Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Human Anatomy & Physiology Chap 9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,
front 1 those one that lie around the body's center of gravity | back 1 Axial Skeleton |
front 2 bones of the limbs or appendages | back 2 Appendicular Skeleton |
front 3 which cover the one ends at movable joints | back 3 Articular cartilage |
front 4 smooth and homogenous | back 4 compact bone |
front 5 Spongy bone | back 5 composed of small trabeculae of one and lots of open space |
front 6 are much longer than they are wide | back 6 Long bone |
front 7 typically cube shaped, contain more spongy bone than compact bone | back 7 Short bone |
front 8 generally thin, with two wafer/like layers of compact bone | back 8 Flat bone |
front 9 ones that do not fall into one of the preceding categories | back 9 irregular bone |
front 10 special types of short bones formed in tendons | back 10 sesamoid bones |
front 11 shaft | back 11 Diaphysis |
front 12 fibrous membrane covering | back 12 Periosteum |
front 13 the end of the long bone | back 13 epiphysis |
front 14 compact bone appears to be dense and homogenous | back 14 Trabeculae |
front 15 Framework for support and movement | back 15 Skeletal System |
front 16 Skeletal System Stores | back 16 minerals and lipids |
front 17 Tissue that the skeletal system is made up of | back 17 connective tissue Bone & Cartilage |
front 18 Main components Skeletal System are | back 18 Bone & Cartilage |
front 19 INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL TEXTURES OF BONE | back 19 Compact & Spongy (cancellous) |
front 20 composed of small trabeculae of one and lots of open space it is the inside layer of compact bone | back 20 spongy bone |
front 21 runs parallel to the long axis of the bone and carries blood vessels, nerves and lymph vessels through the bony matrix | back 21 Central(haversian) canal |
front 22 are living tissue | back 22 bones |
front 23 a central canal and all the concentric lamellae surrounding it are referred to as | back 23 an osteon |
front 24 cells living in bone | back 24 OSTEOCYTES cells |
front 25 ARE RESPONSIBLE FOR BONE GROWTH AND CHANGES IN THE SHAPE OF BONES | back 25 OSTEOCYTES |
front 26 Calcium from Microcrystallinen, non living matrix is very dense/hard calcium crystals called | back 26 Hydroxyapatite |
front 27 Hydroxyapatite is just a | back 27 fancy name for bone |
front 28 tiny canals radiating outward from a central canal to the lacunae of the first lamella and then from lamella to lamella. | back 28 Canaliculi |
front 29 We look at bone based on how they | back 29 grow |
front 30 when the body produces calcium in areas the a tendon irritates the area this is how you get | back 30 sesamoid bones |
front 31 SHAFT OF A LONG BONE | back 31 diaphysis |
front 32 the end of the long bone | back 32 epiphyis |
front 33 WHEN DESCRIBING SECTIONS OF A LONG BONE WHEN TALKING ABOUT ENDS OF THE LONG BONE | back 33 proximal epiphysis distal epephysis |
front 34 epiphsyatal line that separate spongy and compact bone | back 34 growth plate |
front 35 hollow section in the diaphysis is called | back 35 the medullary cavity |
front 36 is found in the medullary cavity | back 36 yellow bone marrow |
front 37 pointed, pen-like | back 37 styloid |
front 38 -Axial
| back 38 RIBS |
front 39 1. Diaphysis
| back 39 PARTS OF LONG BONES |
front 40 supports the skull | back 40 -The atlas (1st vertebra) |
front 41 support for trunk | back 41 -Bones in legs and pelvis provide |
front 42 -Oval-shaped condyle fits with elliptical cavity of another bone
| back 42 Condyloid Joint |
front 43 -Nearly flat/slight curved surface
| back 43 Gliding Joint |
front 44 What is a movable joint? | back 44 A joint that allows the body to move forward... |
front 45 A plate near the ends of long bones. | back 45 What is the epiphyseal plate? |
front 46 The junction of two bones | back 46 articulation |
front 47 a projection adjacent to a condyle | back 47 epicondyle |
front 48 a narrow, slitlike opening through a bone | back 48 fissure |
front 49 shaped like a shallow socket | back 49 glenoid |
front 50 a club-shaped or hammer-shapped process | back 50 malleolus |
front 51 Types of cartilage growth? (2 types) | back 51 1. appositional growth 2. interstitial growth |
front 52 The skull is composed of two sets of bones. These are called? | back 52 1. The cranium 2. the facial bones |
front 53 An opening above each orbit allowing blood vessels and nerves to pass. | back 53 Supraorbital forameN |
front 54 The smooth area between the eyes? | back 54 Glabella |
front 55 Posterolateral to the frontal bone, forming sides of cranium. | back 55 Parietal Bone |
front 56 Midline articulation point of the two parietal bones. | back 56 Sagittal suture |
front 57 Inferior to the parietal bones on lateral skull. | back 57 Temporal bone |
front 58 A bridgelike projection joining the zygomatic bone anteriorly. Together these 2 bones form the zygomatic arch. | back 58 Zygomatic process |
front 59 Rounded depression on the inferior surface of the zygomatic process, forms the socket for the mandibular condyle, the point where the mandible (lower jaw) joins the cranium. | back 59 Mandibular fossa |
front 60 Point of articulation of parietals with frontal bone. | back 60 Coronal suture |
front 61 a prominent, rounded epiphysis | back 61 HEAD |
front 62 a narrow, prominent ridgelike projection | back 62 CREST |
front 63 -Convex surface fits with concave surface of another bone
| back 63 Hinge Joint |
front 64 -Cylindrical surface of one bone fits in a ring formed by another bone/ligament
| back 64 Pivot Joint |
front 65 Both concave and convex bone surface
| back 65 SADDLE JOINT |
front 66 Head of bone fits into socket of another
| back 66 Ball and Socket Joint |
front 67 Skeletal muscles attach to bones via | back 67 tendons |
front 68 -Axial
| back 68 Vertebrae |
front 69 Are ribs axial or appendicular? | back 69 Axial |
front 70 What is the primary inorganic component that makes up the skeletal system? | back 70 Calcium phosphate |
front 71 the line of union in an immovable articulation | back 71 suture |
front 72 an indentation of v-shaped depression | back 72 notch |
front 73 found on joints | back 73 hyaline cartilage |
front 74 What is the membrane surrounding individual bones? It's called | back 74 periosteum |
front 75 peri means | back 75 around |
front 76 THE SKULL IS THE BODY'S MOST COMPLEX BONEY STRUCTURE IT IS FORMED BY THE? | back 76 cranial bones and facial bones |
front 77 cranial bones protect | back 77 the brain |
front 78 facial bones protect the ??
