Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Bio II Final Review; Test 1
front 1 One major advantage of using Arabidopsis thaliana as a model system
for studies of plant form and function is its | back 1 A |
front 2 Which of the following is derived from the ground tissue system?
| back 2 D |
front 3 Which of the following have unevenly thickened primary walls that
support young, growing parts of the plant? | back 3 B |
front 4 Which cells are no longer capable of carrying out the process of DNA
transcription? | back 4 A |
front 5 All of the following cell types are correctly matched with their
functions except | back 5 E |
front 6 Additional vascular tissue produced as secondary growth in a root
originates from which cells? | back 6 A |
front 7 As a youngster, you drive a nail in the trunk of a young tree that is
3 meters tall. The nail is about 1.5 meters from the ground. Fifteen
years later, you return and discover that the tree has grown to a
height of 30 meters. About how many meters above the ground is the
nail? | back 7 B |
front 8 What tissue makes up most of the wood of a tree? | back 8 B |
front 9 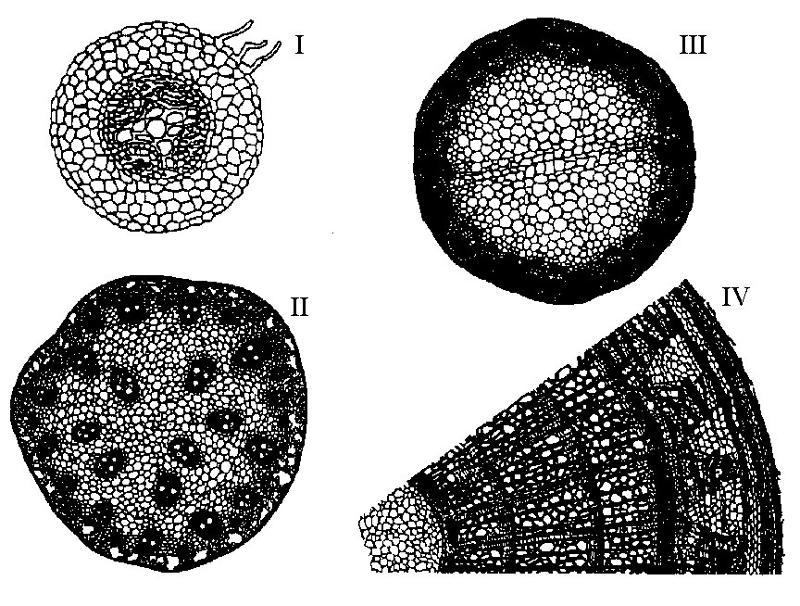 The following question are based on the drawing of root or stem cross
sections shown in Figure 35.2. | back 9 D |
front 10 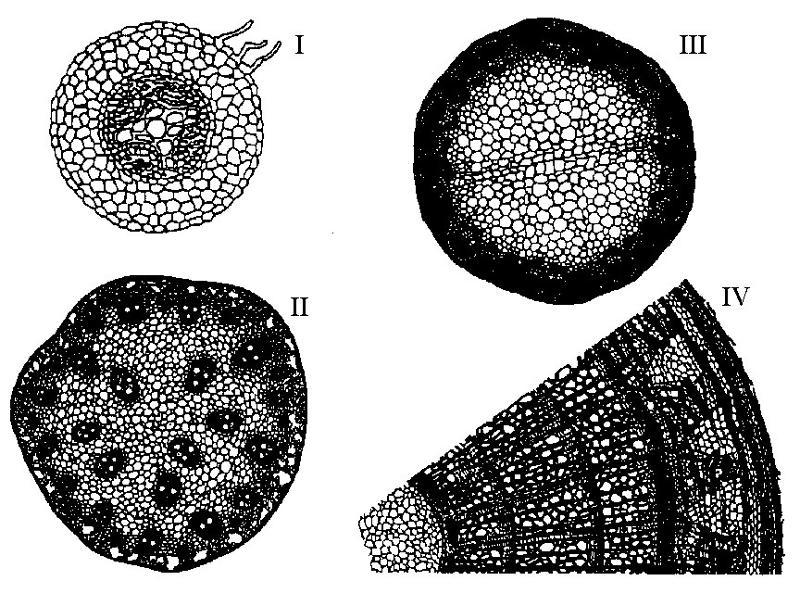 A monocot stem is represented by | back 10 B |
front 11 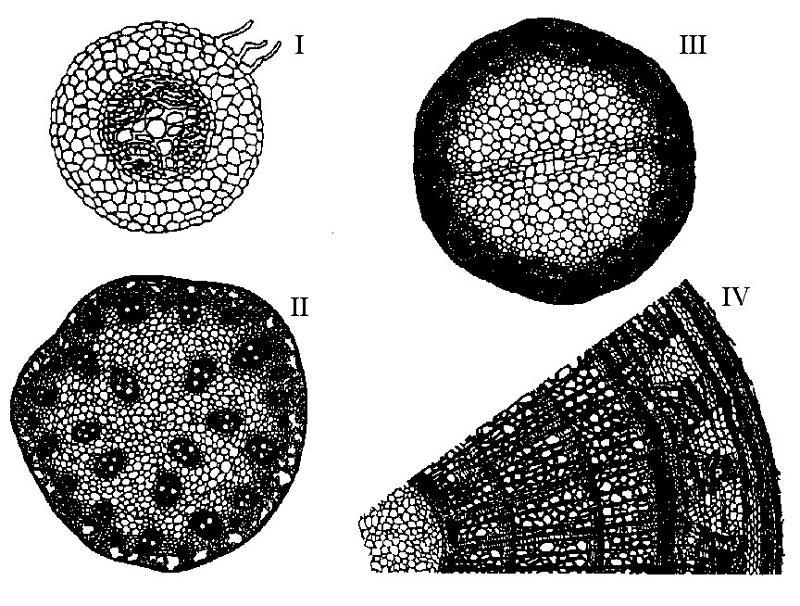 A plant that is at least 3 years old is represented by | back 11 D |
front 12 Which of the following would be least likely to affect osmosis in
plants? | back 12 C |
front 13 A water molecule could move all the way through a plant from soil to
root to leaf to air and pass through a living cell only once. This
living cell would be a part of which structure? | back 13 D |
front 14 What drives the flow of water through the xylem? | back 14 C |
front 15 Phloem transport is described as being from source to sink. Which of
the following would most accurately complete this statement about
phloem transport as applied to most plants in the late spring?
| back 15 B |
front 16 Which structure or compartment is part of the symplast? | back 16 B |
front 17 In plant roots, the Casparian strip is correctly described by which
of the following? | back 17 D |
front 18 Which of the following is responsible for the cohesion of water
molecules? | back 18 C |
front 19 Cells produced by lateral meristems are known as A) secondary tissues B) pith C) dermal and ground tissue D) shoots and roots | back 19 A |
front 20 Photosynthesis ceases when leaves wilt, mainly because | back 20 C |
