Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Multichoice The Muscular System
front 1 Most muscles cross at least one a) tendon b) joint c) bone d) ligament e) body plane | back 1 b |
front 2 The attachment of a muscle’s tendon to the stationary bone is called the _____; the attachment of the muscle’s other tendon to the movable bone is called the _____. a) origin, action b) insertion, action c) origin, insertion d) insertion, origin e) insertion, action | back 2 c |
front 3 A lever is acted on at two different points by two different forces which are called the a) fulcrum and resistance. b) leverage and load. c) lever and resistance. d) effort and load. e) lever and effort. | back 3 d |
front 4 Motion will occur in a muscle when the _____ supplied exceeds the _____. a) effort, load b) resistance, lever c) load, effort d) load, resistance e) lever, effort | back 4 a |
front 5 Which of the following is NOT a common arrangement of muscle fascicles? a) pennate b) triangular c) oval d) parallel e) fusiform | back 5 c |
front 6 This type of fascicle arrangement has the fascicles spread over a broad area and converges at a thick central tendon.
| back 6 a |
front 7 The muscle that serves as the “prime mover” during a movement is called the a) antagonist. b) agonist. c) synergist. d) asynergist. e) fixator. | back 7 b |
front 8 This type of muscle works by stabilizing the origin of the agonist so that it can act more efficiently. a) synergist b) agonist c) antagonist d) fixator e) secondary mover | back 8 d |
front 9 Which of the following is NOT a characteristic commonly used to name skeletal muscles? a) Size b) Shape c) Number of origins d) Sites of origins e) Thickness of fibers | back 9 e |
front 10 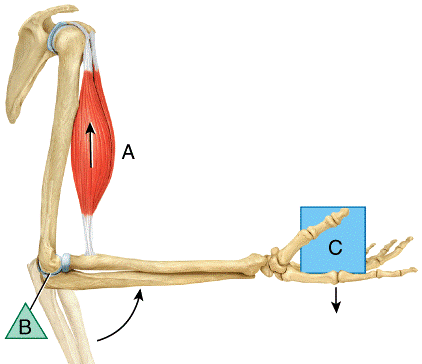 In the diagram, where is the fulcrum?
e) None of these choices | back 10 b |
front 11 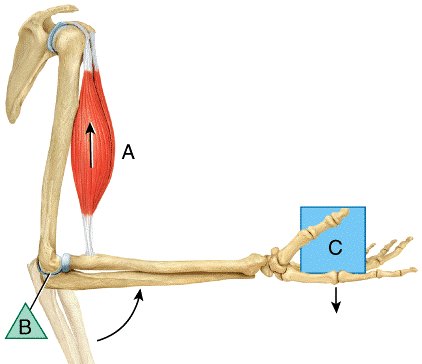 In the diagram, where is the effort?
| back 11 a |
front 12 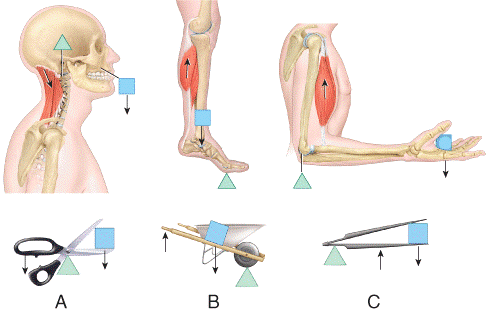 Which one represents a second-class lever?
| back 12 b |
front 13 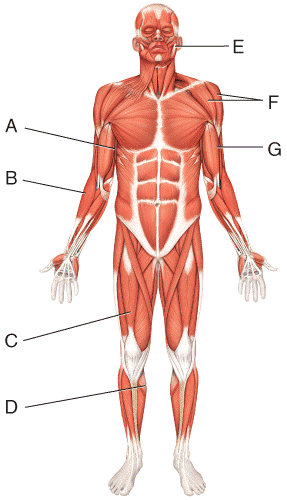 Where is the rectus femoris?
