Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
multi choice: skeletal sytsem joints
front 1 2) Which of the following types of joints lacks a joint cavity and is
held together by a fibrous connective tissue? a) 1 only b) 2 only c) 3 only d) 1 and 2 e) All of these choices | back 1 a |
front 2 Which of the following types of joints do NOT have a synovial cavity? 1. Fibrous joints 2. Cartilaginous joints 3. Synovial joints
e) All of these choices | back 2 d |
front 3 Which functional class of joints contains joints that are freely
movable? a) 1 only b) 2 only c) 3 only d) Both 2 and 3 e) All of these choices | back 3 c |
front 4 Which of the following is a type of fibrous joint composed of a thin
layer of dense irregular fibrous connective tissue found between the
bones of the skull? a) 1 only b) 2 only c) 3 only d) Both 1 and 2 e) None of these choices | back 4 c |
front 5 A suture joint fits into which functional joint classification?
| back 5 a |
front 6 The epiphyseal plate in a long bone is an example of which type of joint?
| back 6 e |
front 7 The joint between the first rib and the manubrium of the sternum is classified as a) a synchondrosis. b) a synarthrosis. c) a cartilaginous joint. d) All of these choices. e) None of these choices. | back 7 d |
front 8 Which of the following is NOT a common characteristic of synovial joints? a) Contain a joint cavity b) Are freely moveable c) Articulating bones are covered with hyaline cartilage d) Include elastic cartilage e) Have ligaments holding the joint together | back 8 d |
front 9 Which of the following is(are) made from dense regular connective tissue? a) Ligaments b) Articular cartilage c) Articular fat pads d) Synovial membrane e) Synovial fluid | back 9 a |
front 10 Which of the following structures include the fibular and tibial collateral ligaments of the knee joint? a) Synovial membranes b) Articular fat pads c) Menisci d) Extracapsular ligaments e) Tendon sheath | back 10 d |
front 11 Another term for menisci is a) articular fat pads. b) articular discs. c) articular spaces. d) capsular fat pads. e) capsular discs. | back 11 b |
front 12 Articular discs a) 1 only b) 2 only c) 3 only d) 4 only e) 1 and 2 | back 12 e |
front 13 Which of the following structures is used to reduce friction in
joints? a) 1 only b) 2 only c) 3 only d) 4 only e) 1 and 2 | back 13 e |
front 14 Which type of motion results from relatively flat bone surfaces moving back and forth and from side to side with respect to one another? a) Flexion b) Extension c) Gliding d) Circumduction e) Hyperextension | back 14 c |
front 15 Which of the following represents a type of movement where there is a decrease in the angle between articulating bones? a) Flexion b) Extension c) Gliding d) Circumduction e) Rotation | back 15 a |
front 16 Bending the trunk forward at the intervertebral discs is an example of what type of angular movement? a) Flexion b) Extension c) Lateral flexion d) Hyperextension e) None of these choices | back 16 a |
front 17 Flexion and extension usually occur along which plane?
| back 17 c |
front 18 Moving the humerus laterally at the shoulder joint is an example of which type of movement? a) Lateral flexion b) Hyperextension c) Adduction d) Abduction e) Gliding | back 18 d |
front 19 Which type of movement involves a continuous sequence of flexion, abduction, extension, and adduction resulting in a distal body part moving in a circle? a) Gliding b) Lateral flexion c) Hyperextension d) Circumduction e) Elevation | back 19 d |
front 20 Which of the following is not considered a “special movement” that occurs at only certain joints?
| back 20 e |
front 21 What type of special movement occurs in your clavicles at your acromioclavicular and sternoclavicular joints when you cross your arms in front of your body?