| back 78 eyes, muscles |
front 79 only bone that moves inside the skull is the | back 79 mandible |
front 80 the irregular edges of the bones interlock and are united by very short connective tissue fibers | back 80 sutures |
front 81 THE CORONAL, SAGITTAL SQUAMOUS AND LAMBDOID SUTURES CONNECT CRANIAL BONES ARE | back 81 THE MAJOR SKULL SUTURES |
front 82 The cranium is divided into two major areas, what are these areas called? | back 82 cranial vault & cranial floor |
front 83 FORMING THE SUPERIOR,LATERAL AND POSTERIOR WALLS OF THE SKULL | back 83 cranial vault |
front 84 FORMING THE SKULL BOTTOM | back 84 cranial floor |
front 85 internally the cranial floor has three distinct concavities | back 85 ANTERIOR MIDDLE AND POSTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSAE |
front 86 FORMING SIDES OF THE CRANIUM | back 86 parietal bone |
front 87 FORMS FOREHEAD | back 87 frontal bone |
front 88 inferior to the parietal bone on the lateral skull | back 88 temporal bone |
front 89 ARMS OF GLASSES | back 89 temples |
front 90 FORMS THE LATERAL PORTIONS OF THE SKULL | back 90 TEMPORAL bone |
front 91 POSTERIOR BONE OF THE CRANIAL FORMS FLOOR AND BACK WALL OF THE SKULL | back 91 occipital bone |
front 92 cheek bone | back 92 zygomatic bone |
front 93 FORMS THE UPPER JAW BONE AND PART OF THE ORBITS | back 93 maxilla |
front 94 bone that flaps when you talk | back 94 mandible |
front 95 means the butterfly | back 95 sphenoid bone |
front 96 means crying | back 96 lacrimal bone |
front 97 Provides sturdy support with some resilience or "give" | back 97 hyaline cartilage |
front 98 MAXILLARY, SPHENOID ETHMOID AND FRONTAL AIR CAVITIES | back 98 PARANASAL sinuses |
front 99 LOCATED IN THE THROAT SERVES AS A POINT OF ATTACHMENT FOR TONGUE AND NECK MUSCLES | back 99 hyloid |
front 100 bone fractured from strangulation | back 100 hyloid bone |
front 101 Four pairs, named for the bones they reside in.
| back 101 Paranasal bones |
front 102 24 bones stacked in the | back 102 vertebral column |
front 103 7 BONES C1-C7 | back 103 cervical vertebrae |
front 104 12 BONES IN MID BACK t1-t12 | back 104 thoracic region |
front 105 extending from the skull to the pelvis body's major axial support | back 105 vertebral column |
front 106 in the vertebral column they're 24 single bones called? two fused bones called the ?? and the ?? | back 106 vertebrae, sacrum, coccyx |
front 107 5 BONES LOWER BACK L1-L5 IS CALLED | back 107 THE LUMBAR REGION |
front 108 ONCE HAD 5 BONES NOW FUSED TOGETHER MAKING ONLY 1 BONE | back 108 THE SACRUM |
front 109 4 BONES FUSED TOGETHER TO MAKE ONE BONE | back 109 COXXYX |
front 110 IN A VERTEBRA THE PART THAT BARES WEIGHT IS CALLED | back 110 THE BODY |
front 111 IN A VERTEBRA THE HOLLOW PART IN THE CENTER WHERE THE SPINAL CORD GOES THROUGH IS CALLED | back 111 VERTEBRAL ARCH |
front 112 is a part of the vertebra that connects to the spinous process. | back 112 THE LAMINA |
front 113 From a lateral perspective, the posterior extensions directly off the vertebral body and are located on each side. | back 113 PEDICAL |
front 114 a HOLE IN A BONE IS CALLED A | back 114 FORAMINA |
front 115 cervical VERTEBRAE SMALL AND LIGHT AND THE VEREBRAL FORAMEN IS ?? IN SHAPE | back 115 TRIANGULAR |
front 116 A FLAT JOINT | back 116 FACET |
front 117 What is located within the intervertebral joints and are tightly bound to adjacent vertebral bodies for spinal stability but allow for flexibility and movement of the vertebral column? | back 117 intervertebral disks |
front 118 The joints located along a portion of the vertebral column and articulates with the ribs to the thoracic vertebra. | back 118 costal joints |
front 119 The joints found between the vertebral bodies. | back 119 intervertebral joints |
front 120 Where was the term "atlas" for C1 derived from? | back 120 a Greek god who bore the world upon his shoulders |
front 121 What is the distinquishing feature of C1? | back 121 t has no body but a thick arch of bone called the anterior arch which includes a small anterior tubercle |
front 122 What is another term used to describe the second vertebra, C2? | back 122 axis |
front 123 What is the most distinctive feature of C2? | back 123 dens; odontoid process |
front 124 How many divisions are in the vertebral canal? | back 124 5; cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, coccyx |
front 125 What is the vertebral column? | back 125 a complex succession of many bones called vertebrae |
front 126 VISIBLE THROUGH THE SKIN | back 126 C-7 |
front 127 Where does the rotation of the head primarily occur? | back 127 between C1 and C2 |
front 128 C1 is the most bulky and solid part. What is it's purpose | back 128 support the weight of the head and assist in rotation of the head |
front 129 What acts as a pivot for rotation of the head? | back 129 dens |
front 130 What extends posteriorly from the vertebral body | back 130 RING OR ARCH |
front 131 much more flexible than hyaline; tolerates repeated bending better; external ear and epiglottis | back 131 elastic cartilage |
front 132 Where does the rotation of the head primarily occur? | back 132 between C1 and C2 |
front 133 The vertebral body is a thin ring of dense cortical bone | back 133 Vertebrae |
front 134 compose the middle segment of the vertebral column, between the cervical vertebrae and the lumbar vertebrae T-1- T-12 | back 134 THORACIC VERTEBRAE |
front 135 is derived from the Latin word “lumbus,” meaning lion, and arns its name. It is built for both power and flexibility L-1-L-5 | back 135 LUMBAR VERTABRA |
front 136 THE BONY THORAX IS COMPOSED OF THE STERNUM, RIBS,AND THORACIC VERTEBRAE | back 136 THORACIC CAGE |
front 137 the largest and strongest in the movable part of the spinal column.
