Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Anatomy and Physiology 2: Final Exam Review
front 1 WHICH IS THE LARGEST LYMPHATIC ORGAN? | back 1 SPLEEN |
front 2 T/F Lymphatic capillaries are permeable to proteins. | back 2 TRUE |
front 3 T/F Lymph always flows away from the heart. | back 3 FALSE |
front 4 T/F Because lymph vessels are very low-pressure conduits, movements of adjacent tissues are important in propelling lymph through the lymphatics. | back 4 TRUE |
front 5 T/F Lymphocytes reside temporarily in lymphoid tissue, then move to other parts of the body. | back 5 TRUE |
front 6 T/F All the lymphoid organs are well developed before birth | back 6 FALSE |
front 7 T/F ) The cisterna chyli collects lymph from the lumbar trunks draining the upper limbs and from the intestinal trunk draining the digestive organs. | back 7 FALSE |
front 8 T/F All lymphatic organs are composed of epithelial tissue | back 8 FALSE |
front 9 T/F The most important role of the spleen is to provide a site for lymphocyte proliferation and immune surveillance and response. | back 9 FALSE |
front 10 T/F The simplest lymphoid organs are the lymph nodes. | back 10 FALSE (TONSIL) |
front 11 Which lymphatic structure drains lymph from the right upper limb and the right side of the head and thorax? A) right lymphatic duct B) lumbar trunk C) cisterna chyli D) thoracic duc | back 11 A |
front 12 The lymphatic capillaries are ________. A) more permeable than blood capillaries B) as permeable as blood capillaries C) less permeable than blood capillaries D) completely impermeable | back 12 A |
front 13 Antibodies that act against a particular foreign substance are released by ________. A) T lymphocytes B) medullary cords C) lymph nodes D) plasma cells | back 13 D |
front 14 Which of the following would not be classified as a lymphatic structure? A) pancreas B) Peyer's patches of the intestine C) spleen D) tonsils | back 14 A |
front 15 Functions of the spleen include all of those below except ________. A) storage of blood platelets B) forming crypts that trap bacteria C) storage of iron D) removal of old or defective blood cells from the blood | back 15 B |
front 16 When the lymphatic structures are blocked due to tumors, the result is ________. A) increased pressure in the lymphatics proximal to the blockage B) shrinkage of tissues distal to the blockage due to inadequate delivery of lymph C) abnormally high lymph drainage from the distal region D) severe localized edema distal to the blockage | back 16 D |
front 17 Select the correct statement about lymphoid tissue. A) Once a lymphocyte enters the lymphoid tissue, it resides there permanently. B) Lymphoid macrophages secrete antibodies into the blood. C) T lymphocytes act by ingesting foreign substances. D) Lymphoid tissue is predominantly reticular connective tissue. | back 17 D |
front 18 What is a bubo? A) a lobe of the spleen B) an infected Peyer's patch C) a wall in a lymph node D) an infected lymph node | back 18 D |
front 19 The thymus is the only lymphoid organ that does not: A) produce hormones B) have a cortex and medulla C) have lymphocytes D) directly fight antigens | back 19 D |
front 20 Digestive tract-associated lymphatic tissue includes all of the following except ________. A) palatine tonsils B) lingual tonsils C) islets of Langerhans D) Peyer's patches | back 20 C |
front 21 Which of the following is not a method that maintains lymph flow? A) breathing B) valves in lymph vessel walls C) smooth muscle contraction D) skeletal muscle contraction | back 21 C |
front 22 Which of the following is not a function of the lymphatic system? A) transporting dietary fats B) carrying out immune responses C) transporting respiratory gases D) draining excess interstitial fluid | back 22 C |
front 23 A sentinel node is ________. A) a small node in the spleen B) the first node at the junction of all the lumbar trunks C) the first node to receive lymph from an area suspected to be cancerous D) a lymph node found in the intestinal lamina propria | back 23 C |
