Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Urinary SYstem
front 1 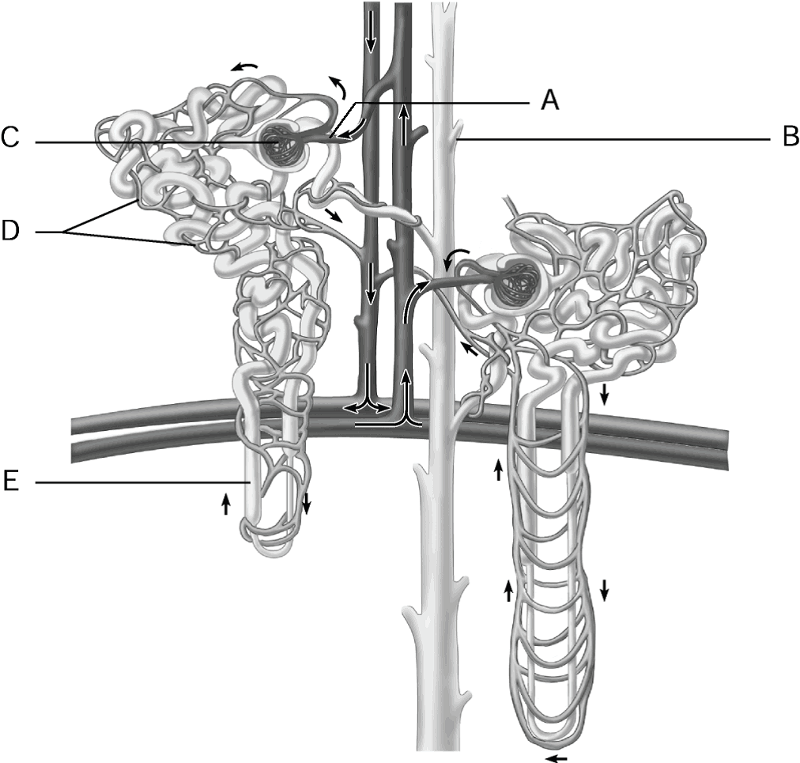 1) Glomerulus. 2) Afferent arteriole. 3) Collecting duct. 4) Loop of Henle. 5) Peritubular capillaries. 6) Structue most closely associated with granular cells. 7) Medulla of the kidney. | back 1 1) C 2) A 3) B 4) E 5) D 6) A 7) E |
front 2  8) Podocyte 9) Is composed of simple squamous epithelium. 10) Collecting duct cells. 11) Proximal convoluted tubule cells. | back 2 8.B 9. A 10. C 11. E |
front 3 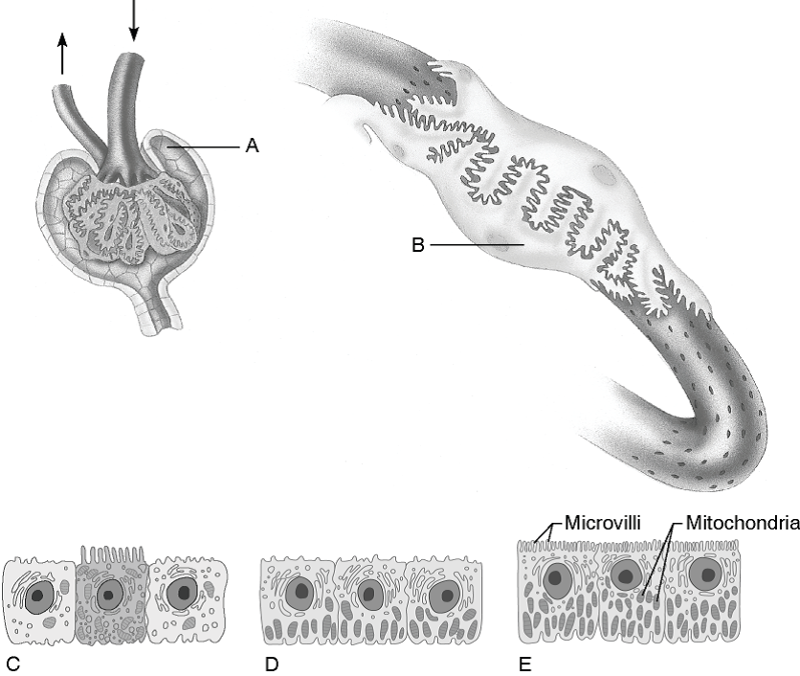 12) Filtrate at the site of these cells is about the same osmolarity as blood plasma. 14) Cells that reabsorb virtually all the nutrients. 15) Cells that are most affected by ADH. 16) Almost no water is absorbed in these cells. | back 3 12. E 13. E 14. E 15. A 16. C |
front 4 17) Proximal convoluted tubule. A) Site that drains the distal | back 4 17) E |
front 5 18) Glomerulus. A) Site that drains the distal | back 5 18) B |
front 6 19) Peritubular capillaries. A) Site that drains the distal | back 6 19) C |
front 7 20) Collecting duct. A) Site that drains the distal | back 7 20) A |
front 8 21) Arcuate vein. | back 8 21) D |
front 9 1) The mechanism that establishes the medullary osmotic gradient
depends most on the | back 9 A) loop of Henle |
front 10 2) Urine passes through the ________. | back 10 B) pelvis of the kidney to ureter to bladder to urethra |
front 11 3) Which of the following is associated with the renal
corpuscle? B) a vasa recta D) an efferent arteriole | back 11 B) a vasa recta |
front 12 4) An increase in the permeability of the cells of the collecting tubule to water is due to ________. | back 12 B) an increase in the production of ADH |
front 13 5) The urinary bladder is composed of ________ epithelium. | back 13 A) transitional |
front 14 6) The kidneys are stimulated to produce renin ________. | back 14 C) by a decrease in the blood pressure |
front 15 7) Blood vessels of the renal columns are called ________. | back 15 C) interlobar |
front 16 8) Which gland sits atop each kidney? | back 16 A) adrenal |
front 17 9) The ________ artery lies on the boundary between the cortex and medulla of the kidney. | back 17 B) arcuate |
front 18 10) The glomerulus differs from other capillaries in the body in that it ________. | back 18 C) is drained by an efferent arteriole |
front 19 11) The descending limb of the loop of Henle ________. | back 19 D) contains fluid that becomes more concentrated as it moves down into the medulla |
front 20 12) Select the correct statement about the ureters. A) Ureters contain sphincters at the entrance to the bladder to
prevent the backflow of urine. | back 20 C) The ureters are capable of peristalsis like that of the gastrointestinal tract. |
