Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 1 - The Human Body: An Orientation
front 1 True or False: Anatomy is the study of body structures and their relationships. | back 1 True |
front 2 True or False: Physiology is the science of how body parts function. | back 2 True |
front 3 Name the 3 major subdivision of anatomy. | back 3
|
front 4 Physiology concerns the ________________ of specific organs organ systems. | back 4 functioning |
front 5 What 2 principles explain Physiology? | back 5
|
front 6 The ______________ principle explains the reasoning why anatomy and physiology are inseparable. | back 6
Anatomy and physiology are inseparable: What a body can do depends on the unique architecture of its parts. |
front 7 Name the levels of structural organization of the body, from simplest to the most complex. | back 7
|
front 8 Name the 11 organ systems of the body. | back 8
The immune system is a functional system closely associated with the lymphatic system. |
front 9 Name the 7 vital functional activities necessary of life. | back 9
|
front 10 Name the 5 survival needs necessary for life. | back 10
|
front 11 True or False: Homeostasis is NOT a dynamic equilibrium of the internal environment. | back 11 False
|
front 12 Name the 3 control mechanisms of the body that work together during homeostasis. | back 12
|
front 13 __________ __________ _________ reduce the effect of the original stimulus, and are essential for maintaining homeostatic control | back 13
Body temperature, heart rate, breathing rate and depth, and blood levels of glucose and certain irons are regulated by negative feedback mechanisms. |
front 14 _________ ____________ __________ intensify the initial stimulus, leading to an enhancement of the response during homeostatic control. | back 14
Positive feedback mechanisms rarely contribute to homeostasis, but blood clotting and labor contraction are regulated by such mechanisms. |
front 15 True or False: With age, efficiency of negative feedback mechanisms declines. These change underlie certain disease conditions. | back 15 True |
front 16 What position is represented by: the body erect, facing forward, feet slightly apart, arms at sides with palms facing forward | back 16
|
front 17 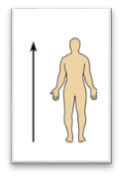 Name the Orientation and directional term. | back 17
toward the head end or upper part of thea structure or the body; above - head is superior to the abdomen. |
front 18 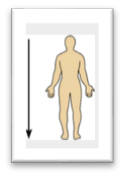 Name the Orientation and directional term. | back 18
Away from the head end or oward the lower part of a structur or the body, below - the navel is inferior o the chin. |
front 19 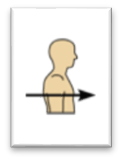 Name the Orientation and directional term. | back 19
Toward or at the front of the body; in front of - the breastbone is anterior to the spine. |
front 20 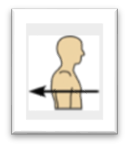 Name the Orientation and directional term. | back 20
Toward or at the back of the body; behind - the heart is posterior to the breastbone. |
front 21 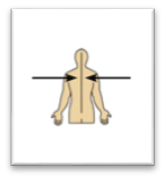 Name the Orientation and directional term. | back 21
Toward or at the midline of the body; on the inner side of - the heart is medial to the arm. |
