Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
OB 4
front 1 When is organogenesis complete? | back 1 12 weeks |
front 2 When is the GB seen? | back 2 20 weeks |
front 3 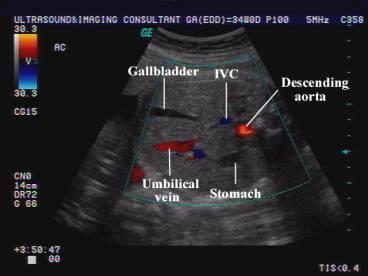 | back 3 Fetal GB |
front 4 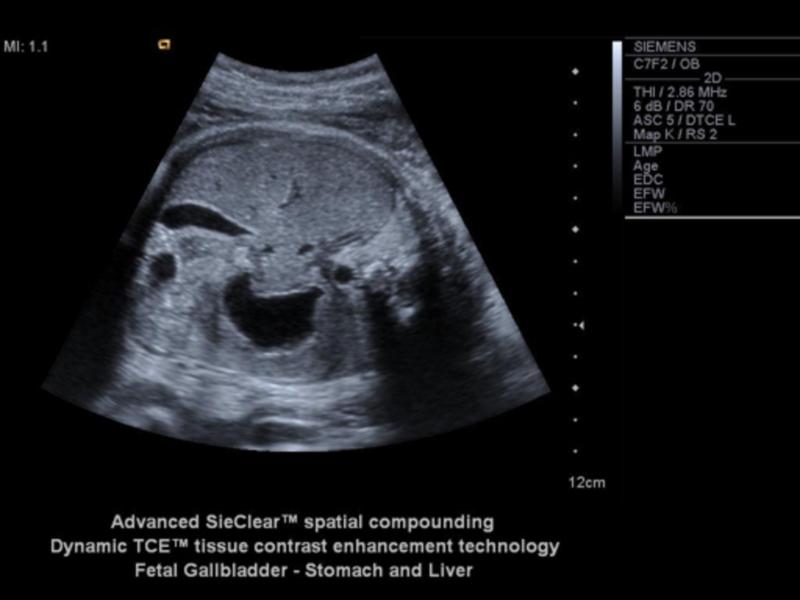 | back 4 Fetal GB |
front 5 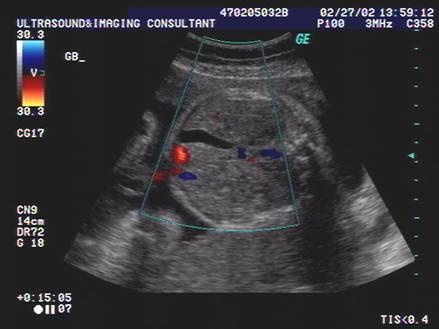 | back 5 Fetal GB |
front 6 What is suspected when the spleen is enlarged in a fetus? | back 6 Rh immunoIncompatibility |
front 7 When can the stomach be seen? | back 7 14 weeks |
front 8 If the stomach is not seen by 16 weeks, what could be the problem? | back 8 esophageal atresia |
front 9 What is the stomach a landmark for? | back 9 AC |
front 10 What does the intestines act as in utero? | back 10 resevor for meconium |
front 11 Why does the the fetus not poo in utero | back 11 peristalisis does not occur until birth anal sphincter is closed *unless in distress |
front 12 kidney / testis crisscross | back 12 no data |
front 13 what is meconium made of | back 13 amniotic fluid + fetal cells bacteria and enzymes added |
front 14 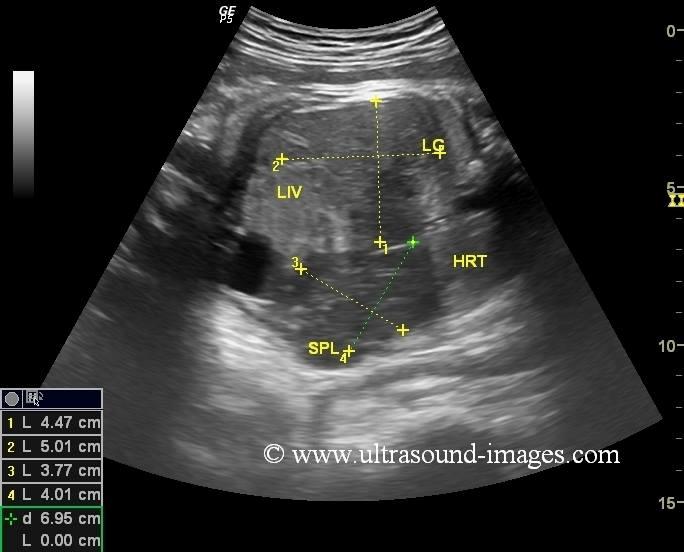 | back 14 spleenomegaly |
front 15 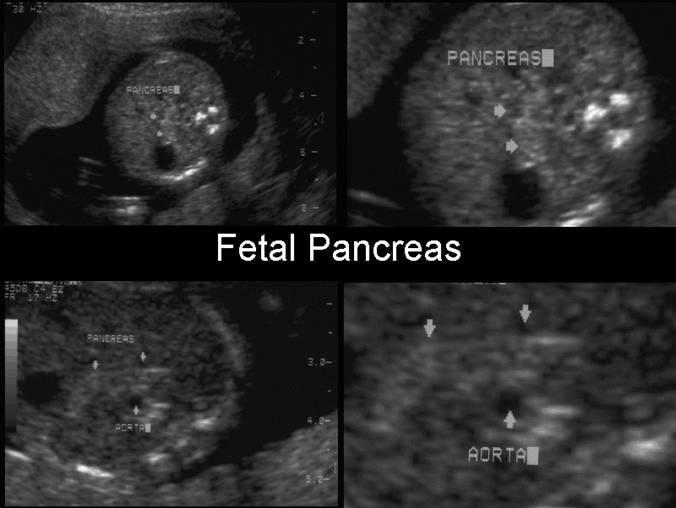 | back 15 Pancreas |
front 16 What is the size of the adrenals in a fetus? | back 16 20x larger in fetus than adults can mimic kidneys |
front 17 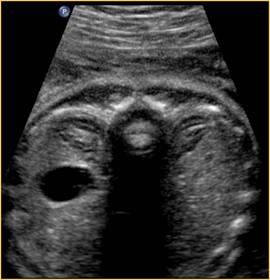 | back 17 adrenal |
front 18 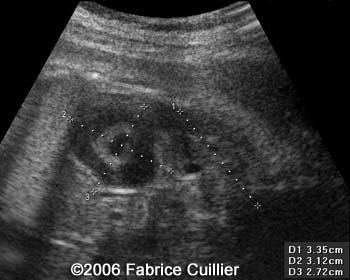 | back 18 adrenal |
front 19 ______________ is directly proportional to AC. | back 19 liver size |
front 20 What is hypoxic? | back 20 pertaining to low oxygen |
front 21 What does the umbilical arteries become after birth? | back 21 hypogastric ligament |
front 22 What does the umbilical vein become after birth? | back 22 ligament venosum |
front 23 What measurements do we take involving the abdomen? | back 23 AC renal length |
front 24 What is the AC landmarks? | back 24 trans spine - 3 oss center J - portal vein stomach & GB |
front 25 What is esophageal atresia? | back 25 congenital atresia of the esophagus |
front 26 What causes esophageal atresia? | back 26 failure of recanalization of the GIT a blind end tube is result |
front 27 What is present in most cases of esophageal atresia? | back 27 tracheo-esophageal fistula |
front 28 What percent of esophageal atresia have a tracheo-esophageal fistula present? | back 28 90% |
front 29 What is the sonographic appearance of esophageal atresia? | back 29 polyhydramnios stomach usually not identified |
front 30 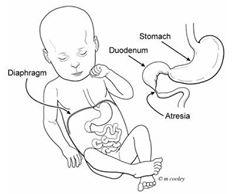 | back 30 Duodenal atresia |
front 31 What is duodenal atresia usually associated with? | back 31 Downs syndrome |
front 32 What is the sonographic appearance of duodenal atresia? | back 32 Double bubble polyhydramnios |
front 33 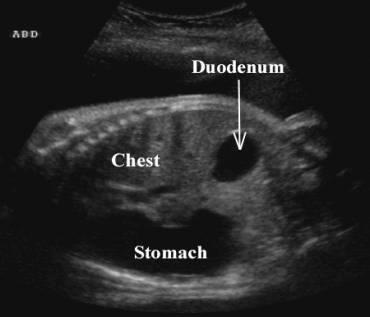 | back 33 Duodenal atresia |
front 34 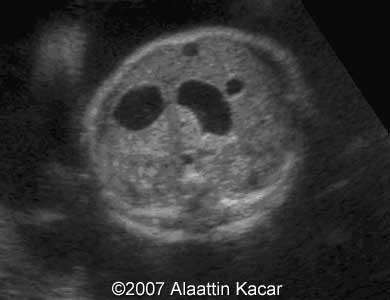 | back 34 Double bubble |
front 35 When can duodenal atresia be seen? | back 35 24 weeks |
front 36 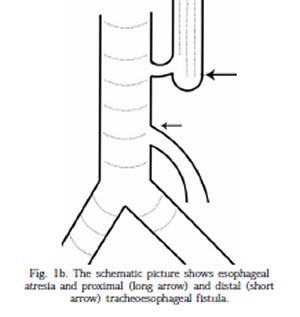 | back 36 tracheo-esophageal fistula |