| back 21 a |
front 22 Which special movement occurs when you bend your foot at the ankle in the direction of the foot’s superior surface as would occur when you stand on your heels? a) Inversion b) Eversion c) Dorsiflexion d) Plantar flexion e) Supination | back 22 c |
front 23 Which special movement involves moving your thumb across the palm to touch the tips of the fingers on the same hand? a) Pronation b) Supination c) Eversion d) Retraction e) Opposition | back 23 e |
front 24 Which of the following is NOT a structural category of synovial joints? a) Planar b) Hinge c) Condyloid d) Suture e) Saddle | back 24 d |
front 25 In which type of synovial joint does a rounded or pointed surface on one bone articulate with a ring formed partly by another bone and partly by a ligament? a) Pivot joint b) Planar joint c) Hinge joint d) Ball-and-socket joint e) Saddle joint | back 25 a |
front 26 A condyloid joint a) is also called an ellipsoidal joint. b) is considered to be biaxial. c) allows both flexion–extension and abduction–adduction of the joint. d) can be found in the wrist. e) is All of these choices | back 26 e |
front 27 Which of the following is NOT a factor affecting range of motion of a joint? a) Structure of articulating bones b) Tension of the muscles c) Hormones d) Disuse e) Eversion | back 27 e |
front 28 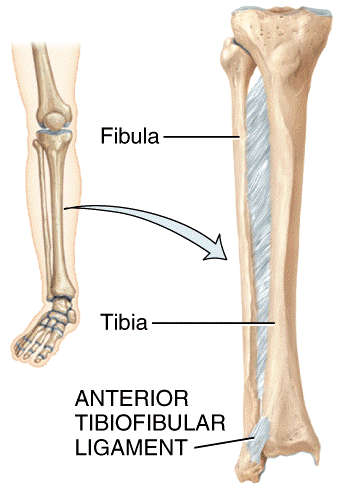 What type of joint is shown in the diagram?
| back 28 b |
front 29 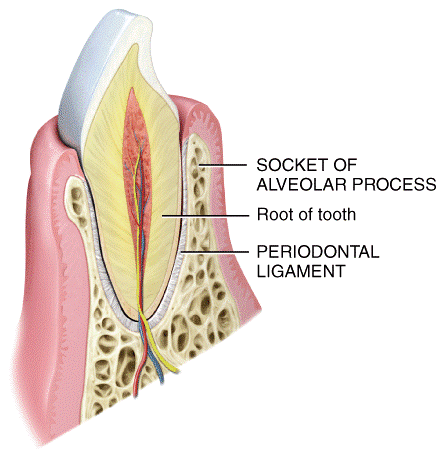 What type of joint is shown in the diagram?
| back 29 e |
front 30 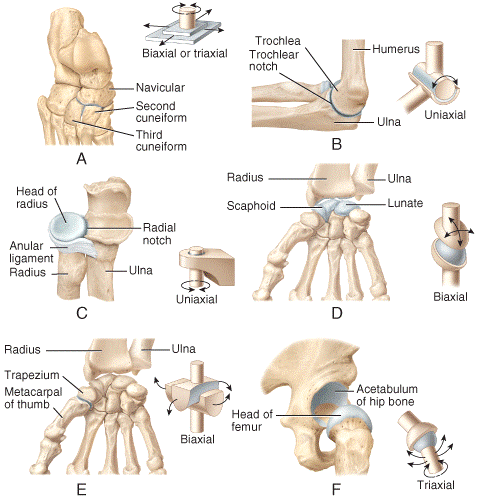 ) In the figure, what represents a saddle joint?
| back 30 e |
front 31 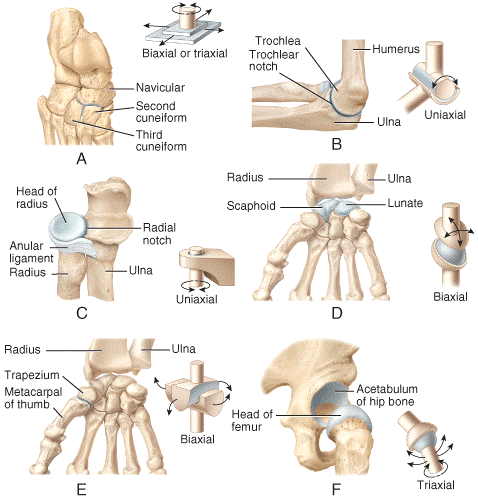 ) In the diagram, what represents a pivot joint?
| back 31 c |
front 32 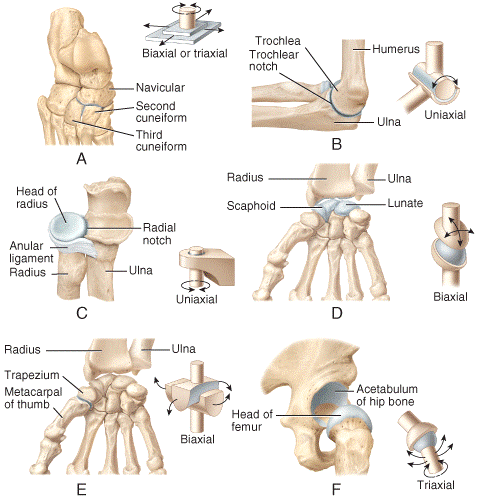 Which of the joints shown in the figure is classified as a multiaxial joint?
