Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
MB: Quiz for Exam 4
front 1 Among the virulence factors produced by Staphylococcus aureus are hemolysin, coagulase, hyaluronidase, and enterotoxin. which of these factors contribute(s) to the ability of S. aureus to invade the body? a. hemolysin b. hyaluronidase c. coagulase d. enterotoxin e. coagulase and hemolysin | back 1 b. hyaluronidase |
front 2 Diseases that are induced by modern medical procedures are referred to as _____ infections. a. opportunistic b. endogenous c. iatrogenic d. subacute e. exogenous | back 2 c. iatrogenic |
front 3 The incidence of tuberculosis in the year 2000 in the United States was 12.43/100,000 cases. This means a. 12.43 of every 100,000 people died of tuberculosis in the U.S. in the year 2000 b. 12.43 in every 100,000 people in the United States had tuberculosis in the year 2000 c. 12.43 of every 100,000 cases of tuberculosis were treated in the United States in the year 2000 d. there were 12.43 new cases of tuberculosis for every 100,000 people in the United States in the year 2000 e. there were 12.43 tuberculosis bacilli per 100,000 microbes in the United States in the year 2000 | back 3 d. there were 12.43 new cases of tuberculosis for every 100,000 people in the United States in the year 2000 |
front 4 A strain of Neisseria gonorrhea has a mutation which has caused it to lose the ability to produce fimbriae and become less virulent as a consequence. What function has this pathogen lost? a. the ability to prevent phagocytes killing it b. the ability to establish a latent infection c. the ability to produce an endotoxin d. the ability to move from one location in the body to another e. the ability to adhere to cells of the body | back 4 e. the ability to adhere to cells of the body |
front 5 A new influenza strain appears and is spreading rapidly. What measures might be taken by public health agencies to stop the spread? a. Educate members of the public about ways to protect themselves b. Educate the public, promote vaccination, and treat those who are infected c. shut down public transportation d. identify and treat people who are infected e. facilitate access to vaccines | back 5 b. educate the public, promote the vaccination, and treat those who are infected. |
front 6 Which of the following statements is TRUE of eosinophils? a. they produce the coating of a pathogen by complement b. they secrete toxins onto the surface of helminth parasites c. they are in intact skin, sebum, tears, etc. d. they decline during allergic reaction e. they release prostaglandins and leukotrienes in response to microbes | back 6 b. they secrete toxins onto the surface of helminth parasites |
front 7 The role of dendrites in the adaptive immune response is to a. attack and destroy invading pathogens b. process endogenous antigens for presentation on MCH I molecules c. distinguish between endogenous and exogenous antigens d. detect autoreactive lymphocytes and trigger apoptosis e. degrade exogenous antigens for presentation on MHC II molecules | back 7 e. degrade exogenous antigens for presentation on MHC II molecules |
front 8 Pathogens may be attenuated for use in vaccines by a. genetic manipulation b. raising the pathogen for several generations on tissue culture cells c. treatment with formaldehyde d. genetic manipulation coupled with treatment with formaldehyde e. genetic manipulation and/or raising the pathogen for several generations in tissue culture cells | back 8 e. genetic manipulation and/or raising the pathogen for several generations in tissue culture cells |
front 9 An infectious disease researcher isolates the pathogen responsible for an emerging disease. The microbe is grown in the lab for many generations. A preparation of the laboratory-grown microbe is treated with ionizing radiation and then tested for its potential as a vaccine. What type of vaccine is this? a. attenuated b. toxoid c. combination d. subunit e. inactivated whole | back 9 e. inactivated whole |
front 10 monoclonal antibodies can be used for a. labeled antibodies in immunoassays b. passive immunization c. active immunization d. passive immunization and labeled antibodies in immunoassays e. active immunization and agglutination assay reagents | back 10 D |
front 11 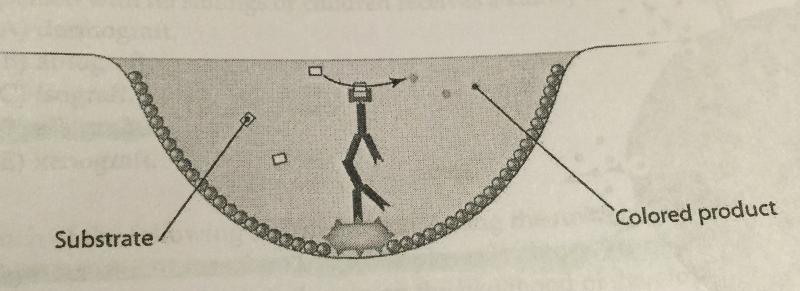 Which type of antibody assay is represented in this figure? a. a direct ELISA b. a western blot c. an immunodiffusion assay d. an indirect ELISA e. an indirect immunofluorescence assay | back 11 D |
front 12 which of the following is NOT considered a hypersensitivity reaction? a. immune system attack on the thyroid gland b. itchy eyes and a runny nose in a dusty environment c. a rash caused by poison ivy d. dermatitis at the site of a metal watchband e. breaking into hives after eating strawberries | back 12 A |
