Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Multi choice, The Skeletal system: The Axial Skeleton
front 1 The branch of medicine that deals with correction of disorders of the musculoskeletal system is called a) Rheumatics b) Podiatry c) Orthopedics d) Cardiology e) Dermatology | back 1 c |
front 2 Which of the following statements is NOT true? a) The axial skeleton has 80 bones. b) The appendicular skeleton has 126 bones. c) The axial skeleton is composed of the bones that run through the axis of the body. d) Children have more bones than adults. e) The appendicular skeleton does not include the pelvic and pectoral girdles. | back 2 e |
front 3 Which of the following bones is NOT part of the axial skeleton?
| back 3 d |
front 4 Which of the following bones is part of the axial skeleton? a) Tarsals b) Tibia c) Sphenoid d) Scapula e) Clavicle | back 4 c |
front 5 Which following types of bone is the occipital bone? a) Long bone b) Short bone c) Flat bone d) Irregular bone e) Sesamoid bone | back 5 c |
front 6 Which of the following is NOT true of surface markings on bone? a) They allow the passage of nerves and blood vessels. b) They provide sites of attachment for muscles. c) They allow bones to shorten or lengthen. d) They help form joints. e) They can be depressions or projections. | back 6 c |
front 7 An opening or hole in a bone through which blood vessels, nerves and ligaments pass is called a
| back 7 b |
front 8 A rounded articular projection supported on a constricted portion (neck) of a bone is called a a) foramen. b) condyle. c) tuberosity. d) head. e) trochanter. | back 8 d |
front 9 A prominent ridge or elongated projection on a bone is called a
| back 9 a |
front 10 Bones in the following area protect the brain.
| back 10 a |
front 11 Which of following facial bones is a single (unpaired) bone in the human skull?
| back 11 d |
front 12 Which of the following is NOT a facial bone?
| back 12 a |
front 13 Which of the following statements is NOT true with regard to bones of the skull? a) Some skull bones are covered with a mucous membrane. b) The only movable bone in the skull is the mandible. c) The bones of the skull contain foramina but no fissures. d) The facial bones provide support for the entrance of the digestive system. e) Some bones of the skull contain sinus cavities. | back 13 c |
front 14 Which of the listed cranial bones form the inferior lateral aspects of the cranium and part of the cranial floor?
| back 14 b |
front 15 Which of the listed cranial bones contain the organs of hearing and balance, and articulate with the mandible?
| back 15 b |
front 16 Which cranial bone is called the “keystone” of the cranial floor because it articulates with every other cranial bone?
| back 16 e |
front 17 Which cranial bone is anterior to the sphenoid and posterior to the nasal bones and contains foramina for the olfactory cranial nerve?
| back 17 a |
front 18 Which facial bone articulates with teeth?
| back 18 d |
front 19 Which of the following is NOT a facial bone?
| back 19 d |
front 20 Which bone of the axial skeleton does NOT articulate with any other bone? a) Vertebrae b) Ethmoid c) Sternum d) Hyoid e) Ilium | back 20 d |
front 21 The hyoid bone is suspended by ligaments and muscle that extend from the _____ of the temporal bone. a) mastoid process b) styloid process c) occipital condyle d) zygomatic process e) superior nuchal line | back 21 b |
front 22 Joe was found dead. His hyoid bone was broken. What was the most likely cause of death? a) Natural causes b) Cardiac arrest c) Gun shot d) Strangulation e) Choking | back 22 d |
front 23 Ribs that have costal cartilage that attaches directly to the sternum are called a) floating ribs. b) vertebrochondral ribs. c) false ribs. d) true ribs. e) separated ribs. | back 23 d |
front 24 The tubercle found on the neck of a rib articulates with a facet found on the a) spinous process of a thoracic vertebra. b) spinous process of a lumbar vertebra. c) transverse process of a thoracic vertebra. d) xiphoid process of the sternum. e) manubrium of the sternum. | back 24 c |
front 25 The tubercle found on the neck of a rib articulates with a facet found on the a) spinous process of a thoracic vertebra. b) spinous process of a lumbar vertebra. c) transverse process of a thoracic vertebra. d) xiphoid process of the sternum. e) manubrium of the sternum. | back 25 c |
front 26 What is the purpose of the nucleus pulposus region of intervertebral discs? a) To compress the vertebral bones b) To help absorb vertical shock to the spinal column c) Calcium storage d) Spinal fluid reservoir e) Muscle attachment | back 26 b |
front 27 The two primary curves of the adult vertebral column are the a) thoracic and sacral curves. b) lumbar and sacral curves. c) cervical and lumbar curves. d) cervical and thoracic curves. e) cervical and sacral curves. | back 27 e |
front 28 What bone marking found on the second cervical vertebra projects superiorly into the anterior portion of the vertebral foramen of the atlas? a) Primary projection b) Occular process c) Odontoid process d) Cervical projection e) Cervix | back 28 c |
front 29 Which of the vertebrae listed below would be the largest and strongest vertebra in adult humans?
