Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Review for Chapters 12, 13, 16, 17
front 1 Why does a cell divide because of its size? | back 1 1. DNA doesn't grow with the cell, so as the cell gets larger, it demands more of DNA. To reduce strain, a cell must not grow anymore 2. Cells lose efficiency if too large because waste and nutrients do not move across the cell membrane. |
front 2 Define Interphase (basic idea) | back 2 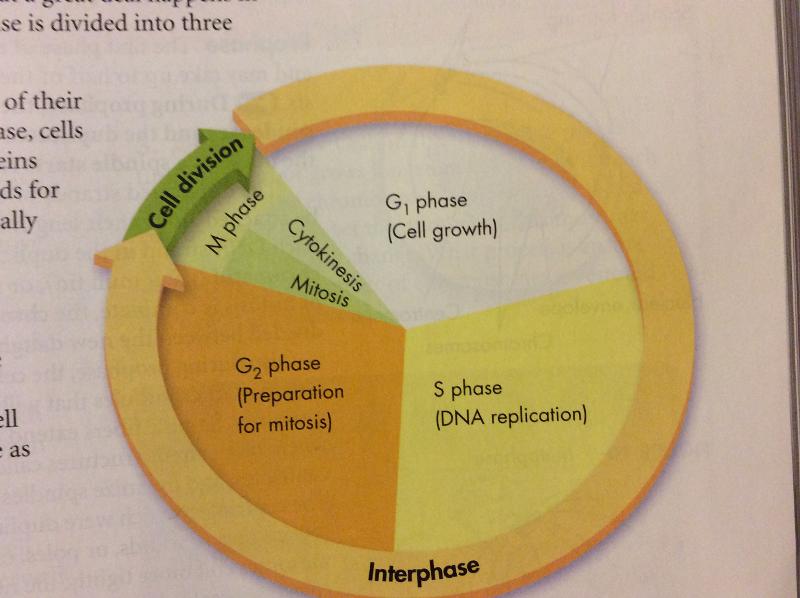 The "in between growth of a cell". There are 3 parts: G1, S, G2 |
front 3 Describe G1 phase (interphase) | back 3 Phase of cell growth. Cell increases in size. Cell synthesizes new proteins and organelles |
front 4 Describe S Phase (interphase) | back 4 DNA replication. DNA is synthesized and chromosomes are replicated. 2x the DNA |
front 5 Describe G2 Phase (interphase) | back 5 Preparing for cell division. Shortest of the phases organelles and molecules for division are produced |
front 6 what is the M Phase that follows interphase? | back 6 It is the cell division follows interphase produces 2 daughter cells. Consists of mitosis and cytokinesis |
front 7 Mitosis | back 7 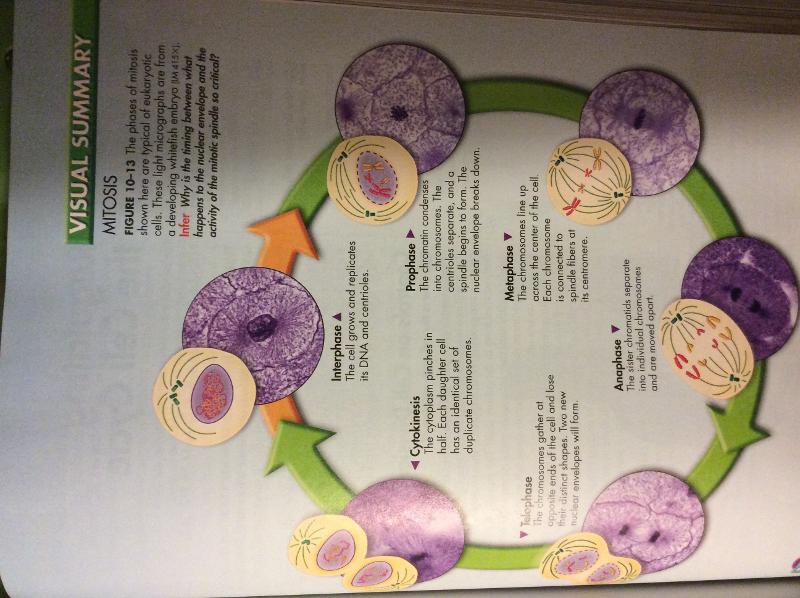 1st stage of cell division. It's the division of the cell nucleus. There are 4 phases |
front 8 Mitosis: Prophase | back 8 Usually the longest genetic material inside nucleus condenses and duplicated chromosomes become visible. outside the nucleus, spindles begin to form |
front 9 centromere | back 9 Where duplicated DNA molecules attach along their length |
front 10 sister chromatid | back 10 Each DNA strand in the duplicated DNA chromosome |
front 11 centrioles | back 11 Where spindles extend from in animal cells. |
front 12 Mitosis: metaphase | back 12 Usually the shortest phase. sister chromatids line up in the middle of the cell. centrioles are at opposite ends, spindles connect to the centromes |
front 13 mitosis: anaphase | back 13 Sister chromatids separate and move apart. each sister chromatids is now considered an individual chromosome chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell anaphase ends when the movements stops and the chromosomes are completely separated. |
front 14 Mitosis: telophase (final phase) | back 14 Chromosomes begin to spread into tangle of chromatin nuclear envelope reforms around each cluster of chromosomes spindles begin to break a part nucleus becomes visible in each daughter cell mitosis is complete |
front 15 Cytokinesis | back 15 Result of mitosis splitting of 1 cell into 2. |
front 16 Difference between plant and animal cells in cytokinesis? | back 16 Animal cells get furrows, and cytoplasm is eventually pinched into two equal parts. In plant cells, first a cell plate forms. Nucleus separates. Then a cell wall forms. |
front 17 Genome | back 17 All the DNA in a cell |
front 18 What is DNA packaged into? | back 18 Chromosomes |
front 19 chromatin | back 19 Complex of DNA & protein that condenses during cell division |
front 20 Somatic cells | back 20 Unreproductive cells 46 chromosomes! |
front 21 Gametes | back 21 Reproductive cells have 1/2 as many chromosomes as somatic cells they have 23 chromosomes! |
front 22 G 0 Phase | back 22 Most cells are in this phase. These cells are not replicating. Some cells never leave this phase! Like Nerve cells, heart cells. |
front 23 Aster | back 23 Array of short microtubules extends from each centrosome |
front 24 What does a Spindle include? | back 24 Centrosomes spindle microtubules the asters |
