Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Respiratory Therapy, Chapter 6 (Exam #4)
front 1 Define Humidity. | back 1 are individual molecules in a vapor or gaseous state. It's can not transmit bacteria. |
front 2 Define absolute humidity. | back 2 The actual content or weight of water present in a given volume of gas content. - It is recorded as g/m3 or mg/L |
front 3 What happens to the AH (absolute humidity) when the temperature increases? | back 3 The AH goes up as well. |
front 4 What does AH equal? | back 4 AH= 44 mg/L |
front 5 What is water vapor pressure? | back 5 47 mmHg |
front 6 Define Relative Humidity. | back 6 It is the ratio of content to capacity. |
front 7 What is the formula for RH? | back 7 Measured Humidity Content / water capacity X 100 |
front 8 What causes condensation? What must be used to prevent aspiration in patients? | back 8 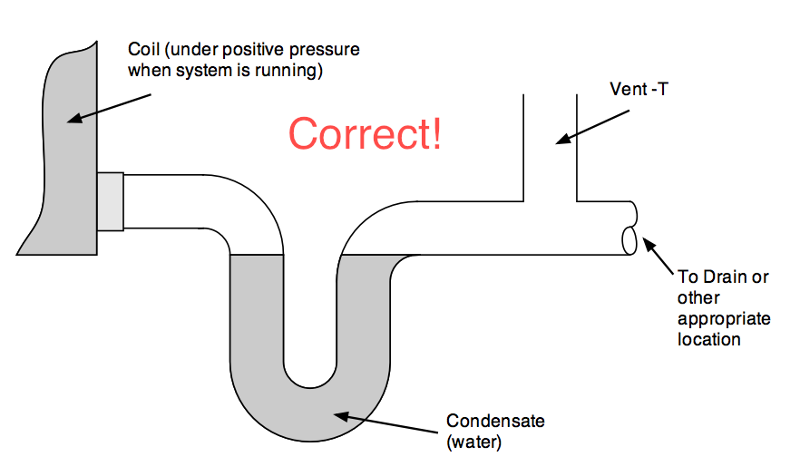 Condensation occurs when temperature decreases and gas can't hold as much moisture anymore. The moisture falls out of suspension. Because water tends to pool at the lowest point in the tubing, a water trap is required to prevent patients from aspirating this water. |
front 9 Define Body Humidity. | back 9 It is the maximum amount of water that can be held at body temperature. |
front 10 What formula can you use to solve for Body humidity? | back 10 Content MG/L / water capacity X 100 |
front 11 Define Humidity deficit | back 11 The difference between the actual water content and body humidity |
front 12 What is the formula for HD? | back 12 Body Humidity - Ambient (what the device is giving) = HD |
front 13 Where is isothermic saturation boundary? | back 13 It is 5 cm below carina |
front 14 What symptoms does an intubated patient with no humidity experience? | back 14 They experience dried out lungs and inspissated secretions. The reason why is because The lungs provide the humidity and moisture to the airways instead. At the carina, the temp: 30 , RH: 95% aand AH: 30.4 mg/L |
front 15 What are 4 results of long standing Humidity Deficit? | back 15 1. Airway Drying 2. Retention of secretions 3. Airway plugging 4. Increased chance of infection |
front 16 What are some clinical signs and symptoms of inadequate humidification? | back 16 1. Atelectasis 2. Dry, non productive cough 3. Thick dehydrated secretions 4. Increased RAW 5. Increase chance of infection 6. Substernal Pain |
front 17 What is the overall goal of Humidity Therapy? | back 17 To minimize of eliminate the humidity deficit while the patient is breathing a dry, medical gas. (basically in order to provide 100% humidity at body tempt) |
front 18 What is meant by invasive mechanical ventilation? List some examples of two airways that provide this? | back 18 Intubation. ETT, or tracheostomy. |
front 19 What is noninvasive ventilation.? | back 19 Ventilation without entering the body. |
front 20 What is another name for noninvasive ventilation? | back 20 CPAP or BPAP |
front 21 What is meant by the term active humidification? | back 21 Active humidification increase heat and moisture of inspired gas, like a Wicks Humidifier, |
front 22 What is meant by the term passive humidification? | back 22 Passive Humidification takes patients exhaled gas and utilizes it |
front 23 What is the recommendation for humidification for patients on invasive mechanical ventilation? | back 23 Humidification is recommended for all patients on invasive mechanical ventilation |
front 24 What type of humidification is recommended for noninvasive mechanical ventilation? | back 24 Active humidification is recommended because it improves adherence and patient comfort. |
front 25 What level and type of humidification is recommended for invasive mechanical ventilation. | back 25 Recommendation is 33-44 mgH20/L of water at 34-41 degree celcius at the WYE piece and 100% room humidity. |
front 26 What do they recommend if you are using passive humidification on invasive mechanical ventilation? | back 26 An HME which must provide a minimum of 30 mgH20/L |
front 27 What type of humidification is NOT recommended for noninvasive ventilation? | back 27 An HME because it collects dead space. |
front 28 If your patient is receiving a lung protective strategy, what type of humidification is not recommended? | back 28 Heat and moisture exchanges. |
front 29 Should HME's be used as preventative strategy for vap? | back 29 NO. |
