Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
lab 3rd test
front 1  | back 1 Agar plate orientation |
front 2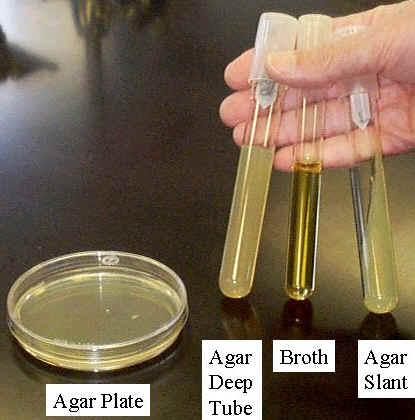  | back 2 Different medium |
front 3 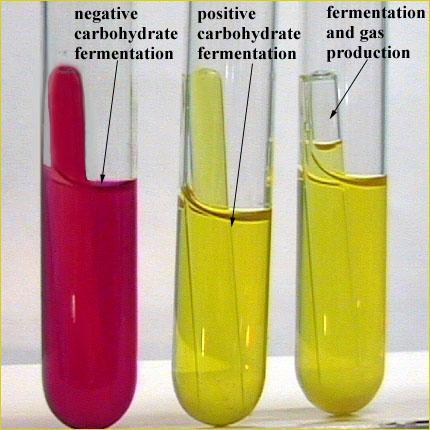 What type of tube is this? | back 3 Carbohydrate Fermentation tube Used to determine the ability to ferment carbohydrates (glucose,
lactose, mannitol, sucrose & maltose broths w/ phenol red
indicator) |
front 4 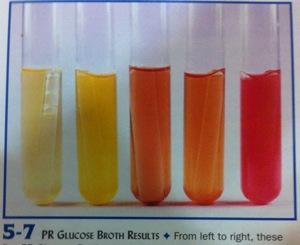 | back 4 Glucose (Carb. test) Left: Fermentation with acid & gas production (A/G) bubble in
tube |
front 5 IMViC | back 5 Methyl red, Voges-Proskauer, Indole and Citrate used to distinguish between members of the family Enterobacteriasea and differentiate them from other Gram-negative rods |
front 6  | back 6 Methyne red Mixed acid fermentation Left MR-positive (+) red / mixed acid fermentation Right MR-negative (-) no color change/ yellow / no mixed acid fermentation |
front 7  | back 7 Voges–Proskauer left VP- negative (-) / copper color at top means reaction of KOH and alfa-naphthol / no color change / no 2, 3 butanediol fermentation (no acetoin produced) right VP-positive (+) / red / 2, 3 butanediol fermentation (acetoin produced) |
front 8  | back 8 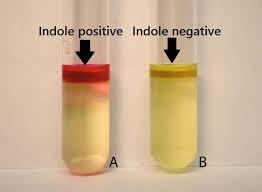 Indole Organism converts tryptophan to indole |
front 9  | back 9 Simmons Citrate slants Left tube: uses citrate (+) blue Simmons Citrate Agar-used to determine if capable of using citrate as the sole source of carbon w/ production of enzyme citratase. -Medium contains sodium citrate, ammonium salts & brom thymol
blue (pH indicator) |
front 10  | back 10 Nitrate Organism reduces NO3 --> NO2 |
front 11 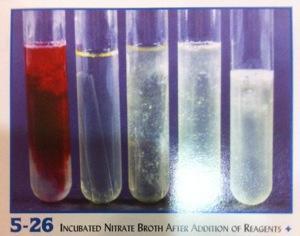 Nitrate. Reagents A+B added. Interpret tubes | back 11 Tube 1 (left): red, positive result. Nitrate reduced to
nitrite |
front 12 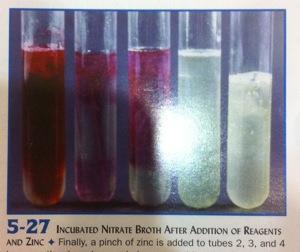 | back 12 Nitrate. +Zinc, interpret tubes 3, 4 Tube 3: red color indicates nitrate is still present. Negative
result. Organism does not reduce nitrate. |
front 13 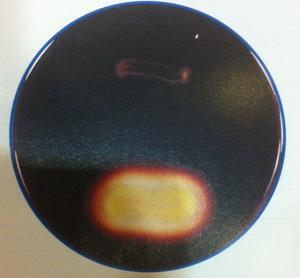 | back 13 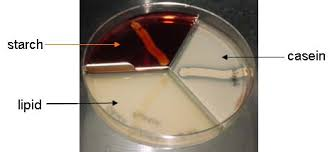 Starch Hydrolysis Top: no clearing, organism does not break down starch. Bottom: clearing in medium, organism breaks down starch (amylase is present) Microorganisms excrete hydrolytic extracellular enzymes in order to degrade starch Glucose That will be transported into the cell and use for energy production (Glycolysis) |
