Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Multi Choice: The Skeletal System: Bone tissue
front 1 1) Which of the following is NOT a major function of the skeletal system? a) communication b) support c) protection d) mineral homeostasis e) blood cell production | back 1 a |
front 2 2) Which region of a long bone articulates with other bones? a) diaphysis b) epiphysis c) metaphysis d) periosteum e) marrow | back 2 b |
front 3 ) What is another name for the shaft of a long bone? a) diaphysis b) epiphysis c) metaphysis d) periosteum e) marrow | back 3 a |
front 4 Which a layer of hyaline cartilage reduces friction between bones involved in a joint?
| back 4 d |
front 5 Which layer of hyaline cartilage allows the diaphysis to grow in length?
| back 5 e |
front 6 What is the region of long bone found between the diaphysis and the epiphysis called? a) epiphyseal plate b) epiphyseal line c) metaphysis d) diaphyseal line e) diaphyseal plate | back 6 c |
front 7 What is the fibrous covering on the surface of bone that is involved in thickening of the bone called?
| back 7 a |
front 8 Which of the following are considered to be bone-building cells? a) fibroblasts b) osteoclasts c) osteocytes d) osteoblasts | back 8 d |
front 9 What are bone-dissolving cells called? a) osteogenic cells b) osteoclasts c) osteocytes d) osteoblasts e) all of these choices | back 9 b |
front 10 Which of the following structures contain osteocytes? a) central (Haversian) canals b) perforating (Volkmann’s) canals c) concentric lamellae d) lacunae e) canaliculi | back 10 d |
front 11 What are the extracellular fluid filled extensions of the lacunae called?
| back 11 d |
front 12 How are osteons in compact bone tissue aligned? a) horizontal to the metaphysis. b) parallel to the epiphysis. c) parallel to the length of the diaphysis. d) randomly between the epiphyseal plates. e) parallel to the perforating canals. | back 12 c |
front 13 Which of the following statements about bone remodeling is FALSE? a) It occurs throughout your lifetime. b) It involves bone resorption. c) It involves bone deposition. d) It occurs at different rates at different locations. e) It occurs at a faster rate in compact bone than spongy bone. | back 13 e |
front 14 Which of the following activities has the greatest effect on bone remodeling and bone deposition? a) walking b) sleeping c) running. d) jumping. e) both c and d | back 14 e |
front 15 18) Which of the following two minerals are needed in large quantities when bones are growing? a) calcium and chlorine b) magnesium and sulfur c) calcium and phosphorous d) manganese and sulfur e) potassium and phosphorous | back 15 c |
front 16 Which of the following correctly lists the order of the four zones of cartilage found within the growth plate starting at the epiphysis and extending to the diaphysis? a) calcified cartilage, resting cartilage, proliferating cartilage, hypertrophic cartilage b) resting cartilage, proliferating cartilage, calcified cartilage, hypertrophic cartilage c) proliferating cartilage, resting cartilage, hypertrophic cartilage, calcified cartilage d) resting cartilage, proliferating cartilage, hypertrophic cartilage, calcified cartilage e) hypertrophic cartilage, calcified cartilage, proliferating cartilage, resting cartilage | back 16 d |
front 17 During adulthood, which of the following does NOT significantly contribute to bone remodeling and growth? a) parathyroid hormones b) vitamin D c) epinephrine d) sex steroids e) human growth hormone | back 17 c |
front 18 Which type of fracture is considered a partial fracture and is only seen in children? a) open b) comminuted c) impacted d) greenstick e) stress | back 18 d |
front 19 About 25% of all stress fractures involve which bone?
| back 19 e |
front 20 Bone mass reduction is promoted by which hormone? a) calcitriol b) calcitonin c) human growth hormone d) parathyroid hormone e) insulin | back 20 d |
front 21 An increase in bone growth is promoted by which hormones? a) calcitriol and parathyroid hormone b) calcitonin and calcitriol c) human growth hormone and parathyroid hormone d) parathyroid hormone and insulin e) All of the other selections are correct. | back 21 b |
front 22 Which of the following hormones is the most important for Ca2+ regulation?
| back 22 a |
front 23 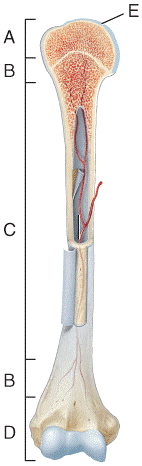 In which region of the diagram would you find the medullary cavity?
| back 23 c |
front 24 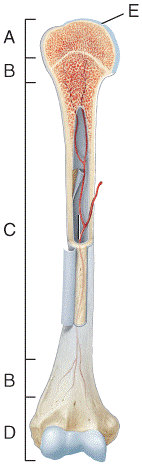 Where in the diagram can you find red bone marrow in an adult?