front 37 What causes a double bubble? | back 37 duodenal atresia duodenal stenosis annular pancreas jejunal atresia |
front 38 What is an annular pancreas? | back 38 extension of pancreas tissue around duodenal forming a ring |
front 39 What problems does annular pancreas cause in infants? | back 39 feeding problems reflux and vomiting |
front 40 What is the sonographic appearance of jejunal atresia? | back 40 bowel proximal to the blockage dilated |
front 41 What is the first sign of cystic fibrosis? | back 41 meconium ileus echogenic bowel |
front 42 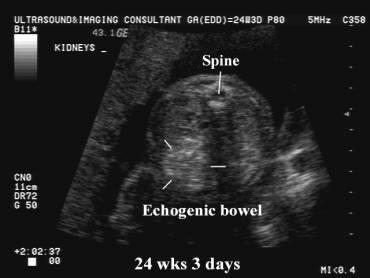 | back 42 meconium ileus |
front 43  | back 43 meconium ileus |
front 44 What is a meconium ileus? | back 44 small bowel disorder, presense of thick meconium in the distal ileum impaction of abnormal thick sticky mecomium |
front 45 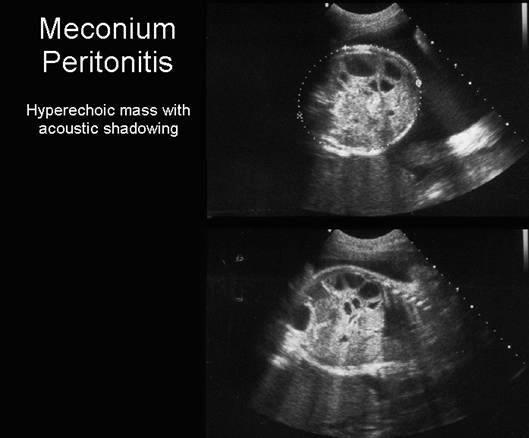 | back 45 Meconium Peritonitis |
front 46 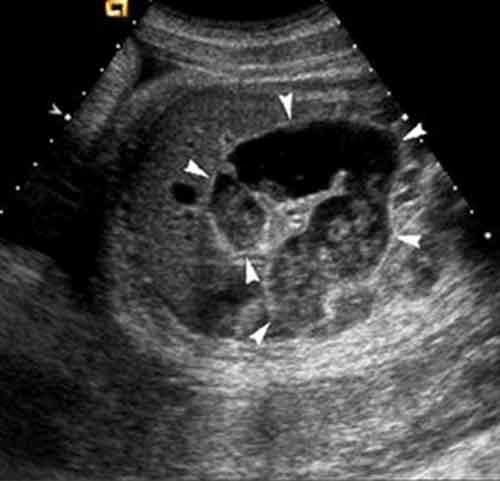 | back 46 Meconium Peritonitis |
front 47 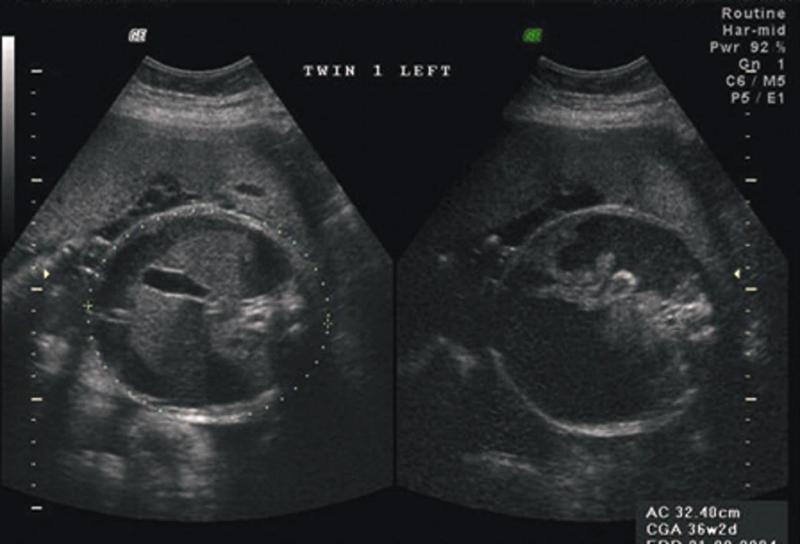 | back 47 Meconium Peritonitis |
front 48 What can obstructed bowel cause? | back 48 perforation and infection |
front 49 What is the sonographic appearance of meconium ileus? | back 49 echogenic small bowel |
front 50 When is the migration of the kidney to the abdomen complete? | back 50 9 weeks |
front 51 What causes pelvic kidneys? | back 51 can be physical or hormonal |
front 52 What are horseshoe kidneys? | back 52 inferior portion fuses early on |
front 53 When should the kidneys and the bladder be seen? | back 53 15 weeks |
front 54 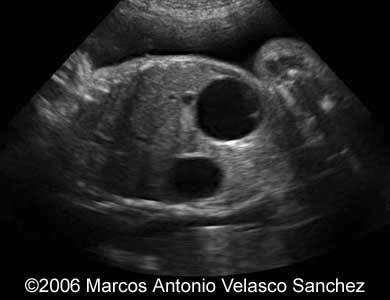 | back 54 bubble sign |
front 55 When should the renal cortex and medulla be differentiated? | back 55 25 weeks |
front 56 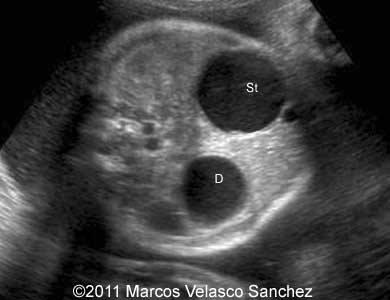 | back 56 bubble sign |
front 57 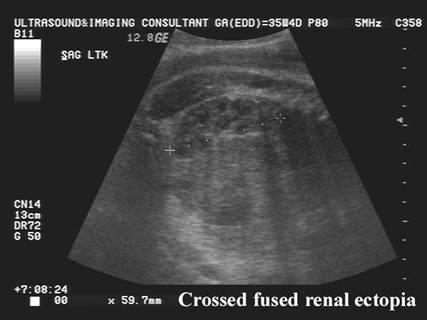 | back 57 Cross-over fusion kidneys |
front 58 What happens with bilateral renal agenesis? | back 58 olighydramnios usuually resulting in miscarriage - always fatal |
front 59 What is Potter's type 2? | back 59 multicystic dysplastic kidneys |
front 60 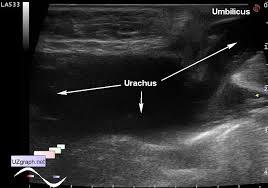 | back 60 Urachal fistula |
front 61 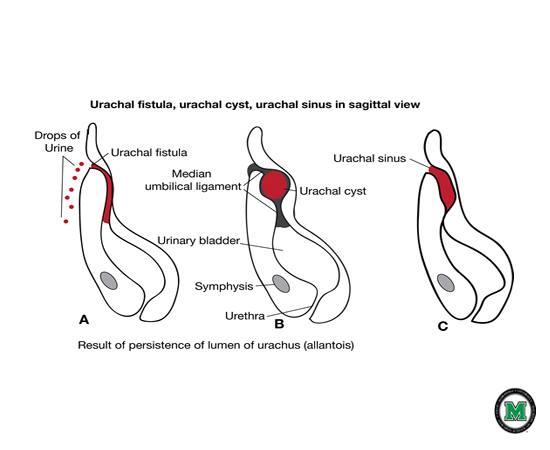 | back 61 Urachal fistula |
front 62 What is a urichal fistula? | back 62 Urachus doesn't close and belly button leaks urin |
front 63  | back 63 Urachal cyst |
front 64 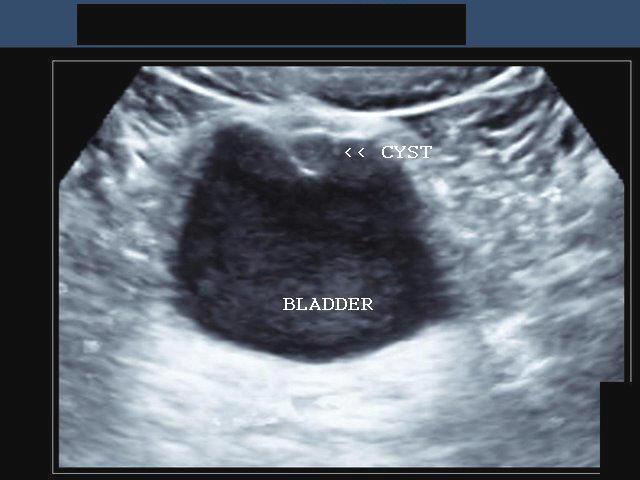 | back 64 Urachal cyst |
front 65 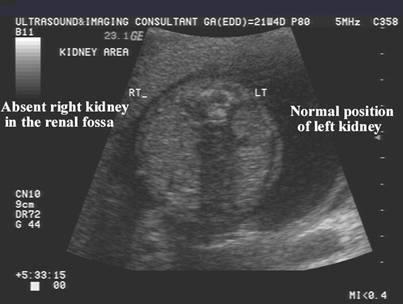 | back 65 Unilateral renal agenesis |
front 66 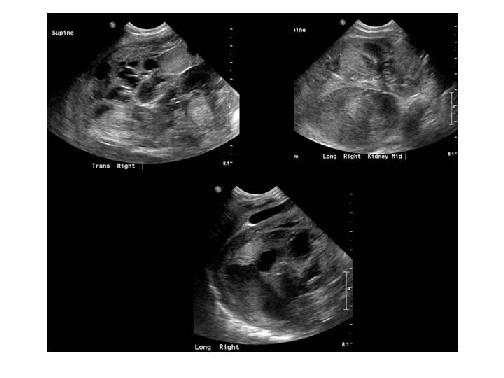 | back 66 Mesoblastic Nephroma AKA: fetal renal harmatoma & congenital Wilm's tumor |
front 67 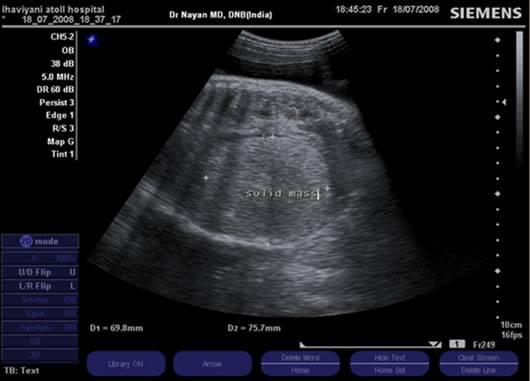 | back 67 Mesoblastic Nephroma AKA: fetal renal harmatoma & congenital Wilm's tumor |
front 68 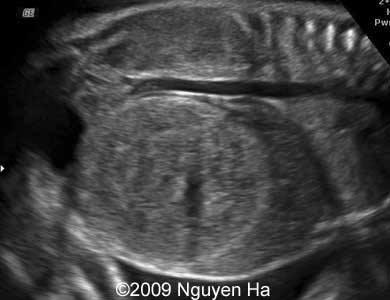 | back 68 Wilm's Tumor AKA: Nephroblastoma |
front 69 What is mesoblastic nephroma? | back 69 Congenital Wilms' tumors big benign mass usually expresses its self by 3 months most common neonatal solid tumor mostly in boys |
