Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Exam 3
front 1 Use the following list of choices for the following questions: I. Helicase II. DNA Polymerase II III. Ligase IV. DNA Polymerase I V. Primase
| back 1 d |
front 2 At a specific area of a chromosome, the sequence of nucleotides below
is present where the chain opens to form a replication fork:
| back 2 a |
front 3 Telomerase is an enzyme involved in the replication of the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes.
| back 3 a |
front 4 What is a transposable element?
| back 4 c |
front 5 Which cluster of terms accurately reflects the nature of DNA replication in prokaryotes?
| back 5 a |
front 6 The enzyme telomerase solves the problem of replication at the ends of linear chromosomes by which method?
| back 6 e |
front 7 During replication, primase adds a DNA primer to RNA.
| back 7 b |
front 8 Which enzyme catalyzes the elongation of a DNA strand in the 5' 3' direction?
| back 8 a |
front 9 Structures located at the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes are called
| back 9 d |
front 10 The leading and the lagging strands differ in that
| back 10 a |
front 11 Reverse transcriptase is an enzyme found in association with retroviral activity. It has the property of
| back 11 d |
front 12 The transforming principle discovered by Griffith is DNA.
| back 12 b |
front 13 Avery, et al. (1944) determined that DNA is the genetic material in T2 bacteriophage.
| back 13 b |
front 14 In ribose, the 2' C has an OH attached to it.
| back 14 a |
front 15 Which of the following are nitrogenous bases of the purine type?
| back 15 c |
front 16 In his transformation experiments, what did Griffith observe?
| back 16 c |
front 17 In RNA, uracil is present instead of thymine (in DNA).
| back 17 a |
front 18 In an analysis of the nucleotide composition of double-stranded DNA to see which bases are equivalent in concentration, which of the following would be true?
| back 18 b |
front 19 Deoxyribonuclease is an enzyme which adds 3'-hydroxyl groups to RNA.
| back 19 b |
front 20 The basic structure of a nucleotide includes the following components:
| back 20 a |
front 21 An Hfr cell can initiate chromosome transfer from one E.coli to another.
| back 21 a |
front 22 Lysogeny is a process which occurs during transformation and conjugation.
| back 22 b |
front 23 Interrupted mating experiments are used to determine what information?
| back 23 b |
front 24 Regarding prokaryotic genetics, which statement is correct?
| back 24 d |
front 25 To produce recombinants in bacteria, one crossover is better than two.
| back 25 b |
front 26 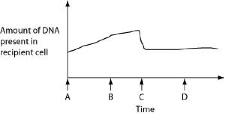 Figure 27.2 depicts changes to the amount of DNA present in a
recipient cell that is engaged in conjugation with an Hfr cell. Hfr
cell DNA begins entering the recipient cell at Time A. Assume that
reciprocal crossing over occurs (in other words, a fragment of the
recipient's chromosome is exchanged for a homologous fragment from the
Hfr cell's DNA). Use Figure 27.2 to answer the following
questions.
| back 26 b |
front 27 Name the general category into which double-stranded circular extrachromosomal DNA elements such as F factors, ColE1, and R would fall.
| back 27 a |
front 28 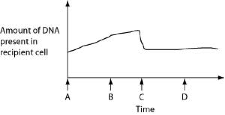 Figure 27.2 depicts changes to the amount of DNA present in a
recipient cell that is engaged in conjugation with an Hfr cell. Hfr
cell DNA begins entering the recipient cell at Time A. Assume that
reciprocal crossing over occurs (in other words, a fragment of the
recipient's chromosome is exchanged for a homologous fragment from the
Hfr cell's DNA). Use Figure 27.2 to answer the following
questions.
| back 28 e |
front 29 The transfer of genetic material between bacteria in direct physical contact is called
| back 29 b |
front 30 This type of recombination does not require homologous sequences and is important for the integration of viral genomes into bacterial chromosomes
| back 30 b |
front 31 Griffith in 1928 conducted an experiment showing that a "transforming principle" from a dead virulent bacterial strain was responsible for converting a live harmless bacterial strain into a virulent one. Later, Avery, MacLeod and McCarthy identified this "transforming principle" to be DNA. What did they use to achieve this?
| back 31 e |
front 32 Hershey and Chase used 32P and 35S to label what molecules?