| back 137 LUMBAR REGION |
front 138 rib articulates with the vertebral column Costovertebral MEANS | back 138 RIB JOINTS |
front 139 C-1 IS ALSO KNOWN AS THE | back 139 ATLAS |
front 140 C-2 IS KNOWN AS THE | back 140 AXSIS |
front 141 C1 SPINS ON THE | back 141 DENS |
front 142 HOW MANY RIBS | back 142 24 12 ON EACH SIDE |
front 143 HOW MANT PAIRS OF RIBS ARE THERE | back 143 12 PAIR |
front 144 RIB PAIRS 1-7 | back 144 TRUE RIBS |
front 145 RIB PAIRS 8-12 | back 145 FALSE RIBS` |
front 146 RIB PAIRS 11-12 | back 146 FLOATING RIBS |
front 147 ATTACH TO THE VERTEBRA AND ATTACH TO THE BREAST BONE | back 147 TRUE RIBS |
front 148 HOW MANY TRUE RIBS DO YOU HAVE | back 148 14 |
front 149 HOW MANY FALSE RIBS DO YOU HAVE | back 149 10 |
front 150 ATTACH TO THE VERTEBRA AND DO NOT ATTACH | back 150 FALSE RIBS |
front 151 A TYPICAL FLAT BONE IS THE RESULT OF THE FUSION OF THREE BONES.. | back 151 THE STERNUM |
front 152 FORMS THE BULK OF THE STERNUM | back 152 GLADIOLUS AKA BODY |
front 153 which cover the one ends at movable joints | back 153 Articular cartilage |
front 154 Provides sturdy support with some resilience or "give" | back 154 Hyaline Cartilage |
front 155 THE POINT WHERE THE STERNAL BODY AND XIPHOID PROCESS FUSE LIES AT THE LEVEL OF THE NINTH THORACIC VERTEBRA | back 155 XIPHISTERNAL JOINT |
front 156 tolerates repeated bending
| back 156 Elastic cartilage |
front 157 Round or oval opening through a bone | back 157 Foramen |
front 158 Shallow depression or groove such as that on the bony surface | back 158 Sulcus |
front 159 Air-filled cavity | back 159 Sinus |
front 160 Large, irregularly shaped projection | back 160 Trochanter |
front 161 Raised area on or above a condyle | back 161 Epicondyle |
front 162 Projection or prominence | back 162 Process |
front 163 smooth, nearly flat articular surface | back 163 facet |
front 164 great tensile strength and can withstand heavy compression | back 164 Fibrocartilage |
front 165 a thin area of hyaline cartilage that provides for longitudinal growth of the bone during youth | back 165 epiphyseal plate |
front 166 thin bone covering the epiphyseal plate after the growth stops | back 166 epiphyseal line |
front 167 compact bone appears to be dense and homogenous | back 167 Trabeculae |
front 168 lacunae arranged in concentric circles around the central canal | back 168 Circumferential lamellae |
front 169 a central canal and all the concentric lamellae surrounding it | back 169 an osteon |
front 170 tiny canals radiating outward from a central canal to the lacunae of the first lamella and then from lamella to lamella. | back 170 Canaliculi |
front 171 canal that runs into the compact bone and marrow cavity form the periosteum at right angles of the shaft. | back 171 Perforating(Volkmann's) canal |
front 172 immovable joints | back 172 synarthroses |
front 173 slightly movable joints | back 173 amphiarthroses |
front 174 freely movable joints | back 174 Diarthrases |
front 175 bones joined by fibrous tissue | back 175 Fibrous joint |
front 176 the irregular edges of the bones interlock and are united by very short connective tissue fibers | back 176 suture |
front 177 the articulating bone ends are connected by a plate or pad of cartilage | back 177 cartilaginous joints |
front 178 the bones are connected by a broad,flat disc of fibrocartilage | back 178 symphyses |
front 179 the bony portions are united by hyaline cartilage | back 179 synchondroses |
front 180 those in which the articulating bone ends are separated by a joint cavity containing synovial fluid | back 180 synovial joint |
front 181 a HUMAN FETUS ABOUT TO BE BORN HAS HOW MANY BONES | back 181 275 |
front 182 are soft spots on a baby's head which, during birth, enable the bony plates of the skull to flex, allowing the child's head to pass through the birth | back 182 FONTANELS |
front 183 ANTERIOR FONTANELLES ARE LOCATED BETWEEN THE | back 183 2 PARIETAL BONES AND THE FRONTAL BONE |
front 184 THE SPHEROIDAL FONTANEL IS LOCATED BETWEEN THE | back 184 FRONTAL BONE, SPHEROIDAL BONE AND THE TEMPORAL PARIETAL BONE |