front 21 All of the following normally enter the plant through the roots
except | back 21 A |
front 22 Which of the following plant structures shares the most common
features and functions with a fungal hyphae? | back 22 D |
front 23 Most of the water taken up by a plant is | back 23 C |
front 24 A soil well suited for the growth of most plants would have all of
the following properties except | back 24 E |
front 25 Which of the following statements is false about bulk flow? A) It depends on the force of gravity on a column of water B) It is driven primarily by pressure potential C) It is more effective than diffusion over distances greater than 100mm D) It depends on a difference in pressure potential at the source and sink | back 25 A |
front 26 A person working with plants may reduce the inhibition of apical
dominance by auxin via which of the following? | back 26 A |
front 27 Which of the following soil minerals is most likely leached away
during a hard rain? | back 27 D |
front 28 A farming commitment that embraces a variety of methods that are
conservation-minded, environmentally safe, and profitable is called
| back 28 E |
front 29 Which of the following would be the most effective strategy to remove
toxic heavy metals from a soil? | back 29 D |
front 30 The bulk of a plant's dry weight is derived from | back 30 B |
front 31 Nitrogen fixation is a process that | back 31 D |
front 32 If a plant is infected with nitrogen-fixing bacteria, what is the
most probable effect on the plant? | back 32 D |
front 33 An example of a mutualistic association between a plant and a fungus
would be | back 33 D |
front 34 Epiphytes are | back 34 E |
front 35 Some of the problems associated with intensive irrigation include all
but | back 35 B |
front 36 Which of the following is the correct sequence during the alternation
of generations life cycle in a flowering plant? | back 36 A |
front 37 Which of the following are true of most angiosperms? | back 37 D |
front 38 The ovary is most often located on/in the | back 38 B |
front 39 Microsporangia in flowering plants are located in the | back 39 A |
front 40 Which of the following is the correct order of floral organs from the
outside to the inside of a complete flower? | back 40 D |
front 41 Which of the following types of plants are incapable of
self-pollination? | back 41 A |
front 42 All of the following are primary functions of flowers except | back 42 B |
front 43 Which of the following statements regarding flowering plants is
false? | back 43 B |
front 44 Which of the following "vegetables" is botanically a fruit?