front 30 Name one type of low flow active humidifier? | back 30 bubble humidifier. |
front 31 Name two types of high flow active humidifiers? | back 31
|
front 32 Name on type of high flow passive humidifier? | back 32 HME |
front 33 What does a bubble humidiifer deliver at flows < 5 L/M? | back 33 It delivers flows of 10-20 mg/L and 20% RH at BTPS |
front 34 What is the purpose of a diffuser? | back 34 To create more bubbles = more surface area |
front 35 What are 4 factors that increase the effectiveness of a humidifier? | back 35 1. The surface area 2. The temperature 3. The time of contact 4. The thermal mass |
front 36 At what psi will the pop off alarm activate at? (W/ a bubble humidifier? | back 36 2 psi |
front 37 A bubble humidifier can only be attached to _______ bore tubing. | back 37 small |
front 38 When is active High Flow Humidity devices used? | back 38 They are used when supplying all the inspiratory gas to intubated or trached patients. |
front 39 What is the recommended min humidity for these devices? | back 39 33 mg H20/L |
front 40 Active High Flow Humidity devices can only be attached to _______ bore tubing. | back 40 large. |
front 41  What is shown? | back 41 A fisher & paykel passover humidifier that may or may not contain a heated wire circuit. It provides 100% RH at various temperatures. |
front 42 There are three common types of passover humidifiers, describe the first, simple reservoir models. | back 42 Simple reservoirs direct gas over the surface of a volume of water. These are used to provide heated humidified gases during mechanical ventilation. Fisher and Paykel heated humidifier is an example. |
front 43 Describe Wick Units. | back 43 On a wick humidifier, gas passes over or through water saturated material.No bubbling or aerosol is produced, As dry air enters the chamber, it flows around the wick, quickly picking up heat and moisture, leaving the chamber fully saturated with water vapor. Hudson RCI ConchaTherm IV is an example. |
front 44 Describe membrane devices: | back 44 The water is separated from the gas steam by a hydrophobic membrane. Water vapor molecules can pass, but liquid water and pathogens can not. Bubbling and aerosol dont happen. Vapotherm 2000i is an example. |
front 45 What is an open humidity system? | back 45 a system that physically needs to be opened and filled with sterile water. |
front 46 What are some problems that can occur with this type of system? | back 46
|
front 47 Describe a Manual system and its disadvantages. | back 47 A manual system refill simple large reservoir systems with sterile or distilled water. However, manually refilling can:
|
front 48 Describe a Gravity (continuous) feed system and its advantages. | back 48 A small inlet port in the wall of the humidifier chamber attached to a gravity feed-fed water bag allows refilling w/o interrupting ventilation. |
front 49 What must you still do with these systems? | back 49 These system still require constant checking and manual replenishment. If not checked regularly, the reservoir in these systems can go dry, placing the patient at risk. |
front 50 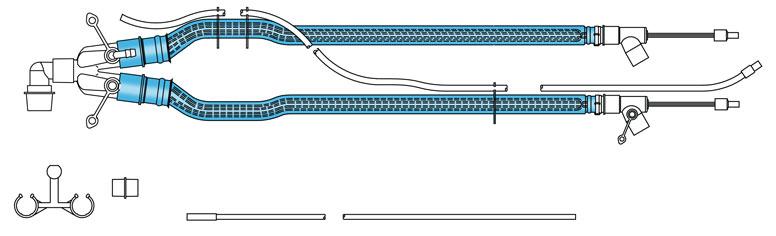 What is shown and what is it's function. | back 50 Heated Wire Circuit. It functions in decreasing rainout/condensation with a humidifier. If this technology is not used, a water trap should be. |
front 51 What happens if the Heated Wire Circuit is warmer than the humidifier outlet? | back 51 Gas will not be fully saturated and a humidity deficit will occur. |
front 52 What are 3 reasons why not using a water trap may be a problem? | back 52
|
front 53  What is shown? | back 53 Vapor Transfer Cartridge |
front 54  What is shown? | back 54
Disposable water path & delivery tube |
front 55  Describe Vapotherm Precision Flow. How much RH does it provide? Mg of water? Tempt range? | back 55 Molecular water passes into gas stream without direct contact between the two. It utilizes shortened nasal cannula or may be used with other devices such as a transtracheal catheter or CPAP.) Provides 95-100% RH Provides up to 55 Mg H20/ L Tempt range of 33-43 degrees celcius |
front 56 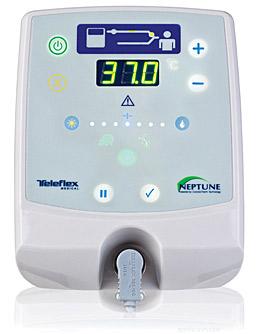 What is shown? List its functions. | back 56 ConchaTherm humidification system
|
front 57 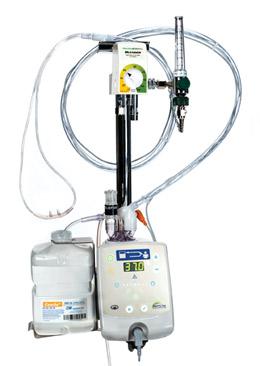 What is shown? | back 57 Hudson RCI comfort flo humidification system. |