| back 13 c |
front 14 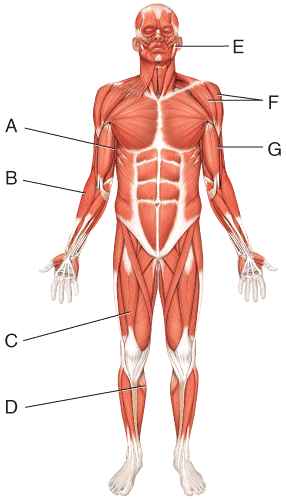 Where is the deltoid?
| back 14 c |
front 15 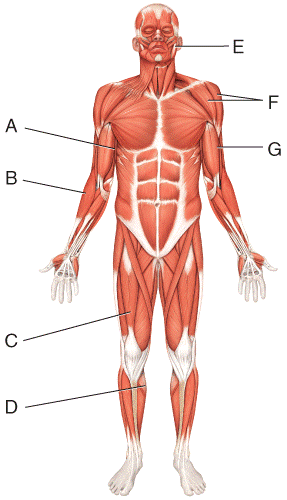 ) Where is the masseter?
| back 15 e |
front 16 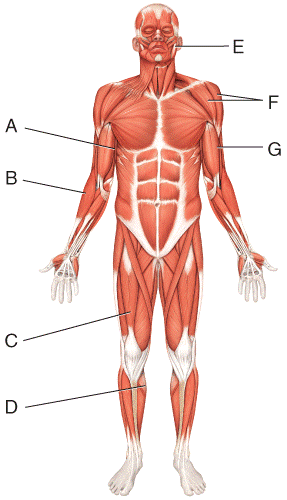 Where is the gastrocnemius?
| back 16 b |
front 17 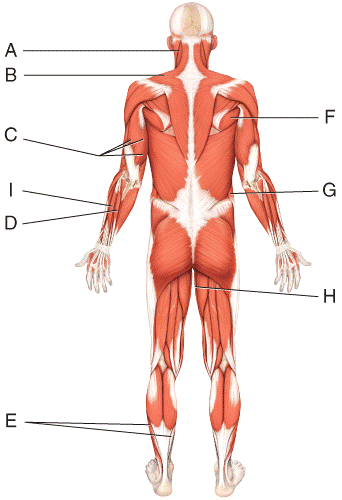 Where is the soleus?
| back 17 c |
front 18 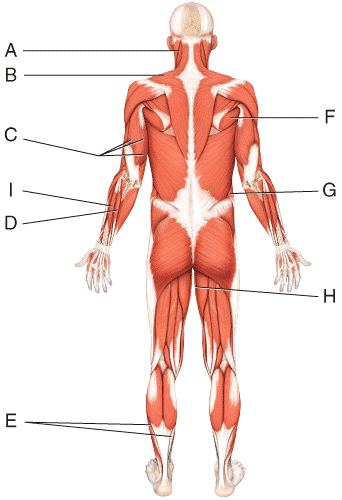 Where is the external oblique?
| back 18 b |
front 19  Where is the masseter?
| back 19 b |
front 20 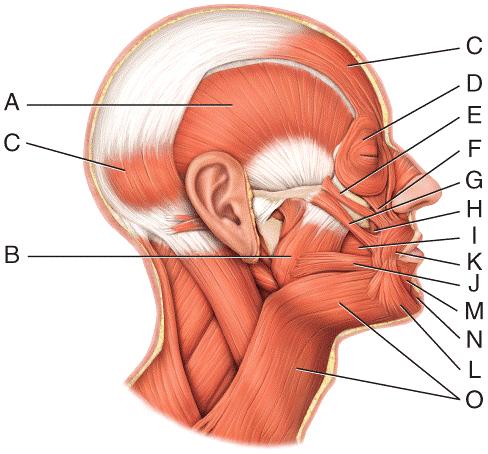 Where is the orbicularis oculi?