| back 44 E |
front 45 Fruits develop from | back 45 D |
front 46 Which of the following is a successful example of the commercial use
of transgenic crops? | back 46 A |
front 47 Double fertilization means that | back 47 C |
front 48 A small flower with green petals is most likely | back 48 D |
front 49 What is the first step in the germination of a seed? | back 49 C |
front 50 Which of the following could be considered an evolutionary advantage
of asexual reproduction in plants? | back 50 A |
front 51 Charles and Francis Darwin concluded from their experiments on
phototropism by grass seedlings that the part of the seedling that
detects the direction of light is the | back 51 A |
front 52 Why do coleoptiles grow toward light? | back 52 D |
front 53 The detector of light during de-etiolation (greening) of a tomato
plant is (are) | back 53 C |
front 54 The ripening of fruit and the dropping of leaves and fruit are
principally controlled by | back 54 D |
front 55 Which of the following hormones is commonly used as an herbicide, such as 2, 4-D? A) gibberellins B) cytokinins C) auxins D) abscisic acid | back 55 C |
front 56 If a farmer wanted more loosely packed clusters of grapes, he would
most likely spray the immature bunches with | back 56 B |
front 57 The hormone that helps plants respond to drought is | back 57 E |
front 58 If you were shipping green bananas to a supermarket thousands of
miles away, which of the following chemicals would you want to
eliminate from the plants' environment? | back 58 C |
front 59 The synthesis of which of the following hormones would be a logical
first choice in an attempt to produce normal growth in mutant dwarf
plants? | back 59 C |
front 60 A short-day plant will flower only when | back 60 D |
front 61 The initial response of the root cells of a tomato plant watered with
seawater would be to | back 61 C |
front 62 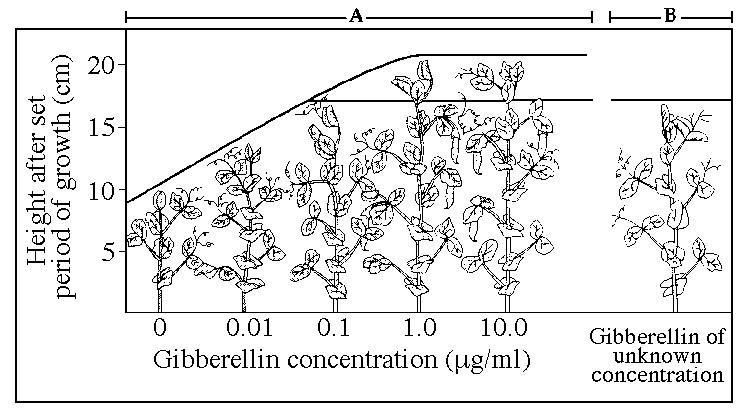 The results of this experiment, shown on the left of the graph (area
A), may be used to | back 62 D |
front 63 If you wanted to genetically engineer a plant to be more resistant to
drought, increasing amounts of which of the following hormones might
be a good first attempt? | back 63 A |
front 64 Seed packets give a recommended planting depth for the enclosed
seeds. The most likely reason some seeds are to be covered with only
1/4 inch of soil is that the | back 64 C |