeletal muscle contraction is production of heat. | back 117 True |
front 118 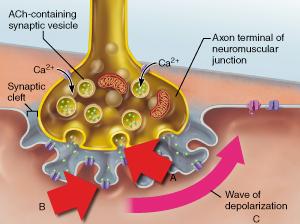 What specific neurotransmitter is released from the axonal terminus as shown in A? | back 118 acetylcholine |
front 119 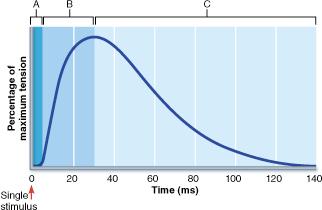 In which phase of the muscle twitch shown in the above figure would the maximum amount of ATP be consumed by myosin head groups? | back 119 B |
front 120 What structure in skeletal muscle cells functions in calcium storage? | back 120 sarcoplasmic reticulum |
front 121 Muscle contraction will always promote movement of body parts regardless of how they are attached. | back 121 False |
front 122 Slow oxidative muscle fibers are best suited for ________. | back 122 running a marathon |
front 123 What is the functional role of the T tubules? | back 123 enhance cellular communication during muscle contraction |
front 124 The force of muscle contraction is controlled by multiple motor unit summation or recruitment. | back 124 True |
front 125 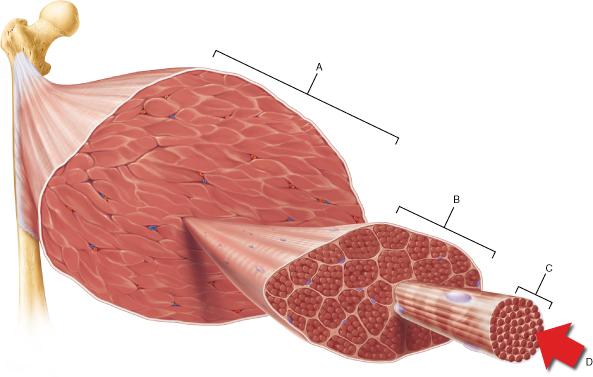 Which of the following is the smallest structural unit in which the distinctive striated bands characteristic of skeletal muscle are observed? | back 125 D |
front 126 A contraction in which the muscle does not shorten but its tension increases is called isometric contraction. | back 126 True |
front 127 The connective tissue sheaths of skeletal muscle, in order from internal to external, are the ________. | back 127 endomysium, perimysium, and epimysium |
front 128 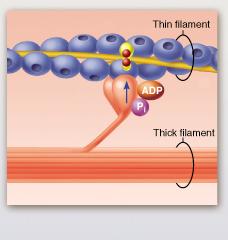 The protein troponin is shown in this figure to be bound to which substance? | back 128 calcium ion |
front 129 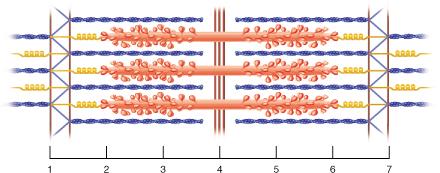 The smallest contractile unit within skeletal muscle would correspond to the distance between which two points in the figure? | back 129 1 and 7 |
front 130  Which of the following describes the neurons shown in this figure? | back 130 somatic motor neurons |
front 131 An increase in the calcium ion level in the sarcoplasm starts the sliding of the thin filaments. When the level of calcium ions declines, sliding stops. | back 131 True |
front 132 Which muscle cells have the greatest ability to regenerate? | back 132 smooth |
front 133 Once a motor neuron has fired, all the muscle fibers in a muscle contract. | back 133 False |
front 134 The distance between Z discs ________ during muscle contraction. | back 134 decreases |
front 135 Creatine phosphate functions in the muscle cell by ________. | back 135 storing energy that will be transferred to ADP to resynthesize ATP |
front 136 What is the role of tropomyosin in skeletal muscles? | back 136 Tropomyosin serves as a contraction inhibitor by blocking the myosin binding sites on the actin molecules. |