Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
A&P Chapter 5 The Integumentary System
front 1 Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. | back 1 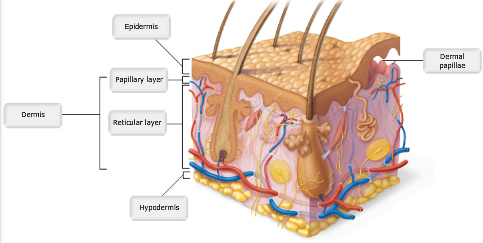 |
front 2 Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. | back 2 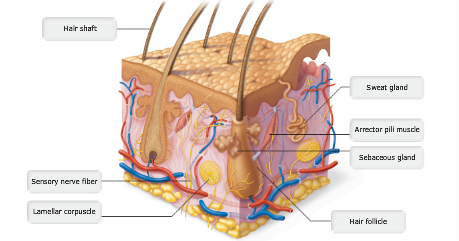 |
front 3 Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. | back 3 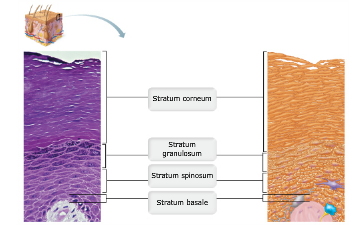 |
front 4 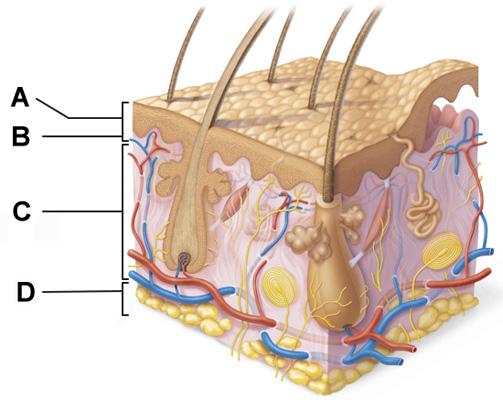 Which of the following terms describes layer D? | back 4 subcutaneous |
front 5 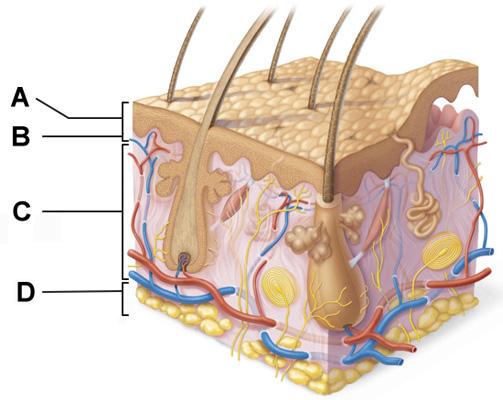 Which of the following correctly describes a common feature of all structures labeled A-D in the figure? | back 5 Structures A, B, C, and D are located in the dermis. |
front 6 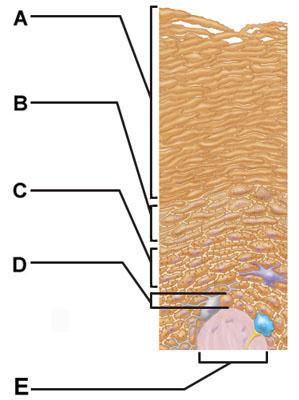 Which of the following would most likely be found in the stratum spinosum? | back 6 dendritic cell |
front 7 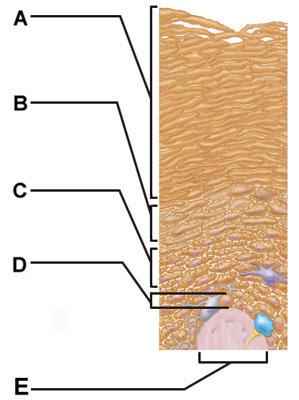 Which skin-color-associated, pigment-producing cell is located in the labeled layer D? | back 7 melanocyte |
front 8 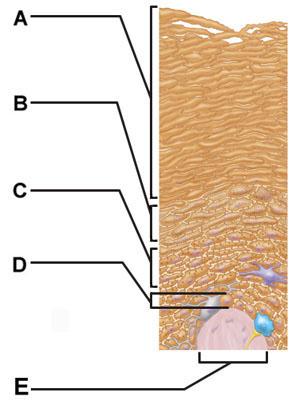 The structure indicated by label E is part of which of the following? | back 8 dermal papilla |
front 9 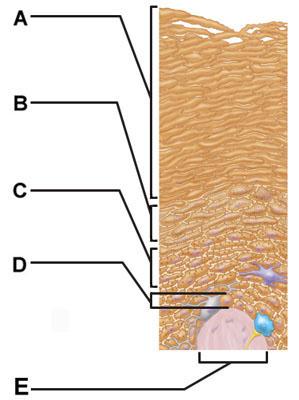 Transformed cells within labeled layer C give rise to which form of cell cancer? | back 9 squamous cell carcinoma |
front 10 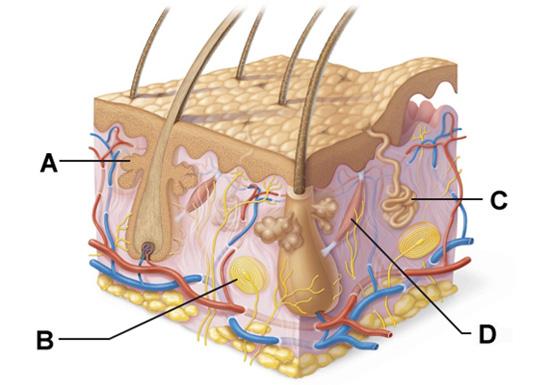 What is the function of structure B? | back 10 detection of pressure stimulus |
front 11 The ________ is a thin translucent band found only in thick skin. | back 11 stratum lucidum |
front 12 Which stratum of the epidermis is responsible for regenerating the more superficial layers? | back 12 stratum basale |
front 13 Melanocytes and keratinocytes work together in protecting the skin from UV damage when keratinocytes ________. | back 13 accumulate the melanin granules on their superficial portion, forming a UV-blocking pigment layer |