front 58 What is shown? Describe. | back 58 HME are classified as passive humidifiers. They capture exhaled heat and moisture and use it to heat and humidify the next inspiration, |
front 59 Which patients are HME's used for? | back 59 They are used for short term spontaneously breathing mechanically ventilated patients with endotracheal and tracheostomy tubes. Best used for:
|
front 60 What is the theory behind HME? | back 60 That the exhaled gas contains 100% RH at 37 degrees Celsius . |
front 61 What are the ISO standards for these devices? | back 61 They must be used on mechanically ventilated patients. |
front 62 In general, what amount of humidity does this device provide? | back 62 10-31 mgH20/L at 30 degrees C needs to be at least 70% efficient. |
front 63 What happens to the devices resistance when it is wet? (HME) | back 63 it increases the resistance and causes the patients WOB to increase. |
front 64 Why are HME not recommended for infants? | back 64 Because they add 30-90 mL of dead-space, often exceeding the Vt of a 5 kg infant. uncuffed ETTs in small infants allow a potion of exhaled gas to leak around the tube, bypassing the HME and reducing its ability to capture exhaled heat and moisture and utilize it. |
front 65 What do you do if a ventilator patient has an HME in place and needs a nebulizer or MDI treatment? | back 65 You remove the HME because the medicine will become clogged in the device. |
front 66  What is shown? | back 66  A gibeck humid-flo HME. Which has an average humidity output over 72 hours. (30.7 mgH2O/L) |
front 67  What is shown? Describe the benefits? | back 67 An active device: King System HME booster which has a hydrophobic membrane which is semi permeable to water. It supposed to last 3 days by adding water into the system. However, it adds more dead space and weight which makes the device susceptible to |
front 68 How is water incorporated in the system? | back 68 Water is fed to the heater through a gravity feed solution bag. |
front 69 How much does the Vt deliver with 500 ml? | back 69 36-39 mgH20/L |
front 70 How much does the Vt deliver with 1000 ml? | back 70 34-36 mgH20/L |
front 71 What are some contraindications for HME use? | back 71 1. Not to be used on Pt with thick and bloody secretions 2. Pt with Vt < 70% 3. Pt's with low Vt cant use HME because they contribute to additional dead space. 4. Pt's with body temps > 32 degrees C 5. Pt's with VE > or equal to 10 L/M 6. Noninvasive ventilation with large air leaks |
front 72 What are the indications? (of HME) | back 72 Mandatory to be used with endotracheal and tracheostomy tube patients. |
front 73 What are the hazards? (of HME) | back 73
|
front 74 What do you need to monitor with an HME? | back 74
|
front 75 What is the definition of an aerosol? | back 75 Solid or liquid particles suspended in a gas. |
front 76 What can be measured with aerosols? | back 76 You can measure and count particles. |
front 77 What can you see with aerosols? | back 77 The mist produced. |
front 78 What should you do if you see that a mist is not being produced during inhalation and what does this mean? | back 78 This means that the patient is not getting adequate aerosol treatment. You should turn up the liter flow in this case. |
front 79 What can transmit bacteria? | back 79 Aerosols/ |
front 80 What percentage is normal saline? | back 80 0.9% |
front 81 What percentage is hypotonic? | back 81 <0.9% |
front 82 What percentage is hypertonic and what is it used for? | back 82 >0.9%. It's used to induce sputum samples by making the airways extra moist, |
front 83 What are three uses of bland aerosol therapy? | back 83 1. To humidify dry medical gases 2. Sputum induction 3. Decrease airway edema |
front 84 What are 5 hazards of bland aerosol therapy? | back 84 1. Cross contamination 2. Over hydration 3. Airway irritation = Bronchospasm 4. Inadequate mist production 5. Swelling of secretions or airway obstruction due to swollen mucus |
front 85 What is the special consideration for pedi patients? | back 85 Bland aerosol therapy is quiet, unlike LVN which are loud. |
front 86 What is the definition of MMAD | back 86 Mass Median Aerodynamic Diameter |
front 87 What does MMAD do? | back 87 It divides so that half are larger and half are smaller |
front 88 Particles are measured in ________. | back 88 microns. |