front 70 What is Nephroblastoma? | back 70 wilms tumor |
front 71 What is the most common malignant tumor of childhood? | back 71 Wilms tumor |
front 72 At what age does wilms tumor usually occur? | back 72 commonly occurs at 3 yrs |
front 73 what is a Urachus? | back 73 a fibrous cord that extends from the umbilicus to the bladder. |
front 74 What is the sonographic appearance of Potter's type 2? | back 74 Severe oligohydramnios Absent kidneys Nondistended bladder |
front 75 What is IPKD? | back 75 disorder associated with multiple bilateral cysts |
front 76 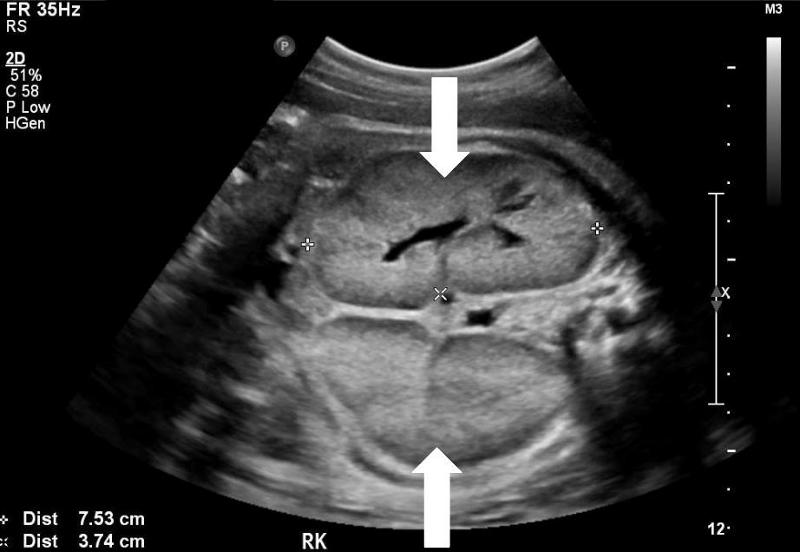 | back 76 Infantile Polycystic Kidney Disease |
front 77 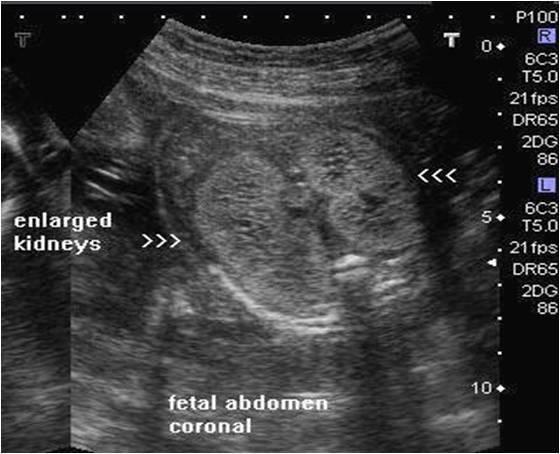 | back 77 Infantile Polycystic Kidney Disease |
front 78 What is another name for IPKD? | back 78 Potter Type 1 |
front 79 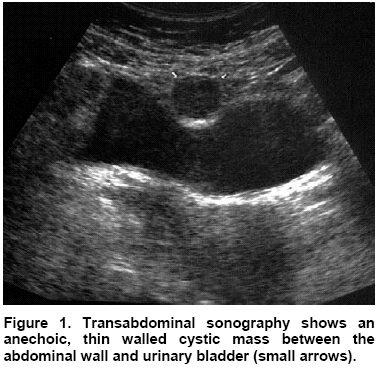 | back 79 Urachal cyst |
front 80 Is IPKD recessive of dominant? | back 80 recessive |
front 81 What are the 4 groups of IPKD? | back 81 Perinatal – renal failure in utero Neonatal Infantile juvenile |
front 82 When does neonatal IPKD occur? | back 82 within 1st month after birth |
front 83 When does infantile IPKD occur? | back 83 3 - 6 months |
front 84 When does juvenile IPKD occur? | back 84 1 - 5 years |
front 85 What is the sonographic appearance of IPKD? | back 85 enlarged hyperechoic homogeneous hyoerechoic large kidneys increased kidney AC small bladder loss of corticomedullary differentiation |
front 86 What is Meckyl-Gruber syndrome? | back 86
|
front 87 What is adult polycystic kidney disease? | back 87 large echogenic |
front 88 What age does APKD usually occur? | back 88 age 30 with hypertension |
front 89 If one person has APKD what is the chance of passing it on to children? | back 89 50% |
front 90 What is polycystic kidney disease? | back 90 auto dominant family history |
front 91 What is multicystic dysplastic kidneys? | back 91 disorder associated with unilateral cystic lesions correspond to dilated collecting tubules Enlarged unilateral nonfunctioning |
front 92 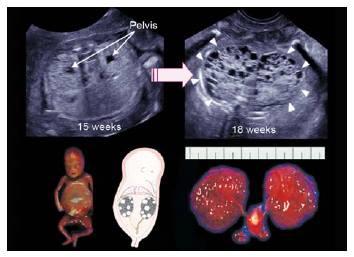 | back 92 Bilateral multicystic dysplastic kidney disease |
front 93 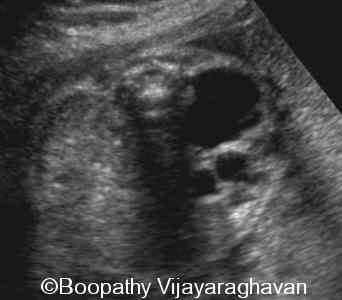 | back 93 unilateral multicystic dysplastic kidney disease |
front 94 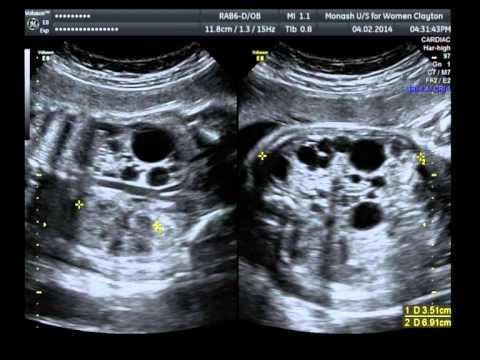 | back 94 unilateral multicystic dysplastic kidney disease |
front 95 What happens to the contralateral kidney with MDK? | back 95 enlarges to compensate |
front 96 What is the sonographic appearance of bilateral MDK? | back 96 multiple, round various sizes bladder not seen olighydramnios Poor Prognosis |
front 97 What is the sonographic appearance of unilateral MDK? | back 97 multiple, round various sizes bladder seen hydronephrosis |
front 98 What is UPJ? | back 98 uritopelvis junction |
front 99 What is UVJ? | back 99 uritovesicilar junction |
front 100 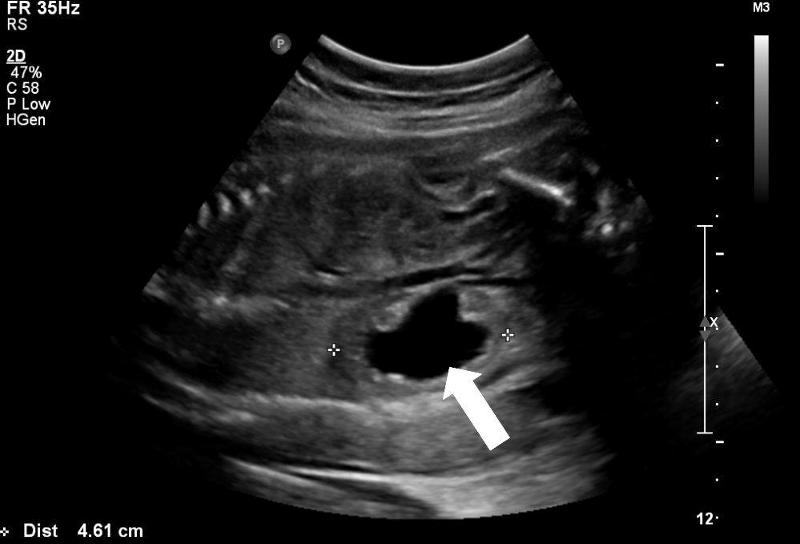 | back 100 Hydronephrosis |
front 101 Where is a double collecting system most likely to have hydro? | back 101 the superior collecting system |
front 102 What is the most common fetal anomaly? | back 102 hydronephrosis |