front 25 kinetochores | back 25 proteins attached to centromere that links sister chromatids to mitotic spindle part of the mitotic spindle |
front 26 What is the importance of the G1 checkpoint in Interphase? | back 26 Provides the stop / go ahead signal that tells a cell to split, or not to split. |
front 27 CDK | back 27 cyclin dependent kinase, adds phosphate to a protein), along with cyclins, are major control switches for the cell cycle, causing the cell to move from G1 to S or G2 to M. |
front 28 What are the 2 types of regulatory proteins involved in cell cycle control? | back 28 Cyclin & Cyclin-dependent kinases (cdks) (this is an enzyme) |
front 29 MPF (maturation-promoting factor) is a cyclin-cdk complex that triggers a cells passage from ___ to ___ phase | back 29 from G2 phase to M phase. |
front 30 HeLa Cells | back 30 cancer cells from Henrietta that never stop replicating. They are used in research |
front 31 What enables a cancer cell to grow? | back 31 It does not receive any signals to stop. It is uncontrollable regulation. |
front 32 How do prokaryotes reproduce? | back 32 binary fission |
front 33 binary fission | back 33 cell division in prokaryotes the chromosome replicates and then 2 daughter chromosomes actively move apart. the plasma membrane pinches inward, dividing the cell in 2 |
front 34 genetics | back 34 the scientific study of heredity and variation |
front 35 heredity | back 35 the transmission of traits from one generation to the next |
front 36 variation | back 36 is demonstrated by the differences in appearance that offspring show from parents and siblings |
front 37 locus | back 37 a gene's specific location on a certain chromosome |
front 38 gametes | back 38 reproductive cells (sperm & egg) Gametes are Haploid! (23 chromosomes) |
front 39 asexual reproduction | back 39 a single individual passes genes to its offspring without the fusion of gametes |
front 40 life cycle | back 40 the generation to generation sequence of stages in the reproductive history of an organism *males are always in life cycle. females exit at menopause From conception to time one reproduces! |
front 41 How many pairs of chromosomes do human somatic cells have? | back 41 23 pairs 23 from mom & 23 from dad |
front 42 homologous chromosomes | back 42 the two chromosomes in each pair of somatic cells * chromosomes in a homologous pair are the same length and carry the same inheritable traits |
front 43 karyotype | back 43 ordered display of the pairs of chromosomes from a cell |
front 44 autosomes | back 44 the chromosomes in a human that are not the sex chromosomes |
front 45 diploid cell | back 45 has 2 sets of chromosomes. (2n) for humans - the diploid # is 46 (2n = 46) somatic cells are diploid |
front 46 Meiosis reduces the number of chromosome sets from ___ to ___ | back 46 diploid to haploid |
front 47 meiosis results in ___ daughter cells | back 47 4 |
front 48 reductional division | back 48 Meiosis I results in 2 haploid daughter cells with replicated chromosomes |
front 49 equational division | back 49 Meiosis II results in 4 haploid daughter cells with unreplicated chromosomes |
front 50  What phase is this? | back 50 Mitosis - Interphase |
front 51 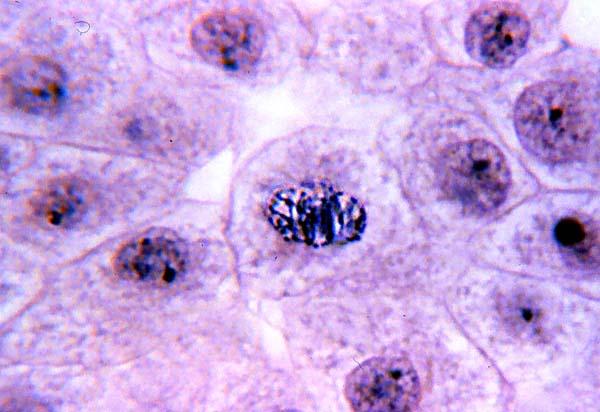 What phase is this? | back 51 Mitosis - prophase |
front 52  What phase is this? | back 52 anaphase - mitosis |
front 53  What phase is this? | back 53 metaphase - mitosis |
front 54  What phase is this? | back 54 mitosis - telophase |
front 55  What phase is this? | back 55 mitosis - cytokinesis |
