Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Set #1 Johnson Intro Bio II Final Review
front 1 One major advantage of using Arabidopsis thaliana as a model system
for studies of plant form and function is its | back 1 Answer: A |
front 2 Choose the option that best describes the relationship between the
cell wall thickness of parenchyma cells versus sclerenchyma cells.
| back 2 Answer: A |
front 3 Which structure is incorrectly paired with its tissue system?
| back 3 Answer: D |
front 4 ________ is to xylem as ________ is to phloem. | back 4 Answer: C |
front 5 A plant has the following characteristics: a taproot system, several
growth rings evident in a cross section of the stem, and a layer of
bark around the outside. Which of the following best describes the
plant? | back 5 Answer: B |
front 6 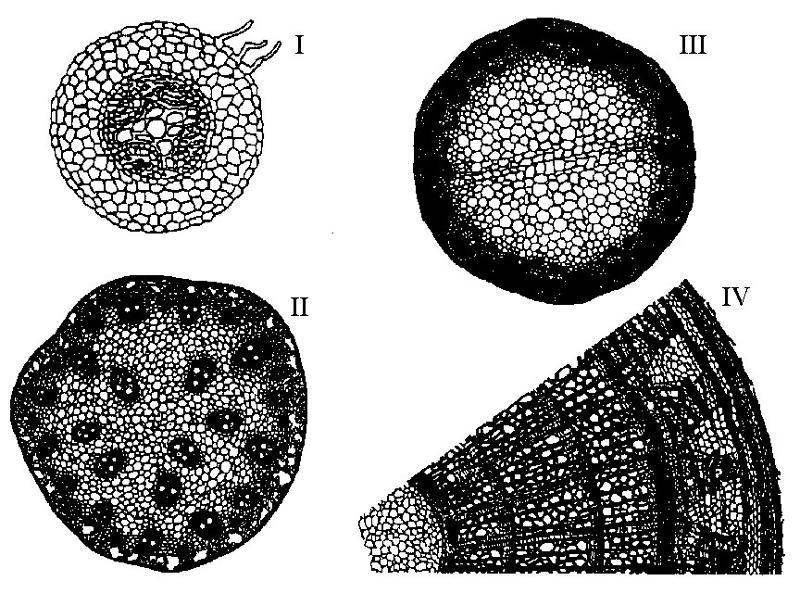 The following question are based on the drawing of root or stem cross
sections shown in Figure 35.2. | back 6 Answer: B |
front 7 Which of the following would be least likely to affect osmosis in
plants? | back 7 Answer: C |
front 8 Active transport of various materials in plants at the cellular level
requires all of the following except | back 8 Answer: A |
front 9 Compared to a cell with few aquaporins in its membrane, a cell
containing many aquaporins will | back 9 Answer: A |
front 10 Which of the following is a correct statement about sugar movement in
phloem? | back 10 Answer: B |
front 11 Which of the following soil minerals is most likely leached away
during a hard rain? | back 11 Answer: D |
front 12 Nitrogen fixation is a process that | back 12 Answer: D |
front 13 A group of 10 tomato plants are germinated and maintained in a large
tray with no drainage. After several weeks they all begin to wilt and
die despite repeated watering and fertilization. The most likely cause
of this die-off is | back 13 Answer: B |
front 14 Two groups of tomatoes were grown under laboratory conditions, one
with humus added to the soil and one a control without humus. The
leaves of the plants grown without humus were yellowish (less green)
compared with those of the plants grown in humus-enriched soil. The
best explanation for this difference is that | back 14 Answer: C |
front 15 Most of the dry mass of a plant is the result of uptake of
________. | back 15 Answer: C |
front 16 Which of the following is the correct order of floral organs from the
outside to the inside of a complete flower? | back 16 Answer: D |
front 17 In which of the following pairs are the two terms equivalent?