| back 32 e |
front 33 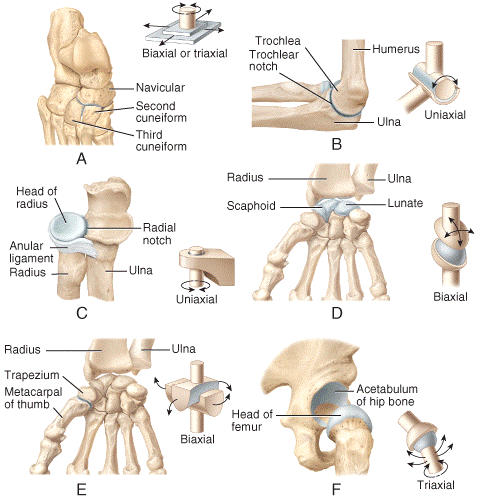 Which of the joints shown in the figure is classified as a biaxial joint?
| back 33 e |
front 34 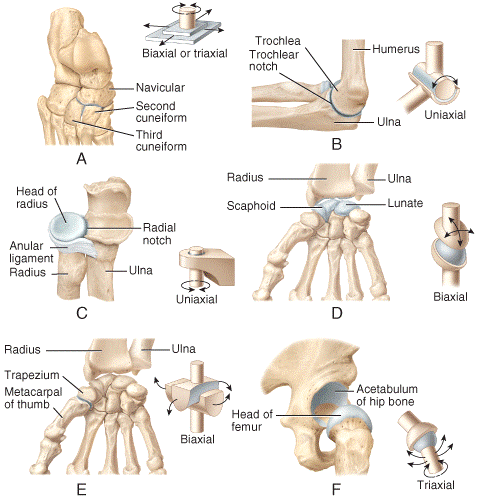 Which of the joints shown in the figure is classified as a monaxial joint?
| back 34 e |
front 35 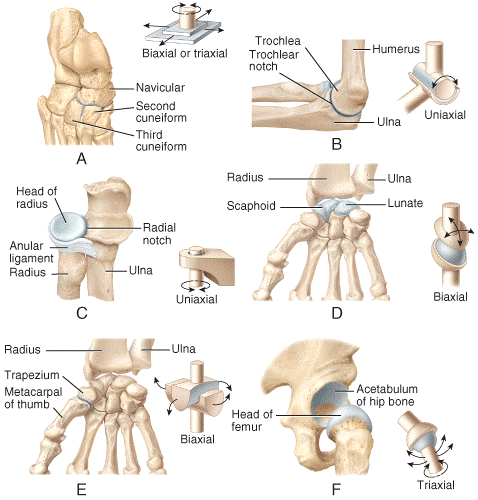 Which of the joints shown in the figure represents a condyloid joint?
| back 35 d |
front 36 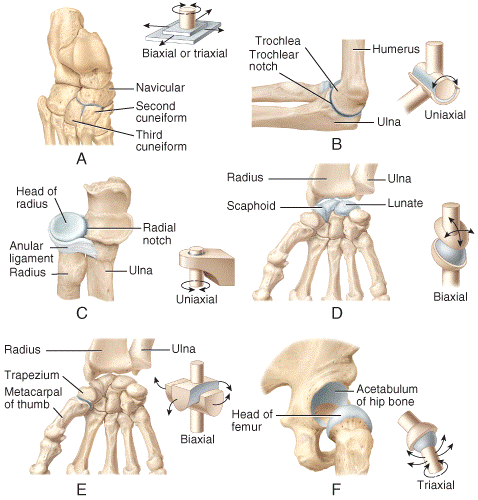 Which of the joints shown in the figure only permits back-and-forth and side-to-side movements between the articulating bones?
| back 36 a |
front 37 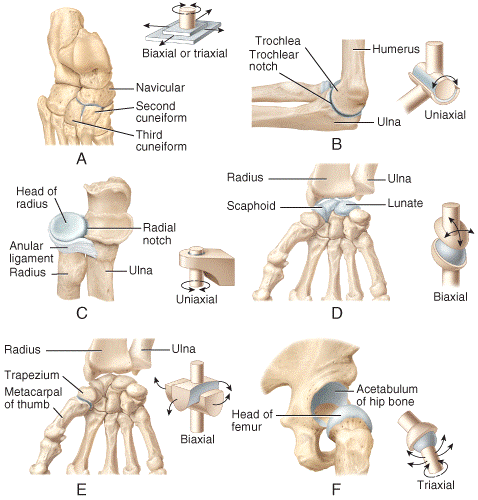 Which of the joints shown in the figure only permits back-and-forth and side-to-side movements between the articulating bones?