front 103 What is hydronephrosis usually caused by? | back 103 UPJ or UVJ obstruction |
front 104 What is a UPJ obstruction caused by? | back 104 bend or kink in ureter |
front 105 What is a UVJ obstruction caused by? | back 105 bad valves at trigone region |
front 106 What do normal ureters measure? | back 106 1 mm |
front 107 Prune belly syndrome usually occurs in _____________ | back 107 boys |
front 108 What is hydronephrosis? | back 108 Dilation of the renal pelvis due to blockage |
front 109 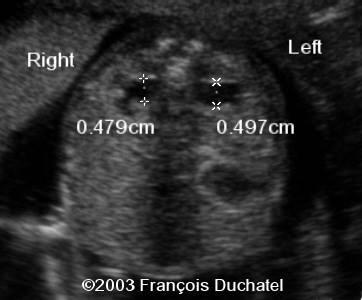 | back 109 Pyelectasis |
front 110 What is pyelectasis? | back 110 abnormal collection of urine within the renal pelvis 5-9 mm |
front 111  | back 111 Caliectasis |
front 112 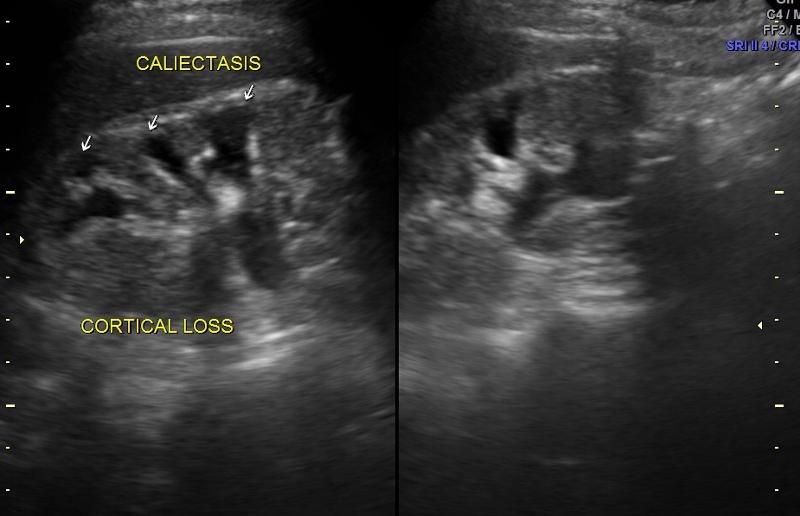 | back 112 Caliectasis |
front 113 What is calyectasis? | back 113 rounded calyces with renal pelvis dilatation |
front 114 What is Prune Belly Syndrome? | back 114 Rare congenital abnormality. A partial or complete lack of abdominal wall muscles w/ renal abnormalities. Usually in males. anterior abdominal wall defect urinary tract obstruction cryptorchidism hypoplastic abdominal wall muscles massive distention of bladder wrinkling urethral obstruction bladder enlarges mega ureter hydronephrosis abdomen enlarges abdominal muscles becomes abnormal Babies are delived c-section |
front 115 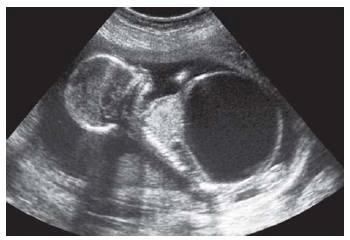 | back 115 Prune Belly |
front 116 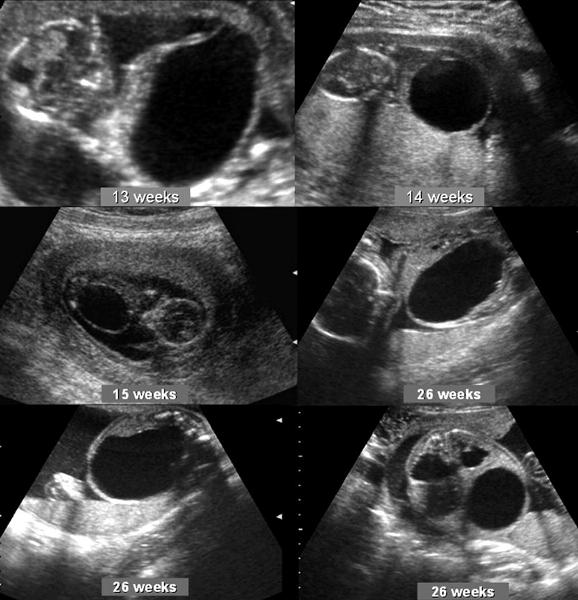 | back 116 Prune Belly |
front 117 What is another name for prune belly syndrome? | back 117 Eagle Barrett syndrome |
front 118 What is the sonographic appearance of prune belly syndrome | back 118 hydronephrosis with echogenic renal parenchyma oligohydramnios urinary ascites a dystrophic bladder peritoneal calcifications |
front 119 What is ureteropelvic junction obstruction? | back 119 Obstruction of the urinary outflow. Can be acquired or congenital. obstruction at the confluence of the kidney and the ureter Sporadic |
front 120 What is the most common cause of hydronephrosis in neonates? | back 120 UPJ obstruction |
front 121 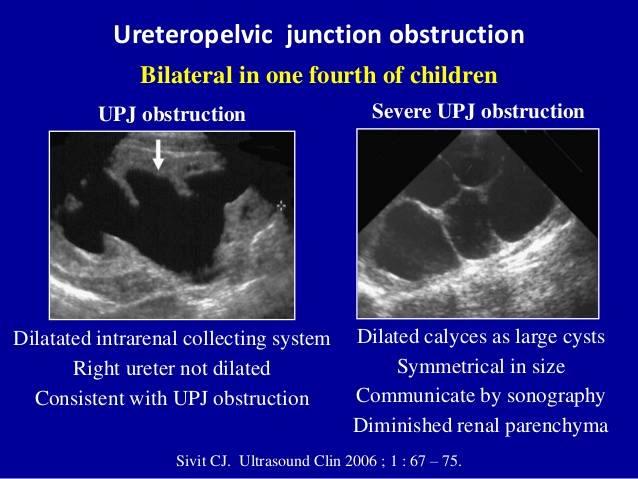 | back 121 UPJ obstruction |
front 122 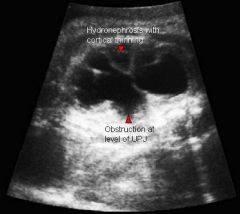 | back 122 UPJ obstruction |
front 123 What is the sonographic appearance of ureteropelvic junction obstruction? | back 123 will often show a dilated renal pelvis Doppler: Kidney w/higher resistive indices hyperechoic kidneys |
front 124 What is Ureterovesicle junction obstruction? | back 124 Obstruction of the uretrovesical junction causing urine to back up into the ureters and kidneys. results from stenotic ureteral valve or fibrosis |
front 125 What is the sonographic appearance of Ureterovesicle junction obstruction? | back 125 megaureter hydronephrosis |
front 126 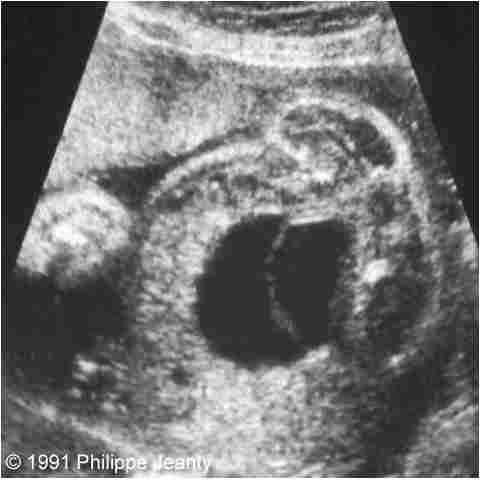 | back 126 Ectopic ureterocele |
front 127 What is a Ectopic ureterocele? | back 127 the distal ureter does not insert into the urinary bladder Congenital cystic dilatations of the terminal submucosal ureter surgical repair or can lead to loss of function bad insertion of ureter into trigone region |