| back 29 b |
front 30 Which gender shows the coccyx pointed inferiorly? a) Females b) Males c) Both genders d) The coccyx does not point inferiorly in either gender | back 30 a |
front 31 What is inflammation of one or more costal cartilage called? a) Costochondritis b) Arthritis c) Cartilaginous distension d) Otitis e) Intercostal space distension | back 31 a |
front 32 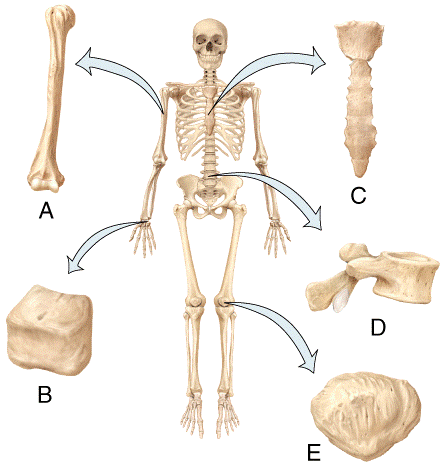 In the diagram, which bone is the flat bone?
| back 32 c |
front 33 In the diagram, which bone is the short bone?
| back 33 b |
front 34 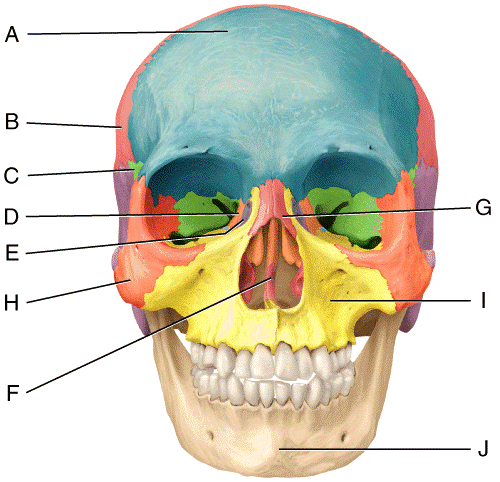 In the diagram, where is the lacrimal bone?
| back 34 a |
front 35 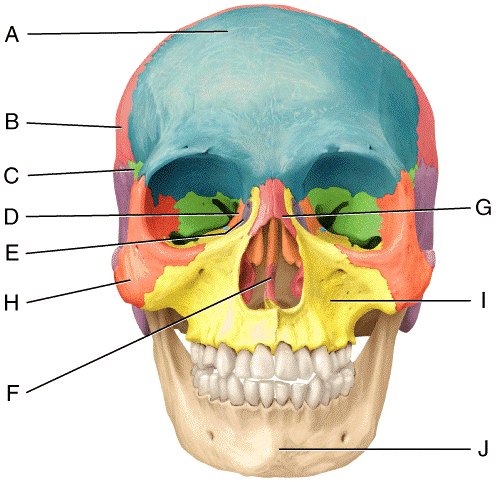 In the diagram, which bone articulates with every other bone of the face except the mandible?