| back 37 a |
front 38 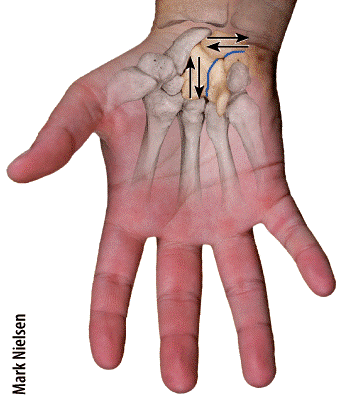 Which type of joint permits this type of movement? 1. Synovial joint 2. Cartilaginous joint 3. Fibrous joint
| back 38 a |
front 39 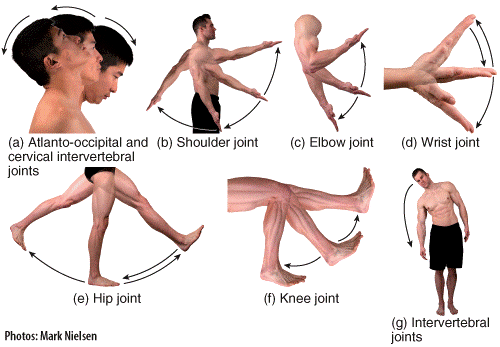 Which of the panels in the figure shows a movement called lateral flexion?
| back 39 c |
front 40 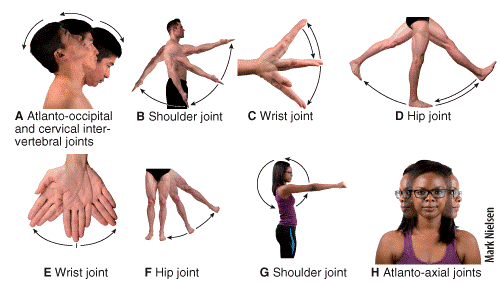 Which of the following types of movement is shown in diagram E? a) supination b) circumduction c) pronation d) rotation e) adduction | back 40 e |
front 41 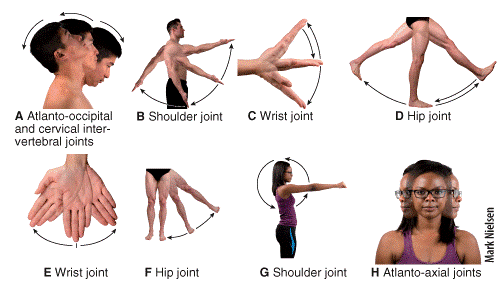 ) Which of the following labeled panels in the figure shows hyperextension? a) C b) E c) F d) G e) I | back 41 a |
front 42 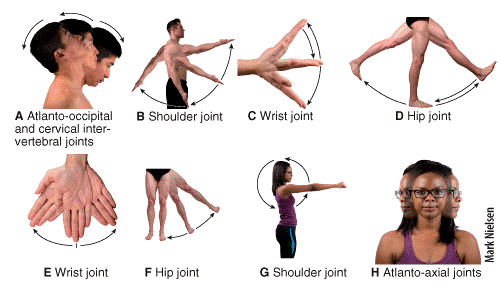 Which of the following labeled panels in the figure shows flexion?
