Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
1403 - Week 9 Homework Assignment
front 1 In temporal summation, a single presynaptic neuron stimulates the creation of action potentials in a postsynaptic neuron when it ------ stops firing long enough to allow the postsynaptic neuron to recover. runs out of neurotransmitter. fires at a steady rate that allows the postsynaptic neuron to return to resting potential. recruits other presynaptic neurons to begin to fire. fires at a fast enough rate that the sum of EPSPs in the postsynaptic neuron moves above threshold. | back 1 fires at a fast enough rate that the sum of EPSPs in the postsynaptic neuron moves above threshold. |
front 2 EPSPs are caused by a hyperpolarization of the post-synaptic membrane. -- True False | back 2 False |
front 3 During repolarization, more sodium ions are brought into the cell to reset the membrane potential. -- True False | back 3 False |
front 4 The generation of an action potential is an electrochemical event. This electrical event occurs: ------ within the neuron only in nerves with neurolemma within the myelin sheath in microglia | back 4 within the neuron |
front 5 Graded potentials: ---- arise when ion movement causes a minor change in the resting membrane potential. usually propagate down the length of an axon. occur when voltage-gated channels open. are most often observed in axons. are usually associated with ion movement through leakage channels. | back 5 arise when ion movement causes a minor change in the resting membrane potential. |
front 6 Consider the cell body of a neuron. Through which types of ion
channel might sodium enter the cell body? Check
all that apply! Na+1/K+1 ATPase ligand-gated channels voltage gated channels leakage channels | back 6 leakage channels |
front 7 Which of the following ions pass through the resting neuronal cell membrane most easily? -- sodium calcium potassium phosphate | back 7 potassium |
front 8 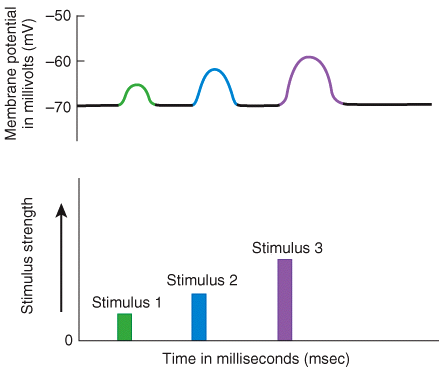 When summation results from buildup of neurotransmitter released simultaneously by several presynaptic end bulbs, it is called Temporal summation Wallerian degeneration Saltatory conduction Spatial summation | back 8 Spatial summation |
front 9 In temporal summation, a single presynaptic neuron stimulates the creation of action potentials in a postsynaptic neuron when it ------ stops firing long enough to allow the postsynaptic neuron to recover. runs out of neurotransmitter. fires at a steady rate that allows the postsynaptic neuron to return to resting potential. recruits other presynaptic neurons to begin to fire. fires at a fast enough rate that the sum of EPSPs in the postsynaptic neuron moves above threshold. | back 9 fires at a fast enough rate that the sum of EPSPs in the postsynaptic neuron moves above threshold. |
front 10 EPSPs are caused by a hyperpolarization of the post-synaptic membrane. ---- True False | back 10 False |
front 11 During repolarization, more sodium ions are brought into the cell to reset the membrane potential. ----- True False | back 11 False |
front 12 The generation of an action potential is an electrochemical event.
This electrical event occurs: within the neuron only in nerves with neurolemma within the myelin sheath in microglia | back 12 within the neuron |
front 13 Graded potentials: arise when ion movement causes a minor change in the resting membrane potential. usually propagate down the length of an axon. occur when voltage-gated channels open. are most often observed in axons. are usually associated with ion movement through leakage channels. | back 13 arise when ion movement causes a minor change in the resting membrane potential. |
front 14 Consider the cell body of a neuron. Through which types of ion
channel might sodium enter the cell body? Check
all that apply! Na+1/K+1 ATPase ligand-gated channels voltage gated channels leakage channels | back 14 leakage channels |
front 15 Which of the following ions pass through the resting neuronal cell
membrane most easily? sodium calcium potassium phosphate | back 15 calcium |
front 16 A resting nerve fiber is polarized because the concentration of Na+ and K+ ions is higher on the inside of the cell membrane Na+ and K+ ions is higher outside the cell membrane Na+ is higher on the inside and K+ is higher on the outside Na+ is higher on the outside and K+ is higher on the inside | back 16 Na+ is higher on the outside and K+ is higher on the inside |
front 17 A depolarizing graded potential ----- makes the membrane less polarized. is the last part of an action potential. is considered a type of action potential. is seen when the cell approaches threshold. makes the membrane more polarized. | back 17 makes the membrane less polarized. |
front 18 When a depolarizing graded potential makes the axon membrane depolarize to threshold, ----- ligand-gated Ca+2 channels close rapidly. voltage-gated Ca+2 channels open rapidly. ligand-gated Na+ channels close rapidly. voltage-gated Na+ channels open rapidly. none of these choices occur. | back 18 voltage-gated Na+ channels open rapidly. |
front 19 During this period, a second action potential can only be initiated by a larger than normal stimulus ---- Latent period Absolute refractory period Relative refractory period All of these choices None of these choices | back 19 Relative refractory period |
front 20 Name the type of membrane channel that opens in response to changes in membrane potential and is located in axons of all types of neurons. ---- voltage-gated channels leakage channel temperature-sensitive channel mechanically gated channels ligand-gated channels | back 20 voltage-gated channels |
front 21 To answer this question, first click here to view the associated animation. In a graded potential, the voltage does not diminish with the distance. ---- True False | back 21 False |
front 22 To answer this question, first click here to view the associated animation. The resting potential is maintained by the presence of ---- many efflux K+ pores the Na+/K+ pump an ATP-driven pump moving K+ into the cell all of these | back 22 all of these |
front 23 To answer this question, first click here to view the associated animation. The larger the diameter of an axon, the faster the conduction of an action potential. ---- True False | back 23 True |
front 24 To answer this question, first click here to view the associated animation. Myelinated axons are capable of salutatory conduction. This allows for more rapid action potential conduction because ----- repolarization occurs across the entire membrane. repolarization occurs only at the Nodes of Ranvier. depolarization occurs only at the Nodes of Ranvier. depolarization occurs across the entire membrane | back 24 depolarization occurs only at the Nodes of Ranvier. |
front 25 To answer this question, first click here to view the associated animation. Which situation will see the fastest conduction rate across an axon? ----- unmyelinated axon in with a thin axon diameter myelinated axon in with a wide axon diameter unmyelinated axon myelinated axon | back 25 myelinated axon in with a wide axon diameter |
front 26 To answer this question, first click here to view the associated animation Some voltage-gated channels do not allow ions to pass through when their activation gate is open because ----- a competitive ion of another type passes through instead. there is a second gate, an inactivation gate, that closes to block the channel. their gate is temporarily surrounded by like charges which repel the ions that normally would pass through. there is a malfunction that occurs in the channel that causes it to change shape and block ion passage. | back 26 there is a second gate, an inactivation gate, that closes to block the channel. |
front 27 To answer this question, first click here to view the associated animation When the threshold of voltage-gated channels is reached and voltage-gated channels open, the resulting change in membrane potential is known as a(n) ----- transition state. graded potential. induction mode. action potential. | back 27 action potential. |
front 28 To answer this question, first click here to view the associated animation If I can block neurotransmitters attaching to chemically-gated sodium channels, what will be the result? ---- The cell will depolarize but not repolarize An action potential will not be produced The cell will die The cell will become hyperactive | back 28 An action potential will not be produced |