front 89 What size particles are exhaled? | back 89 <1 micron particles. |
front 90 Decrease the particle size and you _______where it deposits in the lungs. | back 90 increase. |
front 91 What 4 things effect Aerosol deposition? | back 91 1. Gravity/ sedimentation 2. Inertial impaction 3. Aging 4. Diffusion |
front 92 Larger, less stable particles deposit in the ___________. These particles are ____________. | back 92 central airways. 1-5 microns. |
front 93 Inertial impaction happens with high inspiratory flows greater than what? What size particles does this usually happen with? | back 93 Flows >30 L/M ( like when a patient takes a fast breath in, all it does is cause the particles to hit the back of the throat and settle there, defeating the purpose. The patient has to take a slow breath in so the particles can reach the desired destination.) This usually happens with >5 microns. |
front 94 What does aging cause particles to do? | back 94 Aging causes particles to grow and shrink and fall out of suspension over time. Small particles grow and shrink faster than large particles. |
front 95 What does diffusion causes particles <3 microns to do? | back 95 It causes particles to deposit in respiratory region, adjacent to alveoli because they have low mass. |
front 96 What size particles does Antibiotics need to have? | back 96 They have to have small particles so that they can reach the alveoly. |
front 97 What size particles do bronchodilators need to have? | back 97 Bronchodilators need 3-5 micron particle size so that they reach the small airways and not into the alveolus. |
front 98 What is the best breathing pattern to increase aerosol penetration? | back 98 A slow breath in, hold the breath to allow it to settle in the airways for 4-10 seconds |
front 99 What device should you use for medicated aerosol? | back 99 A mouthpiece. |
front 100 State whether they are used to deliver Humidity Therapy, Aerosol Therapy or both. Aerosol Mask. | back 100 Only delivers Humidity Therapy. |
front 101 State whether they are used to deliver Humidity Therapy, Aerosol Therapy or both. Face tent. | back 101 Can deliver Both. |
front 102 State whether they are used to deliver Humidity Therapy, Aerosol Therapy or both. Tracheostomy Collar | back 102 Both. |
front 103 State whether they are used to deliver Humidity Therapy, Aerosol Therapy or both. Briggs Adapter (T piece) | back 103 Both. |
front 104 State whether they are used to deliver Humidity Therapy, Aerosol Therapy or both. Mouthpiece. | back 104 Aerosol Therapy only. (specially for medicated aerosols.) |
front 105  What is shown? What doesn't this device have? | back 105 An Atomizer. It's missing a baffle. |
front 106 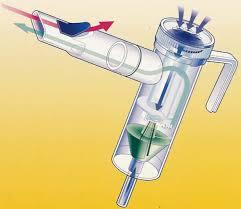 What is shown? | back 106 A large volume nebulizer with a baffle. |
front 107 What 3 things can act as a baffle? | back 107 1. The fluid surface 2. Sides of the container 3. Device in the gas stream |
front 108 By what principle do LVN (jet nebulizers) work? | back 108 They work on the bernoulli principle to produce aerosol. Gas exits a restriction due to the lateral pressure being less than the atmospheric fluid drawn up through the capillary tube. Fluid is then shattered into small particles. |
front 109 What happens if a baffle is in place in a LVN? | back 109 iF A BAFFLE IS IN PLACE YOU GET DECREASED AND MORE UNIFORMED PARTICLE SIZES. |
front 110 What are LVN most used for? | back 110 Bland aerosol Therapy. They are used to get a sputum sample. In order to do so you would need large particles to rain out in the upper airways. |
front 111 What can LVN deliver? | back 111 They can deliver flows 26-35 mh H2O/L, and can entrain room air with specific FiO2's. If you want to change the FiO2 you need to change the collar. remember, liter flow DOES NOT effect FiO2. |
front 112 What happens if water is in the corrugated tubing? | back 112 Water creates backpressure and doesn't allow the device to entrain room air. more fluid = higher FiO2, decreasing the total flow. A water trap should be used. |
front 113 What do bland Aerosols require? | back 113 A water trap to prevent aspiration. |
front 114 What happens to total flow and FiO2 if water is in the tubing? | back 114 total flow decreases, FiO2 increases |
front 115 What happens to total flow and aerosol density as you increase FiO2? | back 115 Total flow decreases, aerosol density increases(meaning more density produced.) |