| back 20 a |
front 21 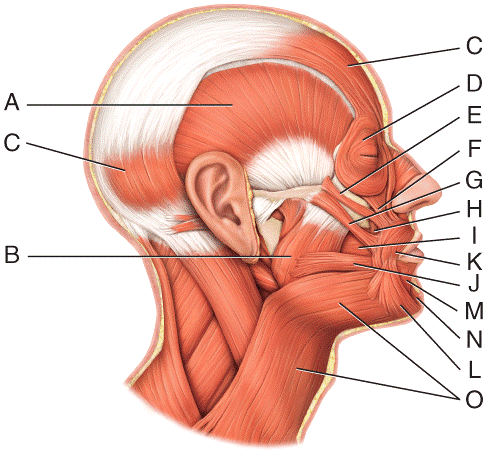 Where is the buccinator?
| back 21 c |
front 22  Where is the mentalis?
| back 22 e |
front 23 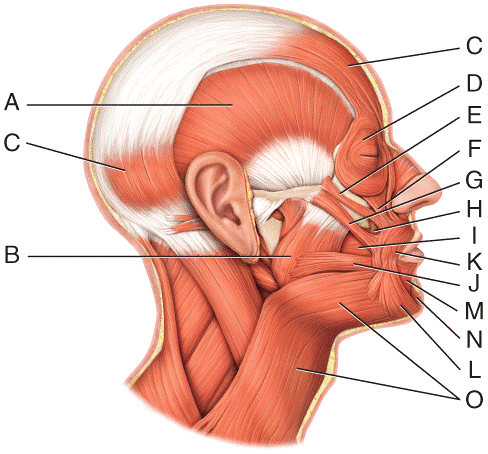 Where is the depressor anguli oris?
| back 23 b |
front 24 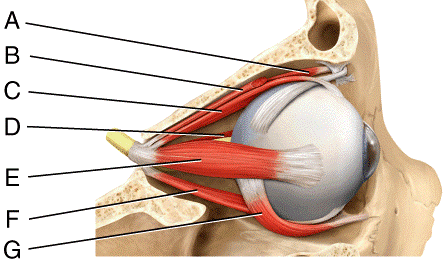 Where is the levator palpebrae superioris?
| back 24 a |
front 25 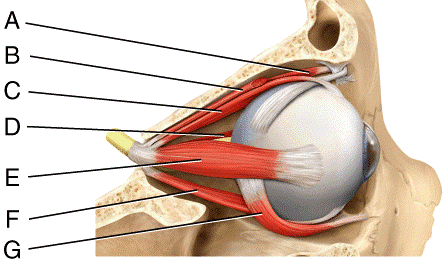 Where is the lateral rectus?
| back 25 c |
front 26 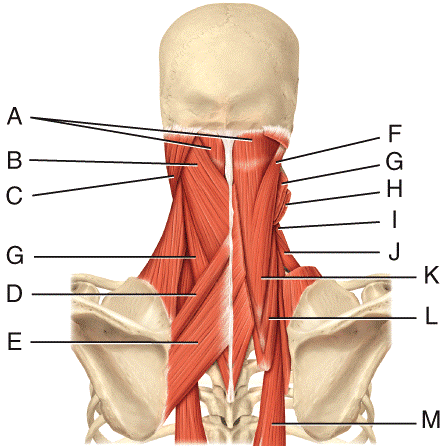 Where is the splenius capitis?