front 185 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #1 | back 185 Acromial (lateral) end |
front 186 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #2 | back 186 Medial (sternal) end |
front 187 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #1 | back 187 Acromion |
front 188 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #2 | back 188 Glenoid cavity |
front 189 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #3 | back 189 Lateral Angle |
front 190 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR # 4 | back 190 Lateral border |
front 191 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #5 | back 191 Inferior angle |
front 192 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #6 | back 192 Medial border |
front 193 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #7 | back 193 Infraspinous fossa |
front 194 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #8 | back 194 Spine of scapula |
front 195 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #9 | back 195 Supraspinous fossa |
front 196 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #10 | back 196 Superior angle |
front 197 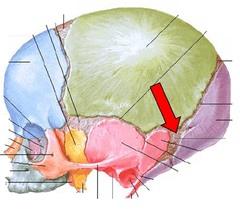 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME | back 197 MASTOID FONTANEL |
front 198 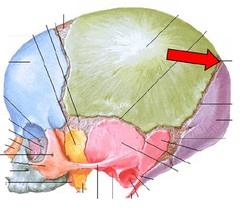 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME | back 198 POSTERIOR FONTANEL |
front 199 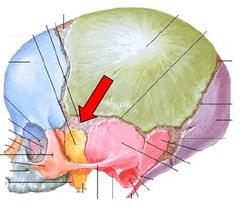 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME | back 199 SPHENOIDAL FONTANEL |
front 200 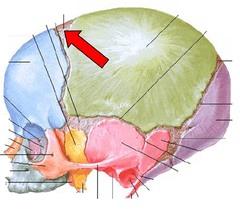 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME | back 200 ANTERIOR FONTANEL |
front 201 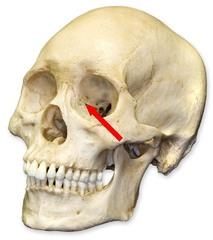 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME | back 201 LACRIMAL |
front 202 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #1
| back 202 Acromion |
front 203 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #2
| back 203 Glenoid cavity |
front 204 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #3
| back 204 Lateral angle |
front 205 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #4
| back 205 Lateral border |
front 206 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #5 | back 206 Inferior angle |
front 207 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #6
| back 207 Medial border |
front 208 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #11 | back 208 Coracoid process |
front 209 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #10
| back 209 Superior angle |
front 210 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #12
| back 210 Subscapular fossa |
front 211 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #13
| back 211 Suprascapular notch |
front 212 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #1
| back 212 Greater Tubercle |
front 213 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #2
| back 213 Lesser Tubercle |
front 214 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #3
| back 214 Deltoid Tuberosity |
front 215 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #4
| back 215 Radial fossa |
front 216 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #5
| back 216 Capitulum |
front 217 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #6
| back 217 Trochlea |
front 218 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #7 | back 218 Medial epicondyle |
front 219 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #8
| back 219 Coronoid fossa |
front 220 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #9
| back 220 Anatomical neck |
front 221 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #10
| back 221 Head of Humerus |
front 222 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #1
| back 222 Greater Tubercle |
front 223 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #3
| back 223 Deltoid Tuberosity |
front 224 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #6 | back 224 Trochlea |
front 225 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #7
| back 225 Medial epicondyle |