| back 35 d |
front 36 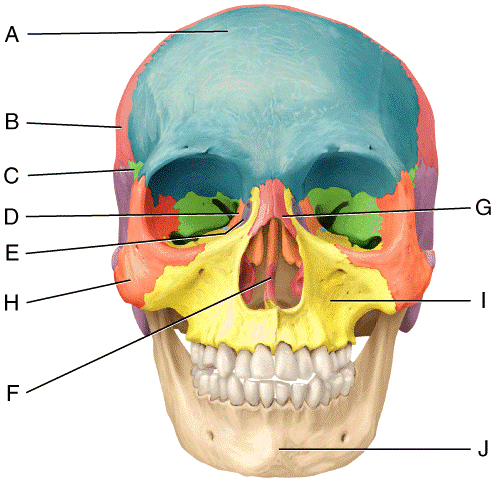 In the diagram, where is the zygomatic bone?
| back 36 b |
front 37 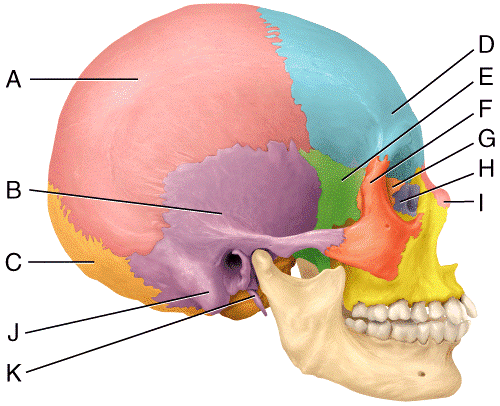 In the diagram, which bone is considered the keystone of the cranial floor?
| back 37 a |
front 38 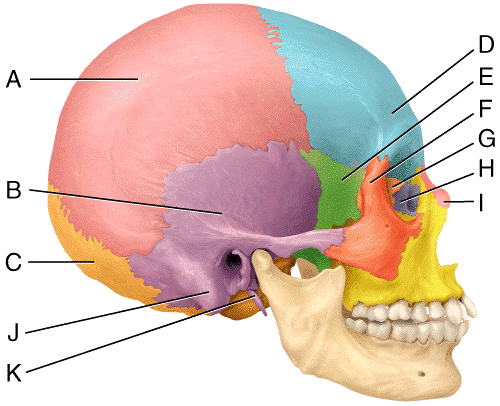 In the diagram, where is the styloid process?
| back 38 b |
front 39 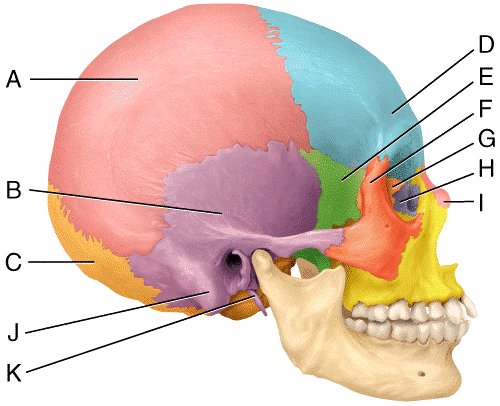 In the diagram, where is the mastoid process?
| back 39 a |
front 40 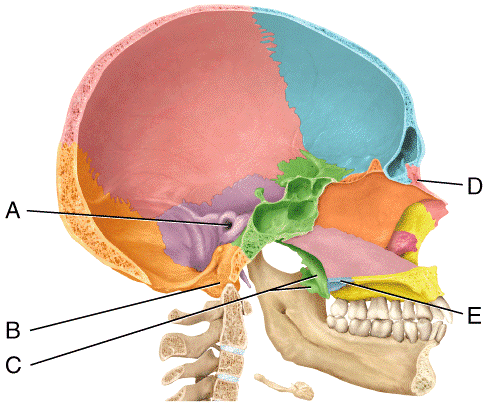 In the diagram, where is the palatine bone?