| back 32 d |
front 33 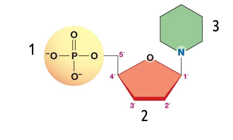 Using illustration below identify the nitrogenous base of a deoxynucleotide:
| back 33 c |
front 34 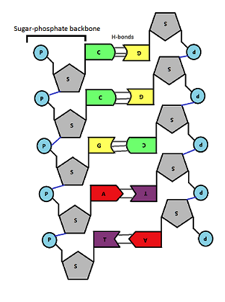 Using following illustration identify the orientation of the DNA strand on the left:
| back 34 a |
front 35 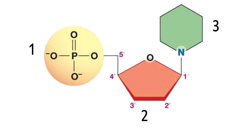 Using illustration below identify a nucleoside:
| back 35 e |
front 36 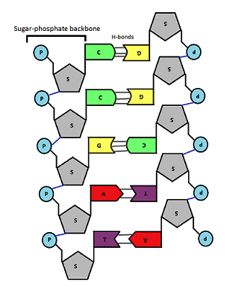 Using the illustration bellow answer the following question. If the left strand acts as a template and the right strain is being newly synthesized, the direction of synthesis would be _____________.
| back 36 b |
front 37 In a DNA strand, what kind of a bond connects two adjacent nucleosides?
| back 37 a |
front 38 At one point, Watson proposed a model in which like bases paired with like, that is C-C, T-T, G-G and A-A. Why does this model fail to explain the data that was available at the time?
| back 38 e |
front 39 DNA polymerase is a DNA-dependent DNA synthase (uses DNA as a template to produce DNA). Reverse transcriptase is __________________.
| back 39 b |
front 40 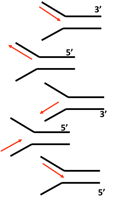 Which one of the following shows the correct orientation of new DNA strain synthesis?
| back 40 c |
front 41 Various issues have to be solved during DNA synthesis. One of them is to reduce increased coiling generated during unwinding. Which enzyme is responsible for this?
| back 41 c |
front 42 Various issues have to be solved during DNA synthesis. One of them is covalently linking newly synthesized fragments of DNA. Which enzyme is responsible for this?
| back 42 d |
front 43 Various issues have to be solved during DNA synthesis. One of them is unwinding of the helix. Which enzyme is responsible for this?
| back 43 a |
front 44 Various issues have to be solved during DNA synthesis. One of them is to synthesize primers for initiation. Which enzyme is responsible for this?
| back 44 e |
front 45 At a specific area of a chromosome, the sequence of nucleotides below
is present where the chain opens to form a replication fork: 3' GGC
TAATCGGA
5'
| back 45 e |
front 46 What is the basis for the difference in how the leading and lagging strands of DNA molecules are synthesized?
| back 46 e |
front 47 Imagine that you are exposing wild type E. coli cultures to UV in order to produce mutants. How do you screen for lysine auxotrophs (bacteria unable to produce lysine)?
| back 47 d |
front 48 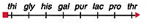 You conducted an interrupted mating experiment using an E.coli Hfr line and following map was obtained. Which one of the following maps represents the obtained data: | back 48 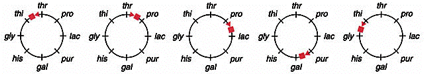 a |
front 49 In an Hfr ´ F– mating, if the order of transfer of loci is leu – azi – ton – lac, one can conclude that _____.
| back 49 b |
front 50 In Benzer’s analysis of the many rII mutants of T4 phage which cannot lyse E. coli strain K12, he conducted a complementation test that yielded the following results: Simultaneous Infection of 2 mutants on E.coli K12 Results (+ = lysis and viruses produced) Mutants 1, 2 + Mutants 1, 3 - Mutants 1, 4 - Mutants 1, 5 + Predict the result of the following simultaneous infection: Mutants 2, 3
| back 50 a |
front 51 You are trying to replicate Benzer’s experiments with rII mutants of T4 phage which cannot lyse E. coli strain K12, but can lyse strain B. After you conducted a complementation test, you found out that simultaneous infection of K12 cells with mutants 1 and 3 did not produce any plaques (they did no complement). However, simultaneous infection of a B strain followed by infection of K12 strain did produce plaques. What is happening?
| back 51 b |
front 52 Complete the following statement: During Hfr-mediated conjugation, the recipient ________________.
| back 52 d |