| back 24 b |
front 25 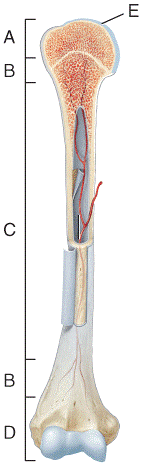 Where in the diagram is the metaphysis?
| back 25 b |
front 26 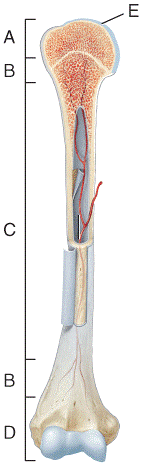 What structure in the diagram is the only place on a long bone NOT covered by the periosteum? a) A b) B c) C d) D e) E | back 26 e |
front 27 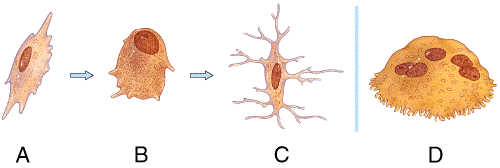 What type of bone cell starts forming the bone matrix? a) A b) B c) C d) D | back 27 b |
front 28 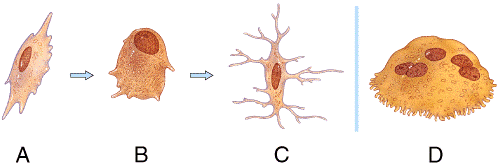 Which bone cell in the diagram below is an osteoclast? | back 28 d |
front 29 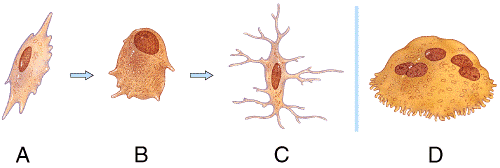 Which bone cell in the diagram below is a mature bone cell that helps maintain bone tissue? | back 29 c |
front 30 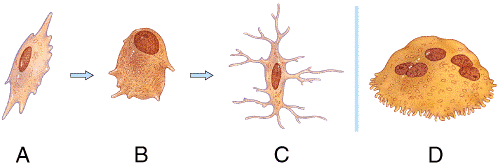 Which bone cell in the diagram below is an osteogenic cell? a) A b) B c) C d) D | back 30 a |
front 31 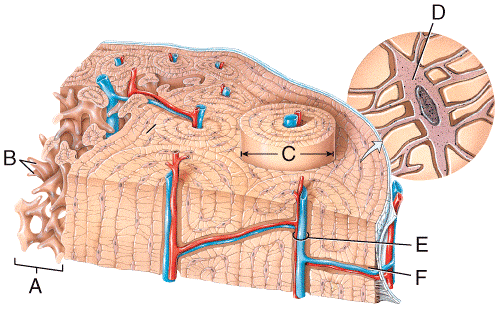 In the diagram, where is the central (Haversian) canal?
| back 31 c |
front 32 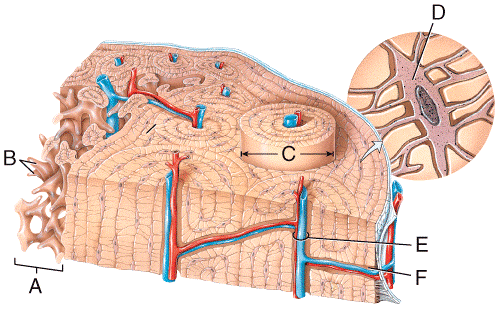 In the diagram, where is the osteon?
| back 32 c |
front 33 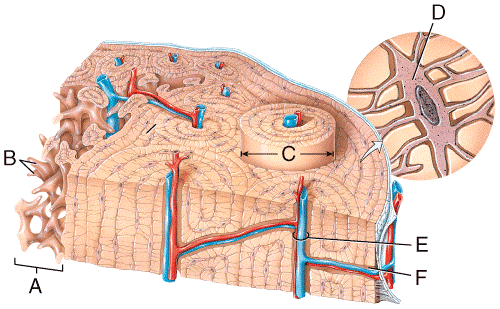 In the diagram, where is the trabeculae?
| back 33 a |
front 34 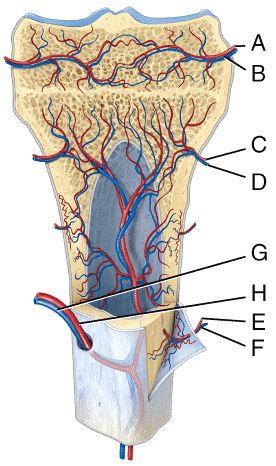 In the diagram, where is the epiphyseal vein?