front 56 What is a tetrad 4? | back 56 The homologous chromosomes in Meiosis 1, each a pair of sister chromatids, join up to form a tetrad |
front 57 chiasma | back 57 x shaped regions in Meiosis 1, where crossing over occurs |
front 58 recombinant chromatids | back 58 breaking & rejoining at the chiasma in Meiosis 1 |
front 59 In metaphase 1, ___ line up at the metaphase plate | back 59 tetrads |
front 60 Anaphase 1 separates _____ | back 60 homologous chromosomes |
front 61 At the end of meiosis there are... | back 61 4 non-identical daughter cells each with a HAPLOID set of unreplicated chromosomes |
front 62 synapsis | back 62 homologous chromosomes loosely pair up, aligned gene by gene |
front 63 What 3 events are unique to Meiosis and ALL occur in Meiosis 1? | back 63
|
front 64 When does DNA replication occur in Mitosis and Meiosis? | back 64 during interphase |
front 65 How many divisions occur in mitosis and meiosis? | back 65 Mitosis = 1 Meiosis = 2 |
front 66 How many daughter cells occur after mitosis, and what is their genetic composition? | back 66 2 - each are identical to the parent cell, with the same number of chromosomes |
front 67 How many daughter cells occur after meiosis, and what is their genetic composition? | back 67 4 - each haploid; genetically different from parent cell AND each other |
front 68 allele | back 68 is one of two or more versions of a gene. An individual inherits two alleles for each gene, one from each parent. |
front 69 What are the 3 mechanisms that contribute to genetic variation? | back 69
|
front 70 What is the independent assortment of chromosomes? | back 70
|
front 71 Crossing over produces _______ which combine DNA inherited from each parent | back 71 recombinant chromosomes |
front 72 How do the sugars in DNA pair up? (C -A - T - G) | back 72 C - G T - A |
front 73 The sugar in DNA is | back 73 deoxyribose |
front 74 The sugar in RNA is | back 74 ribose |
front 75 What are the 3 major differences between RNA & DNA | back 75 DNA: double strand, has thymine (t), and deoxyribose RNA - single strand, has uracel (u), and ribose |
front 76 How do Viruses spread? | back 76 They inject their DNA into a host cell in order to replicate and produce more. |
front 77 Chargaff's Rule | back 77 A bases = T bases & G bases = C bases |
front 78 If asked to solve a question like - A+C=T+G or A+G = T+C Then you should use hypothetical numbers for the nucleotides | back 78 Example: A = 10, Thus T = 10 C = 20, thus G = 20 Plug & Solve: A+C = T + G 10+20 = 10+20 As long as the equation equals, then the variables above work in the combination given. Example of NOT working: A+T = C+G 10+10 = 20+20 |
front 79 What kind of bonds hold DNA strands together? | back 79 hydrogen bond |
front 80 DNA pairs ___ with ____ | back 80 Purine with a pyrimidine |
front 81 DNA replication begins... | back 81 at the origin of replication It can only elongate in the 5 prime - 3 prime direction |
front 82 Replication proceeds in ____ directions from each origin until the entire molecule is copied | back 82 both |
front 83 Replication Fork | back 83 located at each end of the replication bubble. This is where new DNA strands are elongating. |
front 84 helicases | back 84 are enzymes that untwist the double helix at the replication forks |
front 85 single-strand binding proteins | back 85 bind to and stabilize single stranded DNA until it can be used as a template |
front 86 topoisomerase | back 86 corrects overwinding ahead of replication forks by breaking, swiveling, and rejoining DNA strands |
front 87 DNA can only be added to __ prime end | back 87 3 |
front 88 Primer | back 88