| back 42 c |
front 43 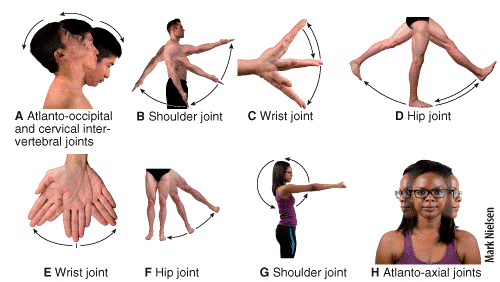 Which of the following labeled panels in the figure shows extension? a) E b) D c) F d) G e) I | back 43 b |
front 44 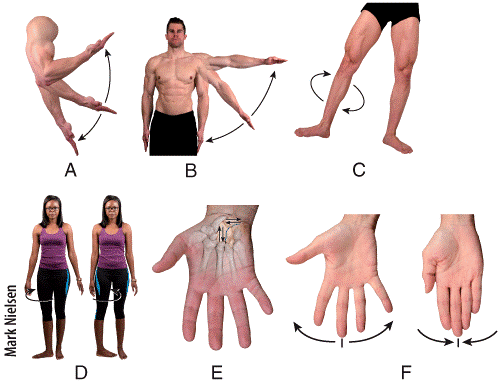 Which two panels in the figure show a movement of a bone away from the midline of the body? a) A and B b) B and D c) D and E d) F and A e) B and F | back 44 e |
front 45 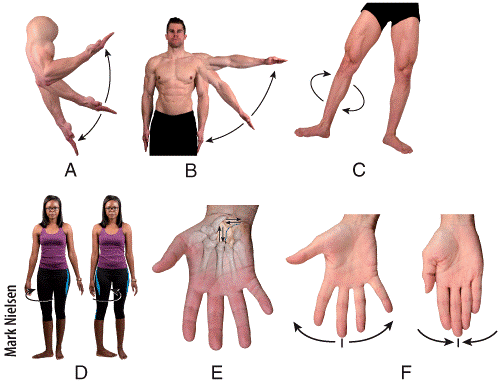 Which diagram shows a movement of a distal end of a body part in a circle, in a continuous a) A b) B c) C d) D e) F | back 45 c |
front 46 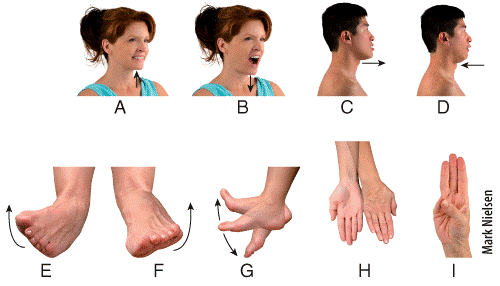 Which panel in the figure shows an example of the movement termed elevation?
| back 46 a |
front 47  Which panel in the figure shows an example of the movement termed inversion?
| back 47 c |
front 48 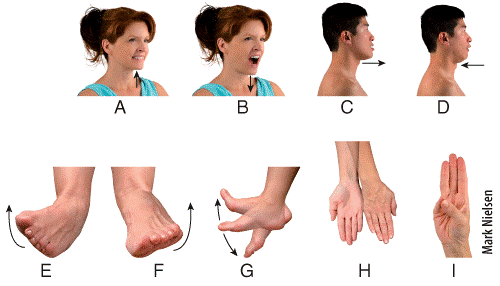 Which panel in the figure shows an example of the movement termed retraction? a) A b) B c) C d) D e) I | back 48 d |
front 49 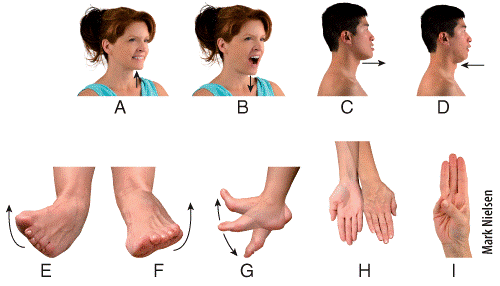 Which panel in the figure shows an example of the movement termed supination?
| back 49 d |
front 50 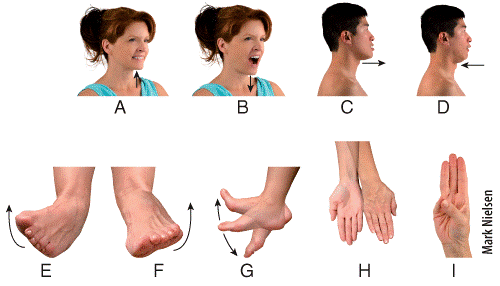 Which panel in the figure shows an example of the movement termed opposition? a) E b) F c) G d) H e) I | back 50 e |
front 51 Which of the following is a degenerative joint disease in which joint cartilage is gradually lost due to a combination of aging, obesity, wear and abrasion of the joints?