front 226 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #9
| back 226 Anatomical neck |
front 227 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #10
| back 227 Head of Humerus |
front 228 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #11
| back 228 Lateral epicondyle |
front 229 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #12
| back 229 Olecranon fossa |
front 230 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #1
| back 230 Head |
front 231 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #2
| back 231 Lesser Trochanter |
front 232 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #3
| back 232 Medial epicondyle |
front 233 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #4
| back 233 Patellar surface |
front 234 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #5
| back 234 Lateral epicondyle |
front 235 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #6
| back 235 Greater Trochanter |
front 236 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #1 | back 236 Head |
front 237 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #2
| back 237 Lesser Trochanter |
front 238 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #3
| back 238 Medial epicondyle |
front 239 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #5
| back 239 Lateral epicondyle |
front 240 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #6
| back 240 Greater Trochanter |
front 241 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #7
| back 241 Lateral condyle |
front 242 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #8
| back 242 Medial condyle |
front 243 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #9
| back 243 Intercondylar notch |
front 244 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #10
| back 244 neck |
front 245 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #1
| back 245 Medial condyle |
front 246 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #2 | back 246 Medial malleolus |
front 247 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #3
| back 247 Anterior crest |
front 248 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #4
| back 248 Tibial tuberosity |
front 249 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #5
| back 249 Lateral condyle |
front 250 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #6
| back 250 Intercondylar eminence |
front 251 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #1
| back 251 Head |
front 252 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #2
| back 252 Lateral Malleolus |
front 253 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #A | back 253 Carpals |
front 254 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #B | back 254 Metacarpals 1 through 5 |
front 255 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #C | back 255 Phalanges |
front 256 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #6 | back 256 Distal phalanx |
front 257 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR # | back 257 Middle phalanx |
front 258 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR # | back 258 Proximal phalanx |
front 259 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #A | back 259 Phalanges |
front 260 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #B | back 260 Metatarsal bones 1 through 5 |
front 261 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #C | back 261 Tarsal bones (7) |
front 262 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #6 | back 262 Talus (ankle) |
front 263 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #7 | back 263 Calcaneus (heel) |
front 264 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #1
| back 264 Head |
front 265 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #2
| back 265 Neck |
front 266 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #3
| back 266 Styloid process of radius |
front 267 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #4
| back 267 Radial tuberosity |
front 268 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #1
| back 268 Olecranon process |