| back 26 b |
front 27 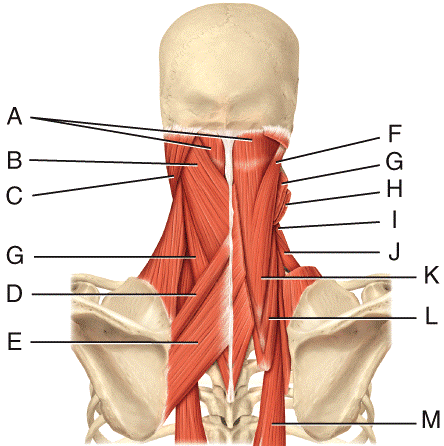 Where is the levator scapulae?
| back 27 a |
front 28 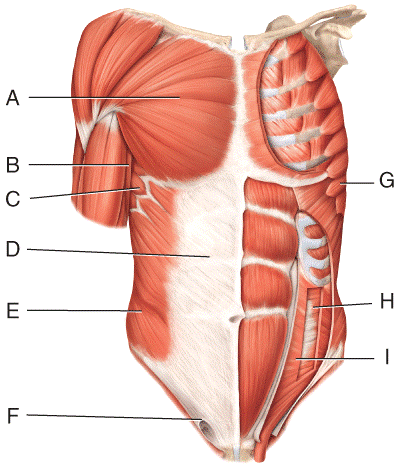 Where is the serratus anterior?
| back 28 c |
front 29 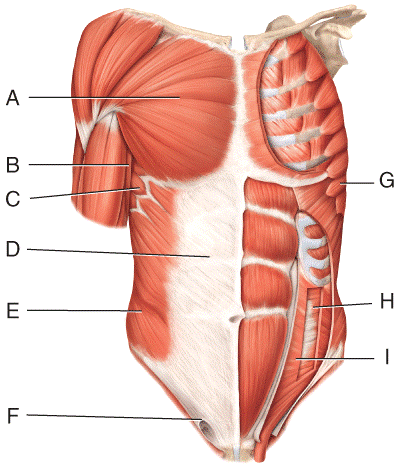 Where is the external oblique?
| back 29 b |
front 30 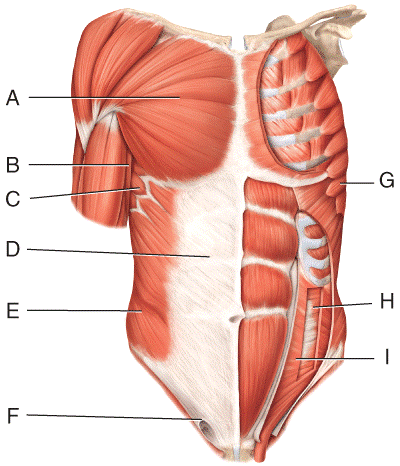 Where is the transverse abdominus?
| back 30 d |
front 31 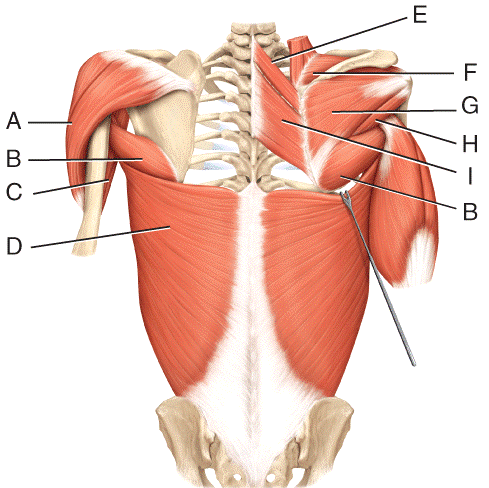 Where is the infraspinatus?
| back 31 c |
front 32 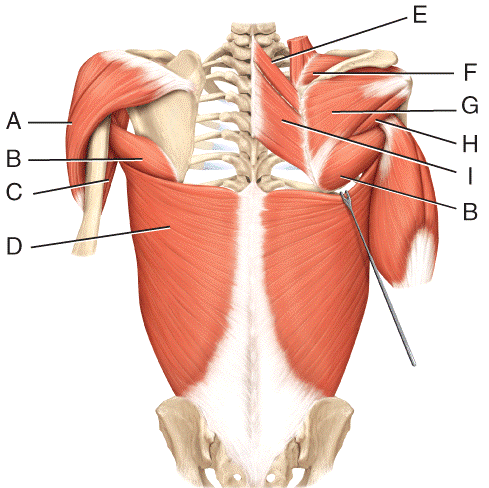 Where is the rhomboid major?