| back 40 e |
front 41 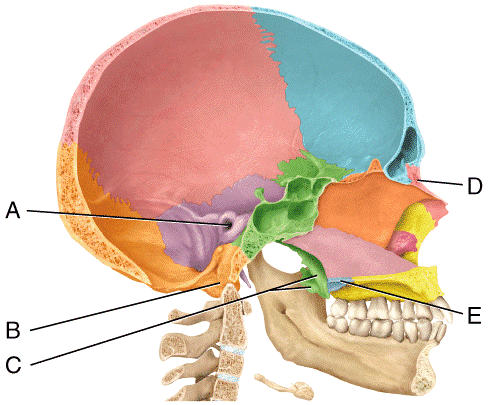 In the diagram, where is the nasal bone?
| back 41 d |
front 42 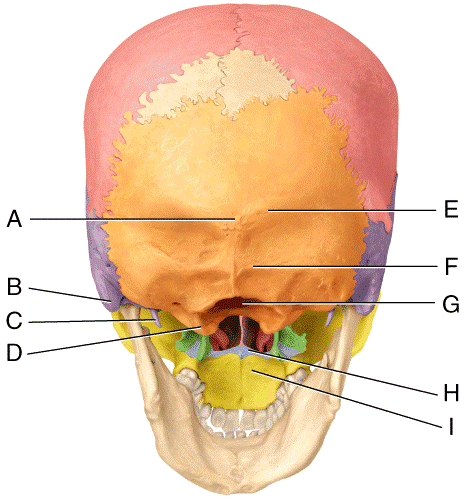 In the diagram, where is the mastoid process?
| back 42 b |
front 43 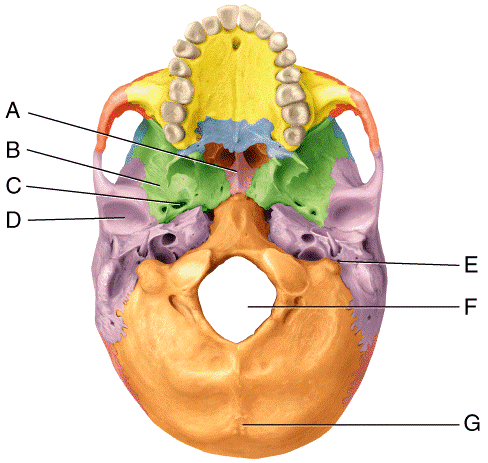 In the diagram, where is the foramen ovale?
| back 43 a |
front 44 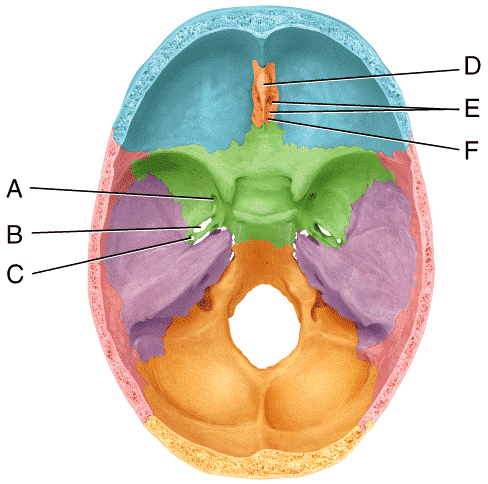 In the diagram, where is the cribriform plate?
| back 44 c |
front 45 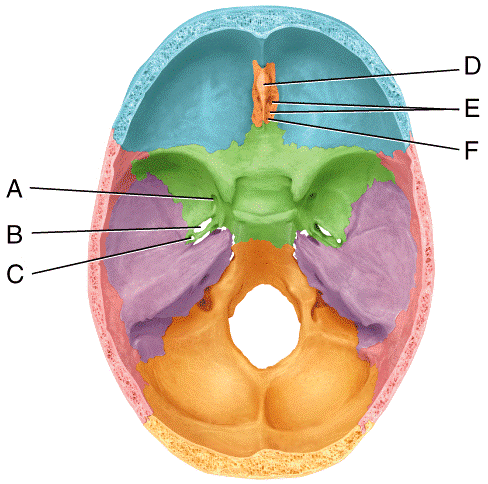 In the diagram, where is the olfactory foramina?