front 13 which of the following immunoglobulins is produced by plasma cells in response to an allergen? a. IgA b. IgG c. IgD d. IgM e. IgE | back 13 E |
front 14 The redness, swelling and itching of urticarial is due to _____ release. a. leukotriene b. kinin and protease c. protease d. histamine e. kinin | back 14 D |
front 15 Which of the following could result in hemolytic disease of the newborn? a. Rh-positive mother and Rh-negative father b. Rh-negative mother and Rh-negative father c. Rh-positive mother and Rh-positive father d. Rh-negative mother and Rh-positive father e. either Rh-positive mother and Rh-negative father or Rh-negative mother and Rh-positive father | back 15 D |
front 16 Which of the following statements concerning rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is TRUE? a. Accumulations of antibody complexes lead to inflammation in and destruction of the joints b. there is no genetic influence on the likelihood of developing RA c. it occurs in humans and animals d. the symptoms are due to damage caused by cytotoxic T cells e. the onset of disease is clearly correlated with having been infected with a specific microbe | back 16 A |
front 17 Biological (sources/vectors/carriers) not only transmit pathogens, but also serve as hosts for the manipulation of the pathogen during some phase of the pathogens life cycle. a. Sources b. Vectors c. Carriers | back 17 B. Vectors |
front 18 The hepatitis C virus normally establishes a (latent/ chronic/ subclinical) infection and may be asymptomatic for a decade. a. latent b. chronic c. subclinical | back 18 a. latent |
front 19 The large population of pathogenic microbes found in health care settings contribute to ______ infections. a. nosocomial b. iatrogenic c. epidemic | back 19 a. nosocomial |
front 20 A new influenza strain appears and is spreading rapidly. what measures might be taken by public health agencies to stop the spread? | back 20 educate the public, promote vaccination, and treat those who are infected |
front 21 The condition called parasitism is characterized as a | back 21 relationship between two organisms where one member harms the other |
front 22 the condition known as microbial antagonism may be defined as | back 22 an unsuccessful microbial invasion due to the presence of preexisting microbes |
front 23 which of the following combinations of pathogen and virulence factor is correct? | back 23 Streptococcus pyogenes and protein M |
front 24 Treatment with high doses of antibiotics may lead to which type of nosocomial infection? | back 24 endogenous infection |
front 25 which of the following is the correct sequence of a disease process? a. incubation, illness, convalescence, prodromal period, decline b. incubation, prodromal period, illness, decline, convalescence c. prodromal period, incubation, illness convalescence, decline | back 25 incubation, prodromal period, illness, decline, convalescence |
front 26 The incidence of tuberculosis in the year 2000 in the U.S. was 12.43/100,000 cases. this means | back 26 there were 12.43 new cases of tuberculosis for every 100,000 people in the U.S. in the year 2000 |
front 27 Ribozymes are required for: a. translation b. RNA splicing c. Capping d. both translation and RNA splicing e. capping, RNA splicing. and translation | back 27 D |
front 28 Probes used for detecting genetic sequences are frequently composed of: a. plasmids with a marker sequence b. silicon chips c. synthetic nucleic acids and labeled conjugates, such as fluorescent dyes d. gold beads coated with DNA | back 28 C |
front 29 Sigma factors are involved in the regulation of bacterial: a. translation b. transformation c. DNA replication d. transcription e. mutation repair | back 29 D |
front 30 How are fungal viruses different form viruses that infect other organisms? a. they cannot pass through a filter b. they have only DNA for genetic material c. they have no extracellular state | back 30 C |
front 31 Host specificity of a virus is due to: a. articular genes that it shares with the infected cell b. differences in size between the viruses and the host cell c. interactions between viral and cellular surface molecules d. the presences of an envelope | back 31 C |
front 32 Which of the following is/are common to chemiosmosis and the light-depended reactions of photosynthesis? a. electron transport only b. reduction of NADP+ only c. a protein gradient only d. both electron and a protein gradient | back 32 D |
front 33 Several antiviral medications used to treat HIV interference on its: a. cell wally synthesis b. assembly of membranes c. nucleic acid synthesis d. folic and synthesis e. protein synthesis | back 33 C |