front 269 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #2
| back 269 Coronoid process |
front 270 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #3
| back 270 Head of ulna |
front 271 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #4
| back 271 Styloid process of ulna |
front 272 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #5
| back 272 Trochlear notch |
front 273 Medial view of left os coxa
| back 273 Illium |
front 274 Formed by the fusion of three bones:
| back 274 Ischium |
front 275 Formed by the fusion of three bones:
| back 275 3) Pubis |
front 276 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #1 | back 276 Iliac crest |
front 277 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #2 | back 277 Anterior superior iliac spine |
front 278 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #3 | back 278 Anterior inferior iliac spine |
front 279 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #4 | back 279 Acetabulum |
front 280 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #5 | back 280 5) Pubis |
front 281 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #6 | back 281 Obturator foramen |
front 282 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #7 | back 282 Ishial ramus |
front 283 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #8 | back 283 Ishial Tuberosity |
front 284 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #9 | back 284 Ishial spine |
front 285 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #10 | back 285 Greater sciatic notch |
front 286 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #11 | back 286 Posterior inferior iliac spine |
front 287 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #12 | back 287 Posterior superior iliac spine |
front 288 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #1 | back 288 Posterior Superior Iliac spine |
front 289 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #2 | back 289 Posterior Inferior Iliac spine |
front 290 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #3 | back 290 Greater sciatic notch |
front 291 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #4 | back 291 Ischial spine |
front 292 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #5 | back 292 Ischial tuberosity |
front 293 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #6 | back 293 Ischial ramus |
front 294 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #7 | back 294 Obturator foramen |
front 295 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #8 | back 295 Pubis |
front 296 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #9 | back 296 Anterior inferior iliac spine |
front 297 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #10 | back 297 Anterior superior iliac spine |
front 298 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #11 | back 298 Iliac crest |
front 299 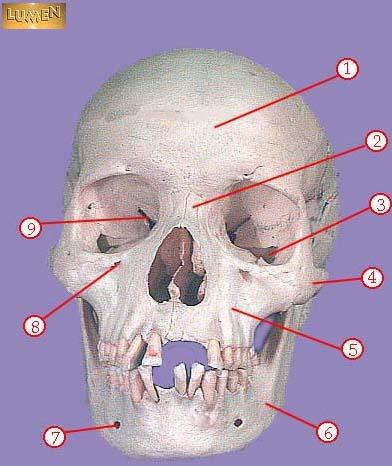 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #1 | back 299 frontal bone |
front 300 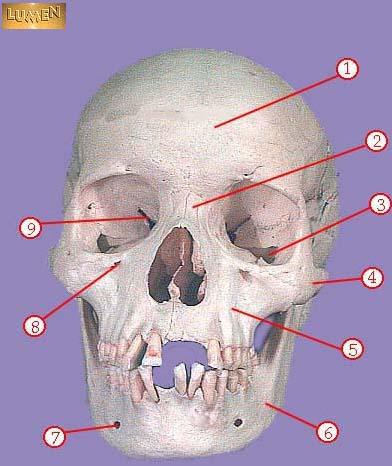 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #2 | back 300 nasal bone |
front 301 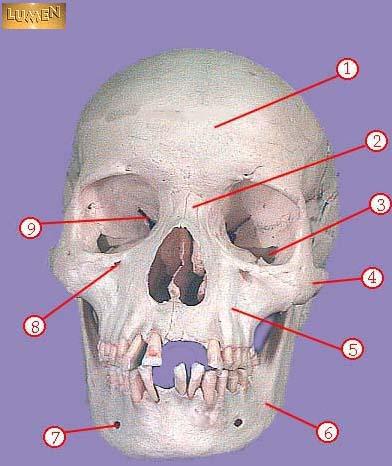 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #3 | back 301 inferior orbital fissure |
front 302 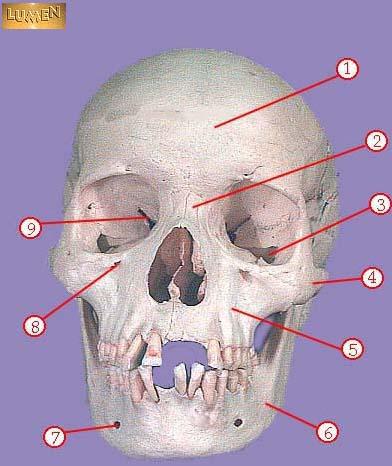 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #4 | back 302 zygomatic |
front 303 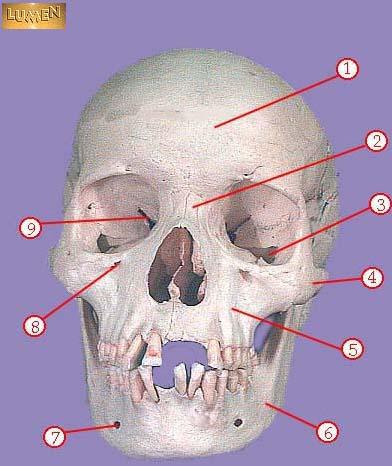 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #5 | back 303 maxilla |
front 304 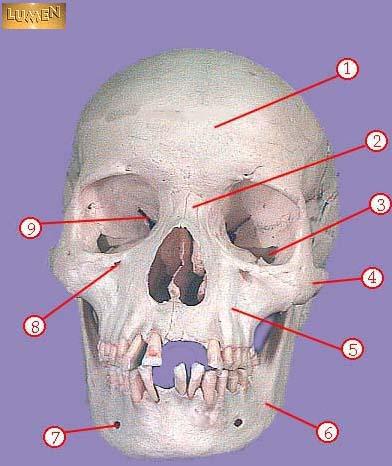 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #6 | back 304 mandible |
front 305 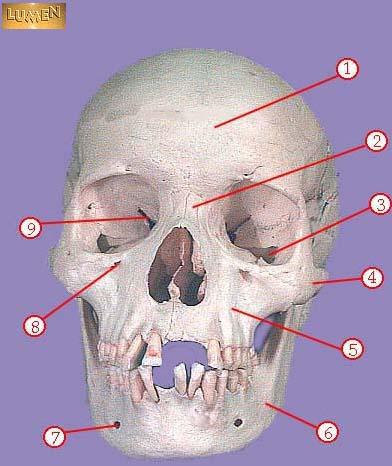 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #7 | back 305 mental foramen |
front 306 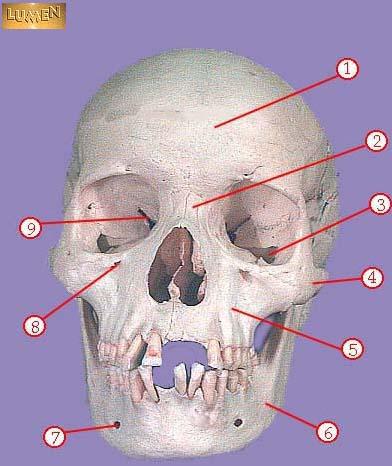 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #8 | back 306 infraorbital foramen |
front 307 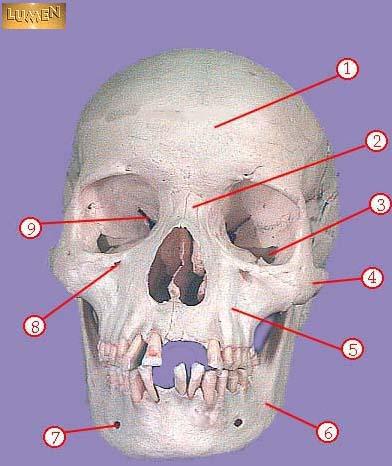 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #9 | back 307 superior orbital fissure |
