Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 15 - Special Senses
front 1 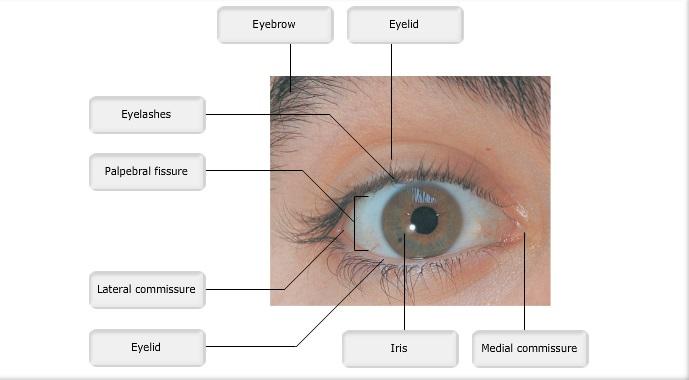 Art-labeling Activity: Figure 15.1a | back 1 Label the Eye |
front 2 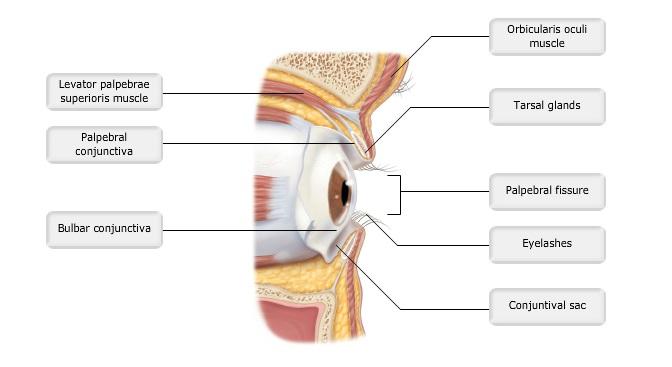 Art-labeling Activity: Figure 15.1b | back 2 Label the Eye |
front 3 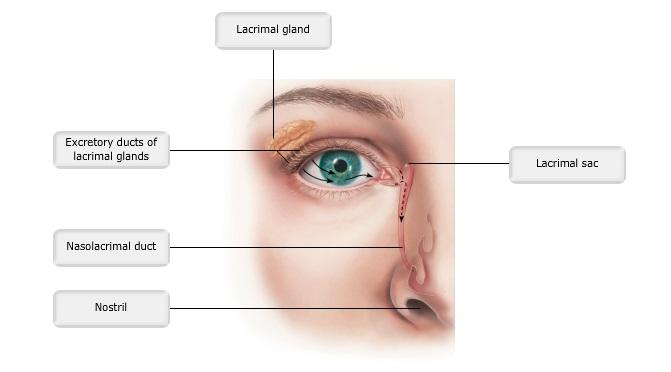 Art-labeling Activity: Figure 15.2 | back 3 Label the Eye |
front 4 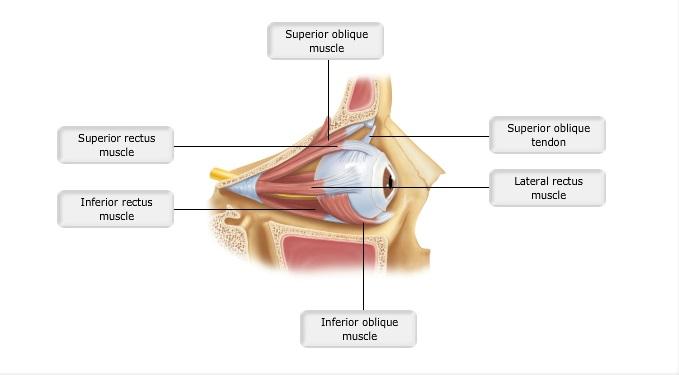 Art-labeling Activity: Figure 15.3a | back 4 Label the Eye |
front 5 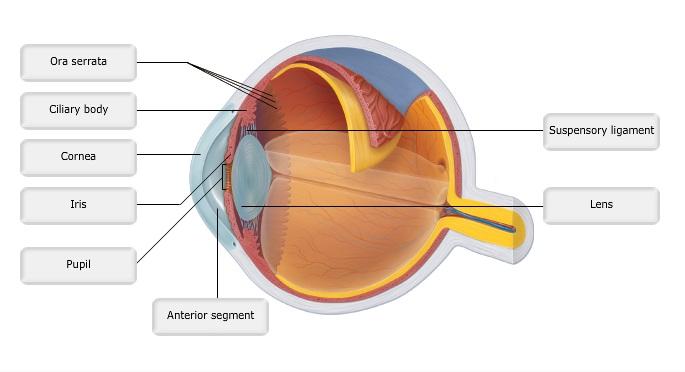 Art-labeling Activity: Figure 15.4a | back 5 Label the Eye |
front 6 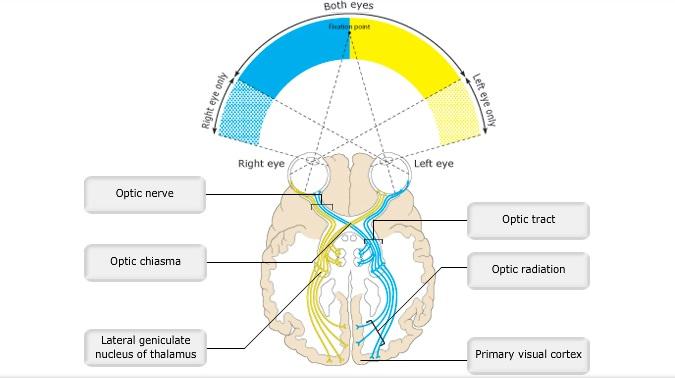 Art-labeling Activity: Figure 15.19a | back 6 Label the Brain |
front 7 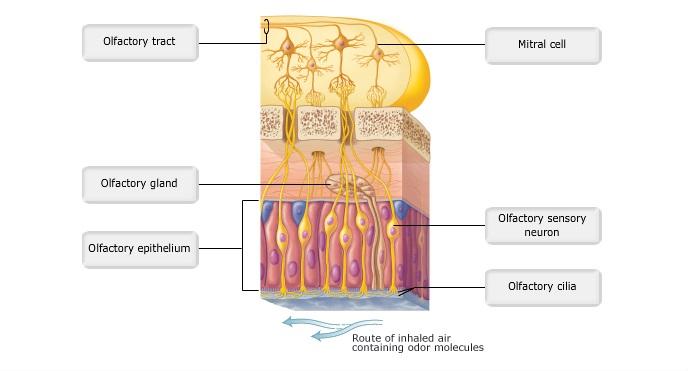 Art-labeling Activity: Figure 15.20b | back 7 Label the parts of the Olfactory receptors |
front 8 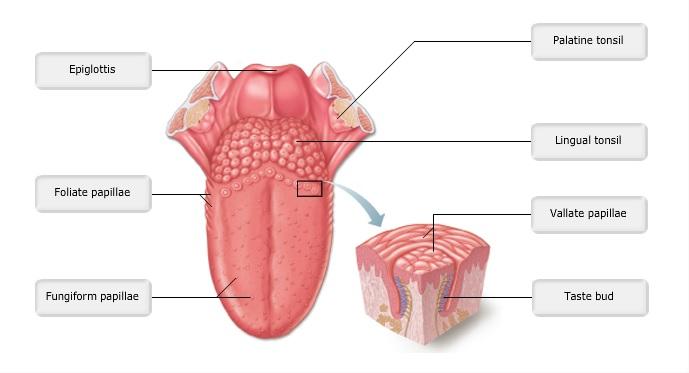 Art-labeling Activity: Figure 15.22a | back 8 Label the tongue |
front 9 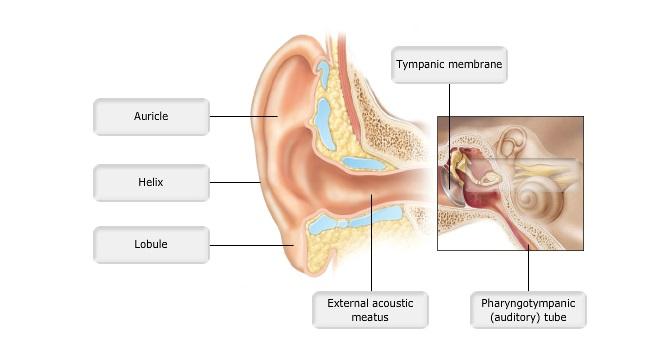 Art-labeling Activity: Figure 15.24a | back 9 Label the Ear |
front 10 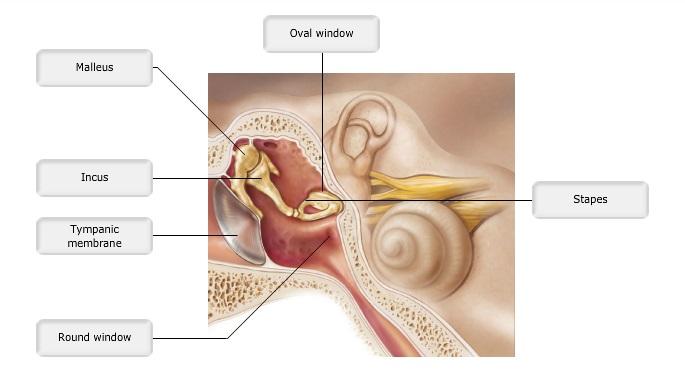 Art-labeling Activity: Figure 15.24b (1 of 2) | back 10 Label the Ear |
front 11 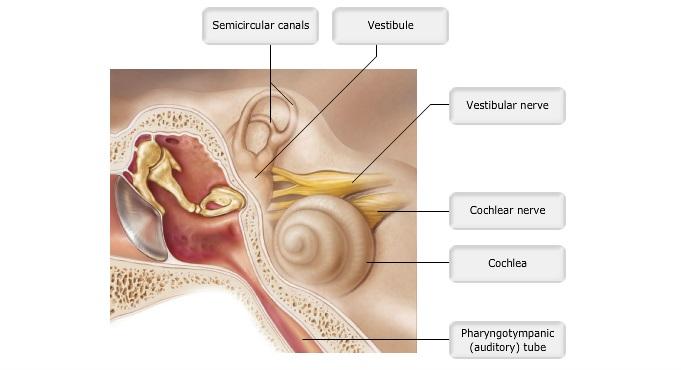 Art-labeling Activity: Figure 15.24b (2 of 2) | back 11 Label the Ear |
front 12 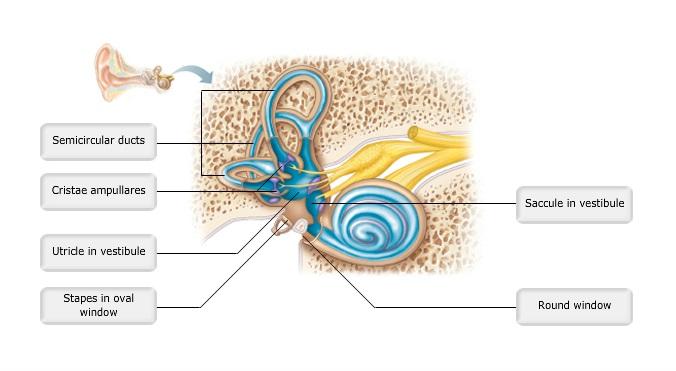 Art-labeling Activity: Figure 15.26 | back 12 Label the Ear |