front 116 With a __________ device you must deliver all the inspiratory needs of a patient or the patient will inhale room air and the FiO2 will decrease. | back 116 High Flow |
front 117 When must you use a double flow set up? | back 117 For FiO2's >50% |
front 118 What FiO2 should you set each nebulizer at on a double flow set up? | back 118 You would set it at the same FiO2 for both. (as well as the same liter flow for both) |
front 119 What is the total flow of a 100% double flow set up running at 15 LPM? | back 119 30 L/M. Remember, each flow meter is set at the same liter flow, so you multiply 15 x 2. |
front 120 High Flow Nebulizers requires ______ gas flow sources. | back 120 two |
front 121 High flow nebulizers offers flows from? | back 121 40-110 L/M |
front 122 High flow nebulizers have _____ mm fitting so device can attach to sterile water bottles. | back 122 38 |
front 123 High flow nebulizers use _______ gas to drive the nebulizer and _________to nebulizer o increase flow to > 40 LPM. | back 123 primary, add gas |
front 124 For 21-50% oxygen, you connect to ________ and inject _________/ | back 124 Room air, Oxygen |
front 125 For 50-100% oxygen, you connect to ________ and inject ______________. | back 125 Oxygen, Room air |
front 126 Describe what High flow set ups use? | back 126 They use a humidifier and a blender to deliver high flows at a specific oxygen concentration. |
front 127 What is the advantage of high flow set ups? | back 127 It is much quieter and supplies heated air if hypothermia is an issue. |
front 128 What is the goal of medicated Aerosol Therapy? | back 128 To deliver a therapeutic dose of medication to the desired site of action.. |
front 129 What is the most common use of aerosol therapy? | back 129 Medicated aerosol |
front 130 What are three advantages of Medicated Aerosol? | back 130 1. Delivers where it needs to work 2. Decreases systemic side effects. 3. Rapid absorption and onset of action. |
front 131 What are 6 hazards of medicated aerosols? | back 131 1. Reaction to medicine 2. Infection 3. Bronchospasm 4.Drug concentration changes 5. Eye irritation 6. Exposure to secondhand aerosol |
front 132 What type of aerosol has a filter to protect RT's from secondhand inhalation? | back 132 Respiguard Aerosol. |
front 133 Small Volume Nebulizers have a ______mL reservoir tube that helps increase aerosol deposition. The average MMAD is __________microns. | back 133 50, 1-5 |
front 134 How much medication actually gets delivered to the patient? | back 134 only 10%. A SVN is very inefficient, it nebulizes when the patient is inhalation and exhaling, causes medication to be lost. |
front 135 2-5 microns for ______________________. | back 135 airway depostion. |
front 136 2-5 microns are best for what? | back 136 Bronchodilators and steroid. |
front 137 1-2 microns for ______________. | back 137 parenchymal deposition. |
front 138 1-2 microns are best for what? | back 138 Antibiotics. |
front 139 How full should a SVN be? | back 139 4-5 ML |
front 140 What is dead space volume? | back 140 Amount of volume that can't be nebulized. |
front 141 What liter flow should you use for SVN? | back 141 8 L/M |
front 142 Describe how you would disinfect a SVN at Home? | back 142 You would soak the parks in a 1:3 ratio of water and white vinegar for at least 30 mins.A final rinse should be used with plain tap water. Parts should be disinfected 1-2x per week. |
front 143 How far from the patient should you place a SVN? | back 143 Place 18 inches from the patients airway and 6 inches from the patients WYE. |
front 144 How should SVN be used on mechanical ventilation? | back 144 It should only nebulize on inspiration and use the same oxygen concentration as patient. |
front 145 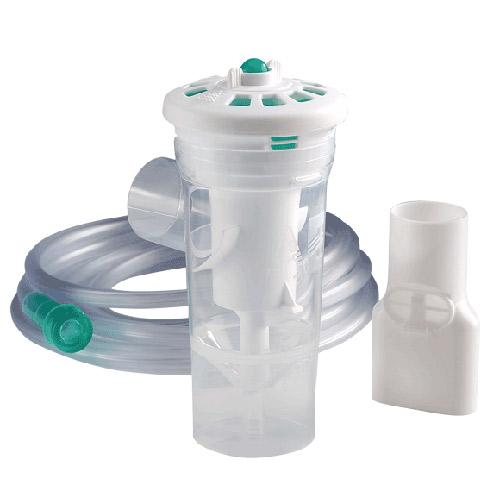 What is shown? Describe it. | back 145 Breath Actuated Nebulizer. (BAN) which only nebulizers on inspiration which eliminates the waste of medicine, increases delivered doses (3x greater than other nebs) and decreases treatment time and number of treatments needed. Con: It cost more. |
front 146 When would a BAN be most likely used? | back 146 In an emergency setting, for short term use since its expensive. It needs to be used with a mouthpiece. |
front 147 Describe BENs (Breath Enhanced Nebulizers.) | back 147 They generate Aerosol continuously. Increasing delivered dose over simple medication nebs and decreases aerosol waste. |