|
front 89 Primase | back 89 enzyme starts an RNA chain and adds RNA nucleotides one at a time using the parental DNA as a template The primer is short - and the 3' end serves as the starting point fro the new DNA strand. |
front 90 DNA Polymerases | back 90 catalyze the elongation of new DNA at a replication fork. Most require a primer & DNA template strand |
front 91 Nucleotide triphosphate | back 91 each nucleotide that is added to a growing DNA strand |
front 92 DNA can only elongate in the | back 92 5' to 3' direction BECAUSE nucleotides are added only to the free 3' end of a growing strand |
front 93 the DNA polymerase synthesizes a _______ continuously toward the replication fork. | back 93 leading strand |
front 94 to elongate the other new strand, the _____, DNA polymerase must work in the direction away from the replication fork. | back 94 lagging strand |
front 95 Okazaki fragments | back 95 synthesize the lagging strand segments which join them together through DNA Ligase |
front 96 mismatch repair of DNA | back 96 repair enzymes correct errors in base pairing |
front 97 DNA can be damaged by... | back 97 chemicals, radioactive emissions, X-rays, UV light, and certain molecules (like in cigarette smoke) |
front 98 nucleotide excision repair | back 98 a nuclease cuts out and replaces damaged stretches of DNA |
front 99 telomeres | back 99 postpone the erosion of genes near the ends of DNA *Like junk DNA, no specific coding for function *May be connected to how we age |
front 100 telomerase | back 100 enzyme that catalyzes the lengthening of telomeres in germ cells |
front 101 a chromosome consists of a _____ packed together with ____. | back 101 DNA molecule; proteins |
front 102 chromatin | back 102 complex of DNA and protein, found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells Organized in fibers |
front 103 ribosomes | back 103 They are the sites of translation. they consist of rNA and proteins. They are assemble proteins of the cell; free floating or bound |
front 104 What sugar is on RNA that is not on DNA? | back 104 Uracil |
front 105 Proteins are the links between ____ & ____. | back 105 genotype & phenotype |
front 106 genotype | back 106 genetic make up of an organism |
front 107 phenotype | back 107 observable differences of an organism determined by genetics and environmental factors |
front 108 Alleles | back 108 Alternative forms of the same gene that occupy the same location on a chromosome. *At any given locus, there are 2 (1 on each chromosome in the pair) – you get 1 a from your mother and 1 from your father. |
front 109 RNA | back 109 bridge between genes and the proteins for which the code |
front 110 What is transcription? | back 110 the synthesis of RNA, directed by DNA - this produces mRNA |
front 111 mRNA | back 111 Messenger RNA |
front 112 What is translation of RNA? | back 112 synthesis of a polypeptide from amino acids, under the direction of mRNA |
front 113 What is central dogma? | back 113 the concept that cells are governed by a cellular chain of command DNA --> RNA --> to protein |
front 114 Describe the Transcription in Prokaryotes. | back 114 DNA ---> mRNA ---> Ribosome |
front 115 Describe the Transcription process in Eukaryotic Cells | back 115 DNA ---> Pre mRNA ---> mRNA ---> leave nucleus ---> ribosome ----> then to protein |
front 116 What is involved in RNA Synthesis? | back 116 RNA synthesis is catalyzed by RNA Polymerase, which pries the DNA strands apart and hooks together the RNA nucleotides |