| back 34 a |
front 35 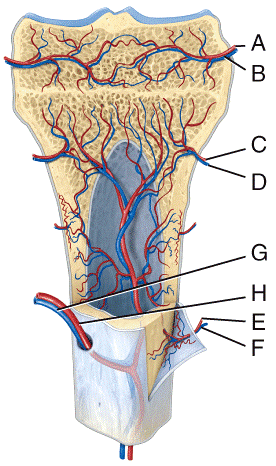 In the diagram, where is the nutrient artery?
| back 35 e |
front 36 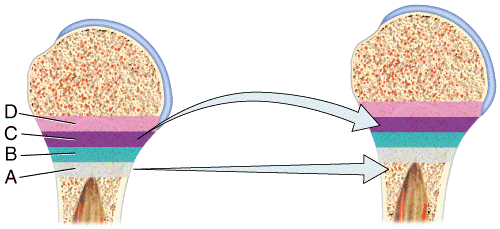 In the diagram, where is the zone of hypertrophic cartilage?
| back 36 b |
front 37 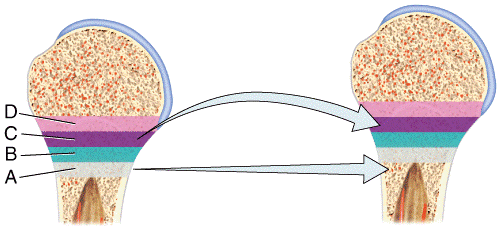 In the diagram, where is the zone of resting cartilage?
| back 37 d |
front 38 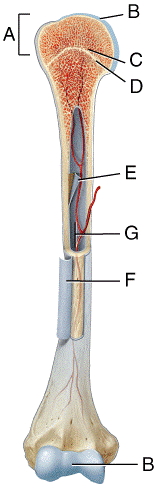 Which of the following labeled structures in the diagram is a site of red blood cell production in adult bones?
| back 38 a |
front 39 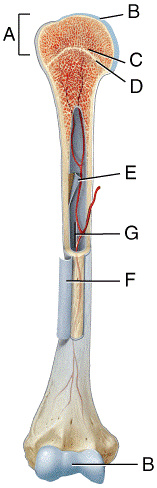 Which of the following labeled structures in the diagram stores triglycerides in adult bones?
| back 39 e |
front 40 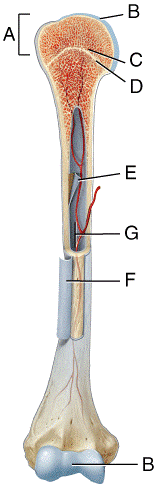 Which of the labeled structures in the diagram is formed as the result of cartilage being replaced by bone after the cessation of bone growth?
| back 40 a |
front 41 Where in the diagram is articular cartilage located?
| back 41 a |
front 42 Where in the diagram is the endosteum located?
| back 42 d |
front 43 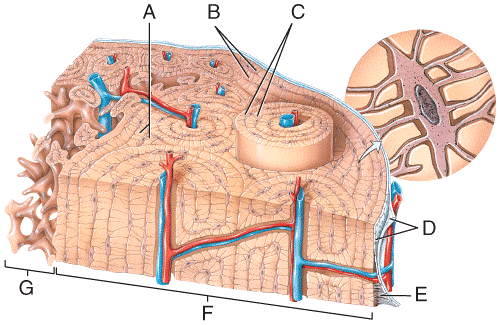 Which of the labeled structures in the diagram are fragments of older osteons that have been partially destroyed during bone rebuilding or growth?