front 148 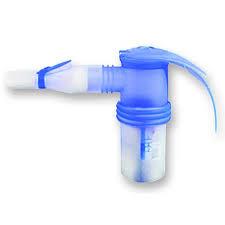 What is shown? Describe how it works? Where would this device be used in? | back 148 A Pari Jet Sprint Nebulizer. 1. Air from the compressor breaks down liquid medication into smaller breathable particles which form a mist. 2. As patient inhales, the valve at the top opens, letting air in and speeding up mist generation. 3. As patient exhales, the top valve closes, slowing down mist production. the mouth flap opens, letting the patients breath out. Device would be used in a home setting. |
front 149  What is shown? | back 149 A NebuTech HDN |
front 150 Describe A NebuTech HDN | back 150 It can be used with a mouth piece or mask. It uses 8 L of flow. |
front 151 If using a mask with the NebuTech HDN, you move the green valve from _______ to ________ port. | back 151 top, side |
front 152 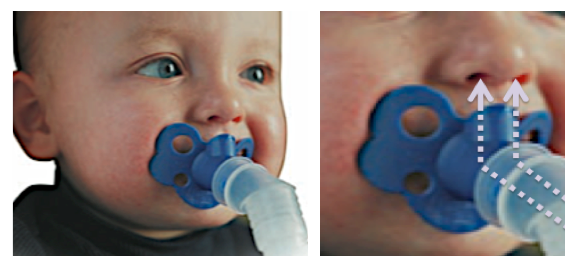 What is shown? | back 152 A PediNeb |
front 153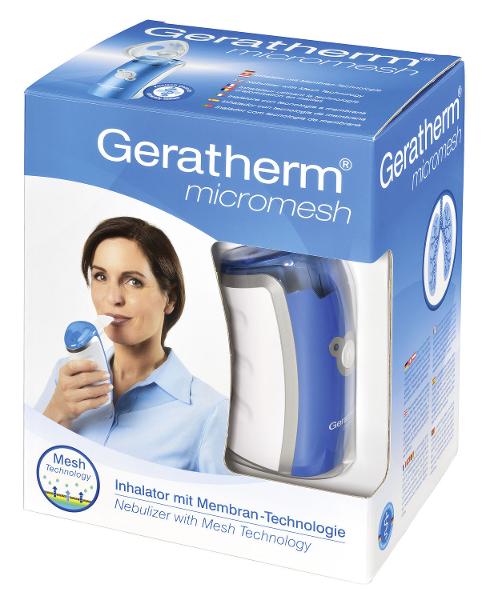  What are the advantages of Vibrating Mesh Technology? | back 153 
|
front 154 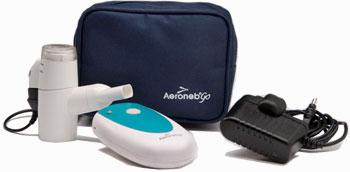 What is shown? What is the average particle size that it produces? It's med cup capacity? | back 154 AeronebGo It's average particle size is 3.1 microns MMAD It's medication cup capacity maximum is 6 ml |
front 155 What is an aeronebgo mainly used for? | back 155 used as a bronchodilator therapy. |
front 156 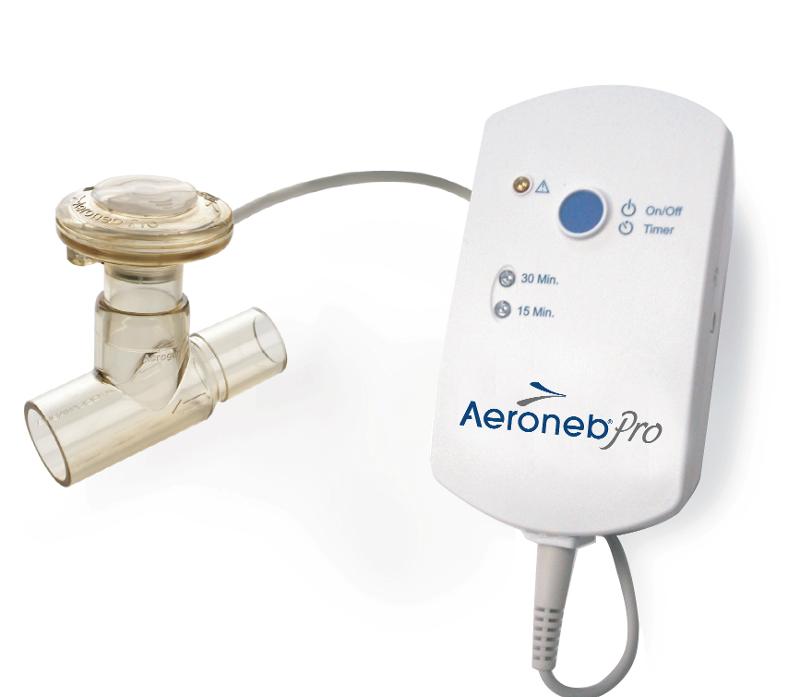 What is shown? What is used for | back 156 An Aeroneb Pro X Can be used with a ventilator or with a mouth piece for spontaneously breathing patients |
front 157 Where can an Aeroneb Pro X be used? | back 157 In an emergency room to stop an asthma episode and prevent future treatment. Also can be used for continuous bronchodilator therapy, can be hooked up right before the patients humidifier. |
front 158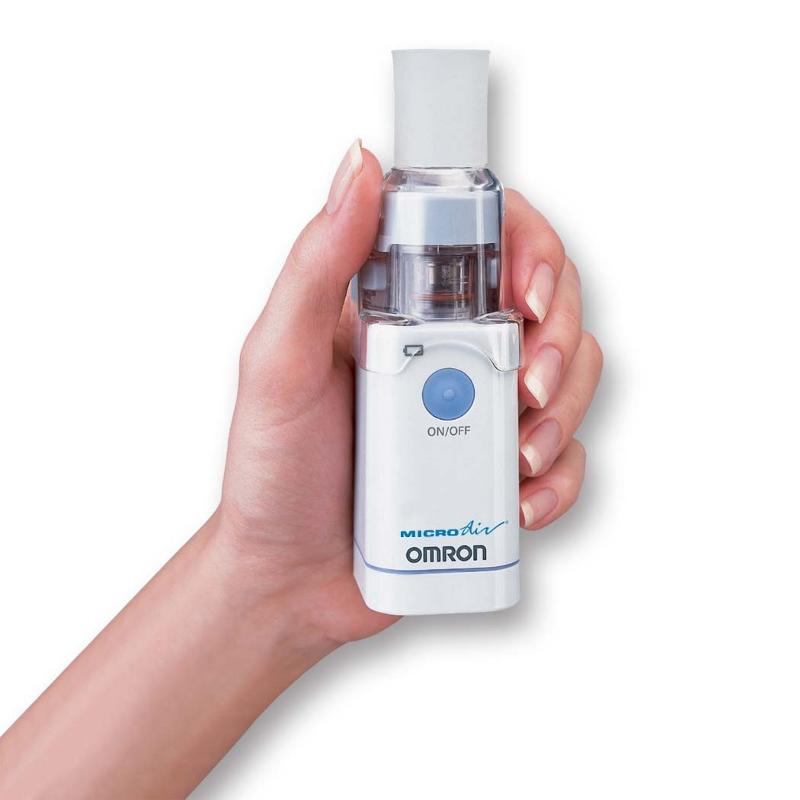  What is shown? How many treatments can it provide? | back 158 MicroAir Uses 2 AA batteries and provides 40 treatments. |
front 159 What patients benefit from a MicroAir? | back 159 Patients who are unable to use MDI's, DPI's, and who are out and about. |
front 160 What are 4 engineering controls that may be utilized to reduce exhaled aerosols? | back 160 1. Place patient in environmental chamber with HEDA filter 2. Use exhalation filter (like respiguard) 3. Place in a negative pressure room (or wear Hepa masks) 4. Use BAN nebulizers |
front 161 Where would you put a patient with tuberculosis? | back 161 In an environmental chamber with hepa filters in order to trap small sized particles. |
front 162 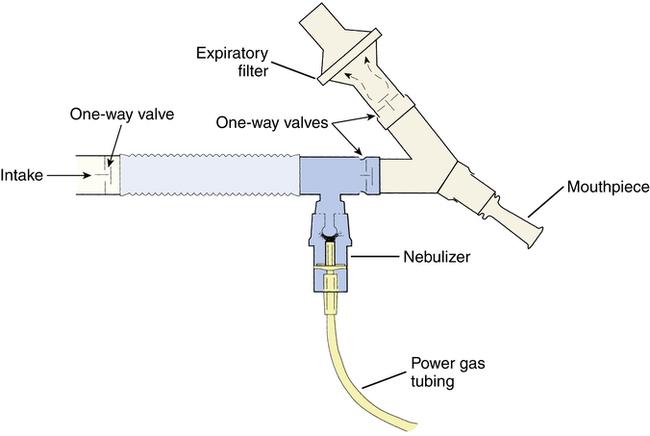 Describe Respirguards filters | back 162 They are used for pentamadine delivery and use one way valves to make particles smaller and protect the practitioner, This filter provides the protection, |
front 163 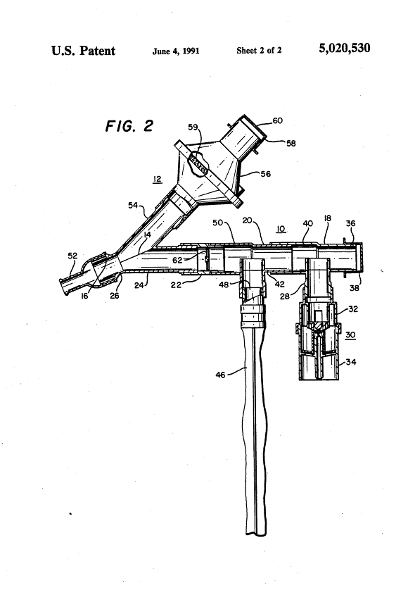 What is shown? Describe it | back 163 Cadema : Protect the patient as well, it has a one way valve on inspiratory side and one way valve on expiratory side. |
front 164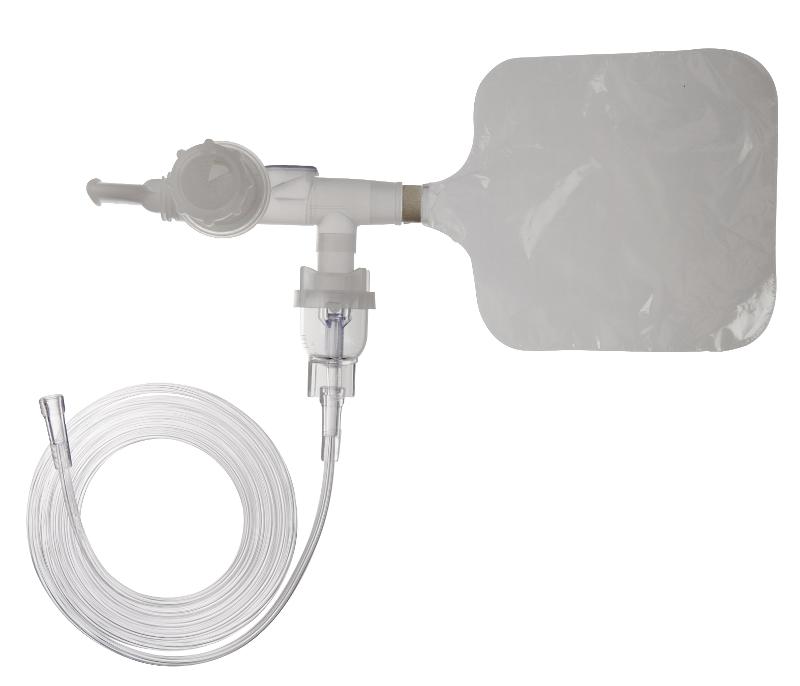  What is shown. | back 164 A circulair neb, which uses a bag to collect extra medication mist, which means the patient gets more meds on the next breath. |
front 165 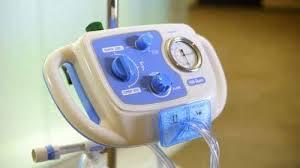 What is the MetaNeb system indicated for? | back 165 It is indicated for the mobilization of secretions, lung expansion therapy and the treatment and prevention of pulmonary atelectasis. |
front 166 Describe the mode CHFO. (Continuous High Frequency Oscillation) | back 166 Delivers medicated aerosol while oscillating the airways with continuous pulses of positive pressure. |
front 167 Describe the mode CPEP (Continuous positive expiratory pressure) | back 167 Provides medicated aerosol combined with continuous positive pressure to assist in holding open and expanding the airways. |
front 168  Describe the I-Neb. What happens when the drug is finished? What is it used to treat? | back 168 The I-Neb is a breath activated adapted neb. It monitors the first 3 breaths and the drug is aerosolized for 50% of inspiration. When the drug is finished the device alarms It's used to deliver iloprost to treat primary pulmonary hypertension. |