front 128 What is the sonographic appearance of a Ectopic ureterocele? | back 128 Echogenic thin-walled cyst-like structures within the bladder |
front 129 What is ectopic ureterocele usually associated with? | back 129 UVJ obstruction |
front 130 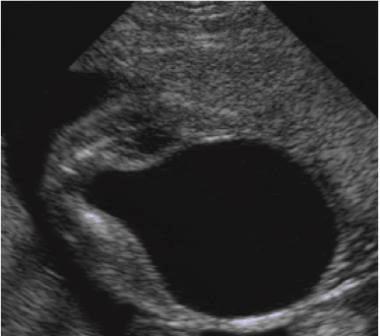 | back 130 Posterior urethral valve |
front 131 What is Posterior urethral valves? | back 131 most common congenital obstructive lesion of the urethra congenital folds act of male urethra act as valves to obstruct excretion |
front 132 What is the sonographic appearance of Posterior urethral valves? | back 132 marked distention bladder hydronephrosis hydroureter oligohydramnios keyhole sign |
front 133 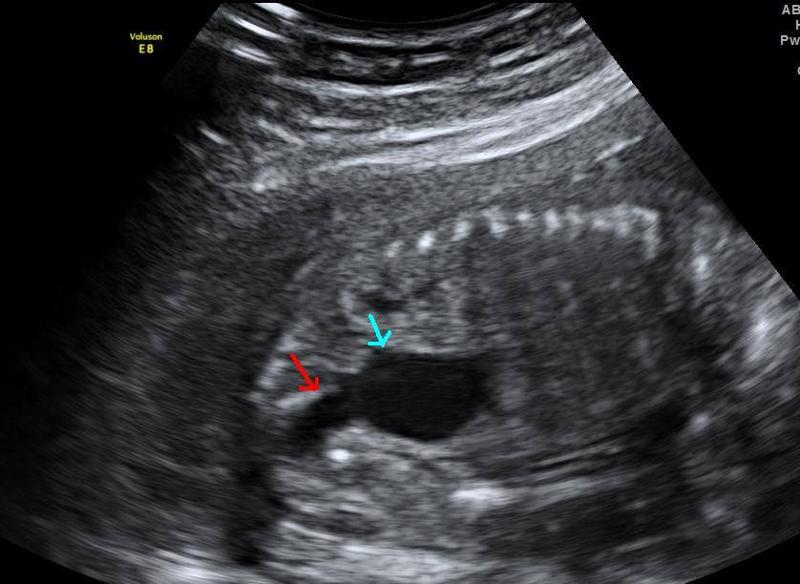 | back 133 Posterior urethral valve |
front 134 What is a keyhole sign? | back 134 no data |
front 135 What is the major concern for babies with posterior urethral valves? | back 135 baby can't urinate leading to olighydramnios pulmonary hyperplasia risk of bladder rupture causing urinary ascites |
front 136 What is the most common cause of death for fetus with posterior urethral valves? | back 136 pulmonary hyperplasia |
front 137 What is cloaca? | back 137 The cloaca is a structure in the development of the urinary and reproductive organs. plays a developmental role in genitals bladder rectum |
front 138 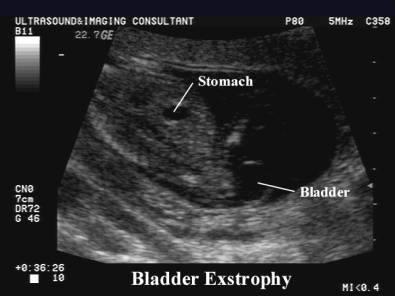 | back 138 Bladder exstrophy |
front 139 What is the most severe form of bladder exstrophy? | back 139 cloacal extrophy colon is affected |
front 140 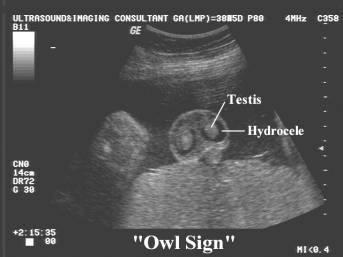 | back 140 Testicular hydrocele |
front 141 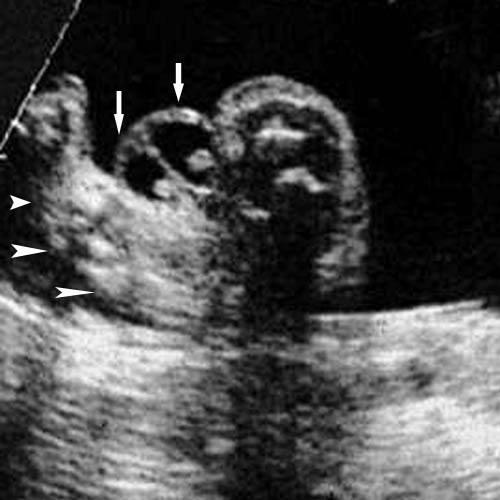 | back 141 Testicular hydrocele |
front 142 What causes a testicular hydrocele? | back 142 process vaginalis does not close completely causing abdominal secretions in scrotal sac. |
front 143 Many testicular hydroceles _____________ within ____________. | back 143 Many testicular hydroceles heal themselves within 24 months. |
front 144 What week do the testicles descend? | back 144 28 weeks |
front 145 What is Bladder exostrophy? | back 145 congenital anomaly, protrusion of the urinary bladder through a defect in the abdominal wall. |
front 146 WHat is the sonographic appearance of Bladder exostrophy? | back 146 soft-tissue mass protruding through abdomen absence of urinary bladder separation of pubic bone |
front 147 What is a differential diagnosis of bladder exostrophy? | back 147 gastroschisis or omphalocele |
front 148 What is a Testicular Hydrocele? | back 148 fluid-filled sac surrounding a testicle usually benign |
front 149 What is the sonographic appearance of Testicular Hydrocele? | back 149 simple fluid collection surrounding the testis. |
front 150 What is Osteochondrodysplasia? | back 150 general term for a disorder of the development of bone and cartilage hard to identify prenatally * filler in multiple choice...usually missed by U/S |
front 151 Explain the TC of a fetus with Osteochondrodysplasia? | back 151 measure small |
