Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
chapter 13
front 1 A triploid cell contains three sets of chromosomes. If a cell of a usually diploid species with 42 chromosomes per cell is triploid, this cell would be expected to have which of the following? | back 1 63 chromosomes in 21 sets of 3 |
front 2 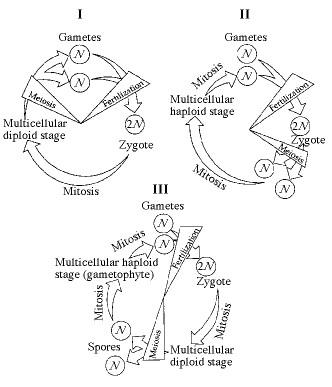 Which of the life cycles is typical for plants and some algae? | back 2 III only |
front 3 Which of the following is true of a species that has a chromosome number of 2n = 16? | back 3 Each cell has eight homologous pairs |
front 4 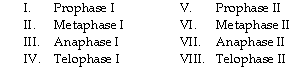 Tetrads of chromosomes are aligned at the equator of the spindle; alignment determines independent assortment. | back 4 II |
front 5 The human genome is minimally contained in which of the following? | back 5 Every human cell |
front 6 Which of these statements is false? | back 6 At sexual maturity, ovaries and testes produce diploid gametes by meiosis. |
front 7 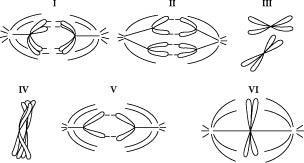 Which diagram represents anaphase I of meiosis? | back 7 I |
front 8 A karyotype results from which of the following? | back 8 the ordering of human chromosome images |
front 9 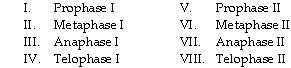 Synaptonemal complexes form or are still present. | back 9 I only |
front 10 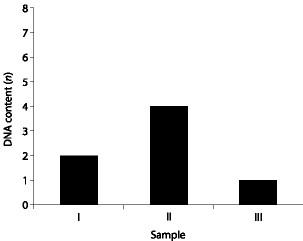 Which sample of DNA might be from a nerve cell arrested in G0 of the cell cycle? | back 10 I |
front 11 When we see chiasmata under a microscope, that lets us know which of the following has occurred? | back 11 prophase I |
front 12 When homologous chromosomes crossover, what occurs? | back 12 Specific proteins break the two strands and re-join them with their homologs. |
front 13 After telophase I of meiosis, the chromosomal makeup of each daughter cell is | back 13 haploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of two chromatids. |
front 14 Which of the following is a true statement about sexual vs. asexual reproduction? | back 14 in sexual reproduction, individuals transmit 50% of their genes to each of their offspring. |
front 15 Homologous chromosomes move toward opposite poles of a dividing cell during | back 15 meiosis I. |
front 16 A human cell containing 22 autosomes and a Y chromosome is | back 16 a sperm |
front 17 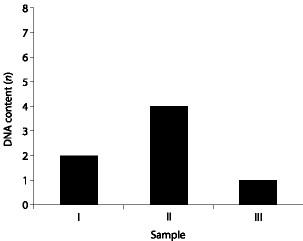 Which sample might represent an animal cell in the G2 phase of the cell cycle? | back 17 II |
front 18 If a horticulturist breeding gardenias succeeds in having a single plant with a particularly desirable set of traits, which of the following would be her most probable and efficient route to establishing a line of such plants? | back 18 Clone the plant asexually to produce an identical one. |
front 19 If a cell has completed the first meiotic division and is just beginning meiosis II, which of the following is an appropriate description of its contents? | back 19 It has half the amount of DNA as the cell that began meiosis. |
front 20 A sexually reproducing animal has two unlinked genes, one for head shape (H) and one for tail length (T). Its genotype is Hh | back 20 HT |
front 21 Chromatids are separated from each other. | back 21 The statement is true for mitosis and meiosis II. |
front 22 A tetrad includes which of the following sets of DNA strands? | back 22 two sets of sister chromatids that have synapsed |
front 23 Which of the following occurs in meiosis but not in mitosis? | back 23 synapsis of chromosomes |
front 24 Which of the following is an example of alternation of generations? | back 24 A diploid plant (sporophyte) produces, by meiosis, a spore that gives rise to a multicellular, haploid pollen grain (gametophyte). |
front 25 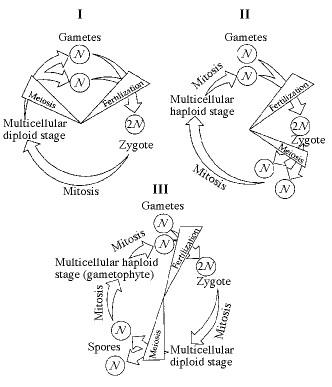 In part III of Figure 13.1, the progression of events corresponds to which of the following series? | back 25 sporophyte, meiosis, spore, mitosis, gametophyte, mitosis, gametes, fertilization |
front 26 Which of the following best describes the frequency of crossing over in mammals? | back 26 at least 1-2 per chromosome pair |
front 27 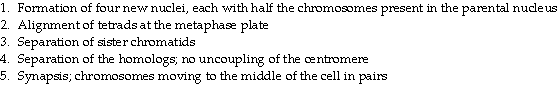 Which of the steps takes place in both mitosis and meiosis? | back 27 3 |
front 28 Which of the following is a true statement about sexual vs. asexual reproduction? | back 28 In sexual reproduction, individuals transmit 50% of their genes to each of their offspring |
front 29 If the DNA content of a diploid cell in the G1 phase of the cell cycle is x, then the DNA content of a single cell at metaphase of meiosis II would be | back 29 x |
front 30 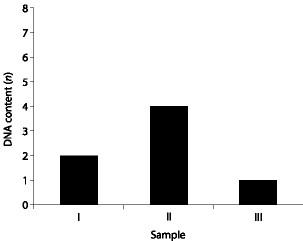 Which sample might represent a zygote? | back 30 I |
front 31 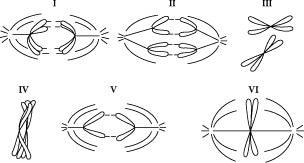 In a human karyotype, chromosomes are arranged in 23 pairs. If we choose one of these pairs, such as pair 14, which of the following do the two chromosomes of the pair have in common? | back 31 Length, centromere position, staining pattern, and traits coded for by their genes. |
front 32 In a life cycle such as that shown in part III of Figure 13.1, if the zygote's chromosome number is 10, which of the following will be true? | back 32 The sporophyte's chromosome number per cell is 10 and the gametophyte's is 5. |
front 33 If the DNA content of a diploid cell in the G1 phase of the cell cycle is x, then the DNA content of the same cell at metaphase of meiosis I would be | back 33 2x |