front 14 Water loss through the epidermis could cause a serious threat to health and well-being. Which of the following protects us against excessive water loss through the skin? | back 14 Lamellated granules of the cells of the stratum granulosum, a glycolipid that is secreted into extracellular spaces. |
front 15 Despite its apparent durability, the dermis is subject to tearing. How might a person know that the dermis has been stretched and/or torn? | back 15 The appearance of visible, silvery-white scars is an indication of stretching of the dermis. |
front 16 The design of a person's epidermal ridges is determined by the manner in which the papillae rest upon the dermal ridges to produce the specific pattern known as handprints, footprints, and fingerprints. Which of the following statements is true regarding these prints or ridges? | back 16 They are genetically determined, therefore unique to each person. |
front 17 Which of the following statements indicates the way in which the body's natural defenses protect the skin from the effects of UV damage? | back 17 Prolonged exposure to the sun induces melanin dispersion, which in turn acts as a natural sunscreen. |
front 18 Skin surface markings that reflect points of tight dermal attachment to underlying tissues are called epidermal ridges. | back 18 False |
front 19 The dermis is rich in blood vessels and nerve fibers. | back 19 True |
front 20 Which of the following represents a difference between eccrine sweat glands and apocrine sweat glands? | back 20 The secretions of apocrine sweat glands contain more fat and protein than do the secretions of eccrine sweat glands. |
front 21 Which of the following statements is INCORRECT? | back 21 Tactile cells anchor the skin to the body. |
front 22 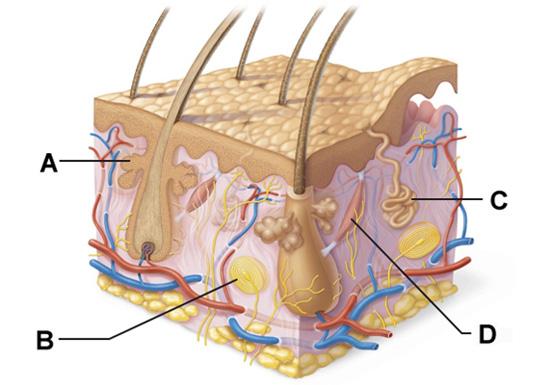 Which structure is a type of sudoriferous gland? | back 22 C |
front 23 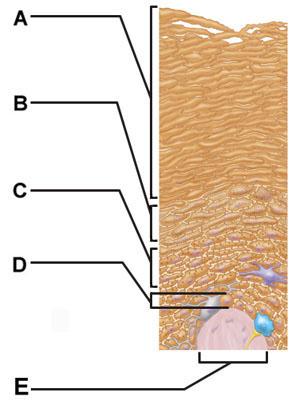 Cell division would be most common amongst cells in which of the labeled layers? | back 23 D |