| back 45 c |
front 46 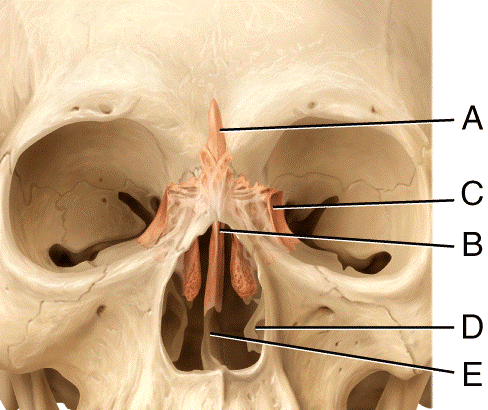 ) In the diagram, where is the crista galli?
| back 46 b |
front 47 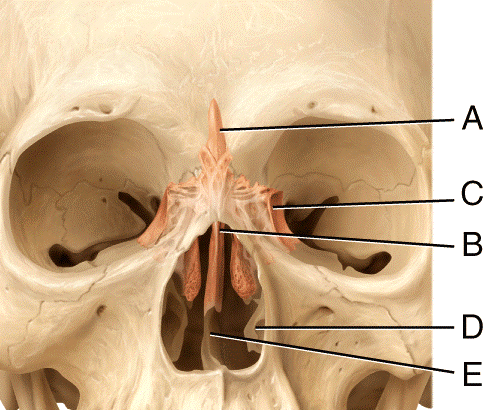 In the diagram, where is the vomer bone?
| back 47 c |
front 48 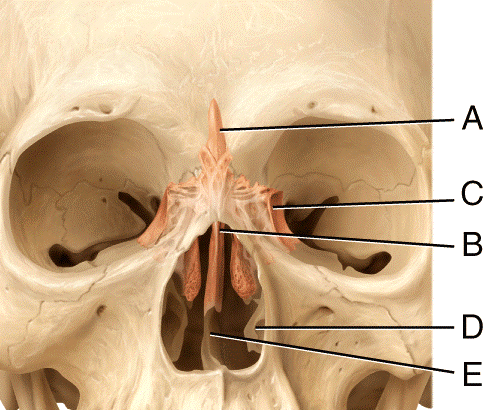 In the diagram, where is the perpendicular plate?
| back 48 b |
front 49 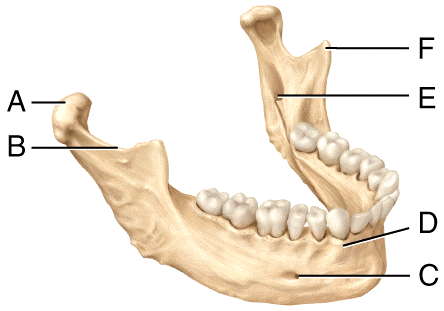 Where is the mental foramen in the diagram?
| back 49 a |
front 50 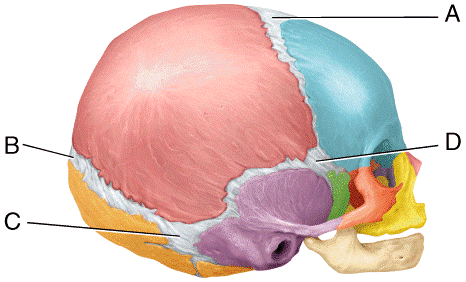 This fontanel usually closes within 18 to 24 months after birth.