front 22 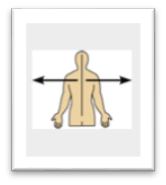 Name the Orientation and directional term. | back 22
Away from the mid-line of the body; on the outer side of - the arms are lateral to the chest. |
front 23 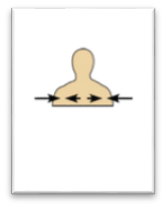 Name the Orientation and directional term. | back 23
Between a more medial and a more lateral structure - the collarbone is intermediate between the breastbone and the shoulder. |
front 24 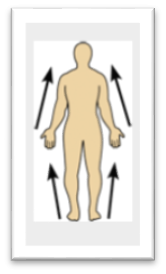 Name the Orientation and directional term. | back 24
Closer to the origin of the body part or attachment of a limb to th ebody ttrunk - the elbow is proximal to the wrist. |
front 25 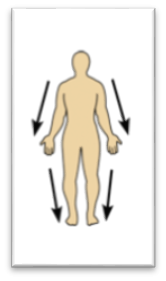 Name the Orientation and directional term. | back 25
Farther from the origin of a body part - the knee is distal to the thigh. |
front 26 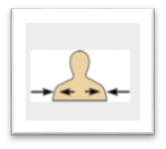 Name the Orientation and directional term. | back 26
toward or at the body surface - the skin is superficial to the skeletal muscles. |
front 27  Name the Orientation and directional term. | back 27
Away from the body surface; more internal - the lungs are deep to the skin |
front 28 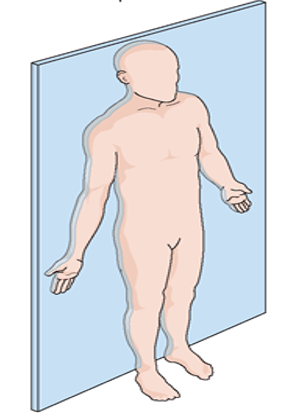 Name the plan in the picture. | back 28
divide the body into anterior and posterior parts |
front 29 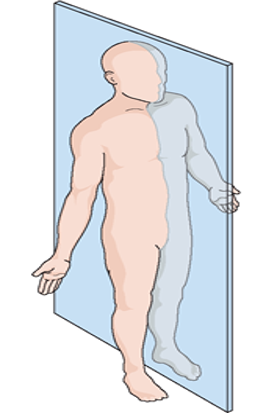 Name the plan in the picture. | back 29
A sagittal plane that lies EXACTLY in the midline |
front 30 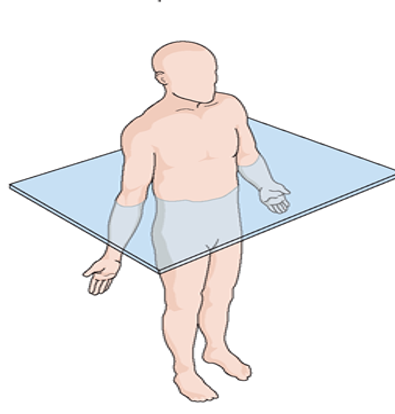 Name the plan in the picture. | back 30
|
front 31 What plane consist of cuts made diagonally between the horizontal and the vertical planes | back 31
|
front 32 A vertical plane that divides the body into right and left sections is refereed to as what? | back 32
|
front 33 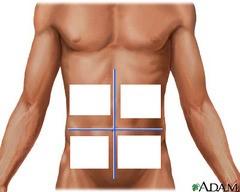 Name four abdominoplevic quadrants. | back 33 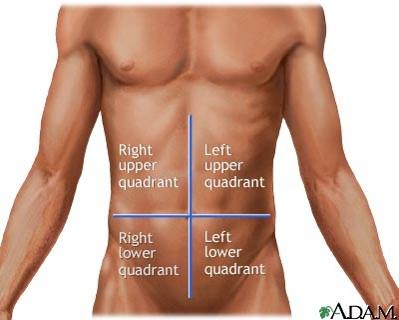
|
front 34 Name the 9 regions of the Ventral body cavity | back 34 
|
front 35 Name the 2 cavities located in the Dorsal body cavity. | back 35
|
front 36 Name the 2 major subdivisions of the Ventral body cavity. | back 36
|
front 37 Which body cavity contains the heart and lungs? | back 37
|
front 38 The liver is located in which adbominoplevic region? | back 38
|
front 39 The gallbladder is locate in which adbominoplevic region? | back 39
|
front 40 The ascending colon of the large intestine is locate in which adbominoplevic region? | back 40
|
front 41 The appedix is locate in which adbominoplevic region? | back 41
|
front 42 The stomach is locate in which adbominoplevic region? | back 42
|
front 43 The transverse colon of large intestine is locate in which adbominoplevic region? | back 43
|
front 44 The urinary bladder is locate in which adbominoplevic region? | back 44
|
front 45 The diaphragm and sleen are locate in which adbominoplevic region? | back 45
|
front 46 The descending colon of large intestine is locate in which adbominoplevic region? | back 46
|
front 47 The initial part of sigmoid colon is locate in which adbominoplevic region? | back 47
|
front 48 Bones and cartilages are part of the ___________ system | back 48
|
front 49 The nasal cavity, lungs, and trachea are __________ system organs. | back 49
|
front 50 _____________ is a term that encompasses all the chemical reaction that occur in the body cells. | back 50
|