front 24 A needle would pierce the epidermal layers of the forearm in which order? | back 24 corneum, granulosum, spinosum, basale |
front 25 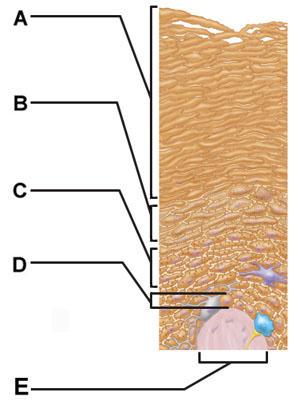 Most of the cells in layers A through D are of which type? | back 25 keratinocyte |
front 26 Regardless of race, all human beings have about the same number of melanocytes. | back 26 True |
front 27 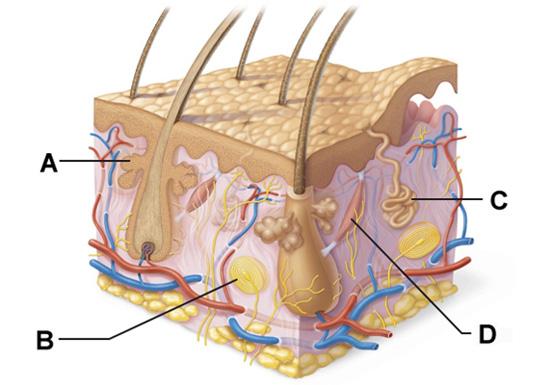 Which structure is a type of cutaneous sensory receptor? | back 27 B |
front 28 Which of the following is a skin sensory receptor for touch? | back 28 Meissner's corpuscle |
front 29 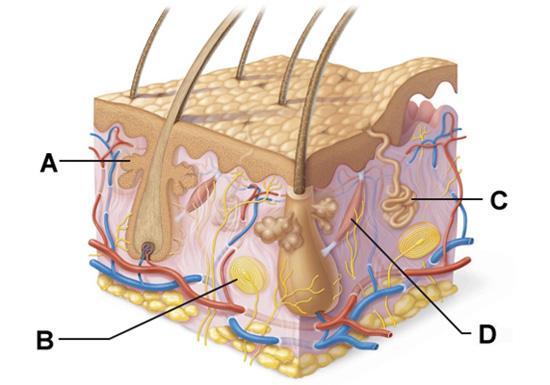 Which labeled structure produces an oily secretion? | back 29 A |
front 30 Which skin pigment is made in the skin itself? | back 30 melanin |
front 31 The most dangerous type of skin cancer is ________. | back 31 melanoma |
front 32 The pinkish hue of individuals with fair skin is the result of the crimson color of oxygenated hemoglobin (contained in red blood cells) circulating in the dermal capillaries and reflecting through the epidermis. | back 32 True |
front 33 A cancerous growth on the skin will likely exhibit ________. | back 33 asymmetry |
front 34 Which of the following cutaneous receptors is specialized for the reception of touch or light pressure? | back 34 Meissner's corpuscles |
front 35 A dendritic or Langerhan cell is a specialized ________. | back 35 phagocytic cell |
front 36 The dense fibrous connective tissue portion of the skin is located in the reticular region of the dermis. | back 36 True |
front 37 The epidermis consists of five layers of cells, each layer with a distinct role to play in the health, well-being, and functioning of the skin. Which of the following layers is responsible for cell division and replacement? | back 37 stratum basale |
front 38 Which is the most common type of skin cancer? | back 38 basal cell carcinoma |
front 39 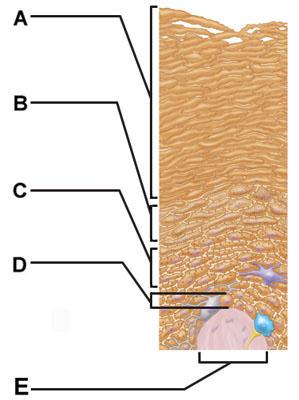 Which skin-color-associated, pigment-producing cell is located in the labeled layer D? | back 39 melanocyte |
