Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
1403- Homework Assignment 9
front 1 Which of the following comparisons of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) and the somatic nervous system (SNS) is not true? .the SNS carries information from the special senses the ANS has sensory receptors called interoceptors tissues of the ANS can function even if their nerve supply is damaged the SNS contains motor neurons which are excitatory and inhibitory angina pectoris is an example of input from the ANS | back 1 the SNS contains motor neurons which are excitatory and inhibitory |
front 2  If the pathway shown in the diagram is a sympathetic division pathway, which neurotransmitter acts at the effector? Serotonin Norepinephrine Acetylcholine Epinephrine Dopamine | back 2 Norepinephrine |
front 3 Which would be found in the anterior root of a thoracic spinal nerve? somatic motor axons somatic sensory axons sympathetic postganglionic axons parasympathetic preganglionic axons | back 3 somatic motor axons |
front 4 The cell bodies of sympathetic preganglionic neurons are located in the terminal ganglia visceral organs spinal cord sympathetic trunk ganglia | back 4 spinal cord |
front 5 Dual innervation describes the situation when effectors are controlled by only one division of the autonomic nervous system. True False | back 5 False |
front 6 All preganglionic neurons are cholinergic. True False | back 6 False |
front 7 Which of the following lists the components of an autonomic reflex arc in the proper sequence of activation? receptor – sensory neuron – motor neuron – effector – integrating center receptor – sensory neuron – integrating center – motor neuron – effector receptor – motor neuron – integrating center – sensory neuron – effector effector – sensory neuron – integrating center – motor neuron – receptor integrating center – receptor – sensory neuron – motor neuron – effector SHOW ANSWER | back 7 receptor – sensory neuron – integrating center – motor neuron – effector |
front 8 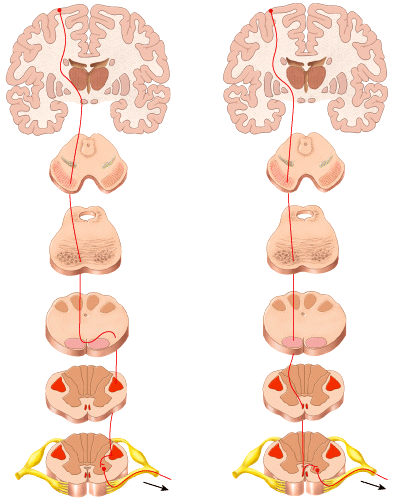 This figure shows 1 only 2 only 3 only 1 and 2 are correct 1 and 3 are correct | back 8 1 and 2 are correct |
front 9 Damage to upper motor neurons results in flaccid paralysis and a loss of reflexes on the same side of the body as the injury. | back 9 False |
front 10 The corticobulbar tracts convey nerve impulses that control movements of the stomach and intestine heart arms and legs head and neck | back 10 head and neck |
front 11 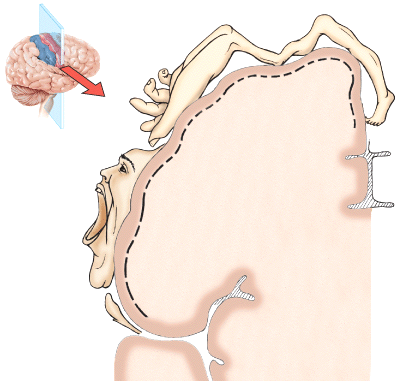 The human-type figure resting on the precentral gyrus tells us that more cortical neurons are specialized for hand movement than for foot movement control of facial muscles requires a large number of cortical neurons relatively little cortical material is devoted to controlling the muscles of the trunk all of these choices are correct none of these choices are correct | back 11 all of these choices are correct |
front 12 Which of the following type of neurons have their cell bodies in the spinal cord or brain stem and their axons terminating in neuromuscular junctions? lower motor neurons somatic sensory neurons upper motor neurons preganglionic autonomic neurons postganglionic autonomic neurons | back 12 lower motor neurons |