front 24 Highly specialized lymph capillaries called ________ are present in the villi of the intestinal mucosa | back 24 LACTEAL |
front 25 The thoracic duct of the lymphatic system empties into the ________. | back 25 LEFT SUBCLAVIAN |
front 26 Tonsils have blind-ended structures called ________. | back 26 CRYPTS |
front 27 Hassall's corpuscles are always found in the lighter-colored ________ regions of the thymus. | back 27 MEDULLARY |
front 28 ) The ________ pulp of the spleen forms cuffs around the central arteries. | back 28 WHITE |
front 29 Describe the mechanisms by which lymphatic fluid is moved through the lymphatics. | back 29 Lymphatic fluid is moved through the lymphatics by the milking action of active skeletal muscles, pressure changes within the thorax during breathing, valves to prevent backflow, and pulsation of adjacent arteries.`` |
front 30 Where are the lymph node aggregations most dense? | back 30 1. INGUINAL 2. CERVICAL 3. AXILLARY |
front 31 What is the special role of the thymus gland? | back 31 thymus gland causes T lymphocytes to become immunocompetent. |
front 32 List the functions of the spleen. | back 32 REMOVE OLD RBC'S AND PLATELETS STORE IRON BLOOD FILTER SITE FOR ERYTHROCYTE PRODUCTION LYMPHOCYTE PROLIFERATION |
front 33 How do the lymph capillaries differ from blood capillaries? | back 33 SIMILAR: SIMPLE SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM VALVES DIFFERENT: ENDOTHELIAL CELLS ARE NOT TIGHTLY JOINED LYMPHATIC CAPILLARIES LARGER IN DIAMETER BUNDLES OF FINE FILAMENTS ANCHOR THE ENDOTHELIAL CELLS TO SURROUNDING STRUCTURES |
front 34 A man involved in a traffic accident is rushed to the emergency room of a hospital with severe internal bleeding. Examination reveals a ruptured spleen. What is the treatment of choice and what is the likely long-term outcome (prognosis)? | back 34 Splenectomy is not as necessary the prognosis is very good, as the functions of the spleen are taken over by the liver and bone marrow. |
front 35 While passing through a village on safari you notice a man with one enormous leg and one normal-sized leg. What could have caused the increased size of the swollen leg? | back 35 ELEPHANTIASIS PARASITIC WORM BLOCKED LYMPH SYSTEM-> EDEMA |
front 36 A nurse palpated enlarged lymph nodes. Describe signs and symptoms that help to distinguish cancerous lymph nodes from infected lymph nodes. | back 36 HARD INDICATE MALIGNANCY TENDER INDICATES INFLAMMATION |
front 37 As the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) progresses, some individuals develop persistent generalized lymphadenopathy. Explain why this may occur. | back 37 THE LYMPH NODES ARE OVERWHELMED BY THE LARGE NUMBER OF VIRUS PARTICLES TRAPPED IN THE NODES |
front 38 SINUSOID CAPILLARY | back 38 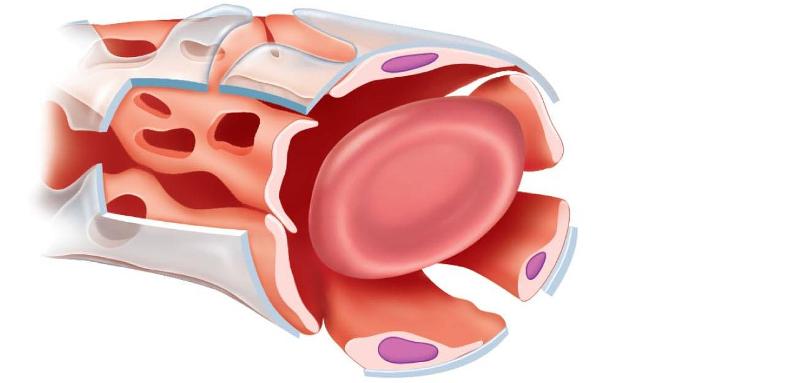 |
front 39 CAPILLARY FOUND IN ENDOCRINE ORGANS THAT ALLOW HORMONES TO GAIN RAPID ENTRY INTO THE BLOOD | back 39 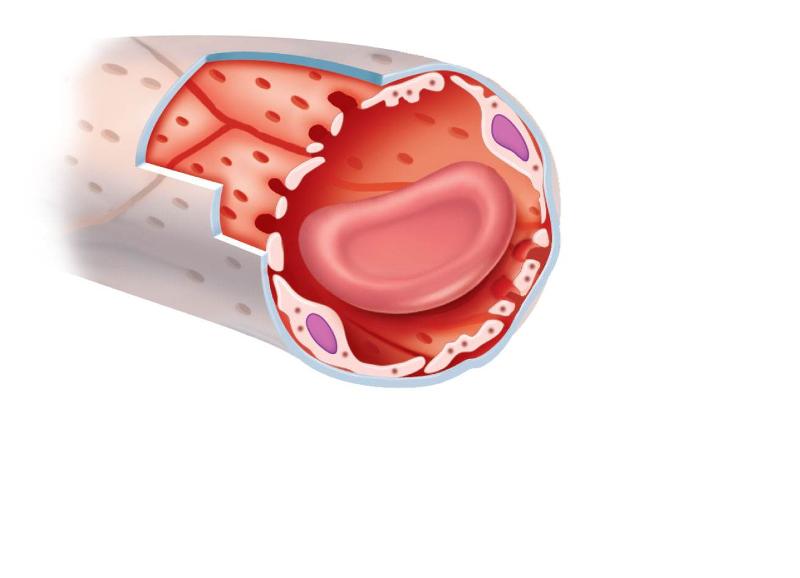 |
front 40 CAPILLARY THAT MAY CONTAIN KUPFFER CELLS IN THE LINNING | back 40  |
front 41 CAPILLARY FOUND WHERE ACTIVE CAPILLARY ABSORPTION OF FILTRATE OCCURS | back 41  |
front 42 SUPPLIES THE DUODENUM AND STOMACH | back 42 COMMON HEPATIC ARTERY |
front 43 MAJOR SUPPLY TO THE CEREBRAL HEMISPHERES A. CELIAC TRUNK B. RADIAL ARTERY C. BRACHIOCEPHALIC TRUNK D INTERNAL CAROTIC ARTERY E EXTERNAL ILIAC ARTERY | back 43 D |
front 44 SUPPLIES THE LOWER LIMBS A. CELIAC TRUNK B. RADIAL ARTERY C. BRACHIOCEPHALIC TRUNK D INTERNAL CAROTIC ARTERY E EXTERNAL ILIAC ARTERY | back 44 E |
front 45 VESSEL COMMONLY USED AS A CORONLY BYPASS VESSEL A. GREAT SAPHENOUS VEIN B. SUPERIOR MESENTERIC ARTERY C. BRACHIAL ARTERY D. PULMONARY VEIN E. FEMORAL ARTERY | back 45 A |
front 46 RECEIVES BLOOD FROM ALL AREAS SUPERIOR TO THE DIAPHRAGM, EXCEPT THE HEART WALL A. EXTERNAL JUGULAR VEIN B. SUBCLAVIAN VEIN C. SUPERIOR VENA CAVA D. PULMONARY TRUNK E. AXILLARY ARTERY | back 46 C |