| back 50 a |
front 51 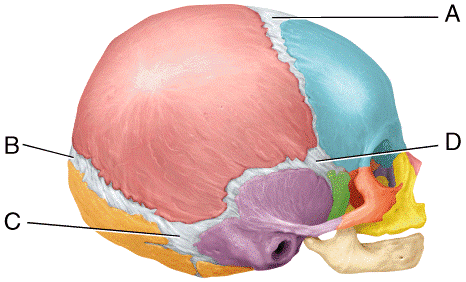 This is largest fontanel in size at birth.
| back 51 a |
front 52 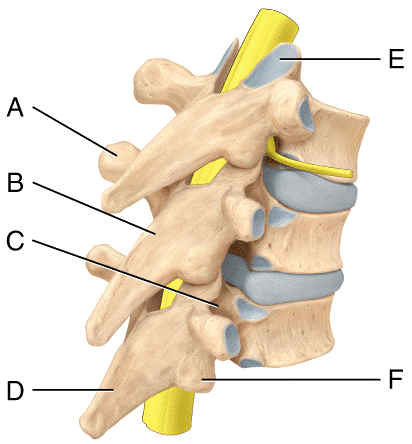 Where is the spinous process in the diagram?
| back 52 c |
front 53 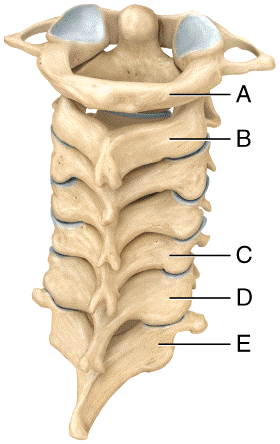 Which of the cervical vertebrae contain a unique process that is responsible for the ability to move your head from side to side signifying “no”?
| back 53 b |
front 54 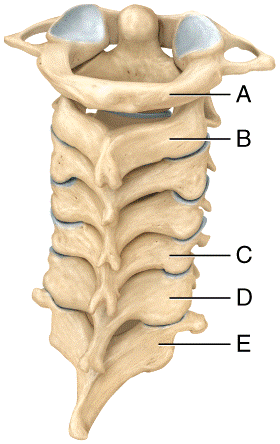 Which of the cervical vertebrae are responsible for permitting the movement of the head seen when saying “yes”?
| back 54 a |
front 55 Where is the vertebral body?
| back 55 c |
front 56 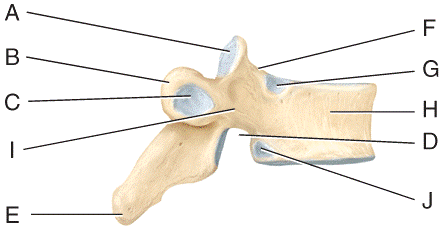 Where is the vertebral body?
| back 56 c |
front 57 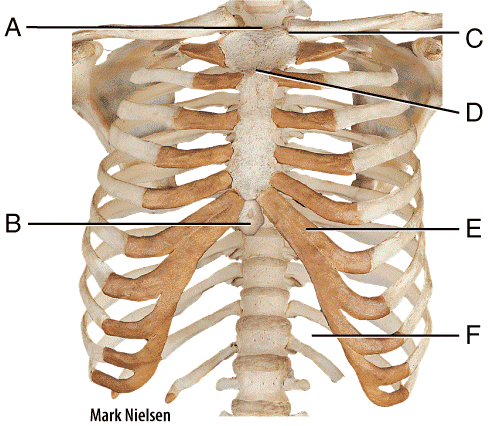 In the diagram, which part is often broken during CPR due to incorrect positioning of hands?
| back 57 b |
front 58 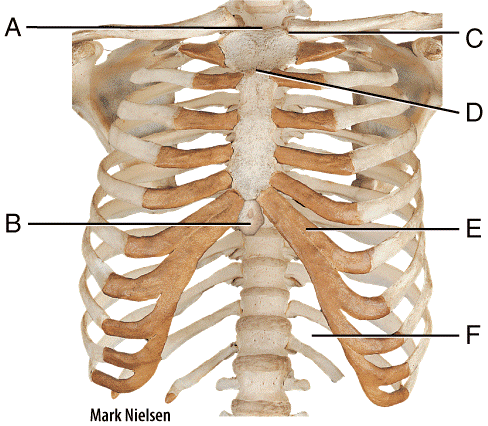 Where is the clavicular notch?