front 13 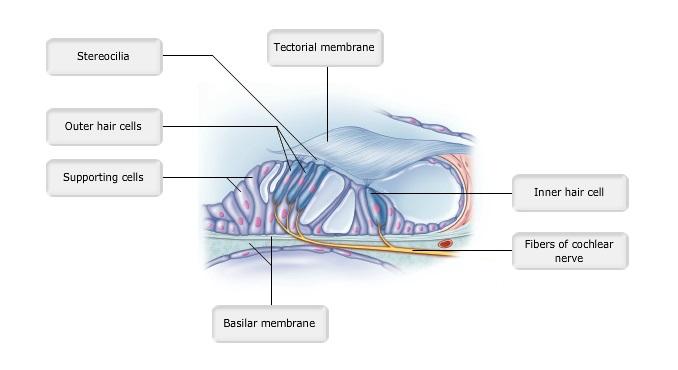 Art-labeling Activity: Figure 15.27c | back 13 Label the Hair Cells in the Organ of Corti |
front 14 What term means that the lens can change shape so that the eye can focus on items either close at hand or far away? | back 14 accommodation |
front 15 What condition results when distant objects focus in front of the retina, rather than on it? | back 15 myopia |
front 16 Which of the following is NOT an accessory structure of the eye? | back 16 retina |
front 17 The visible colored portion of the eye is the __________. | back 17 iris |
front 18 Which of the following is a role of the vitreous humor? | back 18 It supports the posterior surface of the lens |
front 19 Which of the following is a characteristic of the lens? | back 19 The lens focuses light on the retina. |
front 20 Choose the correctly paired terms. | back 20 nyctalopia: night blindness |
front 21 Which accessory eye structures function to produce the tears that cleanse and protect the eye? | back 21 lacrimal glands |
front 22 Which structure in the eye provides nutrition to all eye layers? | back 22 choroid |
front 23 What part of the eye constitutes the blind spot? | back 23 optic disc |
front 24 Which photoreceptors respond to very dim light? | back 24 rods |
front 25 Most taste buds are located __________. | back 25 on the tongue |