front 152 What should you do if the femur measures small? | back 152 red flag marker for trisomy 21 measure humerus |
front 153 What is the key bone measurement? | back 153 femur length |
front 154 When do the long bones begin to ossification? | back 154 end of embryonic period week 12 |
front 155 What is TC? | back 155 thoracic circomuference |
front 156 What are the first bones to ossify? | back 156 mandible & clavicle Week 8 |
front 157 what usually occurs with musculoskeletal abnormalities? | back 157 polyhydramnios fetal structural anomalies family history of recurrent syndrome |
front 158 Why are the most lethal musculoskeletal anomolies easier to identify? | back 158 they have severe presentations |
front 159 What bones can be Acromelia? | back 159 carpal metacarpal tarsels metatarsels phalanges |
front 160 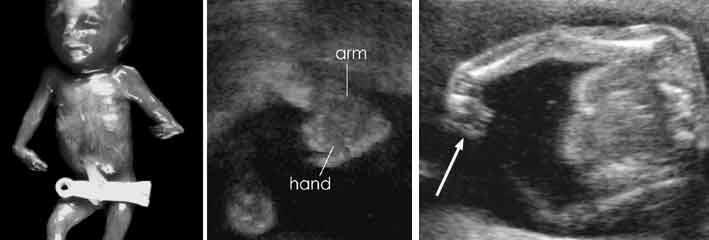 | back 160 Acromelia |
front 161 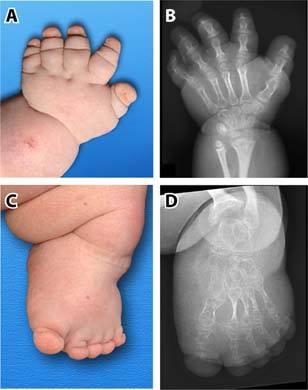 | back 161 Acromelia |
front 162 What is Acromelia? | back 162 Bone abnormality shortening of distal limb segment. |
front 163 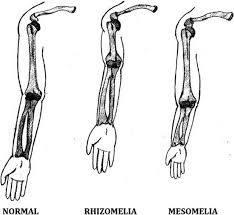 | back 163 Acromelia |
front 164 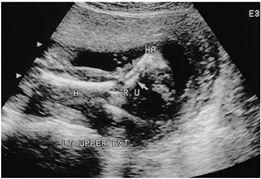 | back 164 Mesomelia |
front 165 What is Mesomelia? | back 165 shortening of middle limb segment. |
front 166 What bones can be Mesomelic ? | back 166 tibia fibula ulnar radius |
front 167 What is Rhizomelic shortening? | back 167 Shortening of proximal limb segment |
front 168 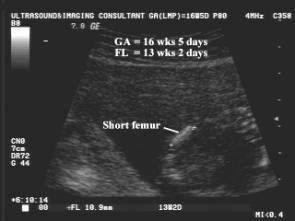 | back 168 Rhizomelia |
front 169 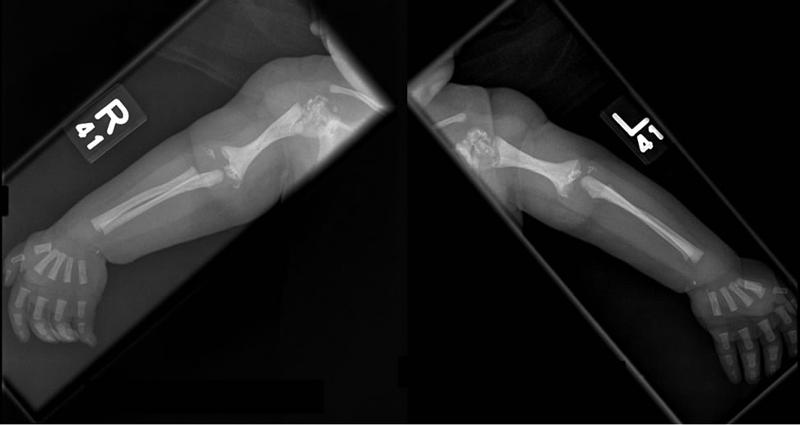 | back 169 Rhizomelia |
front 170 What bones can be Rhizomelic ? | back 170 femur humerus |
front 171 What is Micromelia shortening? | back 171 Shortening of proximal and distal limb segment dwarfism |
front 172 What is Extactyly? | back 172 Absence of fingers or toes |
front 173 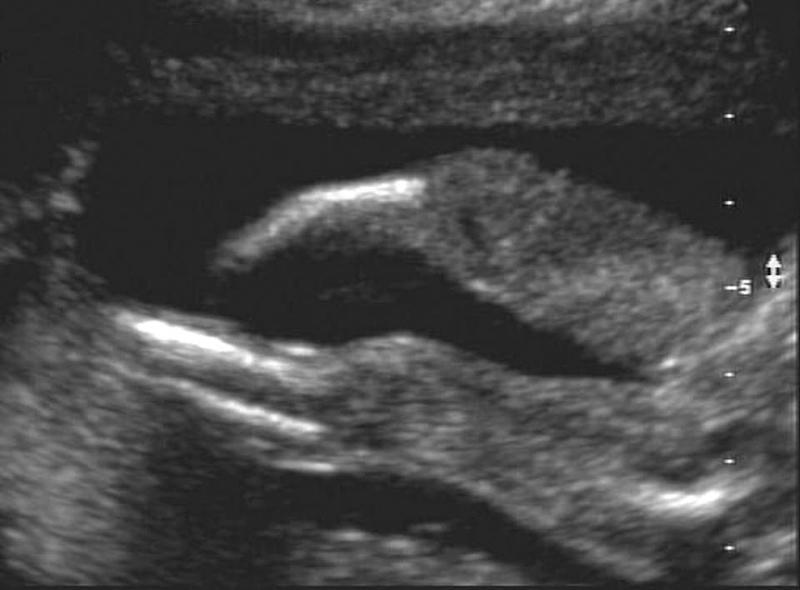 | back 173 Hemimelia |
front 174 What is Hemimelia? | back 174 Absence of below elbow or knee |
front 175 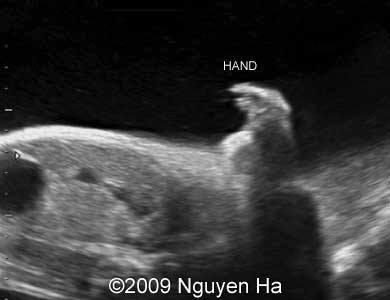 | back 175 Phocomelia |
front 176 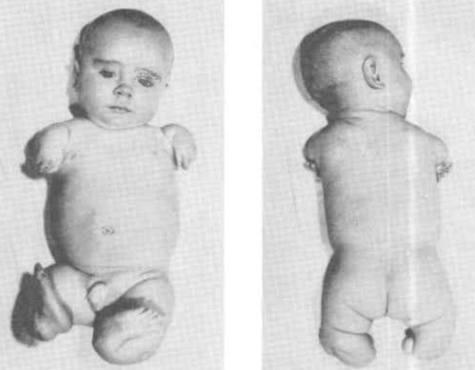 | back 176 Phocomelia |
front 177 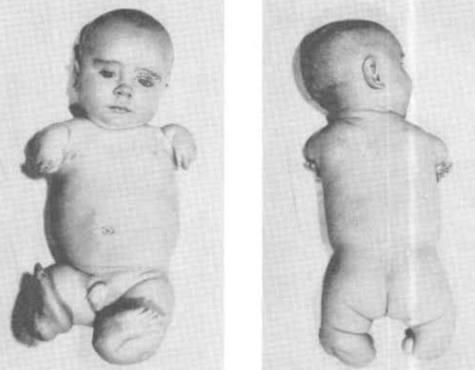 | back 177 Phocomelia |
front 178 What is Phocomelia? | back 178 Absence of middle segment foot and hand would be attached to femur and humerus |
front 179 What is Sirenomelia? | back 179 fusion of legs mermaid syndrome |
front 180 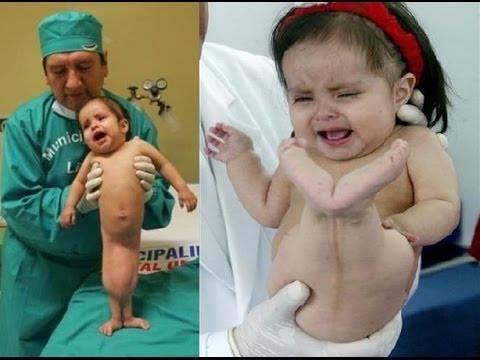 | back 180 Sirenomelia |
front 181 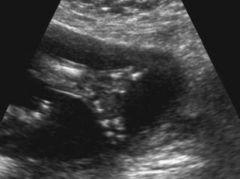 | back 181 Sirenomelia |
front 182  | back 182 Sirenomelia |
front 183 What is Dystoes? | back 183 Absence or malformation of individual bones |
front 184 What is Arthrogryposis? | back 184 rigid extremities |
front 185 What is the possible cause of Arthrogryposis? | back 185 olighydramnios |
front 186 What is the sonographic appearance of Arthrogryposis? | back 186 joint contractures and rigidity. head was severely hyperextended fixed extremities flexed arms clubbed feet clenched hands |
front 187 What is Polydactyly? | back 187 extra fingers or toes. |