front 117 Promoter | back 117 The DNA sequence where RNA polymerase attaches They signal the transcriptional start point |
front 118 transcription unit | back 118 stretch of DNA that is transcribed ; a gene |
front 119 What are the 3 stages of RNA Transcription | back 119 1. Initiation 2. Elongation 3. Termination |
front 120 transcription factors | back 120 mediate the binding of RNA polymerase and the initiation of transcription |
front 121 What happens in the elongation of the RNA strand? | back 121
|
front 122 What is the termination of transcription? | back 122 Eukaryotes: the polymerase continues transcription after the pre-mRNA is cleaved from the growing RNA chain; the polymerase eventually falls off the DNA |
front 123 Why are the ends of mRNA altered? | back 123
|
front 124 How are the ends of mRNA altered? | back 124 5' cap at one end and a poly tail at the other |
front 125 RNA Splicing | back 125 removes introns and joins the exons - creating an mRNA molecule with a continuous coding sequence. [cap] - [intron] - [exon] - [intron] - [exon] - [AAAA] |
front 126 introns | back 126 junk DNA. They don't code for anything |
front 127 exons | back 127 hold the code on mRNA. Left in sequence to be read after the introns are spliced out |
front 128 spliceosomes | back 128 made of a variety of proteins & several small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs) that recognize the splice sites |
front 129 Alternative RNA Splicing | back 129 can make multiple proteins from 1 gene depending on what is spliced out of the sequence |
front 130 Ribozymes | back 130 catalytic RNA molecules that function as enzymes and can splice RNA |
front 131 Once DNA is transcribed to mRNA (messenger RNA), what are the characteristics of the instructions? | back 131
|
front 132 How are the instructions for assembling amino acids into proteins encoded in DNA? | back 132 Genetic Code |
front 133 What is a codon? | back 133 How information is ordered in RNA that is used to translate what protein should be made. Codons are grouped in 3's **determines what protein is to be made |
front 134 tRNA | back 134 Transfer RNA - brings the correct Amino Acid to the Codon |
front 135 anticodon | back 135 on the tRNA. Its the complementary to the codon on the mRNA |
front 136 How many binding sites does tRNA have? | back 136 3 P A E |
front 137 Describe the process of P A E on the tRNA | back 137 a = holds the tRNA that carries the next Amino Acid to be added to the chain p = holds the tRNA e = exit site from which tRNA leaves |
front 138 Where do free ribosomes proteins go? | back 138 they function in the cytosol |
front 139 Where do proteins go that are made in bound ribosomes? | back 139 endomembrane system OR they are secreted from the cell |
front 140 What are the types of point mutations? | back 140 1. base-pair substitutions 2. base - pair insertions or deletions |
front 141 Nucleotide - pair substitution | back 141 replaces one nucleotide and its partner with another pair of nucleotides |
front 142 silent mutations | back 142 have no effect on the amino acid produced by a codon because of the "extra" 3rd spot on the codon |
front 143 missense mutation | back 143 still code for an amino acid - but not the right one |
front 144 nonsense mutations | back 144 bad! these change the amino acid codon into a stop codon. No proteins are then made |
front 145 independent assortment | back 145 stating that when two or more characteristics are inherited, individual hereditary factors assort independently during gamete production, giving different traits an equal opportunity of occurring together. |