Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
1403 - Home assigment week 5-6
front 1 To answer this question, first click here to view the associated animation. The final fate of electrons in the electron transport chain is combining with _____ to form _____. hydrogen, ATP carbon, carbon dioxide oxygen, water None of these | back 1 oxygen, water |
front 2 To answer this question, first click here to view the associated animation. The majority of ATP is produced by which step of cell respiration? Krebs cycle Formation of acetyl CoA Glycolysis Electron transport chain | back 2 Electron transport chain |
front 3 Which of the following is anabolism? Oxidation of amino acids Translation Glycolysis Oxidation of fatty acids | back 3 Translation |
front 4 An oxidation reaction results in the loss of hydrogen atoms in most biologic systems. adds electrons to a molecule. increases the potential energy of a molecule. allows conversion of ATP to ADP. occurs in conversion of pyruvic acid into lactic acid. | back 4 results in the loss of hydrogen atoms in most biologic systems. |
front 5 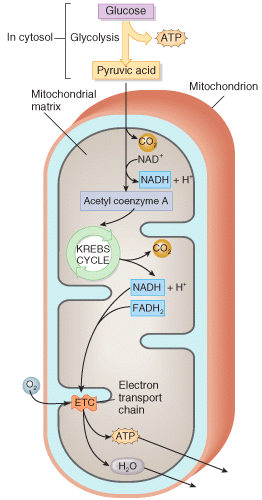 ATP is produced --- 1 only 2 only 3 only 1 and 2 are correct 1, 2, and 3 are correct | back 5 1 and 2 are correct |
front 6 The most abundant product of the reactions of the Krebs cycle is --- Pyruvate Carbon dioxide GTP Reduced coenzymes Water | back 6 Reduced coenzymes |
front 7 ADP is converted to ATP via a process called --- oxidation. dephosphorylation. phosphorylation. none of these. | back 7 phosphorylation. |
front 8 Which of the following will not stimulate lipolysis? ---- Cortisol Insulin Epinephrine Human growth hormone | back 8 Insulin |
front 9 Acetyl CoA formed by beta oxidation of fatty acids can be used to generate ATP during ------ Glycolysis. The Kreb’s Cycle. Fermentation. All of these. | back 9 The Kreb’s Cycle |
front 10 Hydrolyzed amino acids can be converted into proteins via translation which uses all of the following except ----- peroxisomes. mRNA. ribosomes. tRNA. | back 10 peroxisomes |
front 11 This portion of a DNA segment does not code for a protein. ---- RNA Introns Exons Polyribosome Ribosome | back 11 Introns |
front 12 he following is a particular sequence of codon on mRNA: ACU. What is the corresponding anti-codon for the tRNA? UGA UCA TGA TCA AUC | back 12 UGA |
front 13 Paracrines are secreted into the blood stream are secreted into a duct act on the neighboring cell act on the cell that secreted them | back 13 act on the neighboring cell |