Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Campbell Biology Chapter 1 to 20 test preparation
front 1 1. Which of these is reflective of the hierarchical organization of
life from most to least inclusive? | back 1 Answer: c |
front 2 2. Evolution is biology's core theme that ties together all the other
themes. | back 2 Answer: e |
front 3 3. A controlled experiment is one in which | back 3 Answer: c |
front 4 4. About 25 of the 92 occurring elements are known to be essential to
life. Which four of these 25 elements make up approximately 96% of
living matter? | back 4 Answer: d |
front 5 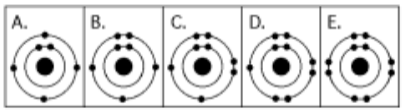 5. Which drawing below depicts the electron configuration of oxygen
(16 8O) | back 5 Answer: c |
front 6 6. What does the reactivity of an atom depend on? | back 6 Answer: d |
front 7 7. A covalent chemical bonds is one in which | back 7 Answer: c |
front 8 8. What results from an unequal sharing of electrons between
atoms? | back 8 Answer: b |
front 9 9. Which bonds must be broken for water to vaporize? | back 9 Answer: d |
front 10 10. One mole (mol) of a substance is | back 10 Answer: e |
front 11 11. One liter of a solution of pH has how many more hydrogen ions
(H+) than 1 L of a solution of pH 6? | back 11 Answer: d |
front 12 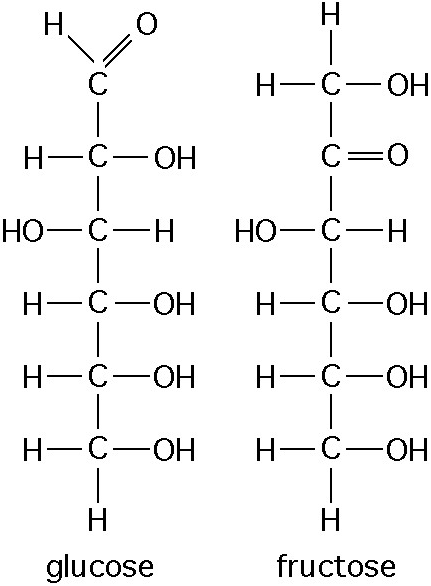 12. Observe the structure of glucose and fructose in the Figure
above | back 12 Answer: d |
front 13 13. Polymers of polysaccharides, fats and proteins are all
synthesized from monomers by which process? | back 13 Answer: c |
front 14 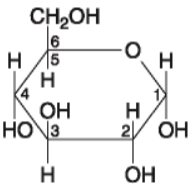 14. If 128 molecules of the general type shown in the figure above
were covalently joined together in sequence, the single molecule that
would result would be a | back 14 Answer: a |
front 15 15. The 20 different amino acids found in polypeptides exhibit
different chemical and physical properties because of
different | back 15 Answer: c |
front 16 16. The tertiary structure of a protein is the | back 16 Answer: c |
front 17 17. What would be an unexpected consequence of changing one amino
acid in a protein consisting of 325 amino acids? | back 17 Answer: e |
front 18 18. Which of the following best describes the flow of information in
eukaryotic cells? | back 18 Answer: a |
front 19 19. All of the following nitrogenous bases are found in DNA
except: | back 19 Answer: c |
front 20 20. Which of the following types of molecules are the major
structural components of the cells membrane? | back 20 Answer: c |
front 21 21. A patient has had a serious accident and lost a lot of blood. In
an attempt to replenish body fluids, distilled water, equal to the
volume of blood lost is transferred directly into one of his veins.
