Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Exam 1
front 1 All the answers are now 100% correct! | back 1 All the answers are now 100% correct! |
front 2 A multicellular organism that has chitin cell walls & absorbs organic material is a(n)
| back 2 c. Fungus |
front 3 In the name Escherichia coli(in italics), coli (italics) is the
| back 3 a. Specific epithet |
front 4 Which of the following is NOT a domain in the three-domain system?
| back 4 d. Animalia |
front 5 Who proved that microorganisms cause disease?
| back 5 d. Koch |
front 6 Which of the following is the best definition of biotechnology?
| back 6 c. The use of living organisms to make desired products |
front 7 You are observing a cell through a microscope & note that it has no apparent nucleus you conclude that it most likely
| back 7 c. Has a peptidoglycan cell wall |
front 8 Which of the following groups include members that lack DNA?
| back 8 d. Viruses |
front 9 Bacteria differ from viruses in that bacteria
| back 9 d. All of the above |
front 10 In figue 3.1, line "a" points to the microscope's | back 10 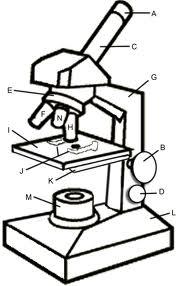 c. Ocular lens (what you look into)
|
front 11 In figure 3.1, line "c." points to the microscope's | back 11 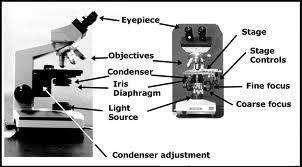 c. Condenser
|
front 12 Which of the following is NOT equal to 1m?
| back 12 d. 100mm |
front 13 Place the steps of the Gram stain in the correct order:
| back 13 2-4-1-3 |
front 14 Which of the follwing pairs is mismatched for Gram Stain?
| back 14 b. Safranin-acid dye |
front 15 The purpose of a mordant in the gram stain is
| back 15 e. To increase the cells' affinty for a stain & to kill the bacteria. |
front 16 Place the following steps in the correct sequence:
| back 16 2-3-1 |
front 17 Simple staining is often necessary to improve contrast in this microscope.
| back 17 b. Compound Light |
front 18 Which microscope achieves the highest magnification & greatest resolution?
| back 18 e. Electron microscope |
front 19 The appearance of gram-negative bacteria after addition of the mordant in the Gram stain.
| back 19 a. Purple |
front 20 The appearance of gram-positive bacteria after adding the counterstain in the gram stain.
| back 20 a. Purple |
front 21 What is the total magnification of a bacteria viewed w/a 10x ocular lens & a 100x objective
| back 21 e. 1000x |
front 22 Which microscope is used to see detail of a 300-nm virus?
| back 22 d. Electron microscope |
front 23 The resolution of a microscope can be improved by changing the
| back 23 d. Wavelenght of light |
front 24 Which of the following statements best describes what happens when a bacterial cell is plced in a solution containing 5% NaCl? Hint: Bacterial cells contain less than 5% NaCl.
| back 24 c. Water will move out of the cell. |
front 25 By which of the following mechanisms can a cell transport a substance from a lower to higher concentration?
| back 25 d. Active transport |
front 26 Which drawing in Figure 4.1 is a tetrad? | back 26 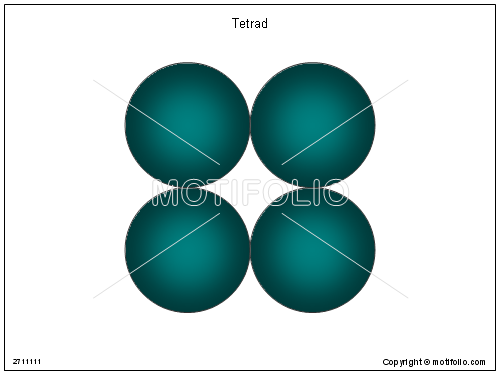 Your answer will be the one that looks like the above image. |
front 27 Which drawing in Figure 4.1 is streptococci? | back 27 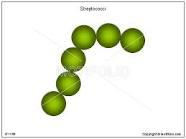 Your answer will be the one that looks like the above image.
|
front 28 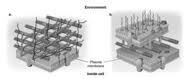 Choice a. is on the left (<-) & b. is on the right (->).
| back 28 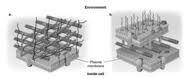 Choice a. is on the left (<-) & b. is on the right (->).
|
front 29 In figure 4.3, which diagram of a cell wall is a gram-negative cell wall? | back 29 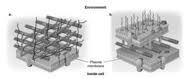 b - the one on the right -> |
front 30 In figure 4.3, which diagram of a cell wall is decolorized by ethyl alcohol? | back 30  b - the one on the right -> |
front 31 In figure 4.3, which diagram of a cell wall contains teichoic acids? | back 31 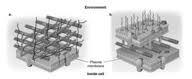 a - the one on the left <- |
front 32 All the answers are now 100% correct! | back 32 All the answers are now 100% correct! |