Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Microbiology Chapter 6
front 1 Microbial Growth refers to | back 1 Increase in number of cells, not cell size.
|
front 2 The requirements for growth
| back 2 1. Temperature
|
front 3 The requirements for growth
| back 3 1. Carbon
|
front 4 Physical Requirements | back 4 Temperature
|
front 5 Psychrotrophs | back 5 * Grow between 0°C & 20-30°C
|
front 6 Food preservation temperatures
| back 6 Between 20°C to 50°C
|
front 7 pH
| back 7 6.5 & 7.5 |
front 8 pH
| back 8 5 & 6 |
front 9 pH
| back 9 acidic |
front 10 Osmotic Pressure
| back 10 Plasmolysis |
front 11 Osmotic Pressure
| back 11 Extreme / obligate halophiles |
front 12 Obligate → | back 12 requires |
front 13 Facultative → | back 13 tolerate |
front 14 Osmotic Pressure
| back 14 Facultative halophiles
|
front 15 Chemical Requirements
| back 15 * Structural organic molecules, energy source
|
front 16 Chemical Requirements
| back 16 * In amino acids & proteins
|
front 17 Chemical Requirements
| back 17 * In amino acids, thiamine, & biotin
|
front 18 Chemical Requirements
| back 18 * In DNA, RNA, ATP & membranes
|
front 19 Chemical Requirements
| back 19 * Inorganic elements required in small amounts
|
front 20 The effect of Oxygen on the growth of various types of bacteria
| back 20 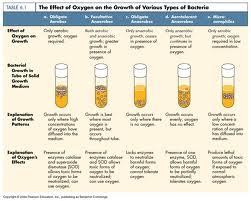 * Only aerobic growth; oxygen required.
|
front 21 The effect of Oxygen on the growth of various types of bacteria
| back 21 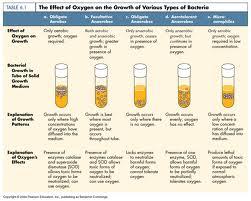 *Both aerobic & anaerobic growth; greater growth in presence of oxygen.
|
front 22 The effect of Oxygen on the growth of various types of bacteria
| back 22 * Only anaerobic growth ceases in presence of oxygen.
|
front 23 The effect of Oxygen on the growth of various types of bacteria
| back 23 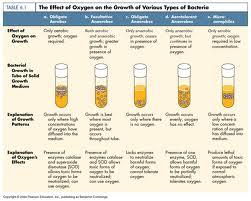 *Only anaerobic growth, but continues in presence of energy.
|
front 24 The effect of Oxygen on the growth of various types of bacteria
| back 24 *Only aerobic growth; oxygen required in low concentration.
|