front 26 Which of the following is NOT a requirement for something to be tasted? | back 26 tastant must contact the basal epithelial cells of the taste buds. |
front 27 Choose the FALSE statement about the olfactory epithelium. | back 27 It is made of simple squamous epithelium. |
front 28 Taste is independent of smell | back 28 False |
front 29 Which of the following is the basic taste quality responsible for the "beef taste" of steak? | back 29 umami |
front 30 The boundary between the external and middle ear is the __________. | back 30 tympanic membrane |
front 31 Ringing in the ears is called __________. | back 31 tinnitus |
front 32 Where are equilibrium receptors located? | back 32 in the semicircular canals and in the vestibule of the ear |
front 33 There are __________ auditory ossicles in the ear. | back 33 three |
front 34 The final step in perceiving sound is __________. | back 34 the auditory cortex is stimulated |
front 35 The receptor organ for hearing is the __________. | back 35 spiral organ (of Corti) |
front 36 Which of the following is true of receptors for dynamic equilibrium? | back 36 The receptors for dynamic equilibrium respond to rotational forces. |
front 37 Information from balance (equilibrium) receptors goes directly to __________. | back 37 the brain stem |
front 38 Which of the following is the receptor organ for hearing? | back 38 spiral organ (of Corti) |
front 39 Vision is fully developed at birth. | back 39 False |