| back 51 d |
front 52 Which of the following is an autoimmune disease that affects the joints? a) gouty arthritis b) Lyme disease c) arthroplasty d) osteoarthritis e) rheumatoid arthritis | back 52 e |
front 53 Which of the following diseases is characterized by sodium urate crystals being deposited in the soft tissues of joints? a) gouty arthritis b) Lyme disease c) ankylosing spondylitis d) osteoarthritis e) rheumatoid arthritis | back 53 a |
front 54 Which of the following is a correct description of arthroplasty? a) resurfacing of cartilage in a joint b) reshaping of the ends of the bones in a joint c) surgically replacing a joint with an artificial joint d) injection of synovial fluid into the joint e) a, b, and d | back 54 c |
front 55 ) Based on the structural classification of joints, which of the following is a fibrous joint? a) Synchondrosis b) Synovial joint c) Symphysis d) Syndesmosis e) Diarthrosis | back 55 d |
front 56 A condition in which a muscle or muscle and tendon is stretched or partially torn is called
e) an arthrosis | back 56 c |
front 57 Which ligament limits hyperextension of the knee and prevents the anterior sliding of the tibia on the femur? a) Fibular collateral ligament b) Anterior cruciate ligament c) Posterior cruciate ligament d) Patellar ligament e) Arcuate popliteal ligament | back 57 b |
front 58 A joint in which there is a complete fusion of two separate bones into one bone is called a
| back 58 e |
front 59 Which of the following is NOT an anatomical component of the elbow? a) articular capsule. b) ulnar collateral ligament. c) radial collateral ligament. d) anular ligament of the radius. e) tendon of the biceps brachii muscle. | back 59 e |
front 60 Bursae are saclike structures that are commonly found between bone and
e) all the other answer selections | back 60 e |
front 61 The hormone relaxin stimulates changes that lead to increased range of motion in the a) shoulder joint. b) pubic symphysis. c) temporomandibular joint d) knee joint. e) coronal suture. | back 61 b |
front 62 Disuse of a limb, like would occur when the limb is in a cast, leads to muscular atrophy and _____ of the affected joint. a) increased range of motion b) decreased range of motion c) increased fluid accumulation in bursa d) loosening of the tendons e) chronic inflammation | back 62 b |
front 63 Which of the following is NOT a factor that influences the type of movement and range of motion possible at a synovial joint? a) structure of the articulating bones. b) strength and tension of the joint ligaments. c) use of the joint. d) arrangement and tension of the muscles. e) hormones. | back 63 c |
front 64 Which feature goes with the knee joint?
e) acetabular labrum | back 64 a |
front 65 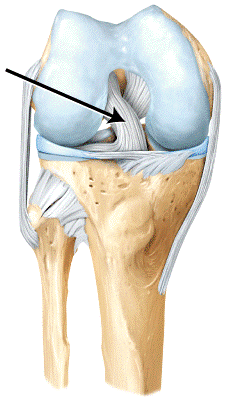
The line is pointing to the _____ ligament. a) fibular collateral b) posterior cruciate c) oblique popliteal d) anterior cruciate | back 65 d |
front 66 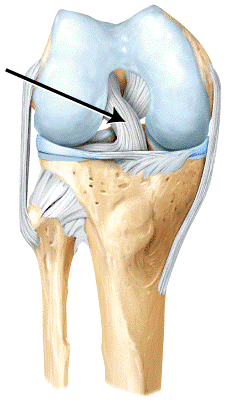
The line is pointing to the _____. a) lateral meniscus b) medial meniscus c) anterior cruciate ligament d) posterior cruciate ligament | back 66 a |
front 67 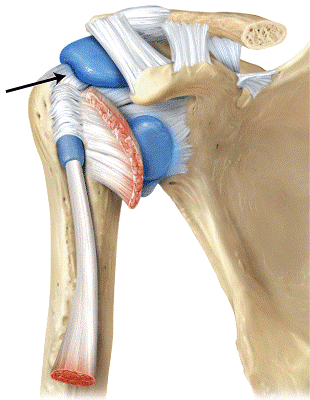
The line is pointing to the _____ ligament. a) coracoacromial b) acromioclavicular c) glenohumeral d) coracohumeral | back 67 d |
front 68 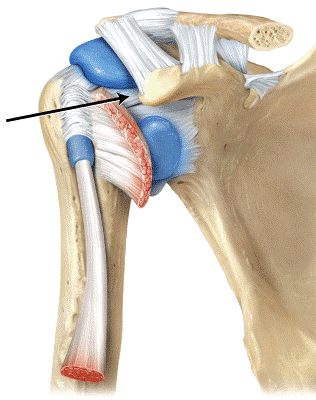
The line is pointing to the _____ ligaments. a) coracoacromial b) acromioclavicular c) glenohumeral d) coracohumeral | back 68 c |