front 21 13) The fatty tissue surrounding the kidneys is important because ________. B) it stabilizes the position of the kidneys by holding them in their normal position | back 21 B) it stabilizes the position of the kidneys by holding them in their normal position |
front 22 14) The renal corpuscle is made up of ________. A) Bowmans capsule and glomerulus | back 22 A) Bowmans capsule and glomerulus |
front 23 15) The functional and structural unit of the kidneys is ________. A) the nephron | back 23 A) the nephron |
front 24 The juxtaglomerular apparatus is responsible | back 24 D) regulating the rate of filtrate formation and controlling systemic blood pressure |
front 25 The fatty tissue surrounding the kidneys is important because ________. | back 25 it stabilizes the position of the kidneys by holding them in their normal position |
front 26 The functional and structural unit of the kidneys is ________. | back 26 A) the nephron |
front 27 17) The chief force pushing water and solutes out of the blood across
the filtration membrane is | back 27 C) glomerular hydrostatic pressure (glomerular blood pressure) |
front 28 18) Which of the following statements describes the histology of the
ureters? | back 28 A) They are trilayered (mucosa, muscularis, and adventitia) |
front 29 19) The first major branch of the renal artery is ________. | back 29 segmental |
front 30 20) Which of the following acts as the trigger for the initiation of
micturition (voiding)? | back 30 A) The stretching of the bladder wall serves as the trigger |
front 31 21) The filtration membrane includes all except ________. | back 31 C) renal fascia |
front 32 22) The mechanism of water reabsorption by the renal tubules is
________. | back 32 B) osmosis |
front 33 23) Most electrolyte reabsorption by the renal tubules
________. | back 33 C) is hormonally controlled in distal tubule segments |
front 34 24) The macula densa cells respond to ________. | back 34 D) changes in solute content of the filtrate |
front 35 25) Which of the following is not reabsorbed by the proximal
convoluted tubule? | back 35 D) creatinine |
front 36 26) The fluid in the glomerular (Bowman's) capsule is similar to
plasma except that it does not | back 36 D) plasma protein |
front 37 27) Alcohol acts as a diuretic because it ________. | back 37 D) inhibits the release of ADH |
front 38 28) The function of angiotensin II is to ________. | back 38 A)constrict arterioles and increase blood pressure |
front 39 29) A disease caused by inadequate secretion of antidiuretic hormone
(ADH) by the pituitary | back 39 B) diabetes insipidus |
front 40 An important characteristic of urine is its specific gravity or