front 169 What are 3 methods of continuous nebulization? | back 169 1. Frequent refilling 2. Use of a nebulizer and infusion pump 3. Use of a large volume nebulizer like a Heart neb. |
front 170 What is shown? What is the MMAD for this device and why . | back 170 Heart nebulizer MMAD: 2.2-3.5 microns , reason is because the goal is to get to the upper airways. |
front 171 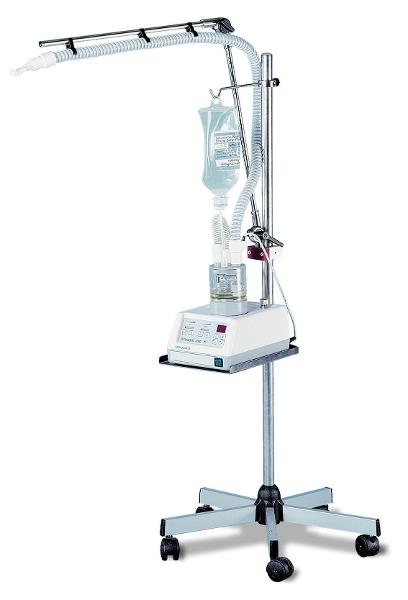 What is shown? | back 171  An Ultrasonic nebulizer |
front 172 What is he purpose of the piezoelectric transducer? | back 172 To change electric currents into sound waves that create a geyser that breaks up medication into smaller particles. |
front 173 Why is the couplant chamber filled with tap water? | back 173 1. To absorb mechanical heat 2. Act as a medium for sound waves |
front 174 Can you change the amplitude on an USN? If so, what does it control? What is the fluid output range? | back 174 Yes! It controls the output of the aerosol. The fluid output is 1-7 ml/min |
front 175 Can you change the frequency? What does it control? What is the particle size ranges and its mean. | back 175 No. It controls the particle size. particles range from 1-10 microns with a mean of 3 microns. |
front 176 Who regulates USN? | back 176 The FCC (Federal communication commission) |
front 177 What is an MDI? How do you take one? | back 177 A metered dose inhaler is a pressurized canister with a drug in a propellant with other ingredients and a mouthpiece. |
front 178 Describe the proper use of taking an MDI. | back 178
|
front 179 How much percent actualy enters the lower airway? where does the rest deposit? | back 179 About 10% enters the lower airways, the rest deposit in the back of the throat. |
front 180 What should you do after not using an MDI for a couple of days? | back 180 You must prime the device following the manufacturers instructions! |
front 181 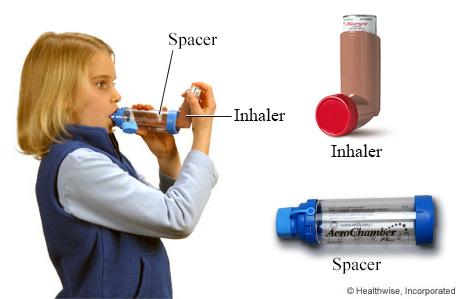 What is the purpose of a spacer? | back 181 It prevents the medication from hitting the back of your throat (inertial impaction.) it adds distance between the MDI and the patients mouth to slow down the flow, improves patient synchronization and minimizes oropharyngeal impaction. |
front 182 What is the purpose of a holding chamber? | back 182 iT ALLOWS EXHALED AEROSOL TO REMAIN IN A CHAMBER AND REMAIN AVAILABLE TO BE INHALED WITH THE NEXT BREATH. |
front 183 What is the difference between a spacer and a holding chamber? | back 183 A spacer doesn't have valves, it needs to be coordinated. A Holding chamber has valves, you don't have to coordinate pushing the button and breathing. you can also take more than one breath. |
front 184 How should you teach a patient on hw to use an MDI? | back 184 Basically teach the patient verbally, then physically, question the patient, have them perform it as well, work on fixing their mistakes then follow up. |
front 185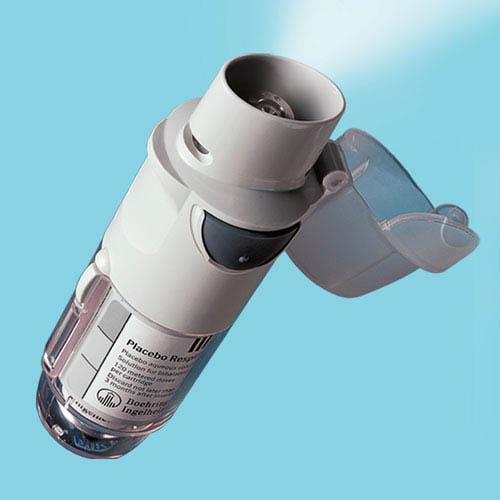  What is shown? Describe the device. | back 185 Respimat inhaler Has 45% deposition which means more meds in! The drug is released as patient takes a slow deep breath, no coordination is needed, all you do is start breathing and it'll activate automatically. |
front 186 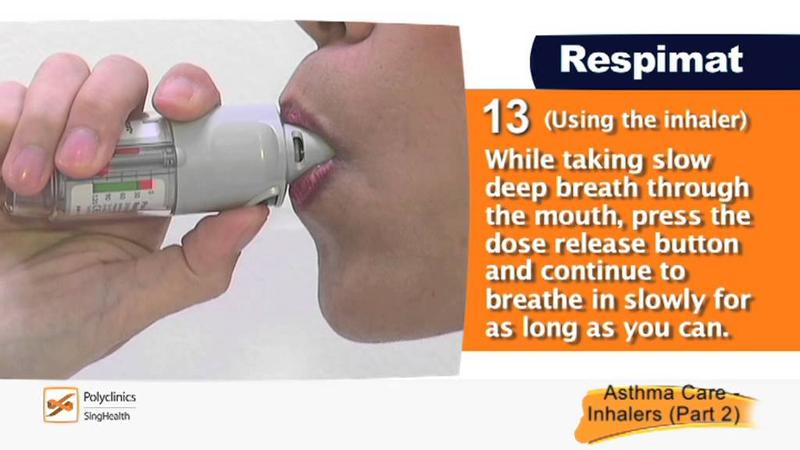 What is shown? Describe the device. | back 186 A combivent respimat inhaler. While taking a slow deep breath in, PRESS the dose release button and continue to breathe in slowly for as long as you can. It has a meter which tells you how much medicine you have left. |
front 187 Describe DPI. | back 187 Dry powdered inhalers do not use CFC or pressurized gas source. The delivery drug is in a powdered form which use lactose or glucose carriers. They are breath activated, meaning your breath creates the aerosol. |
front 188 What inspiratory flow must you be able to generate? | back 188 You must be able to generate a fast breath in ! >40-60 LPM Your breath in generates the movement and particle size (1-3 microns.) |
front 189 Describe the directions for taking a DPI | back 189
|
front 190 Who can't use a DPI? | back 190
|
front 191 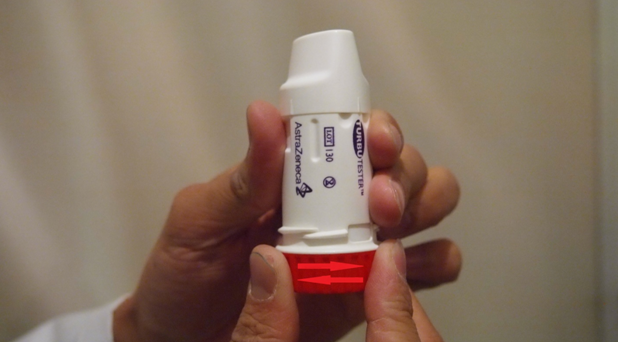 What is shown? | back 191 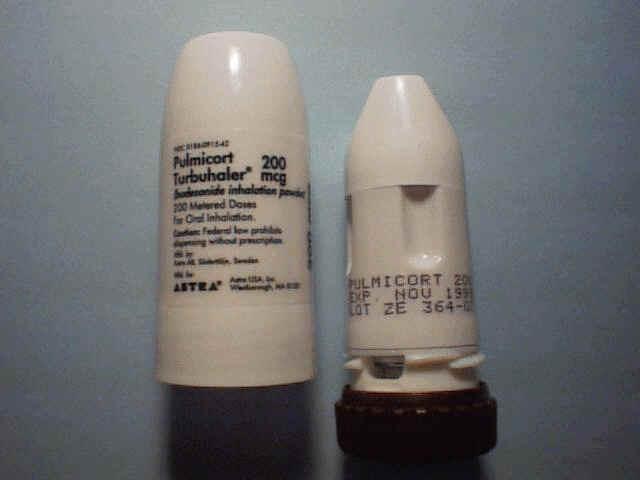 Twist and click to load dose. Patient may not feel or taste the med Do not shake after loading |
front 192  What is shown? | back 192 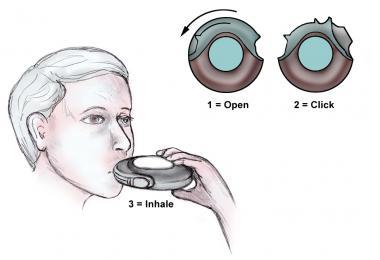 A diskus DPI *remember patient has to hold their breath for 10 seconds. |