| back 32 e |
front 33 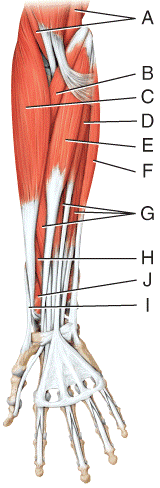 Where is the brachioradialis?
| back 33 c |
front 34 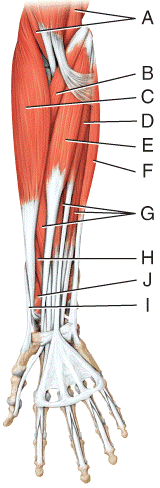 Where is the flexor carpi radialis?
| back 34 b |
front 35 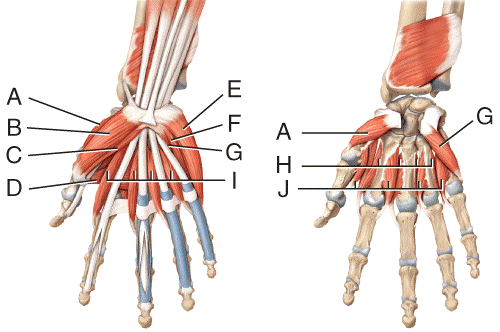 Where is the abductor digiti minimi?
| back 35 c |
front 36 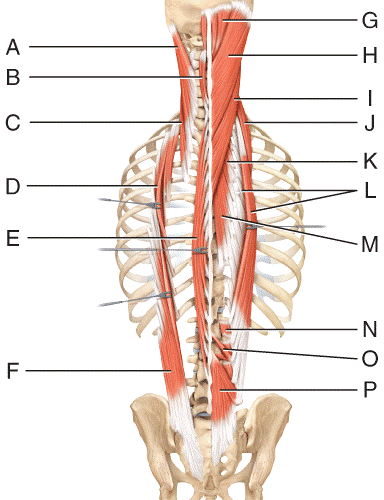 Where is the splenius capitis?
| back 36 e |
front 37 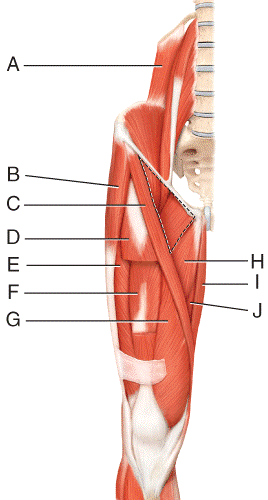 Where is the iliacus?
| back 37 a |
front 38 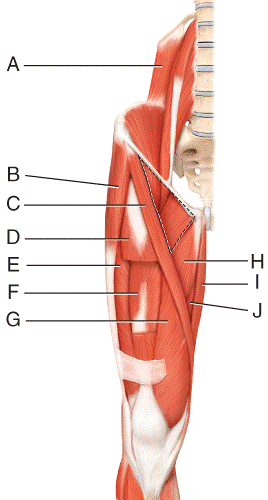 Where is the sartorius?
e) None of these choices | back 38 c |
front 39 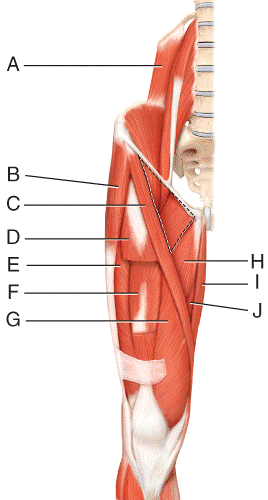 Where is the vastus intermedius?
