Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Exam 2 practice quiz
front 1 1) What is the term for metabolic pathways that release stored energy
by breaking down complex molecules? | back 1 A |
front 2 2) During cellular respiration, a glucose molecule loses an electron
as the result of an oxidation-reduction reaction, | back 2 C |
front 3 3) Which of the following statements about NAD+ is true? | back 3 C |
front 4 4) How many oxygen molecules (O2) are required each time a molecule
of glucose (C6H12O6) is completely | back 4 A |
front 5 5) Which process in eukaryotic cells will proceed normally whether
oxygen (O2) is present or absent? | back 5 A |
front 6 6) In addition to ATP, what are the end products of
glycolysis? | back 6 C |
front 7 7) Energy released by the electron transport chain is used to pump H+
into which location in eukaryotic cells? | back 7 A |
front 8 8) Which of the following are products of the light reactions of
photosynthesis that are utilized as an energy source | back 8 D |
front 9 9) When oxygen is released as a result of photosynthesis, a process
called oxigenic photosynthesis, it is a direct | back 9 C |
front 10 10) What is the main purpose of light-dependent reactions of
photosynthesis? | back 10 C |
front 11 11) In a plant cell, where are the ATP synthase complexes
located? | back 11 B |
front 12 12) Where do the enzymatic reactions of the Calvin cycle take
place? | back 12 B |
front 13 13) What is the primary function of the Calvin cycle? | back 13 D |
front 14 14) How are the light-dependent and light-independent reactions of
photosynthesis related? | back 14 A |
front 15 15) Mendel studied seven different traits in the garden pea. What
genetic term is used to describe an observable | back 15 D |
front 16 16) Two plants are crossed, resulting in offspring with a 3:1 ratio
for a particular trait. This ratio suggests that _____. | back 16 B |
front 17 17) When crossing an organism that is homozygous recessive for a
single trait with a heterozygote, what is the | back 17 A |
front 18 18) Albinism is an autosomal (not sex-linked) recessive trait. A man
and woman are both of normal pigmentation, | back 18 A |
front 19 19) When Thomas Hunt Morgan crossed his red-eyed F1 generation flies
to each other, the F2 generation included | back 19 A |
front 20 20) Which of the following is the meaning of the chromosome theory of
inheritance as expressed in the early | back 20 A |
front 21 21) Which of the following describes the ability of a single allele
to have multiple phenotypic effects (as is the case | back 21 D |
front 22 22) DNA contains the template needed to copy itself, but it has no
catalytic activity in cells. What enzyme catalyzes | back 22 B |
front 23 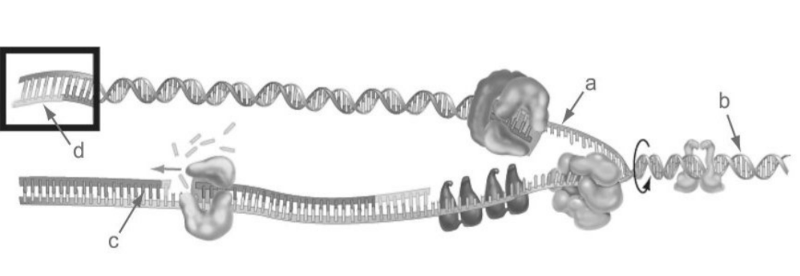 23) In the figure above, which is the template strand? | back 23 A |
front 24 24) The leading and the lagging strands differ in that _____. | back 24 B |
front 25 25) Which of the following help(s) to hold the DNA strands apart
while they are being replicated? | back 25 D |
front 26 26) Eukaryotic telomeres replicate differently than the rest of the
chromosome. This is a consequence of which of | back 26 C |
front 27 27) In a healthy cell, the rate of DNA repair is equal to the rate of
DNA mutation. When the rate of repair lags | back 27 D |
front 28 28) Because of their linear (non-circular) choromosomes, telomere
shortening is a problem in which types of cells? | back 28 A |
front 29 29) Which of the following is NOT synthesized from a DNA
template? B) messenger RNA C) ribosomal RNA D) tRNA | back 29 A |
front 30 30) In the process of transcription, _____. | back 30 B |
front 31 31) The statement "DNA -> RNA -> Proteins"
_____. | back 31 C |
front 32 32) The HIV virus that causes AIDS is an RNA retrovirus, meaning it
is made of RNA and not DNA. A retrovirus | back 32 C |
front 33 33) What does it mean when we say the genetic code is
redundant? | back 33 C |
front 34 34) Which one of the following is true? A codon _____. | back 34 B |
front 35 35) The mutation resulting in sickle-cell disease changes one base
pair of DNA so that a codon now codes for a | back 35 B |
front 36 36) The core enzyme which initiates transcription and is shown in the
figure above is _____. | back 36 A |
front 37 37) Refer to the figure above. The mRNA in eukaryotes is smaller than
the length of the gene in the DNA that codes | back 37 D |
front 38 38) Ribosomes can attach to prokaryotic messenger RNA _____. | back 38 A |
front 39 39) There are sixty-one mRNA codons that specify an amino acid, but
only forty-five tRNAs. This is best explained | back 39 D |
front 40 40) Refer to the figure above. What is the function of the AGU on the
loop of the tRNA? | back 40 C |
front 41 41) Refer to the figure above. What is the function of the CCA sequence at the 3ƍ end? A) It stabilizes the gene.B) It attaches to an amino acid. C) It is the active site of this ribozyme. D) It base pairs with the codon of mRNA. | back 41 B |
front 42 42) Translation directly involves _____. | back 42 B |
front 43 43) Regulating levels of gene expression serves an organism's
survival by _____. | back 43 E |
front 44 44) Which of the following levels of gene expression allows the most
rapid response to environmental change? | back 44 B |
front 45 45) The greatest expression of the lac operon occurs when lactose
levels are _____ and glucose levels are _____. | back 45 A |
front 46 46) The product of the lacI gene is _____. | back 46 B |
front 47 47) The arabinose operon (ara) provides a particularly interesting
example of ___________ in that when arabinose is | back 47 C |
front 48 48) Under what condition is the AraC protein an activator? | back 48 B |
front 49 49) Prokaryotes are classified as belonging to two different domains.
What are the domains? | back 49 A |
front 50 50) While examining a rock surface, you have discovered an
interesting new organism. Which of the following | back 50 D |