Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Biology chapter 10
front 1 Part A Which of the following occurs during meiosis but not during mitosis? A) chromosome replication | back 1 B. Synapsis occurs |
front 2 In alternation of generations, what is the diploid stage of a plant that follows fertilization called? | back 2 Sporophyte |
front 3 Identify all possible products of meiosis in plant and animal life cycles. Gametes Spores Multicellular adult organisma | back 3 Spores and gametes |
front 4 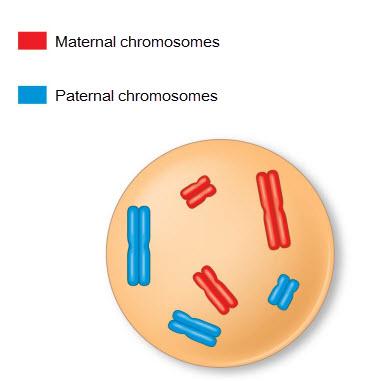 Look at the cell in the figure. Based on this figure, which of the following statements is true? It is impossible to tell whether the cell is haploid or diploid. This cell is diploid. This cell is haploid. | back 4 The cell is diploid |
front 5 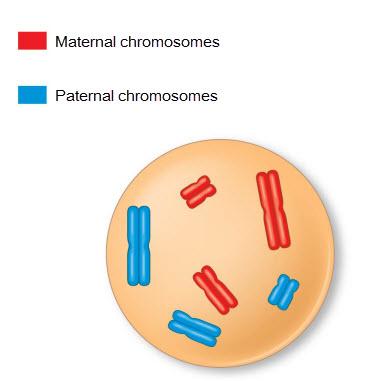 What is the best evidence telling you whether this cell is diploid or haploid? The cell is haploid because the chromosomes are not found in pairs. The cell is diploid because it contains two sets of chromosomes. The cell is diploid because each chromosome consists of two chromatids | back 5 the cell is diploid because it contains two sets of chromosomes |
front 6 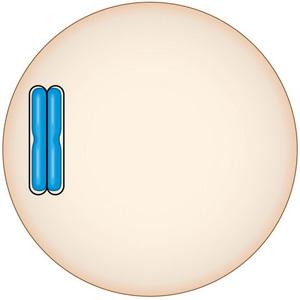 This chromosome has two chromatids, joined at the centromere. What process led to the formation of the two chromatids? The two chromatids were formed by synapsis and the formation of a synaptonemal complex. The two chromatids were formed by fertilization, bringing together maternal and paternal chromatids. The two chromatids were formed by duplication of a chromosome. | back 6 The two chromatids were formed by the duplication of a chromosome |
front 7 Two sister chromatids are joined at the centromere prior to meiosis. Which statement is correct These chromatids make up a diploid chromosome. The cell that contains these sister chromatids must be haploid. Barring mutation, the two sister chromatids must be identical. | back 7 barring mutation the two sister chromatids must be identical |
front 8 Asexual reproduction _____. is limited to plants produces offspring genetically identical to the parent is limited to single-cell organisms requires both meiosis and mitosis leads to a loss of genetic material | back 8 produces offspring genetically identical to the parent |
front 9 What number and types of chromosomes are found in a human somatic cell? n chromosomes 44 autosomes and 2 sex chromosomes 22 autosomes and 1 sex chromosome 21 autosomes and 2 sex chromosomes 45 autosomes and 1 sex chromosome | back 9 44 autosomes and 2 sex chromosomes |
front 10 For what purpose(s) might a karyotype be prepared? for prenatal screening, to determine if a fetus has the correct number of chromosomes to determine whether a fetus is male or female to detect the possible presence of chromosomal abnormalities such as deletions, inversions, or translocations The first and second answers are correct. The first three answers are correct. | back 10 The first three answers are correct |
front 11 How are sister chromatids and homologous chromosomes different from each other? They are not different. Homologous chromosomes and sister chromatids are both identical copies of each other. Homologous chromosomes contain the same gene loci but may have different alleles of a particular gene. Sister chromatids are identical copies of each other produced during DNA replication. Homologous chromosomes are identical copies of each other. One sister chromatid comes from the father, and one comes from the mother. Sister chromatids are only formed during mitosis. Homologous chromosomes are formed during meiosis. Homologous chromosomes are closely associated with each other in both mitosis and meiosis. Sister chromatids are only associated with each other during mitosis. | back 11 Homologous chromosomes contain the same gene loci but may have different alleles of a particular gene. Sister chromatids are identical copies of each other produced during DNA replication |
front 12 Mitosis results in the formation of how many cells; meiosis results in the formation of how many cells? four diploid cells ... four haploid cells two diploid cells ... two haploid cells four haploid cells ... two diploid cells two diploid cells ... four haploid cells two diploid cells ... two diploid cells | back 12 2 dipoid...4 haploid |
front 13 What is crossing over? the movement of genetic material from one chromosome to a nonhomologous chromosome making an RNA copy of a DNA strand the exchange of homologous portions of nonsister chromatids a direct consequence of the separation of sister chromatids also referred to as the "independent assortment of chromosomes" | back 13 The exchange of homologous portions of nonsister chromatids |
front 14 Heritable variation is required for which of the following? the production of a clone meiosis evolution asexual reproduction mitosis | back 14 evolution |
front 15 A human cell containing 22 autosomes and a Y chromosome is a somatic cell of a male. a somatic cell of a female. an egg. a zygote. a sperm. | back 15 A sperm |
front 16 Homologous chromosomes move toward opposite poles of a dividing cell during fertilization . binary fission meiosis II. mitosis. meiosis I. | back 16 meiosis I |
front 17 Which sample(s) of DNA might be from a nerve cell arrested in G0 of the cell cycle? | back 17 I |
front 18 Which sample(s) might represent an animal cell in the G2 phase of the cell cycle? | back 18 II |
front 19 Which sample(s) might represent a zygote? | back 19 I |