e) H | back 39 c |
front 40 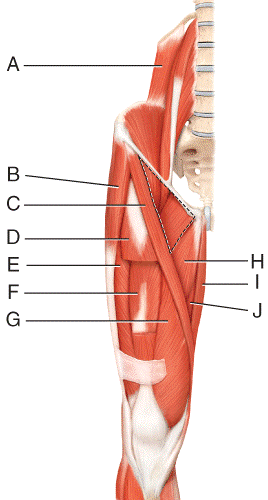 Where is the adductor longus?
| back 40 a |
front 41 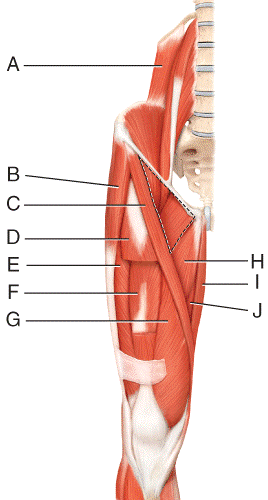 Where is the gracilis?
| back 41 b |
front 42 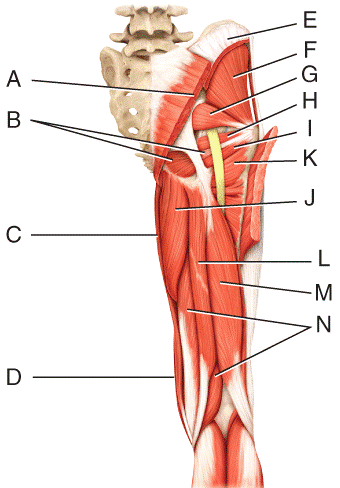 ) Which three muscles make up the hamstring?
| back 42 a |
front 43 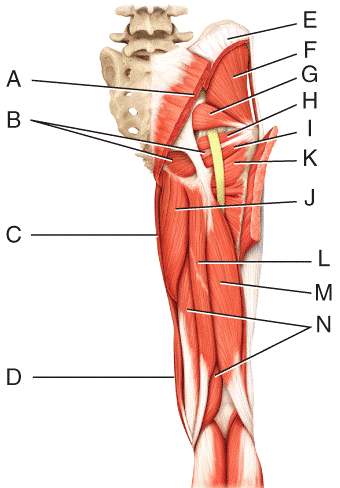 Where is the semitendinosus?
| back 43 c |
front 44 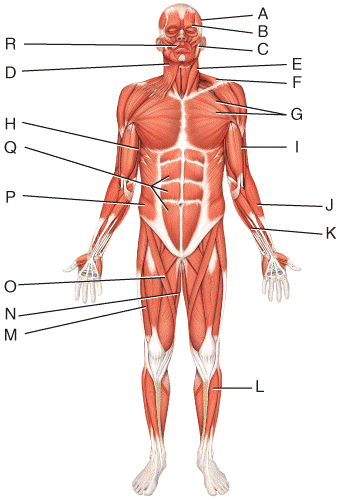 What is the origin of the muscle labeled B?
| back 44 c |
front 45 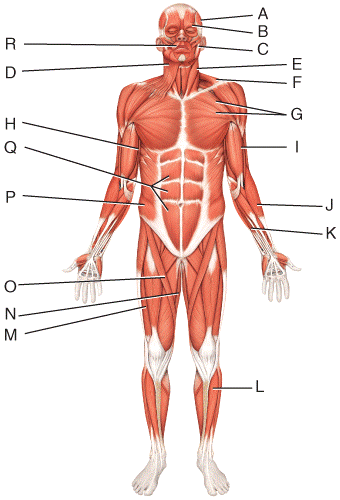 What is the origin of the muscle labeled D?