density, which is ________. | back 40 B) 1.001-1.035 |
front 41 31) Place the following in correct sequence from the formation of a
drop of urine to its elimination | back 41 D) 3, 6, 2, 1, 5, 4 3. nephron, 6. collecting duct, 2. minor calyx, 1. major calyx, 5. ureter, 4. urethra |
front 42 32) Select the correct statement about the nephrons. | back 42 A) The parietal layer of the glomerular capsule is simple squamous epithelium. |
front 43 34) Which of the following is not a part of the juxtaglomerular
apparatus? | back 43 C) podocyte cells |
front 44 35) Tubular reabsorption ________. | back 44 B) by active mechanisms usually involves movement against an
electrical and/or chemical |
front 45 36) Which statement is true about urine? | back 45 C) Urine has nitrogenous waste such as urea and uric acid |
front 46 37) Reabsorption of high levels of glucose and amino acids in the
filtrate is accomplished by | back 46 D) secondary active transport |
front 47 38) While the kidneys process about 180 L of blood-derived fluids
daily, the amount that actually | back 47 C) 1%, or 1.8 L |
front 48 39) Fetal kidneys do not have to work very hard because
________. | back 48 C) the placenta allows the mother's urinary system to clear the waste from fetal blood |
front 49 40) Which of the following best describes kidney function in older adults (70 years or older)? A) Kidney function remains the same throughout life, regardless of
age. | back 49 D) Kidney function decreases due to kidney atrophy. |
front 50 41) The factor favoring filtrate formation at the glomerulus is
________. | back 50 B) the glomerular hydrostatic pressure |
front 51 42) If the Tm for a particular amino acid is 120 mg/100 ml and the
concentration of that amino acid | back 51 C) will appear in the urine |
front 52 43) If one says that the clearance value of glucose is zero, what
does this mean? | back 52 C) Normally all the glucose is reabsorbed. |
front 53 44) Excretion of dilute urine requires ________. | back 53 B) impermeability of the collecting tubule to water |
front 54 45) As the renal artery approaches the kidney, it branches to supply
the renal tissue. Place the | back 54 A) 1, 4, 3, 2 1. segmental 4. interlobar 3. arcuate 2. cortical radiate |
front 55 46) In the ascending limb of the loop of Henle ________. | back 55 D) the thick segment moves ions out into interstitial spaces for reabsorption |
front 56 47) Select the correct statement about urinary system
development. | back 56 A) Kidneys develop from urogenital ridges. |
front 57 48) The disruption in homeostasis known as pyelitis is
________. | back 57 C) an infection of the renal pelvis and calyces |
front 58 49) Which statement is correct? | back 58 A) Reabsorption of water is hormonally controlled. |