Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 14 Autonomic Nervous System
front 1 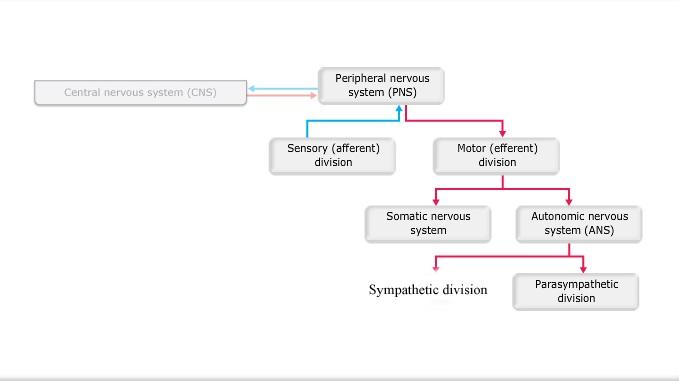 Art-labeling Activity: Figure 14.1 | back 1 ANS In the Nervous System See Diagram |
front 2 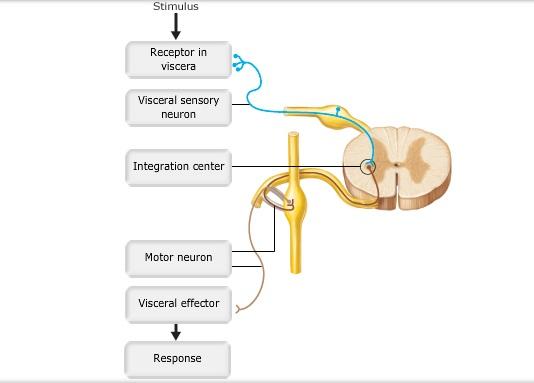 Art-Labeling Activity: Figure 14.7 | back 2 Label the figure |
front 3 Which of the following is a way in which the somatic and autonomic nervous systems are similar? -Both systems share common efferent pathways. -Both systems share common effectors. -Both systems have ganglia in their motor pathways. -Both systems elicit the same target organ responses to their neurotransmitters. -None of the above. | back 3 None of the above. |
front 4 For which of the following activities is the parasympathetic nervous system generally responsible? | back 4 resting and digesting |
front 5 Conduction through the autonomic efferent chain is faster than conduction in the somatic motor system. | back 5 False |
front 6 Which of the following is NOT an autonomic nervous system (ANS) effector? | back 6 skeletal muscle |
front 7 Which of the following is NOT associated with the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system (ANS)? | back 7 emergency action |
front 8 Which autonomic neurons release norepinephrine as a neurotransmitter? | back 8 sympathetic postganglionic neurons |
front 9 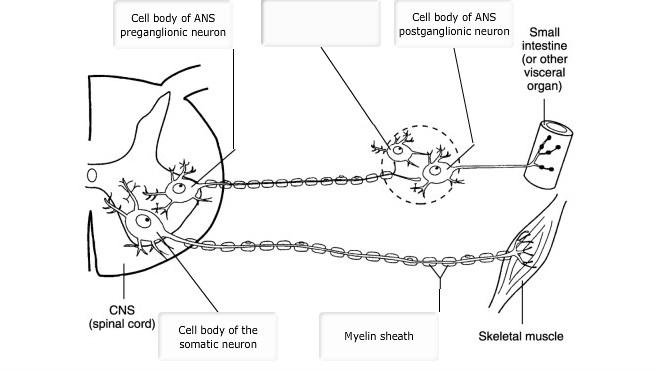 Chapter 14 Matching Questions 1-4 Use the figure to match the following. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. 1 target will be left blank. | back 9 See Diagram. |
front 10 Which component of the ANS is characterized by ganglia located in or near effector organs? | back 10 parasympathetic division |
front 11 Outflow of the sympathetic division occurs from which regions of the CNS? | back 11 thoracic and lumbar |
front 12 Oculomotor nerves are responsible for which of the following functions? | back 12 focusing the eyes on close objects |
front 13 The sympathetic division is also called the "thoracolumbar division" of the autonomic nervous system. | back 13 True |
front 14 The two types of receptors that bind acetylcholine are __________ and __________ receptors. | back 14 nicotinic; muscarinic |
front 15 Which types of drugs are used to help relieve depression? | back 15 Drugs that prolong the activity of norepinephrine on the postsynaptic membrane help to relieve depression. |
front 16 Which of the following best demonstrates an example of cooperation of the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems? | back 16 Parasympathetic stimulation causes vasodilation of blood vessels in the penis, leading to erection; sympathetic stimulation then causes ejaculation. |
front 17 Which of the following is responsible for the overall integration of the autonomic nervous system (ANS)? | back 17 hypothalamus |
front 18 What is the effect of norepinephrine on the heart? | back 18 an increase in heart rate |
front 19 The two divisions of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) normally have a(n) __________ relationship. | back 19 antagonistic |
front 20 Which target organ is NOT affected by the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system (ANS)? | back 20 adrenal medulla |