| back 45 b |
front 46 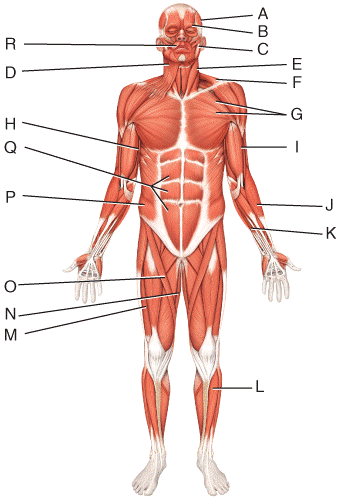 What is the action of the muscle labeled C?
| back 46 e |
front 47 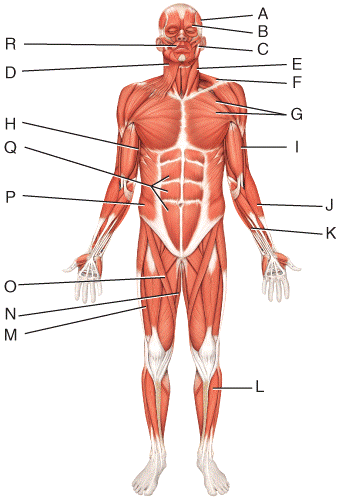 What is the insertion of the muscle labeled E?
| back 47 a |
front 48 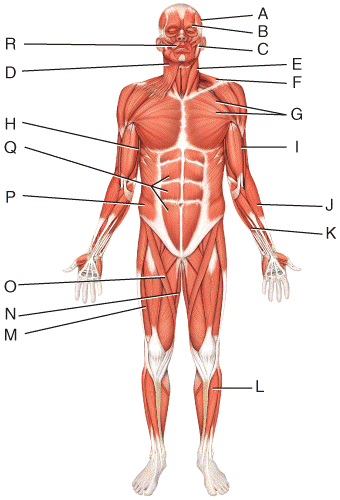 What is the action of the muscle labeled G?
| back 48 a |
front 49 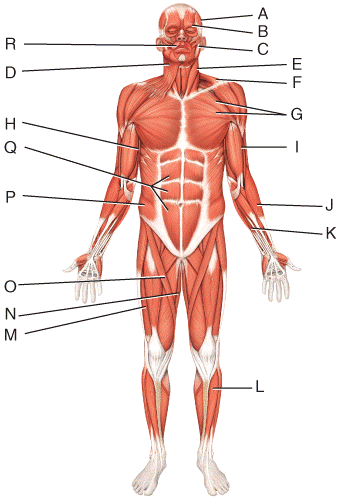 What is the action of the muscle labeled I?
| back 49 b |
front 50 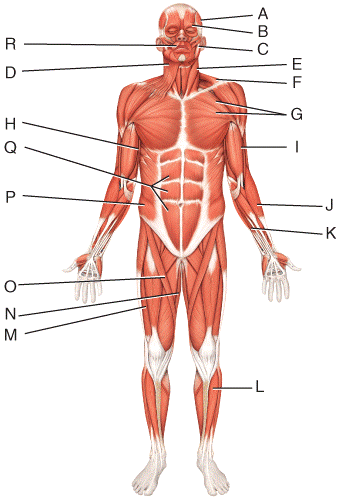 What is the insertion of the muscle labeled Q?
| back 50 b |
front 51 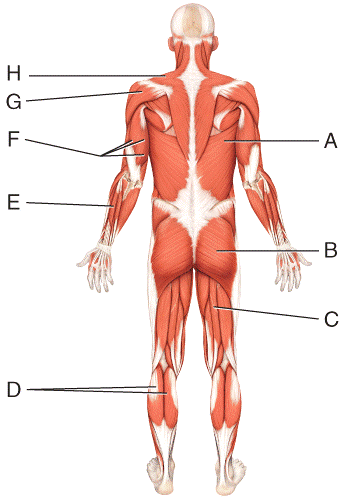 What is the insertion of the muscle labeled F?