| back 58 b |
front 59 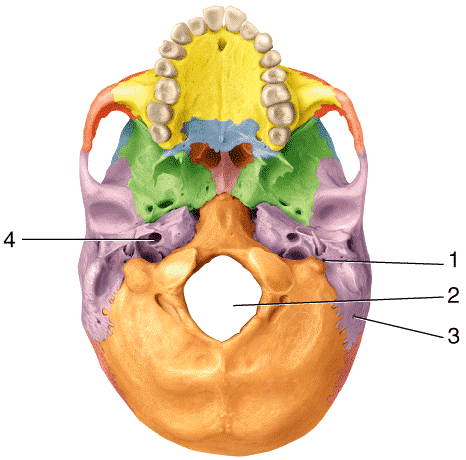 Which of the following structures passes through the opening labeled 2 in the diagram?
| back 59 c |
front 60 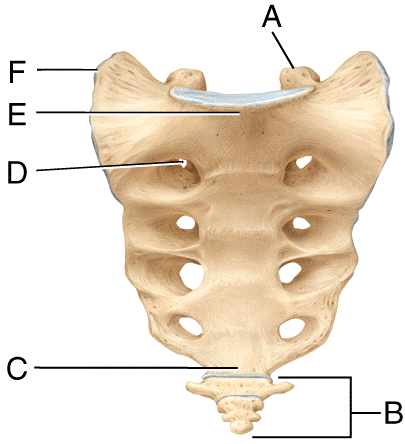 Which structure in the diagram allows for passage of nerves and blood vessels?
| back 60 c |
front 61 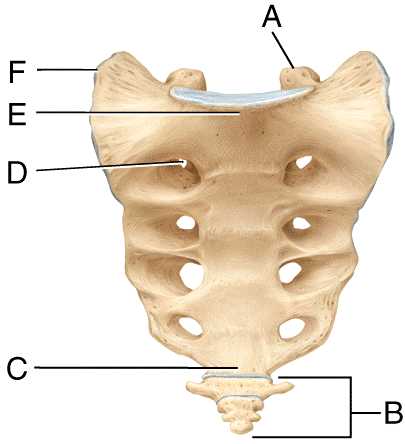 Which structure in the diagram is the superior articular process?
| back 61 a |
front 62 Which condition is characterized by an increase or exaggeration of the lumbar curve of the vertebral column?
| back 62 d |
front 63 Which condition is characterized by an increase in the thoracic curve of the vertebral column?
| back 63 c |
front 64 Which condition is characterized by a lateral bending of the vertebral column in the thoracic region?
| back 64 b |
front 65 Which condition is the protrusion of the nucleus pulposus posteriorly or into one of the adjacent vertebral bodies in the vertebral column?
| back 65 a |
front 66 Which of the following bones contains a sac that collects tears and passes them into the nasal cavity? a) Maxilla b) Sphenoid c) Nasal d) Ethmoid e) Lacrimal | back 66 e |
front 67 Which bones form the zygomatic arch? a) temporal and zygomatic b) sphenoid and maxilla c) temporal and mandible d) temporal and frontal e) temporal and parietal | back 67 a |
front 68 What are the three correct components of the nasal septum? a) inferior nasal concha, vomer and lacrimal bone b) vomer, superior nasal concha, and septal cartilage c) inferior nasal concha, septal cartilage, perpendicular plate of ethmoid d) vomer, septal cartilage, and perpendicular plate of ethmoid e) vomer, septal cartilage, and crista galli of ethmoid | back 68 d |
front 69 Sella turcica is a bony depression found in this cranial bone.
| back 69 a |
front 70 The pituitary gland is contained in a depression found in this cranial bone.
| back 70 b |