| back 43 a |
front 44 Which of the labeled structures in the diagram are composed of trabeculae, which are bony structures that lack osteons? a) B b) C c) D d) F e) G | back 44 e |
front 45 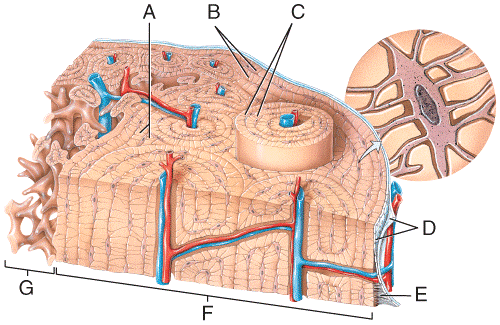 Which of the following labeled structures in the diagram are concentric lamellae? a) A b) B c) C d) D e) G | back 45 c |
front 46 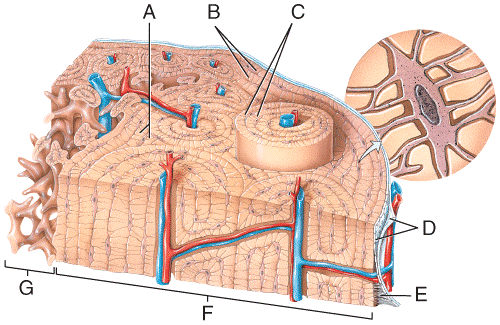 Which of the labeled structures in the diagram are circumferential lamellae? a) A b) B c) C d) D e) G | back 46 b |
front 47 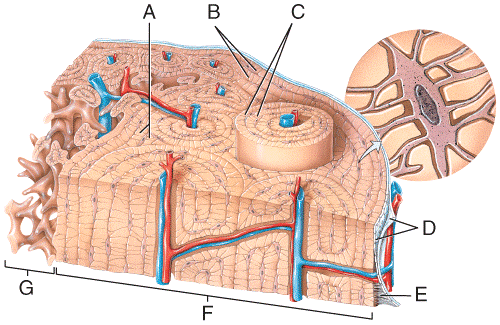 Where in the figure is the periosteum located?
e) G | back 47 c |
front 48 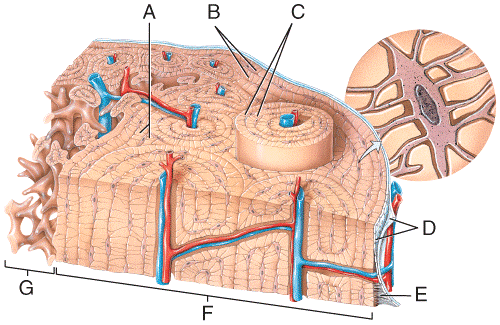 Where in the figure is spongy bone located?
| back 48 e |
front 49 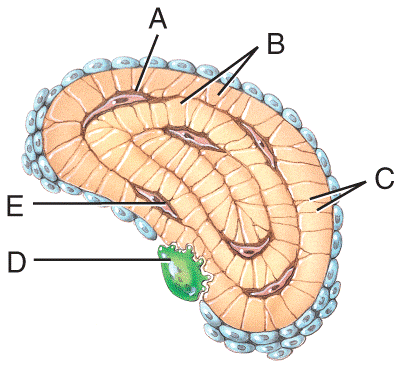 60) Which labeled structures in the figure are lamellae?
| back 49 b |
front 50 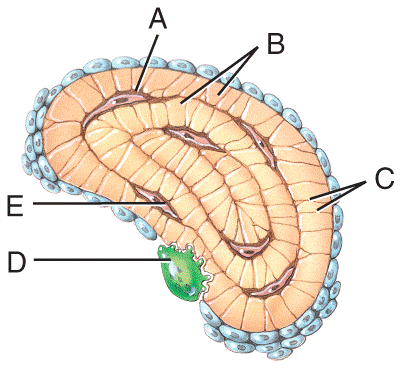 Which labeled structures in the figure are canaliculi?
| back 50 c |
front 51 Which labeled structure in the figure is an osteocyte? a) A b) B c) C d) D e) E | back 51 e |
front 52 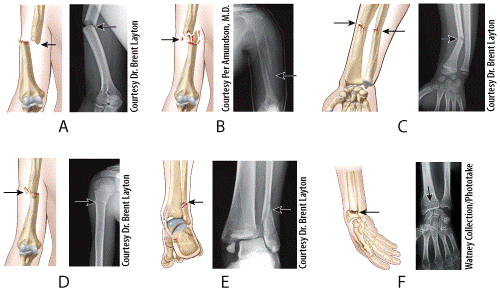 Which illustration and radiograph in the figure shows a Pott’s fracture? a) A b) B c) C d) D e) E | back 52 e |
front 53 Which of the following is the correct sequence of steps in the repair of a bone fracture? a) fracture hematoma, bony callus formation, fibrocartilaginous callus formation, bone remodeling b) fibrocartilaginous callus formation, bony callus formation, fracture hematoma, bone remodeling c) bony callus formation, fracture hematoma, fibrocartilaginous callus formation, bone remodeling d) bone remodeling, fracture hematoma, fibrocartilaginous callus formation, bony callus formation e) fracture hematoma, fibrocartilaginous callus formation, bony callus formation, bone remodeling | back 53 e |
front 54 Which of the following conditions results when the articular cartilages in a joint degenerate to the point where the bony ends of articulating bones touch?
| back 54 d |
front 55 Hypersecretion of human growth hormone during childhood results in a) giantism. b) acromegaly. c) dwarfism. d) rickets. e) no apparent effect. | back 55 a |