front 40 Which of the following is NOT a layer of the epidermis? | back 40 stratum reticulum |
front 41 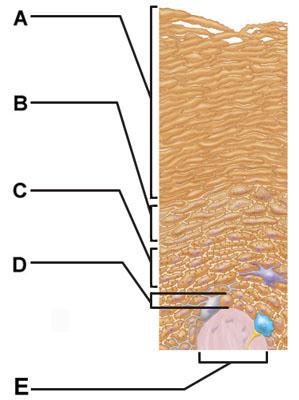 The structure indicated by label E is part of which of the following? | back 41 dermal papilla |
front 42 The protein found in large amounts in the outermost layer of epidermal cells is collagen. | back 42 False |
front 43 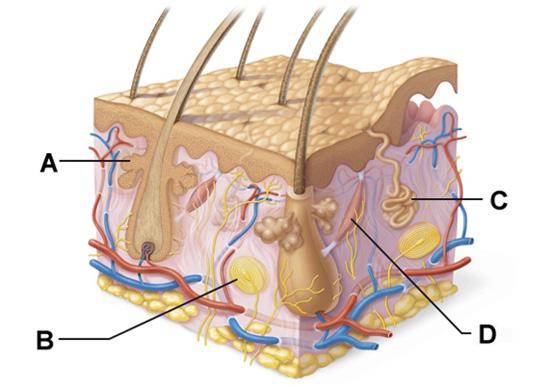 Which of the following terms describes layer D? | back 43 subcutaneous |
front 44 The skin consists of two main regions. From deep to superficial they are the ________. | back 44 dermis and epidermis |
front 45 Which layer of the dermis is directly below the epidermis? | back 45 papillary layer |
front 46 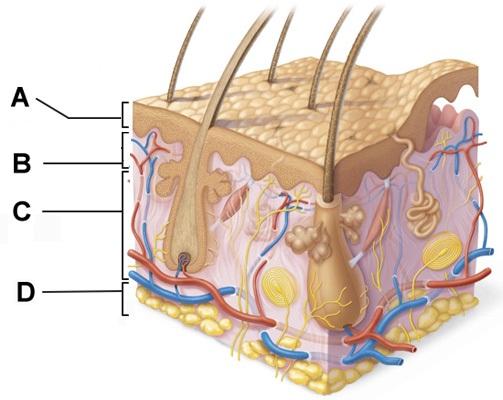 Layer B is composed primarily of ______. | back 46 areolar connective tissue |
front 47 A needle would pierce the epidermal layers of the forearm in which order? | back 47 corneum, granulosum, spinosum, basale |
front 48 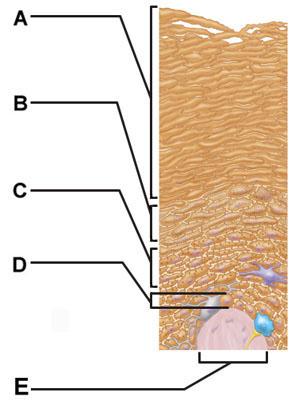 Cell division would be most common amongst cells in which of the labeled layers? | back 48 D |
front 49 The protein found in large amounts in the outermost layer of epidermal cells is collagen. | back 49 False |
front 50 The papillary layer of the dermis is connective tissue heavily invested with blood vessels. The superficial surface has structures called: | back 50 dermal papillae. |
front 51 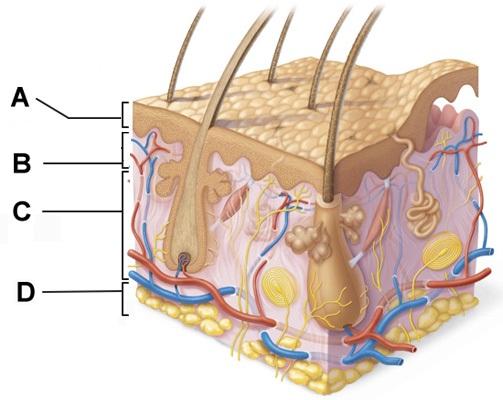 Which of the following terms describes layer D? | back 51 subcutaneous |
front 52 The epidermis consists of five layers of cells, each layer with a distinct role to play in the health, well-being, and functioning of the skin. Which of the following layers is responsible for cell division and replacement? | back 52 stratum basale |
front 53 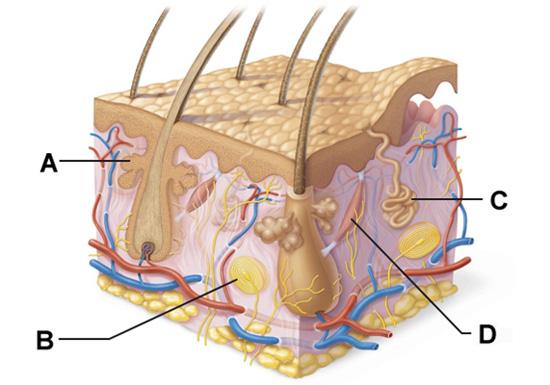 Which structure is a type of sudoriferous gland? | back 53 C |
front 54 The integumentary system is protected by the action of cells that arise from bone marrow and migrate to the epidermis. Which of the following cells serve this function? | back 54 macrophages called dendritic cells (Langerhans Cell) |