| back 17 Answer: B |
front 18 Which of the following is a scientific concern related to creating
genetically modified crops? | back 18 Answer: D |
front 19 Sperm cells are formed in plants by ________. | back 19 Answer: C |
front 20 The egg of a plant has a haploid chromosome number of 12 (n=12). What
is true about the number of chromosomes in the cells of other tissues
of this plant? | back 20 Answer: D |
front 21 A student examining leaf cross sections under a microscope finds many
loosely packed cells with relatively thin cell walls. The cells have
numerous chloroplasts. What type of cells are they? | back 21 Answer: A |
front 22 When you eat beets, including sugar from sugar beets, what are you
eating? | back 22 Answer: B |
front 23 When you eat a celery stalk, what are you eating? | back 23 Answer: B |
front 24 When you eat potatoes, what are you eating? | back 24 Answer: B |
front 25 CO₂ enters the inner spaces of the leaf through the | back 25 Answer: C |
front 26 One important difference between the anatomy of roots and the anatomy
of leaves is that | back 26 Answer: C |
front 27 Trichomes ________. | back 27 Answer: D |
front 28 Which of the following are water-conducting cells that are dead at
functional maturity? | back 28 Answer: A |
front 29 (DIAGRAM) The main function associated with the thin top layer of a
plant leaf is ________. | back 29 Answer: B |
front 30 Plant meristematic cells ________. | back 30 Answer: D |
front 31 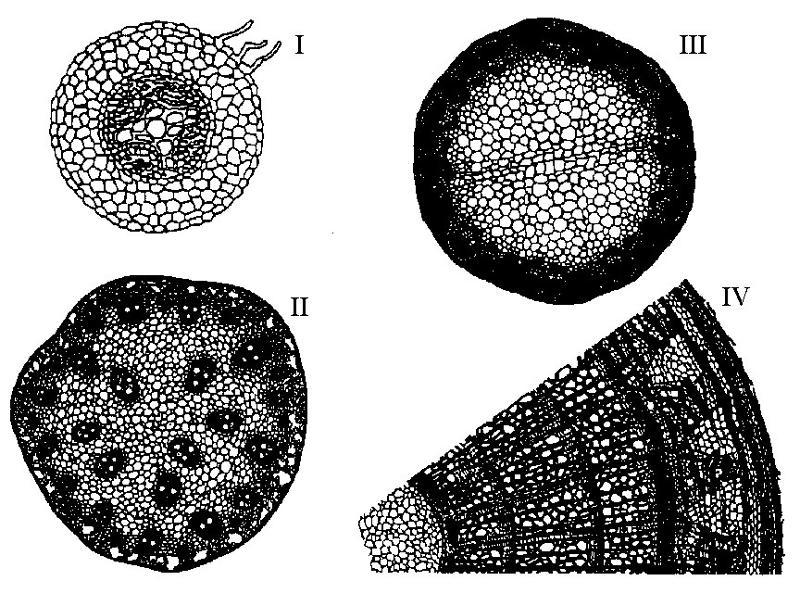 The following question are based on the drawing of root or stem cross
sections shown in Figure 35.2. | back 31 Answer: D |
front 32 What tissue makes up most of the wood of a tree? | back 32 Answer: B |
front 33 Which of the following is true of bark? | back 33 Answer: A |
front 34 Root hairs are most important to a plant because they | back 34 Answer: C |
front 35 A plant developed a mineral deficiency after being treated with a
fungicide. What is the most probable cause of the deficiency? | back 35 Answer: B |
front 36 What regulates the flow of water through the xylem? | back 36 Answer: C |
front 37 The ________ is the most efficient rout of water movement in plants,
while the ________ is the most select. | back 37 Answer: C |
front 38 All of the following normally enter the plant through the roots
except | back 38 Answer: A |
front 39 Which of the following would be least likely to affect osmosis in
plants? | back 39 Answer: C |
front 40 In plant roots, the Casparian strip is correctly described by which
of the following? | back 40 Answer: D |
front 41 Most of the water taken up by a plant is | back 41 Answer: C |
front 42 Which of the following is a similarity between xylem and phloem
transport? | back 42 Answer: A |
front 43 Which of the following us not part of the
transpiration-cohesion-tension mechanism for the ascent of xylem
sap? | back 43 Answer: C |
front 44 Water potential is generally most negative in which of the following
parts of a plant? | back 44 Answer: C |
front 45 Several tomato plants are growing in a small garden plot. If soil
water potential were to drop significantly on a hot summer afternoon,
which of the following would most likely occur? | back 45 Answer: D |
front 46 A group of 10 tomato plants are germinated and maintained in a large
tray with no drainage. After several weeks they all begin to wilt and
die despite repeated watering and fertilization. The most likely cause
of this die-off is | back 46 Answer: A |
front 47 Which of the following soil minerals is most likely leached away