front 47 SITE WHERE RESISTANCE TO BLOOD FLOW IS GREATEST A. LARGE ARTERIES B. CAPILLARIES C. ARTERIOLES D. LARGE VEINS | back 47 C |
front 48 SITE WHERE BLOOD PRESSURE IS LOWEST A. LARGE ARTERIES B. CAPILLARIES C. ARTERIOLES D. LARGE VEINS | back 48 D |
front 49 SITE WHERE VELOCITY OF BLOOD IS SLOWEST A. LARGE ARTERIES B. CAPILLARIES C. ARTERIOLES D. LARGE VEINS | back 49 B |
front 50 SITE THAT IS THE MAJOR DETERMINANT OF PERIPHERAL RESISTANCE A. LARGE ARTERIES B. CAPILLARIES C. ARTERIOLES D. LARGE VEINS | back 50 C |
front 51 T/F The adjustment of blood flow to each tissue in proportion to its requirements at any point in time is termed autoregulation. | back 51 TRUE |
front 52 T/F The thick-walled arteries close to the heart are called muscular arteries | back 52 FALSE (ELASTIC ARTERIES) |
front 53 T/F The carotid sinus reflex protects the blood supply to the brain, whereas the aortic reflex is more concerned with maintaining adequate blood pressure in the systemic circuit as a whole. | back 53 TRUE |
front 54 T/F In infants and young people, congenital vascular problems are less common than congenital heart disease. | back 54 TRUE |
front 55 T/F The azygos vein originates in the abdomen. | back 55 TRUE |
front 56 The arteries that are also called distributing arteries are the ________. A) capillaries B) arterioles C) muscular arteries D) elastic arteries | back 56 C |
front 57 ) Aldosterone will ________. A) promote an increase in blood pressure B) decrease sodium reabsorption C) promote a decrease in blood volume D) result in a larger output of urine | back 57 A |
front 58 Which of the following signs of hypovolemic shock is a relatively late sign? A) cold, clammy skin B) rapid, thready pulse C) rapidly falling blood pressure D) increased heart rate | back 58 C |
front 59 Which of the choices below explains why the arterioles are known as resistance vessels? A) The contraction and relaxation of the smooth muscle in their walls can change their diameter. B) They contain a large quantity of elastic tissue. C) Their prime function is the exchange of nutrients and wastes between the blood and tissue cells. D) They distribute blood to various parts of the body. | back 59 A |
front 60 Which of the following is a type of circulatory shock? A) vascular, due to extreme vasodilation as a result of loss of vasomotor tone B) circulatory, where blood volume is normal and constant C) cardiogenic, which results from any defect in blood vessels D) hypovolemic, caused by increased blood volume | back 60 A |
front 61 The influence of blood vessel diameter on peripheral resistance is ________. A) significant because resistance is inversely proportional to the fourth power of the vessel radius B) the only factor that influences resistance C) significant because resistance is directly proportional to the blood vessel diameter D) insignificant because vessel diameter does not vary | back 61 A |
front 62 The hepatic portal vein ________. A) is actually an artery B) carries oxygen-rich blood from the liver to the viscera C) carries blood from the liver to the inferior vena cava D) carries nutrient-rich blood to the liver | back 62 D |
front 63 Which of the choices below does not explain why low capillary pressures are desirable? A) Capillaries are fragile and high pressures would rupture them. B) Low blood pressure is more desirable than high blood pressure. C) Most capillaries are extremely permeable and thus even low pressures force solute-containing fluid out of the bloodstream. | back 63 B |
front 64 Which of the following do not influence arterial pulse rate? A) activity B) emotions C) postural changes D) the vessel selected to palpate | back 64 D |
front 65 The velocity of blood flow is ________. A) slower in the veins than in the capillaries because veins have a large diameter B) in direct proportion to the total cross-sectional area of the blood vessels C) slower in the arteries than in capillaries because arteries possess a relatively large diameter D) slowest in the capillaries because the total cross-sectional area is the greatest | back 65 D |