front 193  What is shown? | back 193 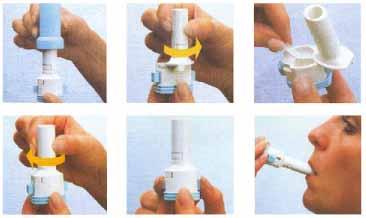 Foradil Aerolizer |
front 194  What is shown? | back 194 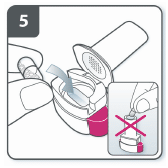 |
front 195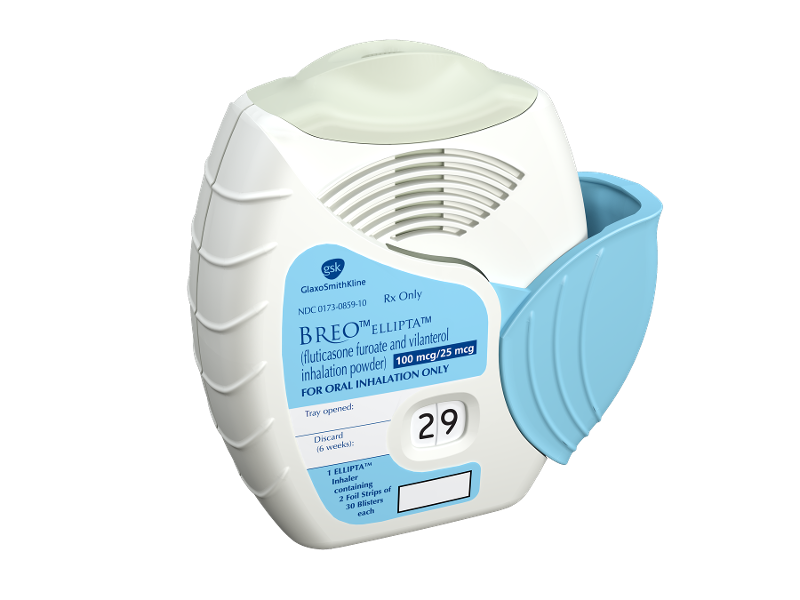  What is shown? | back 195 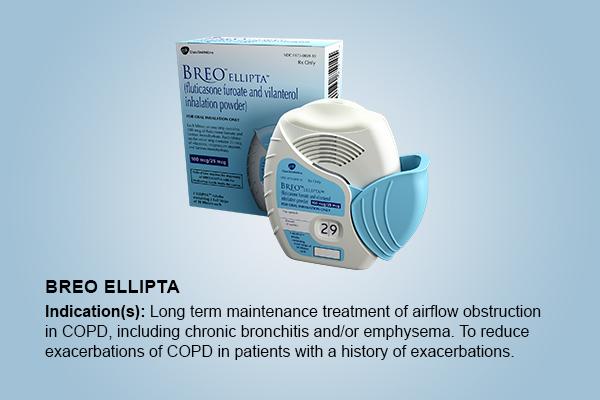 Breo Ellipta *single step activation, you just move the cap |
front 196  What is shown? | back 196  A Turdoza Pressair - Has a dose indicator - Green light = ready to inhale -Take a breath in click sound |
front 197 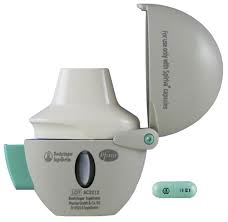 What is shown? | back 197  Spiriva Handihaler - With this you need to insert a capsule - to ensure you get the full dose, you breath in deeply 2x !! |
front 198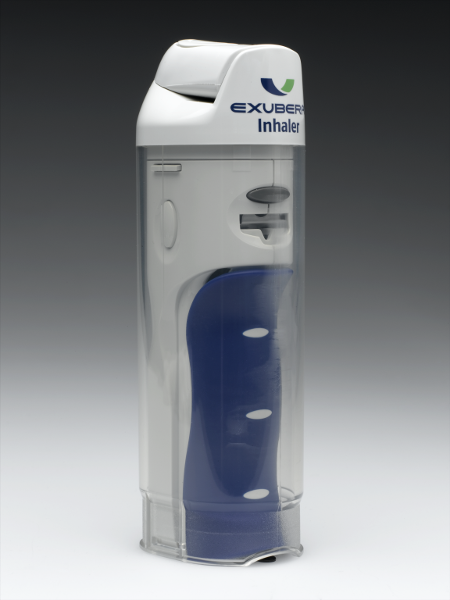  What is shown? | back 198  Exubera powder for insulin delivery. |
front 199 What are 5 considerations when choosing an aerosol delivery system? | back 199 1. Available drug formulation 2. Site of deposition needed 3. The patients disease characteristics 4. Patients ability to use the device 5. Patient preference ! |
front 200 Lab Questions. Why does the type of solution in the couplant make a difference in the amount of mist being produced? | back 200 The minerals in the water help transmit sound waves. |
front 201 Lab Questions. What effect did increasing the amplitude of the USN have on the aerosol output being produced? | back 201 It increased the output |
front 202 Lab Questions. What effect did increased the amplitude of the USN have on the density of aerosol being produced? | back 202 The density increase |
front 203 Lab Questions. What affects aerosol particle size of the USN? | back 203 The frequency |
front 204 Lab Questions. List 2 medications that are delivered in MDI form? Four in DPI? | back 204 MDI 1.Respimat inhaler 2. Combivent respimat DPI 1. Foradil Aerolyzer 2. Pulmicort Flexhaler 3. Breo Ellipta 4. Spiriva handihaler |
front 205 Lab Questions. Provide at least two differences between the filtered nebulizer and a SVN? | back 205 1. WYE 2. One way valves |
front 206 Lab Questions. What 2 advantages are there to using the Heart nebulizer? | back 206 1. Continuously gives medicine 2. Can attach to an oxygen blender |
front 207 Lab Questions. What 2 advantages are there to a circular nebulizer? | back 207 1. Gives Pt a higher volume of medication 2. Conserves medication in the bag |
front 208 Lab Questions. What 2 advantages are there to using an AeronebPro nebulizer? | back 208 1. Run w/o a gas source 2. Doesn't add additional flow |
front 209 Lab Questions. What would be an advantage to using the AeronebPro neb with a patient on mechanical ventilation? | back 209 IT doesn't add additional flow ! |
front 210 Lab Questions. What are 2 differences between the pari nebulizer and the SVN? | back 210 1. Has one way valves 2. only works on inpiration |
front 211 spiLab Questions. A 60 year old, obtunded, male who requires treatment with 0.5 ml Proventil and 3.0 ml of NSS: Aerosol device __________ Interface ____________ | back 211 Small Volume Nebulizer Aerosol Mask |
front 212 Lab Questions. An AIDS patient who requires Pentamidine: Aerosol device ____________ Interface ______________ | back 212 Respiguard nebulizer w/ series of one way valves and a filter Mouthpiece |
front 213 Lab Questions. A 35 yr old female in the recovery room following abdominal surgery and requires a bronchodilator. Aerosol device _____________ Interface ______________- | back 213 Small Volume Neb Aerosol mask |
front 214 Lab Questions. A 55 yr old make with a size 8.0 tracheostomy tube only requiring humidity. Aerosol device _____________ Interface ______________ | back 214 Large volume nebulizer trach mask or trach collar |
front 215 Lab Questions. 30 yr old patient with possible pneumonia, a sputum sample is required Aerosol Device ________ Interface _____________ | back 215 USN (ultra sonic nebulizer) Aerosol Mask |
front 216 Lab Questions. An 18 year old asthmatic who is sensitive to the propellant in the MDI Aerosol Device _______________ Interface _______________ | back 216 Small Volume nebulizer Mouth piece |
front 217 Lab Questions. Status asthmaticus patient is admitted to the intensive care. The patient is not responding to q1-2h treatments. The physician request that you administer high dose bronchodilator therapy. Aerosol Device _____________ Interface ________________ | back 217 Heart Nebulizer Aerosol Mask |