during a hard rain? | back 47 Answer: D |
front 48 Which of the following would inhibit the growth of most
plants? | back 48 Answer: D |
front 49 Which of the following contributed to the dust bowl in the American
southwest during the 1930s? A) II and III | back 49 Answer: B |
front 50 Which of the following would be the most effective strategy to remove
toxic heavy metals from a soil? | back 50 Answer: D |
front 51 Which criteria allow biologists to divide chemicals into
macronutrients and micronutrients? | back 51 Answer: A |
front 52 Why is nitrogen fixation an essential process? | back 52 Answer: B |
front 53 You are weeding your garden when you accidentally expose some roots
of your pea plants. You notice swellings (root nodules) on the roots
and there is a reddish tinge to the ones you accidentally damaged.
Most likely your peas plants | back 53 Answer: C |
front 54 Which of the following is a primary difference between
ectomycorrhizae and endomycorrhizae? | back 54 Answer: C |
front 55 What major benefits do plants and mycorrhizal fungi receive from
their symbiotic relationship? | back 55 Answer: A |
front 56 Carnivorous plants have evolved mechanisms that trap and digest small
animals. The products of this digestion are used to supplement the
plant's supply of | back 56 Answer: D |
front 57 During the alternation of generations in plants, ________. | back 57 Answer: B |
front 58 Retaining the zygote on the living gametophyte of land plants
________. | back 58 Answer: B |
front 59 Angiosperms are the most successful terrestrial plans. Which of the
following features is unique to them and helps account for their
success? | back 59 Answer: A |
front 60 Which of the following is the correct order of floral organs from the
outside to the inside of a complete flower? | back 60 Answer: D |
front 61 Which of the following statements regarding flowering plants is
correct? | back 61 Answer: C |
front 62 Double fertilization means that ________. | back 62 Answer: C |
front 63 What is typically the result of double fertilization in angiosperms?
| back 63 Answer: C |
front 64 Which of the following flower parts develops into a seed? | back 64 Answer: B |
front 65 Which of the following flower parts develops into the pulp of a
fleshy fruit? | back 65 Answer: D |
front 66 The vast number and variety of flower species is probably related to
various kinds of ________. | back 66 Answer: D |
front 67 Unripe fruits protect seeds from predation and early germination.
What is the major function of ripe fruits? | back 67 Answer: C |
front 68 Which of the following could be considered an evolutionary advantage
of asexual reproduction in plants? | back 68 Answer: A |
front 69 Which of the following is a scientific concern related to creating
genetically modified crops? | back 69 Answer: A |
front 70 The detector of light during de-etiolation (greening) of a tomato
plant is (are) | back 70 Answer: C |
front 71 Which of these activities is part of the development of crop plants
from wild relatives? A) I, II, and IV | back 71 Answer: A |
front 72 Genetically engineered plants ________. | back 72 Answer: A |
front 73 External stimuli would be received most quickly by a plant cell if
the receptors for signal transduction were located in the | back 73 Answer: A |
front 74 Plant hormonal regulation differs from animal hormonal regulation in
that ________. | back 74 Answer: A |
front 75 Which of the following plant growth responses is primarily due to the
action of auxins? | back 75 Answer: B |