Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
1403 Week 10 - Homework Assignment 8
front 1 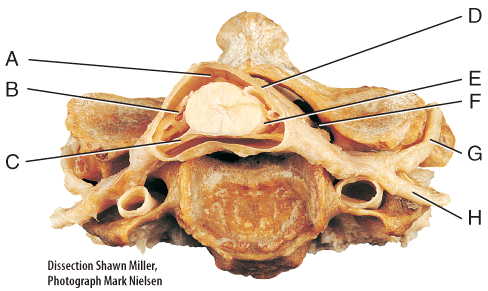 Where is the anterior (ventral) root of a spinal nerve? | back 1 C |
front 2 Which of the following statements is incorrect ? The anterior gray horn, posterior gray horn and lateral gray horns contain myelinated fibers. The anterior and posterior gray horns divide the white matter into columns. The white matter of the spinal cord contains tracts. Sensory tracts carry information to the brain. Motor tracts carry information away from the brain. | back 2 The anterior gray horn, posterior gray horn and lateral gray horns contain myelinated fibers. |
front 3 Which of the following brain structures consists of the medulla oblongata, pons and midbrain? Diencephalon Dura mater Brain stem Cerebrum Cerebellum | back 3 Brain stem |
front 4 The term 'decussation' means: to split in half control of movement a form of sensory input crossing swallowing | back 4 crossing |
front 5 If a person has damage to the visual association area, he/she will not be able to see see, but be unable to understand what he/she is viewing not be able to remember visual experiences from the past, like the color of his/her first car | back 5 see, but be unable to understand what he/she is viewing |
front 6 Diffusion, enzymatic degradation, and uptake by cells are all ways to excite a presynaptic potential remove a neurotransmitter stop a spatial summation continue a temporal summation inhibit a presynaptic potential | back 6 remove a neurotransmitter |
front 7 To answer this question, first click here to view the associated animation. EPSPs are caused by a hyperpolarization of the post-synaptic membrane. True False | back 7 False |
front 8 The process in which the frequency of nerve impulses in the first-order neuron decreases during prolonged stimulus is called modality. adaptation. perception. selectivity. transduction. | back 8 adaptation |
front 9 The postcentral gyri of the parietal lobes of the cerebral cortex provide the ability to move the eyeballs. receive visual information. control voluntary body movements. receive body sensory information. are considered the primary gustatory area. | back 9 receive body sensory information. |
front 10 The process of sensation begins in a _____, which can be either a primary sensory neuron or a separate cell. effector cell. signal transducer cell. association neuron. sensory receptor cell. secondary sensory neuron. | back 10 sensory receptor cell. |
front 11 Third order neurons conduct impulses from the thalamus to the somatosensory area of the cerebrum or to the cerebellum. True False | back 11 True |
front 12 To answer this question, first click here to view the associated animation. Vibration and fine touch sensory impulses are carried by the anterolateral spinothalamic pathway. True False | back 12 False |
front 13 To answer this question, first click here to view the associated animation. Unconscious proprioception sensory impulses are carried by the Posterior column-medial lemniscus pathway Anterolateral spinothalamic pathway Spinocerebellar pathway All of these | back 13 Spinocerebellar pathway |