front 66 Select the correct statement about blood flow. A) It is measured in mm Hg. B) It is greatest where resistance is highest. C) It is relatively constant through all body organs. D) Blood flow through the entire vascular system is equivalent to cardiac output. | back 66 D |
front 67 The short-term controls of blood pressure, mediated by the nervous system and bloodborne chemicals, primarily operate via all but which of the following? A) chemoreceptors B) altering blood volume C) reflex arcs associated with vasomotor fibers D) reflex arcs involving baroreceptors | back 67 B |
front 68 Secondary hypertension can be caused by ________. A) stress B) smoking C) arteriosclerosis D) obesity | back 68 C |
front 69 Where in the body would you find low oxygen levels causing vasoconstriction and high levels causing vasodilation? A) kidney B) liver C) heart D) lungs | back 69 D |
front 70 What do the ductus arteriosus and the foramen ovale become at birth? A) fossa ovalis; ligamentum arteriosum B) ligamentum arteriosum; fossa ovalis C) ligamentum teres; fossa ovalis D) ligamentum arteriosum; ligamentum teres | back 70 B |
front 71 Which of the following would not result in the dilation of the feeder arterioles and opening of th eprecapillary sphincters in systemic capillary beds? A) a decrease in local tissue oxygen content B) an increase in local tissue carbon dioxide C) a local increase in pH D) a local increase in histamine | back 71 C |
front 72 The baroreceptors in the carotid sinus and aortic arch are sensitive to which of the following? A) a decrease in carbon dioxide B) an increase in oxygen levels C) changes in arterial pressure D) a decrease in oxygen levels | back 72 C |
front 73 A family of peptides called ________ are released by the endothelium and are among the most potent vasoconstrictors known. | back 73 ENDOTHELINS |
front 74 ________ shock is due to abnormal expansion of blood vessels and a rapid drop in blood pressure. | back 74 VASCULAR |
front 75 Atherosclerosis is a progressive disease of blood vessels that is responsible for millions of deaths each year. Describe the disease process, noting the involvement of specific cell/tissue types and molecules. | back 75 1. INJURY TO ENDOTHELIAL CELLS 2. fats i.e. cholesterol, LDL, trigylycerides 3. macrophages try to eat the oxidized fat but transform into foam cells 4. foam cells become fatty streaks -> atherosclerotic plaques 5. lumen narrows |
front 76 A woman in her early 50s appeared at a walk-in clinic, complaining of aching pain in her right leg following a fall. Visual examination revealed that the medial aspect of that leg was red and swollen. A diagnosis of phlebitis was made. What is phlebitis, and what more serious condition may result if proper healing does not occur? | back 76 PHBLEBITIS inflammation of the vein if proper healing does not occur it will become THROMBOPHLEBITIS (clot formation) which might become embolus |
front 77 A pregnant patient comes into a clinic and asks about a small dark bulge that is becoming more apparent on her leg. What is it and what caused it? | back 77 VARICOSE VEINS -blood pooling-> enlarges veins-> valves begin to fail |
front 78 A patient lost a lot of blood during surgery and his blood pressure dropped from 120/80 to 90/50. Describe how the kidneys respond to this change in blood pressure. | back 78 when BP declines -> kidney receptors detect this change, thus they secrete renin-> Angiotensin ADH released Aldosterone sodium moves into blood stream |
front 79 The ________ plexus of testicular veins assists in cooling the testis | back 79 pampiniform |
front 80 The ________ cells of the testis nourish the newly formed sperm cells. | back 80 sustentacular |
front 81 The portion of the uterine endometrium that is not sloughed off every month is called the ________. | back 81 Stratnum Basalis |