front 14 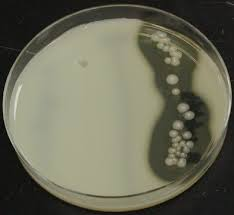 | back 14 Caesin Hydrolysis test Casein (proteases) Organisms producing proteases will show a zone of lipolysis (clear area surrounding the bacterial growth) |
front 15 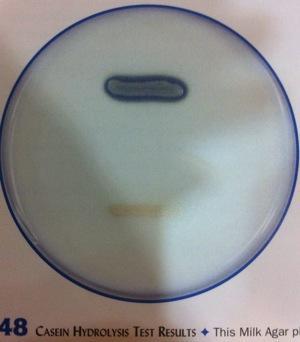 | back 15 Caesin Hydrolysis test Top: casease-positive (+) present of casease |
front 16 no data | back 16 Lipid Hydrolysis test Above lipase-positive (+) lipase present / clearing in agar around growth Below lipase-positive (-) absent of lipase / no clearing in agar around growth |
front 17 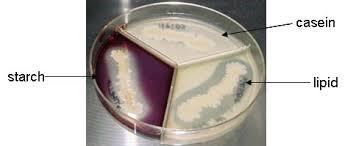 | back 17 Lipid Hydrolysis test Lipid ( tributyrin ) (lipases) Organisms producing lipases will show a zone of lipolysis (clear area surrounding the bacterial growth) |
front 18 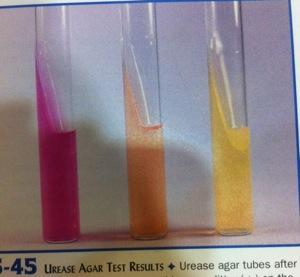 | back 18 Urea hydrolysis
Left urease-positive
(+) rapid urea splitter hydrolysis; strong urease production |
front 19 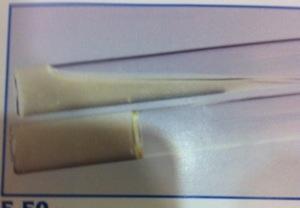 | back 19 Gelatin Hydrolysis test Top: liquid gelatin indicates gelatinase-postive (+) Gelatin is liquid (control is solid) Gelatinase is present in organism Bottom: solid gelatin indicates gelatinase-negative (-) Gelatin is solid. No gelatinase is present in organism Organisms producing proteases will show liquefaction of the gelatin, low temperatures of 4°C will not restore the gel characteristic. |
front 20  | back 20 SIM MEDIA TEST SULFUR POSITIVE vs Sulfur NegativeIndole Negative in both(Note: Indole indicator: Kovac) MOTILITY POSITIVE vs Motility Negative(Note: Motility Indicator: Stabline) |
front 21  | back 21
Sulfur reduction in
SIM medium Left No black in the medium / Sulfur is not reduced / H2 S-negative (-) Right Black in the medium / Sulfur reduced / H2 S-positive (+) |
front 22  | back 22 Indole test Left indole-negative (-) organism Reagent color is unchanged Tryptopha is not broken down into indole ad pyruvate Right indole-positive (+) organism / Red in the alcohol layer of Kovac's reagent. Tryptopha is broken down into indole ad pyruvate |
front 23  | back 23 Motility in SIM Left motile organism / Growth radiating outward from stab line Right nonmotile organism / Non radiating growth |
front 24  | back 24 Litmus milk Medium |