Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Anatomy & physiology: Muscular & Nervous systems
front 1 Muscular System | back 1 Muscular System |
front 2 How do muscles produce movement? | back 2 By contracting in response to nervous stimulation |
front 3 True/False
| back 3 ~TRUE~ |
front 4 True/False
| back 4 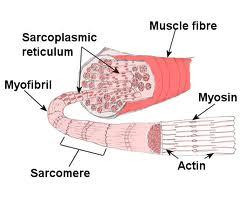 ~TRUE~ |
front 5 What must be present in order for a muscle cell to contract? | back 5 Calcium & Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) |
front 6 What causes the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum? | back 6 Nervous stimulation from the motor neuron. |
front 7 __1_ ions attach to inhibitory _2__ on the _3__ _4__ within the cell, moving them aside so that _5__-__5_ can form between _6__ and _7__ _8__. Using energy supplied by _9__, the _10__ slide together to produce _11__. | back 7 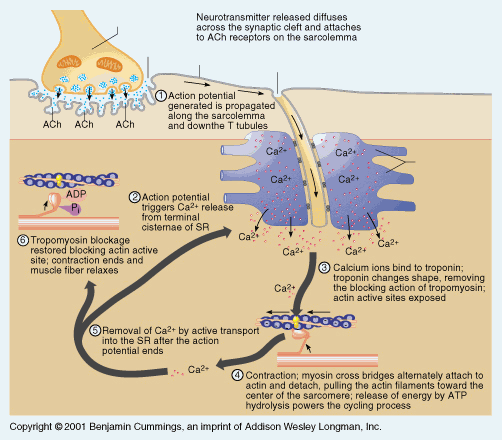 1. Calcium 9. ATP
|
front 8 Skeletal muscle which make up the muscular system, are also called | back 8 Voluntary muscles- because they are under conscious control. |
front 9 True/False
| back 9 ~TRUE~ |
front 10 The muscle that executes a given movement is the _1__, whereas the muscle that produces the opposite movement is the _2__. Other muscles known as _3__ may work in cooperation w/the prime mover. | back 10 1. Prime mover
|
front 11 True/False
| back 11 ~True~ |
front 12 There are flexors & extensors.
| back 12 reduce the angle at the joint.
|
front 13 Abductors | back 13 Draw a limb away from the midline (or body) |
front 14 Adductors | back 14 Return the limb back toward the body (adding to the body). |
front 15 Diagram of the major contour muscles of the body. Study the names,notice their name is related to location & functions. | back 15 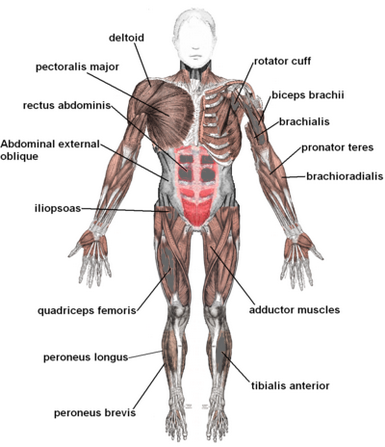 |
front 16 NERVOUS SYSTEM | back 16 NERVOUS SYSTEM |
front 17 The Nervous system consists essentially of the | back 17 BRAIN, SPINAL CORD & THE NERVES |
front 18 The Nervous system is broken into 2 categories the | back 18 CNS & the PNS
|
front 19 CNS consists of | back 19 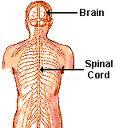 Brain & spinal cord |
front 20 PNS consists of | back 20 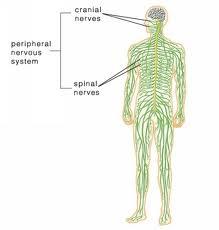 all the nerves & their branches that transmit information to & from the CNS. |
front 21 The Nervous system enables us to | back 21 perceive many of the changes that take place in our external & internal environments & to respond to those changes (seeing, hearing, tasting, smelling & touching are examples of perception). |
