Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 17 - Blood
front 1 In a centrifuged sample of blood, what should NOT be in the plasma portion of the sample? | back 1 platelets |
front 2 Which of the following is NOT a function of blood? | back 2 hormone production |
front 3 Athletes who choose to use industry-produced EPO as a performance-enhancing drug to increase the effects of their naturally-produced EPO, will experience ______. | back 3 decreased production of EPO by their kidneys |
front 4 Which of the formed elements is present in the greatest concentration? | back 4 erythrocytes |
front 5 Which of the following is NOT a functional characteristic of leukocytes? | back 5 leukocytosis |
front 6 Which leukocyte might you expect to find in higher quantities in a person experiencing allergies? | back 6 eosinophil |
front 7 Mature erythrocytes lack a nucleus. T/F | back 7 True |
front 8 Choose the statement that is true concerning hemoglobin. | back 8 It is composed of four protein chains and four heme groups. |
front 9 Which of the following does NOT stimulate erythrocyte production? | back 9 hyperventilating |
front 10 Bilirubin is created when red blood cells are recycled. How is it removed from the blood stream? | back 10 the liver |
front 11 Which of the following is correctly matched? | back 11 pernicious anemia: results from a vitamin B12 deficiency |
front 12 Abnormally low levels of erythrocytes caused by excessive bleeding is called______. | back 12 hemorrhagic anemia |
front 13 On a blood smear slide prepared using Wright's stain, you observe a large cell with a U-shaped nucleus and pale blue cytoplasm. This cell is most likely a(n) __________. | back 13 monocyte |
front 14 Which of the following scenarios could result in HDN (hemolytic disease of the newborn)? | back 14 B-negative female pregnant with an AB-positive baby |
front 15 Choose the incompatible transfusion. | back 15 Donate type B blood to a recipient with type O blood |
front 16 When a person has an acute bacterial infection, such as bacterial meningitis or appendicitis, which type of leukocyte increases in number? | back 16 neutrophils |
front 17 Which type of leukocyte is responsible for antibody production? | back 17 lymphocytes |
front 18 Which of these develops from lymphoid stem cells? | back 18 lymphocytes |
front 19 From which cell do the granulocytes descend? | back 19 myeloblast |
front 20 What part of the pathway to produce platelets is shared with other formed elements? | back 20 hematopoietic stem cell (hemocytoblast) |
front 21 What triggers erythropoietin (EPO) production to make new red blood cells? | back 21 reduced availability of oxygen |
front 22 Which part of the hemoglobin molecule binds carbon dioxide for transport? | back 22 amino acids of the globin |
front 23 What part of the body does erythropoietin (EPO) target to increase erythropoiesis? | back 23 bone marrow |
front 24 What part of the hemoglobin molecule is eventually metabolized to stercobilin in the feces? | back 24 a portion of the heme group |
front 25 What erythrocyte production disorder results from an autoimmune disease associated with vitamin B12 absorption? | back 25 pernicious anemia |
front 26 What protein involved in coagulation provides the activation for the final step in clotting? | back 26 thrombin |
front 27 All lymphocytes are also leukocytes. T/F | back 27 True |
front 28 What factor stimulates platelet formation? | back 28 thrombopoietin |
front 29 Which of the following represents a difference between extrinsic and intrinsic blood clotting pathways? | back 29 One is faster than the other. |
front 30 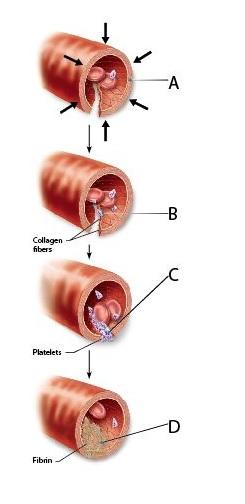 During which event of hemostasis do clotting factors (procoagulants) assist with the transformation of blood from a liquid to a gel? | back 30 D |
front 31 What "clot buster" enzyme removes unneeded clots after healing has occurred during fibrinolysis? | back 31 plasmin |
front 32 During erythroblastosis fetalis, a Rh- mother's anti-Rh antibodies that have crossed the placenta will cause agglutination of the fetus's Rh+ RBCs. However, the reverse problem never happens when a Rh+ mother is pregnant with a Rh- fetus, that is, antibodies produced by the fetus cannot cause agglutination of the mother's Rh+ RBCs. This is true because ______. | back 32 antibodies that can cause this agglutination are not produced by a fetus |
front 33 Which ABO blood type is considered to be the universal recipient? | back 33 AB |
front 34 Digesting a clot after it is formed requires activation of what plasma protein by tPA? | back 34 plasminogen |
front 35 Which of the following would NOT lead to a bleeding disorder? | back 35 excess calcium in the diet |
front 36 A person who lacks agglutinogen A but has agglutinogen B would have blood type __________. | back 36 B |
front 37 What is a hematocrit? | back 37 Hematocrit is the percentage of erythrocytes in a whole blood sample. |
front 38 Which plasma constituent is the main contributor to clotting? | back 38 fibrinogen |
front 39 Which of these represents the majority of whole blood by volume? | back 39 plasma Plasma typically constitutes 55% of whole blood, although this value can vary somewhat. |
front 40 Which of the following is true of the structure of an erythrocyte? | back 40 Erythrocytes can bend and twist to fit through vessels. |
front 41 What is the name of the protein found in erythrocytes that transports respiratory gases? | back 41 hemoglobin |
front 42 How many oxygen molecules can be transported by one hemoglobin molecule? | back 42 four |
front 43 Which formed element can be described as membrane-enclosed cytoplasmic fragments? | back 43 platelets |