front 188 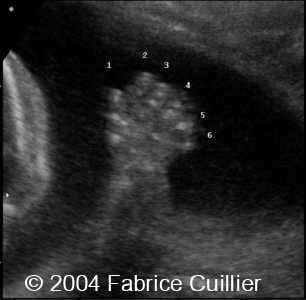 | back 188 Polydactyly |
front 189 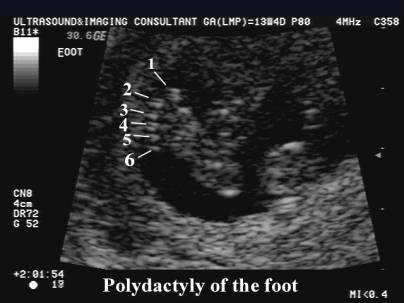 | back 189 Polydactyly |
front 190 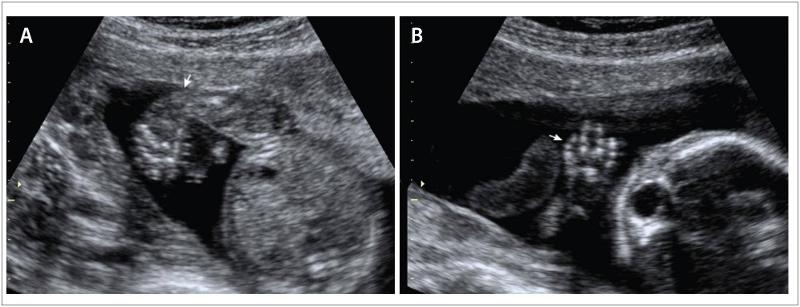 | back 190 Clinodactyly & club foot |
front 191 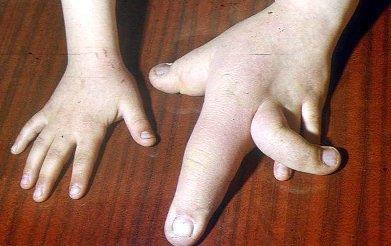 | back 191 Clinodactyly |
front 192 What is Clinodactyly? | back 192 curvature of a digit |
front 193 What is Pterygium? | back 193 webbing across joints |
front 194 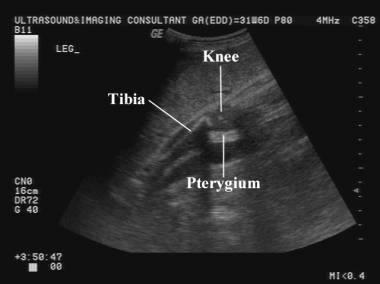 | back 194 Pterygium webbing across joints |
front 195 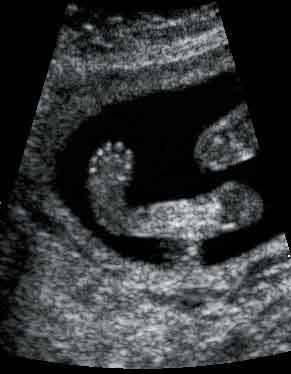 | back 195 Talipes equinovarus |
front 196 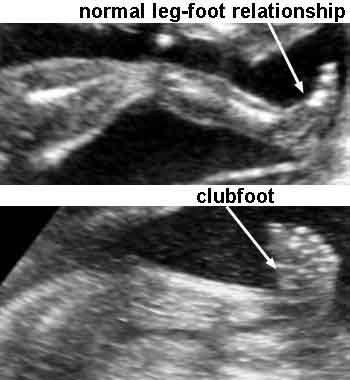 | back 196 Talipes equinovarus |
front 197 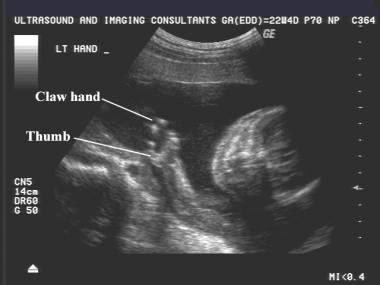 | back 197 Ectrodactyly |
front 198 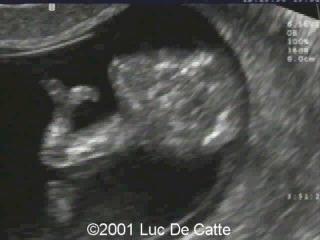 | back 198 Ectrodactyly |
front 199 What is Talipes? | back 199 AKA Club foot. front half of the foot turns inwards and downwards |
front 200 What is Rocker-bottom feet? | back 200 prominent calcaneus and a convex rounded bottom to the foot. The foot resembles the bottom of a rocking chair. marker for trisomy 18 |
front 201 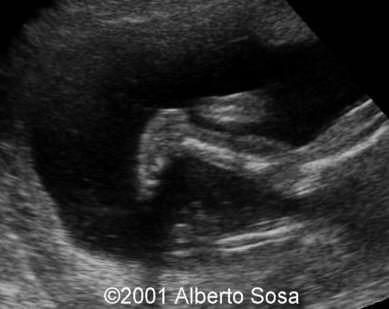 | back 201 Rockerbottom feet |
front 202 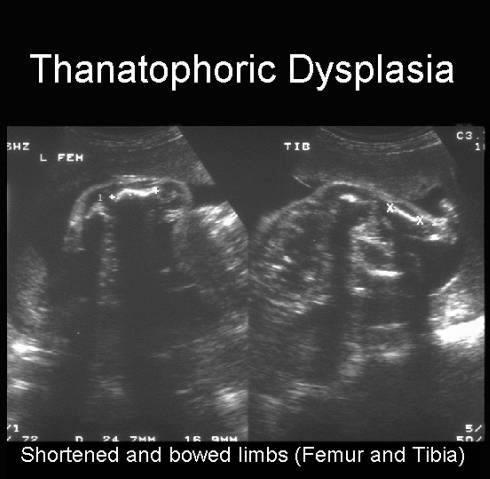 | back 202 Thanatophoric dysplasia |
front 203 What are the lethal forms of Skeletal dysplasia? | back 203 Thanatophoric dysplasia achondrogenesis camptomelic dysplasia osteogenesis imperfectal - Type II Sirenomelia |
front 204 What is the most common non-lethal bone dysplasia? | back 204 achondroplasia |
front 205 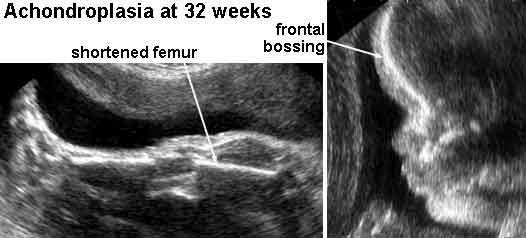 | back 205 Achondroplasia |
front 206 When can rhyzomelia be diagnosed in utero? | back 206 by femur length 27 - 30 weeks measurement of femur length starts dropping off |
front 207 What are the Non-lethal forms of Skeletal dysplasia? | back 207 achondroplasia osteogenesis imperfecta Type IV |
front 208 What is Thanatophporic Dysplasia? | back 208 severe skeletal disorder characterized by extremely short limbs and folds of extra skin on the arms and legs. rhizomelia bowed long bones narrow thorax large head |
front 209 What is the most common form of lethal dwarfism? | back 209 Thanatophporic Dysplasia causes severe micromelia |
front 210 What is the sonographic appearance of Thanatophporic Dysplasia? | back 210 clover leaf skull narrow chest short ribs underdeveloped lungs enlarged head large forehead and prominent, wide-spaced eyes. |
front 211  | back 211 Kleeblattshadels |
front 212 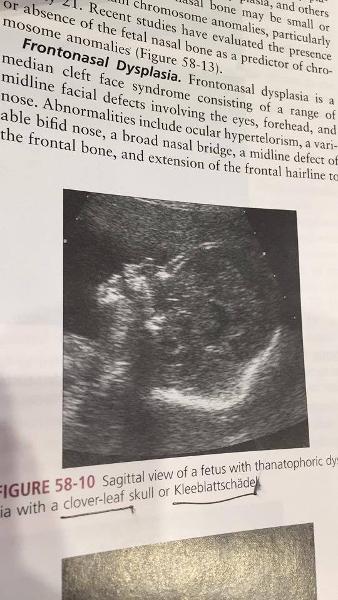 | back 212 Kleeblattshadels |
front 213 What is another name for cloverleaf skull? | back 213 kleeblattschädel |
front 214 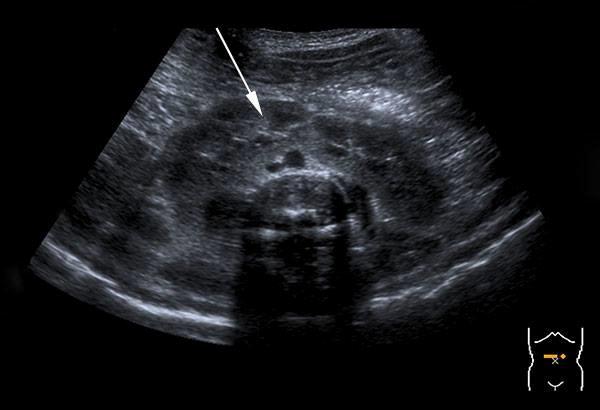 | back 214 horseshoe |
front 215 What are associated anomolies of Thanatophporic Dysplasia? | back 215 cloverleaf skull horseshoe kidneys ASD imperforate anus |
front 216 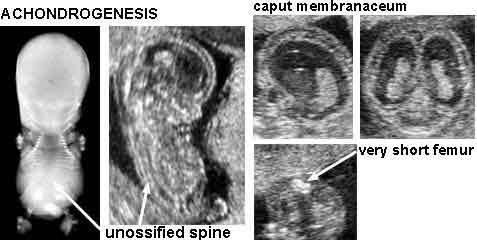 | back 216 Achondrogenesis |
front 217 What is the second most common form of lethal dwarfism? | back 217 Achondrogenesis |