front 22 The Nervous system also enables us to | back 22 think, reason, remember & carry out other abstract activities. |
front 23 The Nervous system makes possible body movements by | back 23 skeletal muscles, by supplying them w/nerve impulses that cause contraction. |
front 24 The Nervous system works closely with the | back 24 endocrine glands, correlating & intergrating body functions such as digestion & reproduction. |
front 25 True/False
| back 25 ~TRUE~ |
front 26 What is the functional unit of the Nervous system? | back 26 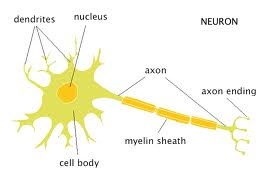 Neuron (nerve cell). |
front 27 The main parts of a neuron are the | back 27 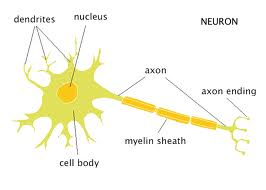 cell body, axon & dendrites. |
front 28 Dendrites transmit the impulse ___ the cell body. | back 28 Towards
|
front 29 Axons transmit the impulse ___ from the cell body. | back 29 Away
|
front 30 Sensory (afferent) neurons transmit nerve impulses ___ the CNS. | back 30 Toward |
front 31 Motor (efferent) neurons transmit nerve impulses ___ from the CNS, toward the effector organs such as muscles, glands & digestive organs. | back 31 Away |
front 32 Motor (efferent neurons) transmit nerve impulses AWAY from the CNs towards | back 32 effector organs such as the muscles, glands & digestive organs. |
front 33 The major parts of the brain are the | back 33 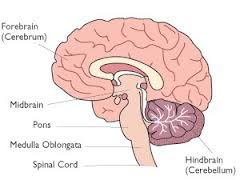 Cerebrum
|
front 34 Cerebrum is associated with | back 34 movement & sensory input |
front 35 Cerebellum is responsible for | back 35 muscular coordination, including balance. |
front 36 Medulla oblongata | back 36 Controls many vital funcitons such as respiration & heart rate. |
front 37 How long is the spinal cord? | back 37 Approximately 18 inches long. |
front 38 True/False
| back 38  ~True~ |
front 39 How many pairs of spinal nerves exit the spinal cord? | back 39 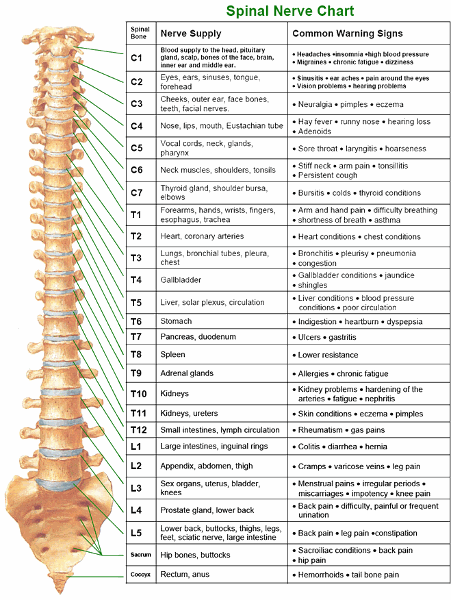 31 |
front 40 Simple (spinal) reflexes are those in which nerve impulses travel through the | back 40 spinal cord only and do not reach the brain. |
front 41 Hesi Hint
| back 41 to & from the brain in ascending & descending tracts of the spinal cord. |
front 42 Hesi Hint
| back 42 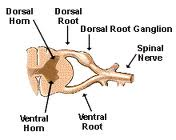 1. Dorsal horns
|
front 43 Thank you for viewing my notecards, I hope you find them helpful. I've added more photos, diagrams & visual aids than the book (hesi study guide) has to offer, hope they help. :-) | back 43 ~Post notecards of your own for others to benefit from as well~ |