front 308 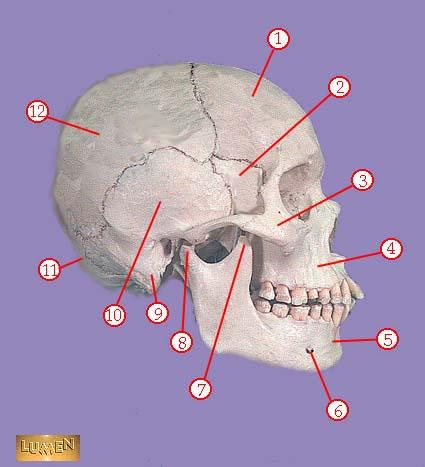 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #1 | back 308 frontal bone |
front 309 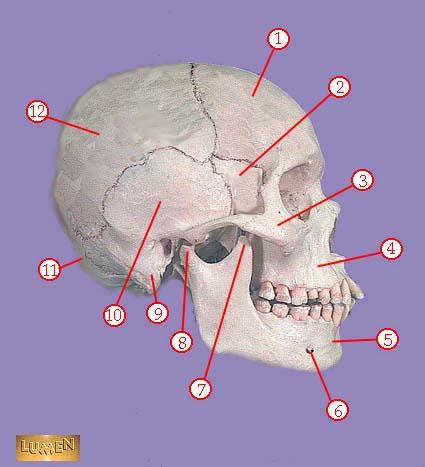 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #2 | back 309 greater wing of sphenoid bone |
front 310 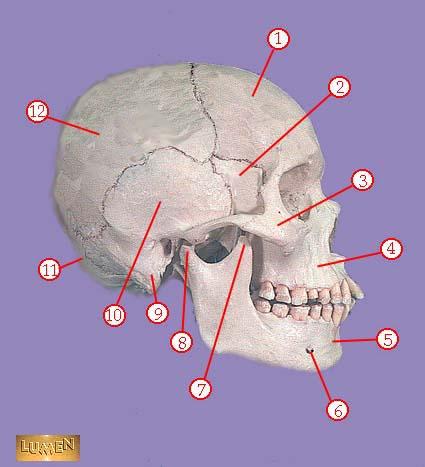 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #3 | back 310 zygomatic bone |
front 311 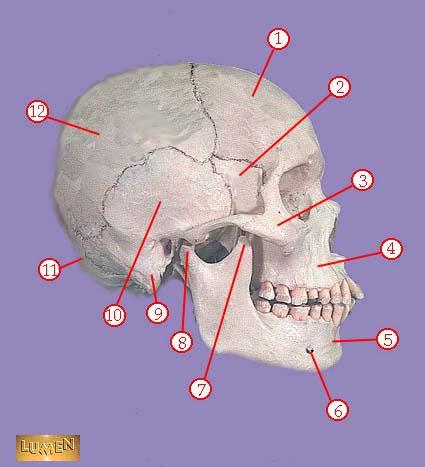 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #4 | back 311 maxilla |
front 312 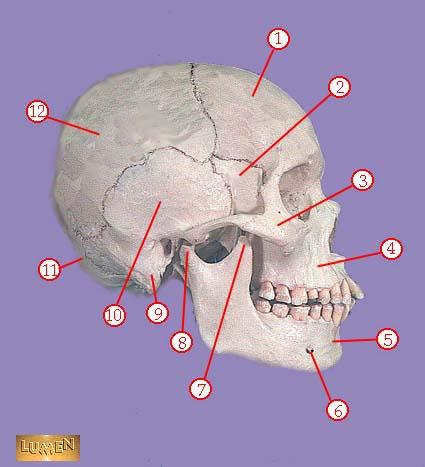 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #5 | back 312 mandible |
front 313 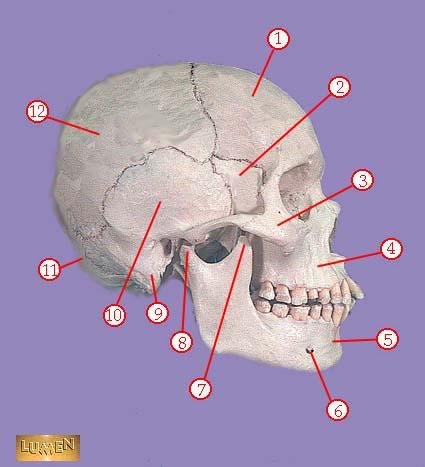 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #6 | back 313 mental foramen |
front 314 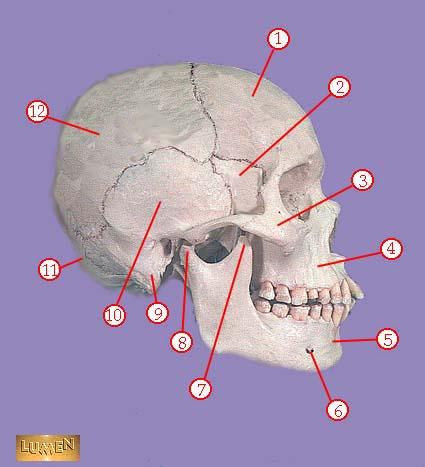 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #7 | back 314 coronoid process of mandible |
front 315 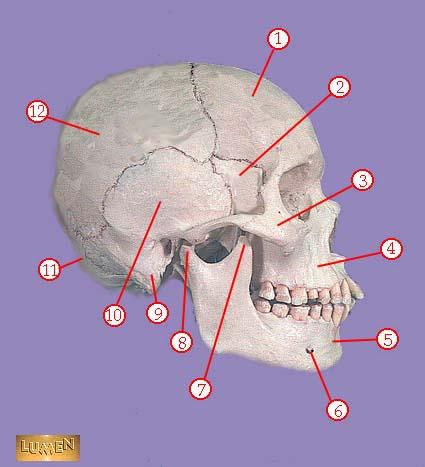 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #8 | back 315 head of mandible |
front 316 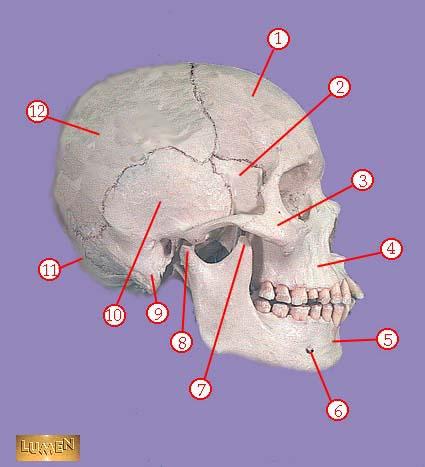 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #9 | back 316 mastoid process |
front 317 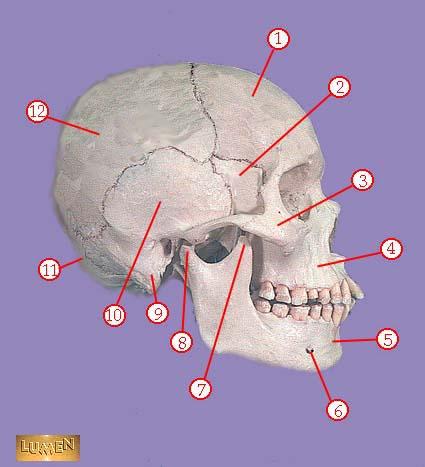 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #10 | back 317 temporal bone |
front 318 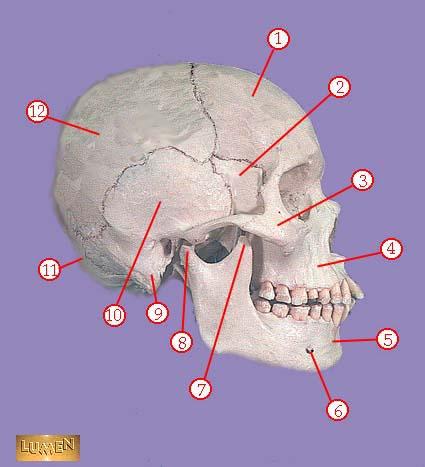 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #11 | back 318 occipital bone |
front 319 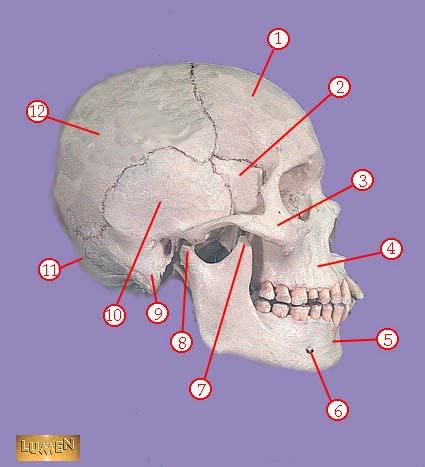 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #12 | back 319 parietal bone |
front 320 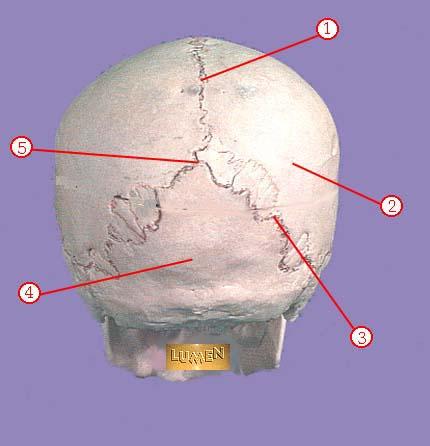 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #1 | back 320 sagittal suture |
front 321 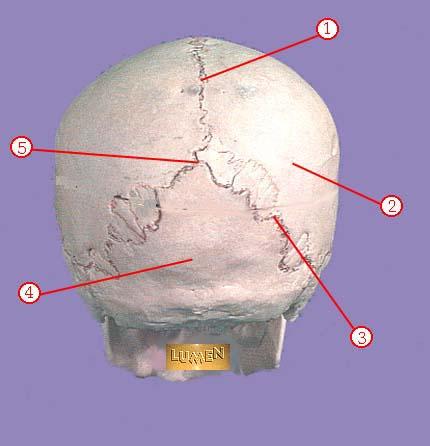 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #2 | back 321 parietal bone |
front 322 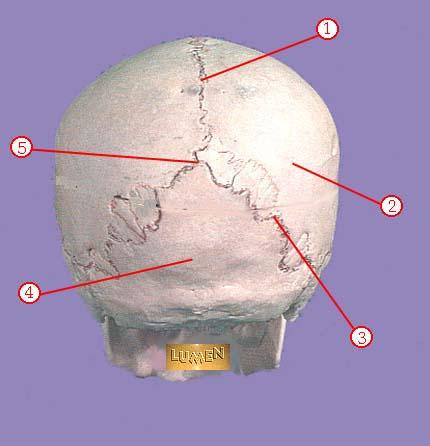 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #3 | back 322 lambdoidal suture |
front 323 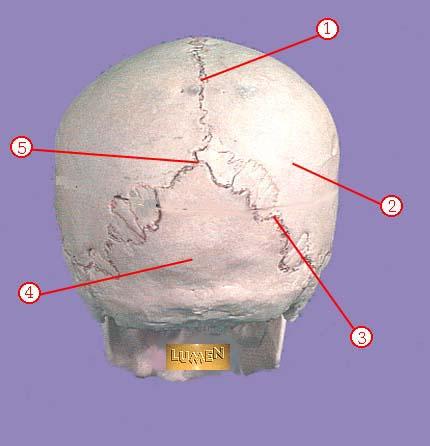 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #4 | back 323 occipital bone |
front 324 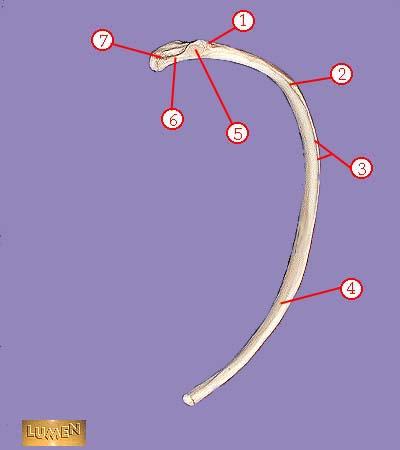 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #1 | back 324 tuberosity |
front 325 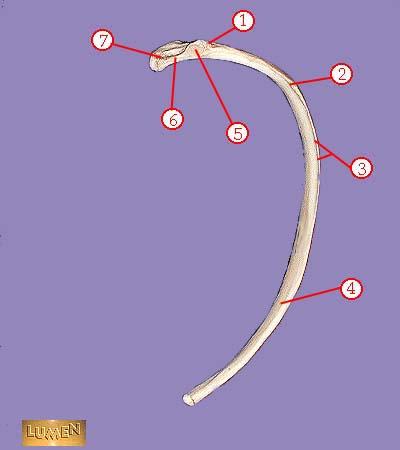 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #2 | back 325 angle |
front 326 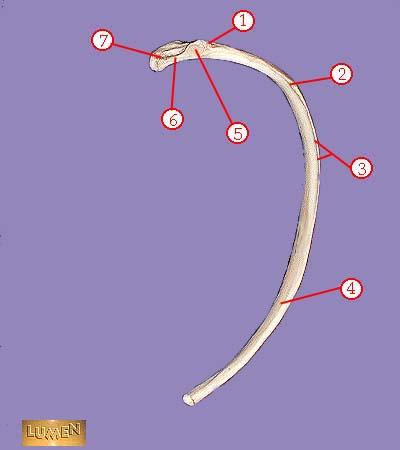 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #3 | back 326 subcostal groove |
front 327 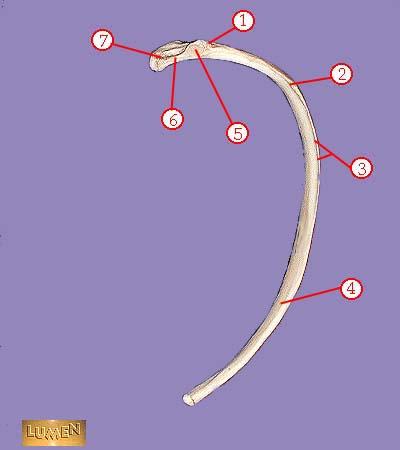 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #4 | back 327 body or shaft |
front 328 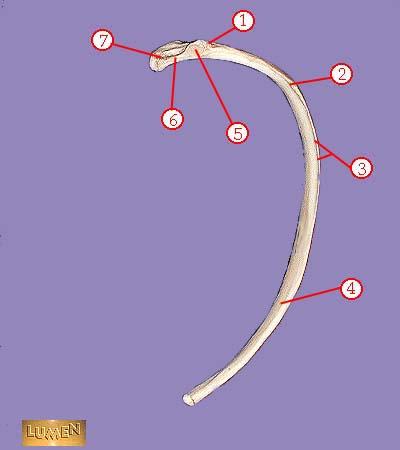 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #5 | back 328 articular part of tuberosity |
front 329 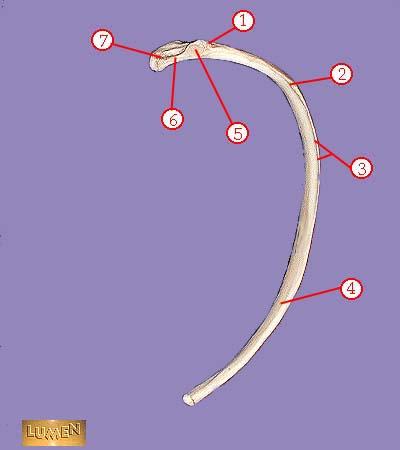 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #6 | back 329 neck |
front 330 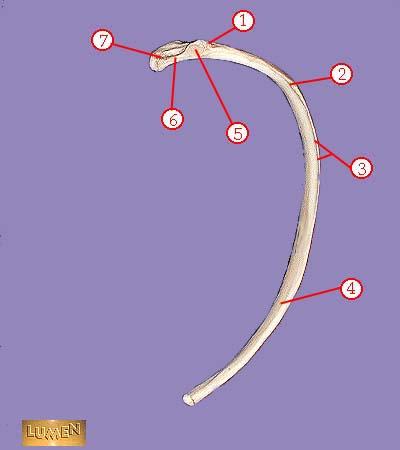 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #7 | back 330 head |
front 331 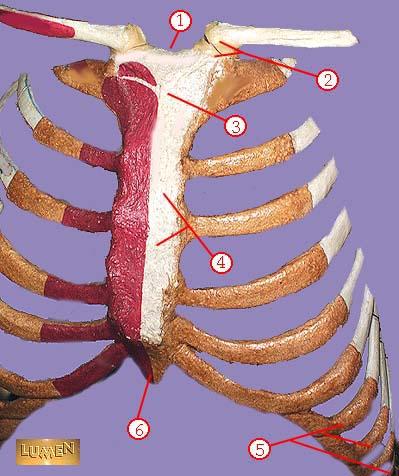 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #1 | back 331 sternal notch |
front 332 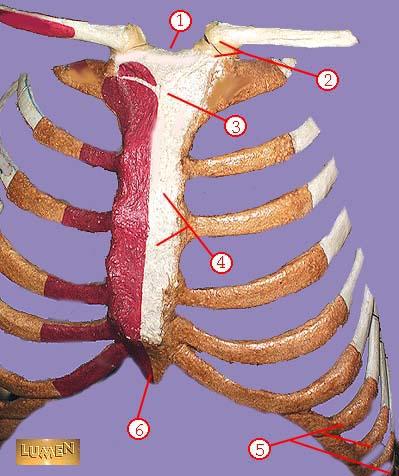 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #2 | back 332 sternoclavicular joint |
front 333 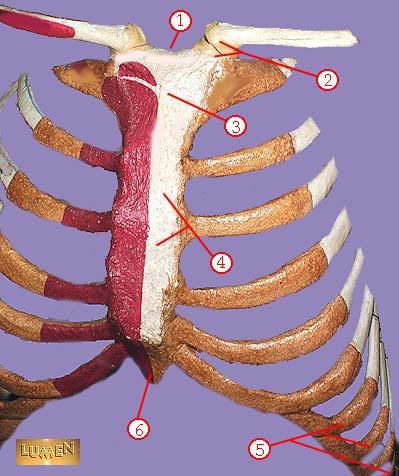 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #3 | back 333 manubrium |
front 334 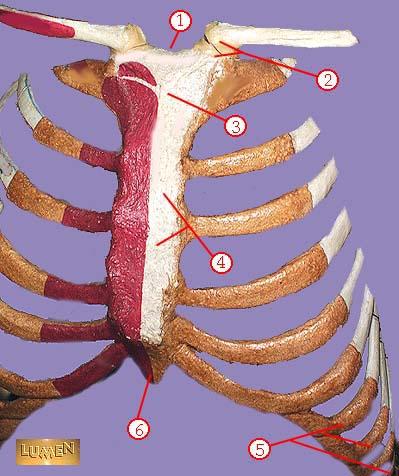 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #4 | back 334 body of sternum GLADIOLUS |
front 335 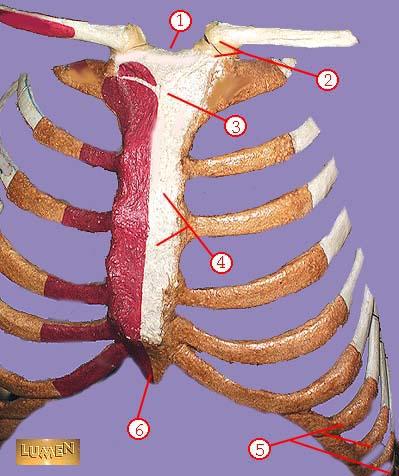 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #5 | back 335 false ribs |
front 336 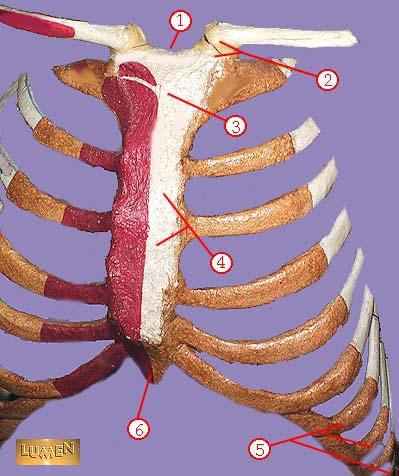 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #6 | back 336 xiphoid process |
front 337 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR # | back 337 no data |
front 338 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR # | back 338 no data |