front 218 What is Achondrogenesis? | back 218 rare lethal form of short limbed dyplasia severe malformation of bones and cartilage. Babies usually still born or die shortly |
front 219 What are the two types of Achondrogenesis? | back 219 no data |
front 220 What is the sonographic appearance of Achondrogenesis? | back 220 demonstration of the triad severely shortened limbs lack of vertebral ossification large head with slightly decreased ossification |
front 221 What is Camptomelic Dysplasia? | back 221 Camptomelic Dysplasia: bowing of the long bones |
front 222 What are the most common bones affected by Camptomelic Dysplasia? | back 222 tibia femur |
front 223 What is the sonographic appearance of Camptomelic Dysplasia? | back 223 bowing of long bones hydrocephalus hydronephrosis |
front 224 What are the anomolies associated with Camptomelic Dysplasia? | back 224 heart disease hydrocephalus hydronephrosis |
front 225 What is caudal regression syndrome caused by? | back 225 early disruption of caudal portion of the neural tube (sacral anomolies) includes a range of anomolies |
front 226 What is caudal regression syndrome? | back 226 fusion of the lower extremities male prevalence 3:1 |
front 227 What is a mild case of caudal regression syndrome? | back 227 sacral anomalies |
front 228 What is the most severe form of caudal regression syndrome? | back 228 Sirenomelia |
front 229 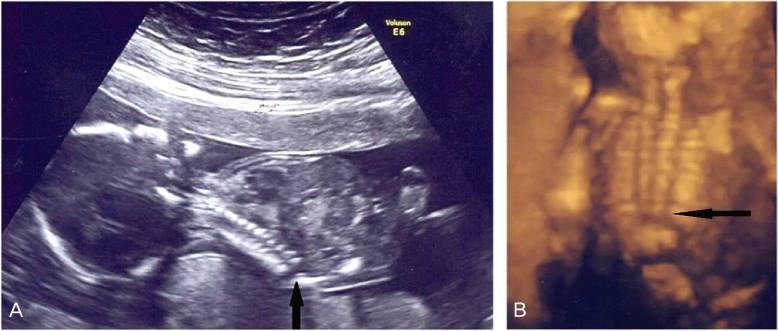 | back 229 Caudal regression syndrome |
front 230 What are the associated anomalies of caudal regression syndrome? | back 230 diabetes monozygotic twins |
front 231 Sirenomelia | back 231 AKA Mermaid Syndrome, very rare congenital deformityin which the legs are fused together |
front 232 What is Osteogenesis Imperfecta Type II? | back 232 disorder of production, secretion or function of collagen most severe form |
front 233 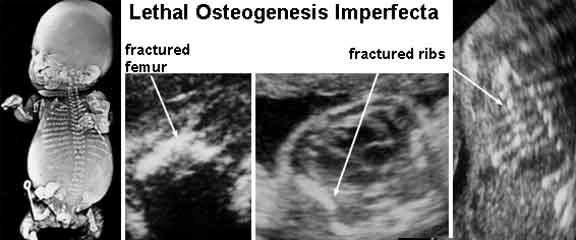 | back 233 Osteogenesis Imperfecta type 2 |
front 234 What is Osteogenesis Imperfecta Type II characterized by? | back 234 bone fragility caused by hypominerization |
front 235 What can delivery trauma lead to with Osteogenesis Imperfecta Type II? | back 235 intracranial hemorrhage stillbirth |
front 236 What is Osteogenesis Imperfecta Type IV? | back 236 AKA Brittle bone fractured or bowed demineralization of bone |
front 237 Whe does Osteogenesis Imperfecta Type IV occur? | back 237 can occur in 3rd trimester usually does not present until after birth |
front 238 What is the sonographic appearance of Osteogenesis Imperfecta Type IV? | back 238 decreased echogenicity fractures cortical bone thinning excessive trabecular bone transparency |
front 239 What is Achondroplasia? | back 239 very short limbs and sometimes a face that is small in relation to the skull |
front 240 What is VACTERL? | back 240 Vertebral defects Anal atresia Cardiac defects TracheoEsophageal atresia Renal anomalies Limb anomolies |
front 241 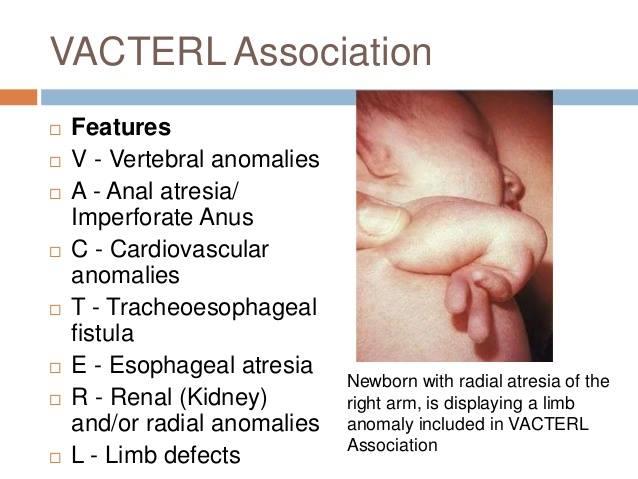 | back 241 vacterl |
front 242 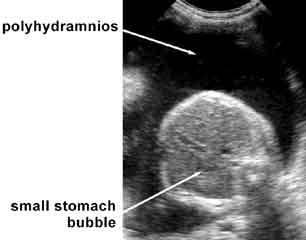 | back 242 Esophageal atresia |
front 243 How many anomalies need to be present to be considered VACTERL? | back 243 3 |