front 55 Sudoriferous (sweat) glands are categorized as two distinct types. Which of the following are the two types of sweat glands? | back 55 eccrine and apocrine |
front 56 Which layer(s) of the skin is(are) damaged in a second-degree burn? | back 56 The epidermis and the superficial region of the dermis are damaged. |
front 57 Which skin pigment is made in the skin itself? | back 57 melanin |
front 58 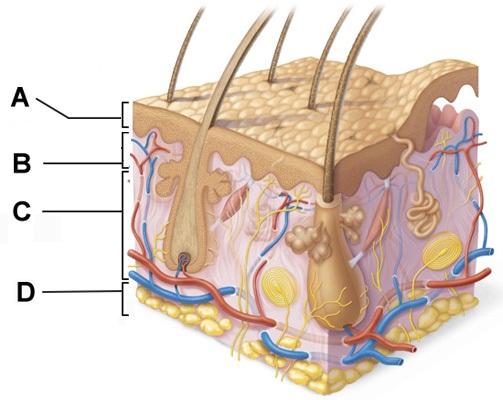 Layers B and C collectively form the ______. | back 58 dermis |
front 59 Which of the following is NOT a layer of the epidermis? | back 59 stratum reticulum |
front 60 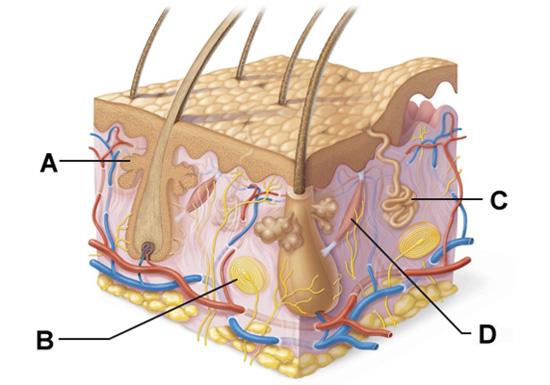 Which labeled structure produces an oily secretion? | back 60 A |
front 61 Which of the following statements is INCORRECT? | back 61 Tactile cells anchor the skin to the body. |
front 62 Regardless of race, all human beings have about the same number of melanocytes. | back 62 True |
front 63 The biggest risk factor for the development of skin cancer is excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation from sunlight. | back 63 True |
front 64 Which is the most common type of skin cancer? | back 64 basal cell carcinoma |
front 65 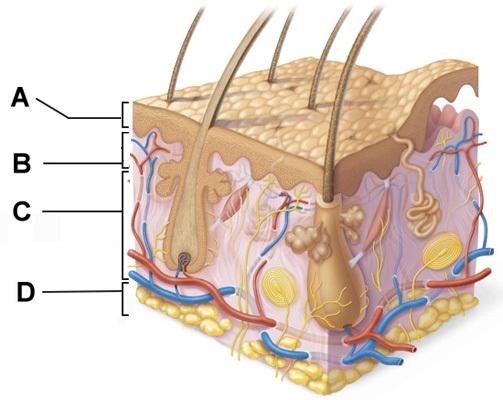 Which structure is a type of cutaneous sensory receptor? | back 65 B |
front 66 Sweat is secreted by ________. | back 66 sudoriferous glands |
front 67 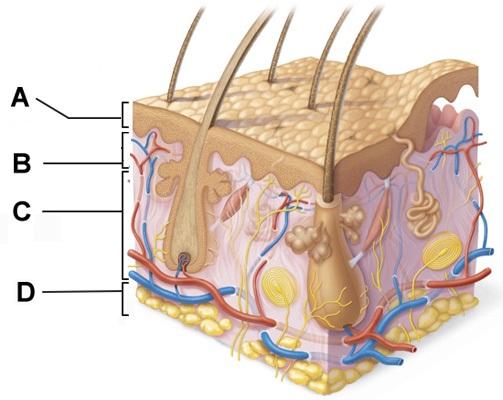 Which layer is composed primarily of stratified squamous epithelium? | back 67 A |
front 68 The most dangerous type of skin cancer is ________. | back 68 melanoma |
front 69 A cancerous growth on the skin will likely exhibit ________. | back 69 asymmetry |
front 70 Apocrine glands, which begin to function at puberty under hormonal influence, seem to play little role in thermoregulation. Where would we find these glands in the human body? | back 70 in the axillary and anogenital area |