What will be the most probable result of this transfusion? | back 21 Answer: c |
front 22 22. The movement of a substance across a biological membrane against
its concentration gradient with the help of energy input is | back 22 Answer: b |
front 23 23. The sodium-potassium is called an electrogenic pump because
it | back 23 Answer: c |
front 24 24. Which term most precisely describes the cellular process of
breaking down large molecules into smaller ones? | back 24 Answer: e |
front 25 25. Living organism increase in complexity as they grow, resulting in
a decrease in the entropy of an organism. How does this relate to the
second law of thermodynamics? | back 25 Answer: d |
front 26 26. Which of the following statements regarding ATP is (are)
correct? | back 26 Answer: e |
front 27 27. Increasing the substrate concentration in an enzymatic reaction
could overcome which of the following? | back 27 Answer: c |
front 28 28. What is the term used for the metabolic pathway in which glucose
(C6O12H6) is degraded to carbon
dioxide (CO2) and water? | back 28 Answer: a |
front 29 29. In addition to ATP, what are the end products of
glycolysis? | back 29 Answer: c |
front 30 30. Which kind of metabolic poison would most directly interfere with
glycolysis? | back 30 Answer: c |
front 31 31. The primary role of oxygen in cellular respiration is to | back 31 Answer: b |
front 32 32. In a plant cell, where are the ATP synthase complexes
located? | back 32 Answer: d |
front 33 33. Which of the following statements best represents the
relationship between the light reactions and the Calvin Cycle? | back 33 Answer: a |
front 34 34. From the perspective of the cell receiving the message, the three
stages of cell signaling are | back 34 Answer: b |
front 35 35. Which of the following is (are) true of ligand-gated ion
channels? | back 35 Answer: e |
front 36 36. The correct sequence of steps in the M phase of the cell cycle
is | back 36 Answer: c |
front 37 37. Which of the following is true of the process of meiosis? | back 37 Answer: c |
front 38 38. What was the most significant conclusion that Gregor Mendel drew
from his experiments with pea plants? | back 38 Answer: b |
front 39 39. Two characters that appear in a 9:3:3:1 ratio in the F2
generation should have which of the following properties? | back 39 Answer: b |
front 40 A woman who has blood type A has a daughter who is type O positive
and a son who is type B negative. Rh positive is a simple dominant
trait over Rh negative. | back 40 Answer: d |
front 41 41. When Thomas Hunt Morgan crossed his red-eyes F1 generation flies
to each other, the F2 generation included both red-and white-eyed
flies. Remarkably, all the white-eyed flies were male. What was the
explanation for this result? | back 41 Answer: a |
front 42 42. How could one explain a test-cross involving F1 dihybrid flies in
which more parental-type offspring that recombinant-type offspring are
produced? | back 42 Answer: a |
front 43 43. Which of the following statements does not apply to the Watson
and Crick model of DNA? | back 43 Answer: d |
front 44 44. The leading and the lagging strands differ in that | back 44 Answer: a |
front 45 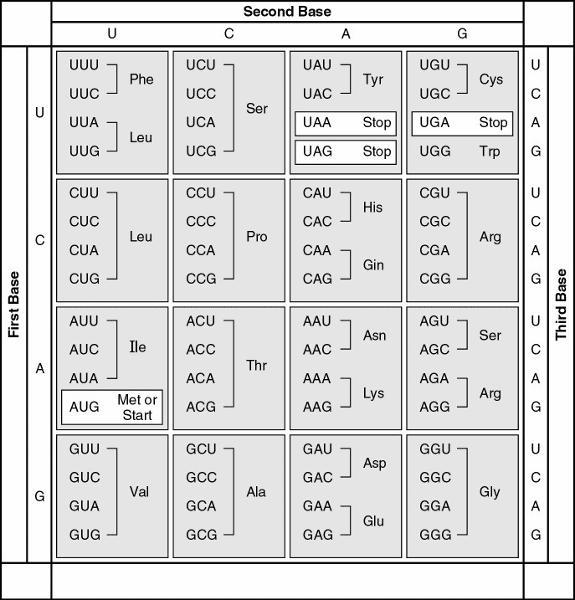 45. A possible sequence of nucleotides in the template strand DNA
that would code for the polypeptide sequence phe-leu-ile-val would
be | back 45 Answer: e |
front 46 46. RNA polymerase and DNA polymerase differ in that | back 46 Answer: d |
front 47 47. A frameshift mutation could result from | back 47 Answer: b |
front 48 48. What is the function of reverse transcriptase in
retroviruses? | back 48 Answer: b |
front 49 49. What are prions? | back 49 Answer: a |
front 50 50.What does the operon model attempt to explain? | back 50 Answer: a |
front 51 51. Which two functional groups are always found in amino
acids? | back 51 Answer: c |
front 52 52. In animal cells, hydrolytic enzymes are packaged to prevent
general destruction of cellular components. Which of the following
organelles function in this? | back 52 Answer: c |
front 53 53. A cell has the following molecules and organelles enzymes: DNA,
ribosomes, plasma membrane, and mitochondria. This could be | back 53 Answer: b |
front 54 54. Plasmodesmata in plant cells are most similar in function to
which of the following structures in animal cells? | back 54 Answer: a |
front 55 55. Which of the following statements concerning prokaryotic and
eukaryotic cells is not correct? | back 55 Answer: b |
front 56 56. Celery stalks that are immersed in fresh water for several hours
become stiff and hard. Similar stalks left in a salt solution become
limp and soft. From this we can deduce that the cells of the celery
stalks are | back 56 Answer: c |
front 57 57. The active site of an enzyme is the region that | back 57 Answer: e |
front 58 58. When you have a severe fever, what may be a grave consequence if
it is not controlled? | back 58 Answer: a |
front 59 59. Where are the proteins of the electron transport chain
located? | back 59 Answer: e |
front 60 60. Inside an active mitochondrion, most electrons follow which
pathway? | back 60 Answer: b |
front 61 61. Which of the following occurs in the cytoplasm of an eukaryotic
cell? | back 61 Answer: a |