Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Anatomy of the veins of the trunk - Lecture 6
front 1 Describe the features and tributaries of the Superior Vena Cava (SVC) | back 1  Tributaries from R. and L.Brachiocephalic veins
Single Azygous vein tributary Begins in lower border of 1st costal cartilage and descends behind 2nd-3rd intercostal spaces into RA L.Lateral border is aortic arch and trachea R.Lateral border is pleura and right upper lobe of lung Anterior border is thymus and manubrium |
front 2 Describe the features and tributaries of the Inferior Vena Cava (IVC) | back 2 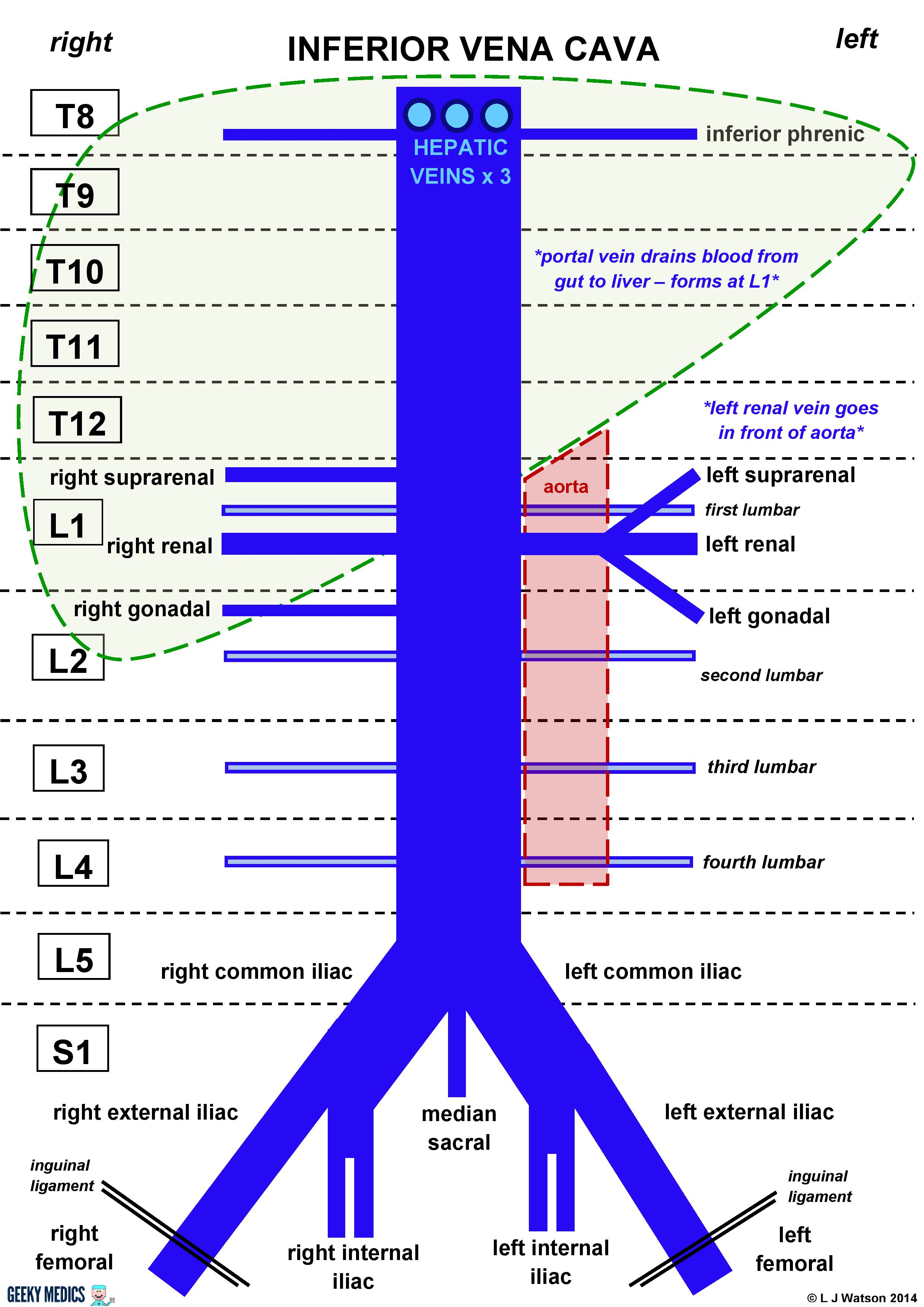 Formed by the joining of the common iliac veins at L5 Is a retroperitoneal structure - Posterior to abdominal cavity next to vertebral colum Anastomoses the azygous system on the Right side of the vertebral column Caval opening is at T8 Right side
Left side
All lumbar and hepatic veins drain into IVC Tributaries from superior to inferior
|
front 3 Describe the epigastric veins, their tributaries and their relationship to the anterior abdominal wall | back 3 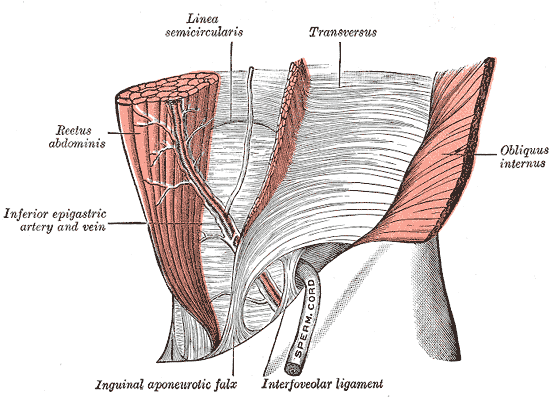 The veins accompany the arteries in the abdominal wall Superior epigastric
Both the superior and inferior anastomose with each other at the level of the umbilicus, and with paraumbilical veins Inferior epigastric vein
|
front 4 Describe the azygous system, its function and the relation to the SVC | back 4  The azygous or hemiazygous vein arise from the ascending lumbar vein from the lumbar veins and lateral sacral vein that come from the common iliac vein
Comprises the azygous, hemiazygous, accessory hemiazygous and the L.superior intercostal vein Function
Azygous
Hemiazygous
Accessory hemiazygous
|
front 5 List all of the veins and their tributaries of the trunk (abdomen, thorax and neck region) | back 5 
|
front 6 Describe in brief the major drainage vessels of the 3 section of the gut (fore, mid and hind) via the hepatic portal system | back 6  Foregut ~ oesophagus, duodenum, stomach
Midgut ~ Small intestine
Hindgut ~ Large intestine
|
front 7 Describe the relationship between surface/cross sectional anatomy and that truncal venous system | back 7 R.1st costal cartilage = Brachiocephalic veins become SVC Manubriosternal joint = Azygous terminates at SVC Transpyloric plane = Confluence of superior mesenteric and splenic veins L5 = Common iliac veins joint o form IVC |