| back 51 c |
front 52 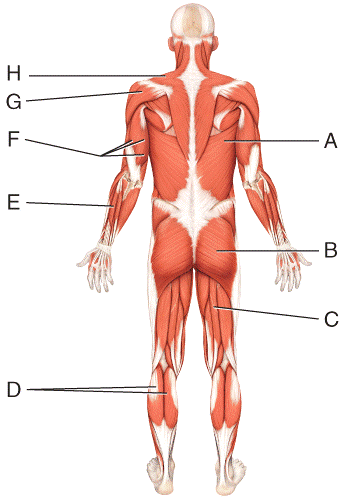 What is the insertion of the muscle labeled G?
| back 52 e |
front 53 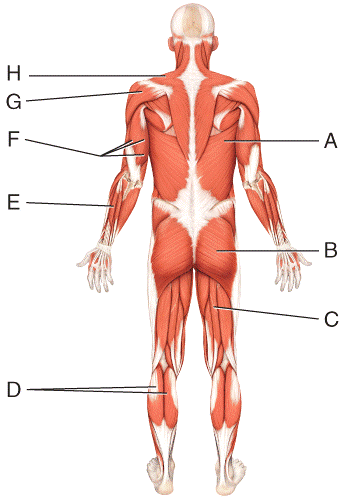 What is the insertion of the muscle labeled D?
| back 53 c |
front 54 If one is stabbed on the lateral side of the abdomen, what abdominal muscles, in order from superficial to deep, will the knife go through?
| back 54 b |
front 55 Protrusion of an organ through a structure that normally contains it is referred to as a a) hernia. b) goiter. c) strain. d) sprain. e) hydrocele. | back 55 a |
front 56 A condition where the two eyeballs are not properly aligned is referred to as
| back 56 b |
front 57 A muscle that has three origins is called a
| back 57 b |
front 58 A muscle that raises or elevates a body part is called a
| back 58 b |
front 59 A muscle that raises or elevates a body part is called a
| back 59 b |
front 60 ) A muscle that decreases the size of an opening is a a) rotator. b) tensor. c) pronator. d) sphincter. e) depressor. | back 60 d |
front 61 Contraction of this muscle presses the cheeks against the teeth and lips as would be observed in whistling, blowing or sucking. a) buccinator b) zygomaticus c) frontalis d) epicranius e) occipitalis | back 61 a |
front 62 All of the following are muscles that move the eyeball EXCEPT a) superior rectus. b) lateral rectus. c) inferior oblique. d) internal oblique. e) superior oblique. | back 62 d |
front 63 Which of the following is a muscle whose insertion is found on the clavicle and acromion process of the scapula within the pectoral girdle?
| back 63 a |
front 64 All of the following are muscles of the lower limb EXCEPT the a) deltoid. b) adductor magnus. c) adductor longus. d) quadriceps femoris. e) vastus medialis. | back 64 a |
front 65 Based on its name, which of the following best describes characteristics of the biceps femoris muscle? a) has two insertions and found in lower leg b) has two bellies and found in the upper leg c) has two origins and found in the upper leg d) has two origins and found in the upper arm e) has two insertions and found in the upper leg | back 65 c |
front 66 Based on its name, which of the following best describes characteristics of the biceps femoris muscle? a) has two insertions and found in lower leg b) has two bellies and found in the upper leg c) has two origins and found in the upper leg d) has two origins and found in the upper arm e) has two insertions and found in the upper leg | back 66 c |
front 67 Which of the following muscles is NOT part of the quadriceps femoris muscle group?
| back 67 b |
front 68 This muscle, which is found in the neck, functions to elevate the hyoid bone and help press the tongue against the roof of the mouth during swallowing. a) mylohyoid b) sternothryroid c) sternocleidomastoid d) digastric e) masseter | back 68 a |