front 339 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR # | back 339 no data |
front 340 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR # | back 340 no data |
front 341 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR # | back 341 no data |
front 342 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR #3 | back 342 no data |
front 343 The process when cartilage turns to bone | back 343 What is ossification? |
front 344 The place where two bones meet. | back 344 What is a joint? |
front 345 -composed of fibrous connective tissue
| back 345 tendon sheaths? |
front 346 Wraps entire muscle. Wrapped by Deep Fascia | back 346 Epimysium |
front 347 Bundles of muscle fibers (myofiber) | back 347 Fascicles |
front 348 Covers the fascicles (each BUNDLE of fibers) | back 348 Perimysium |
front 349 Covers every individual muscle fiber | back 349 Endomysium |
front 350 1) Direction of muscle fibers
| back 350 Naming Muscles (7) |
front 351 Origin vs Insertion | back 351 Origion: tendon attaching the muscle to the less movable bone is called the origin
|
front 352 tendon attaching the muscle to the less movable bone is called the | back 352 Origion |
front 353 tendon attaching to muscle to the MORE movable bone is called the | back 353 Insertion |
front 354 Paris of muscles that act against each other are called what? | back 354 Antagonists |
front 355 Muscles can't push, but they pull
| back 355 TRUE |
front 356 Sarcolemma vs Sarcoplasm | back 356 Sarcolemma: Cell membrane
|
front 357 Protein in muscle, stores oxygen. Unique oxygen binding protein...has a reddish pigment like blood. | back 357 Myoglobin |
front 358 Thousands of protein fibers that run in the length of the cell. Accounting for as much as 80% of the volume of the sarcoplasm
| back 358 Myofibril |
front 359 3 types of contractile proteins in Myofibril | back 359 1) Thinner filaments of actin
|
front 360 Location of mitochondria in the muscle | back 360 sarcoplasm |
front 361 --darker
| back 361 Dark A Bands |
front 362 --lighter
| back 362 Light I bands |
front 363 "muscle segment" is the region between two successive Z discs. The sarcomere is the smallest contractile unit of the muscle cell
| back 363 Sarcomere |
front 364 Factors that affect muscle action | back 364 Temperature
|
front 365 Biceps | back 365 Brachialis |
front 366 Canal leading ot eardrum and middle ear. | back 366 External auditory meatus |
front 367 WHAT IS THE CORRECT NAME FOR # | back 367 no data |
front 368 Needlelike projection inferior to external auditory meatus; attachment point for muscles and ligaments of the neck. This process os often broken off demonstrations. | back 368 Styloid process |
front 369 Rough projection inferior and posterior to external auditory meatus, attatchment site for muscles. | back 369 Mastoid process |
front 370 Tiny opening between the mastoid and styloid processes through which cranial nerve 7 leaves the cranium. | back 370 Stylomastoid foramen |
front 371 Opening medial to the styloid process through which the internal jugular vein and cranial nerves IX, X, and XIpass. | back 371 Jugular foramen |
front 372 Most posterior bone of cranium, forms floor and back wall. Joins sphenoid bone anteriorly via its narrow basioccipital region. | back 372 Occipital Bone |
front 373 Site of articulation of occipital bone and parietal bone. | back 373 Lamboid suture |
front 374 Large opening in base of occipital, which allows the spinal cord to join with the brain. | back 374 Foramen magnum |
front 375 Rounded projections lateral to the foramen magnum that articulate with the first cervical vertebra (atlas). | back 375 Occiptal condyles |
front 376 Bat-shaped portions of the sphenoid anterior to the sella turcica. | back 376 Lesser wings |
front 377 rregularly shaped bone anterior to the sphenoid. Forms the roof of the nasal cavity, upper nasal septum, and part of the medial orbit walls. | back 377 Ethmoid bone |
front 378 Vertical projection providing a point of attachment for the dura mater, helping ot secure the brain within the skull. | back 378 Cristi galli |