Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Human Anatomy and Physiology II Final Exam
front 1 A karyotype is a complete: | back 1 diploid complement display of homologous chromosome pairs. |
front 2 The most common form of fetal testing is: | back 2 amniocentesis. |
front 3 Muscle tissue is formed by the ________. | back 3 mesoderm |
front 4 Humans have ____ pairs of chromosomes | back 4 23 |
front 5 The process by which the three primary germ layers form is known as _______. | back 5 gastrulation |
front 6 Estrogen and progesterone maintain the integrity of the uterine lining and prepare the mammary glands to secrete milk. Which of the following structures makes this possible during the first three months of pregnancy? | back 6 corpus luteum |
front 7 Which sequence shows the correct order of the stages of labor? | back 7 Dilation, expulsion, placental |
front 8 Ovulation in a typical, or "average," cycle usually occurs on day: | back 8 14 |
front 9 The organ that makes estrogen and progesterone is the: | back 9 Ovary |
front 10 Which factor below is NOT considered to be a teratogen? | back 10 Oxygen |
front 11 Which male structure is homologous to the female's clitoris? | back 11 Penis |
front 12 At which stage of labor is the "afterbirth" expelled? | back 12 placental |
front 13 Which of the following disorders is NOT inherited as simple recessive traits? | back 13 Down syndrome |
front 14 Which process listed below separates linked genes during meiosis? | back 14 Chiasma, or crossing over |
front 15 An implantation that takes place in a site other than the uterus is called: | back 15 ectopic. |
front 16 The usual site of fertilization is the: | back 16 uterine tube. |
front 17 The uterine layer shed with each monthly cycle is the: | back 17 functional layer of endometrium. |
front 18 What is the probability of having a child with a recessive trait if both parents are heterozygous for the trait? | back 18 25% |
front 19 The hormone that induces labor and controls labor via a positive feedback mechanism is: | back 19 Oxytocin |
front 20 The first major event of organogenesis is: | back 20 Neurulation |
front 21 All of the following can be considered male secondary sex characteristics except the ________. | back 21 development of testes as opposed to ovaries |
front 22 Which of the following is a newborn's source of energy for the first few days? | back 22 Fat |
front 23 During which stage of labor is the fetus delivered? | back 23 Expulsion Stage |
front 24 Which of the following structures makes up most of the male urethral length? | back 24 Spongy urethra |
front 25 Extrachromosomal inheritance involves genes passed on by the mother's: | back 25 mitochondria. |
front 26 Heterozygous individuals that can pass on recessive, abnormal conditions are referred to as: | back 26 Carriers |
front 27 The surge in LH that occurs during the middle of the ovarian cycle triggers: | back 27 Ovulation |
front 28 The muscular wall of the uterus is called the: | back 28 Myometrium |
front 29 What hormone is responsible for the secondary sex characteristics found in women? | back 29 Estrogen |
front 30 A change in the genetic structure of a gene is called: | back 30 Mutation |
front 31 The reason why the testes are suspended in the scrotum is: | back 31 to provide for a cooler temperature. |
front 32 Implantation involves ________. | back 32 embedding of the blastocyst in the uterine wall |
front 33 A female infant is born with several hundred oocytes, each one genetically unique. This is due to ________. | back 33 independent assortment and random crossover |
front 34 Cells on the dorsal surface of the two-layered embryonic disc migrate to form a raised groove known as the ________. | back 34 Primitive Streak |
front 35 Alternative forms of genes are called: | back 35 Alleles |
front 36 Sex chromosomes of a normal male are ________. | back 36 XY |
front 37 The outermost embryonic membrane is the: | back 37 Chorion |
front 38 A person without a Y chromosome will: | back 38 always show female characteristics. |
front 39 Occasionally three polar bodies are found clinging to the mature ovum. One came from an unequal division of the ovum, but from where did the other two arise? | back 39 The first polar body has also divided to produce two polar bodies. |
front 40 The appearance of freckles is considered: | back 40 The Phenotype |
front 41 If a male inherits a sex-linked gene for color blindness: | back 41 it will always be expressed. |
front 42 Sperm are produced in the: | back 42 seminiferous tubules. |
front 43 The formation of endodermal and ectodermal germ layers occurs at ________. | back 43 Gastrulation |
front 44 Human egg and sperm are similar in that ________. | back 44 they have the same number of chromosomes |
front 45 A person who inherits the A and the O blood type alleles will possess which blood type? | back 45 A |
front 46 Neural tissue is formed by the ________. | back 46 Ectoderm |
front 47 Which hormone produced by the placenta causes the mother's pubic symphysis to loosen and widen? | back 47 Relaxin |
front 48 The sperm's acrosome: | back 48 contains enzymes. |
front 49 After fertilization the zygote goes through a rapid period of cell divisions called: | back 49 Cleavage |
front 50 Prolactin causes: | back 50 milk production by the breast tissue. |
front 51 Males tend to inherit more sex-linked conditions because: | back 51 there is no corresponding allele on their Y chromosomes. |
front 52 Which is the most correct sequence of sperm flow in the male duct system? | back 52 Seminiferous tubules, epididymis, vas deferens, ampulla, ejaculatory duct, urethra |
front 53 Characteristics of the mature sperm include the ________. | back 53 presence of Y chromosomes in approximately half the sperm |
front 54 Genetic variation is NOT enhanced through: | back 54 Mitosis |
front 55 Amy's hand was exposed to X rays. A gene in a skin cell of her hand mutated. This mutant gene will ________. | back 55 replicate itself when the cell divides but will not be passed on to Amy's offspring |
front 56 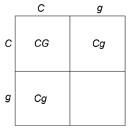 Given the information in Figure 29.1, what would be the genotype of the offspring designated by the blank square? | back 56 gg |