Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Exercise 4 The Cell: Anatomy and Division
front 1 Organelle | back 1 A highly organized intracellular structure that performs a specific (metabolic) function for the cell. |
front 2 Cell | back 2 The basic structural and functional unit of living organisms. |
front 3 Although cells have differences that reflect their specific functions in the body, what functions do they have in common? | back 3 Growing, reproducing, and responding to a stimulus are common functioning characteristics amongst all cells. All cells can maintain their boundaries, metabolize, digest nutrients, and dispose wastes. |
front 4 Plasma membrane | back 4 external boundary of cell; regulates flow of materials into and out of the cell; site of cell signaling |
front 5 Lysosome | back 5 contains digestive enzymes of many varieties; "suicide sac' of the cell |
front 6 Mitochondria | back 6 scattered throughout the cell; major site of ATP synthesis |
front 7 Microvilli | back 7 slender extensions of the plasma membrane that increase its surface area |
front 8 Inclusions | back 8 stored glycogen granules, crystals, pigments, and so on |
front 9 Golgi apparatus | back 9 membranous system consisting of flattened sacs and vesicles; packages protein for export |
front 10 Nucleus | back 10 control center of the cell; necessary for cell division and cell life |
front 11 Centrioles | back 11 two rod-shaped bodies near the nucleus; direct formation of the mitotic spindle |
front 12 Nucleolus | back 12 dense, darkly staining nuclear body; packaging site for ribosomes |
front 13 Microfilaments | back 13 contractile elements of the cytoskeleton |
front 14 Rough ER or endroplasmic reticulum | back 14 membranous system; involved in intracellular transport of proteins and synthesis of membrane lipids |
front 15 Ribosomes | back 15 attached to membrane systems or scattered in the cytoplasm; synthesize proteins |
front 16 Chromatin or Chromatin threads | back 16 threadlike structure in the nucleus; contain genetic material (DNA) |
front 17 Peroxisome | back 17 site of free radical detoxification |
front 18 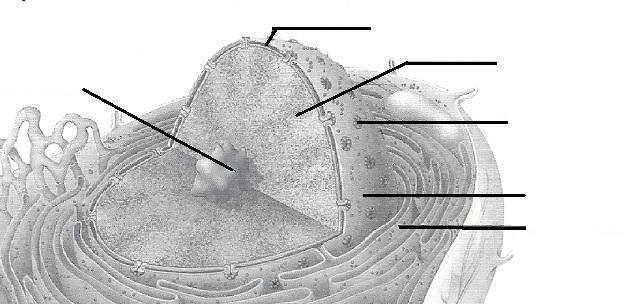 | back 18 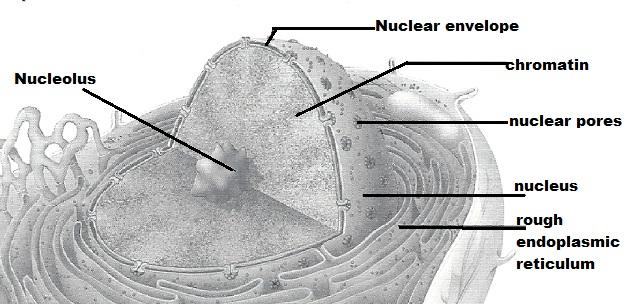 |
front 19 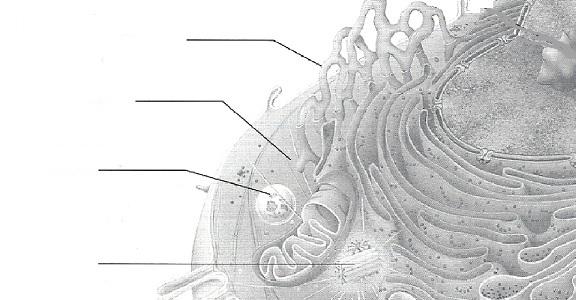 | back 19 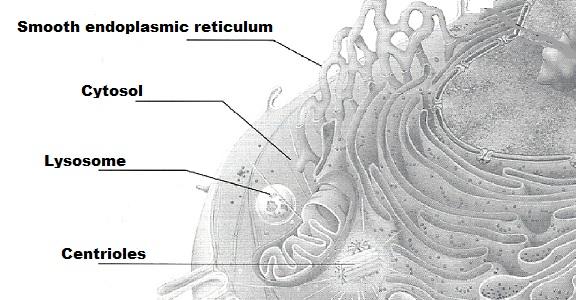 |
front 20 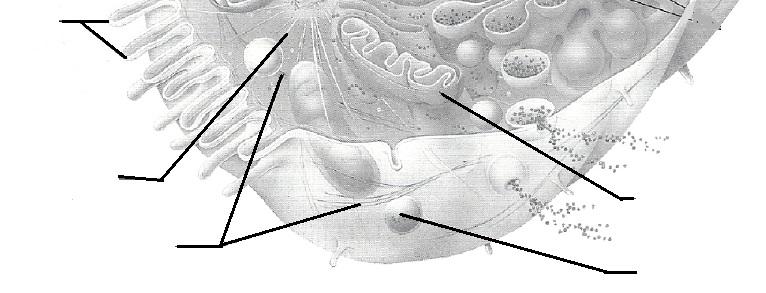 | back 20 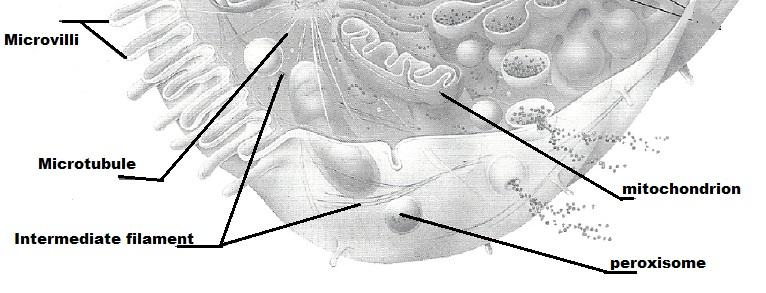 |
front 21 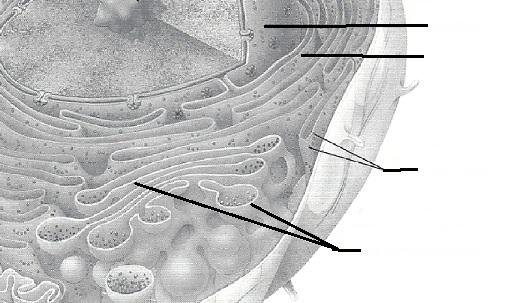 | back 21 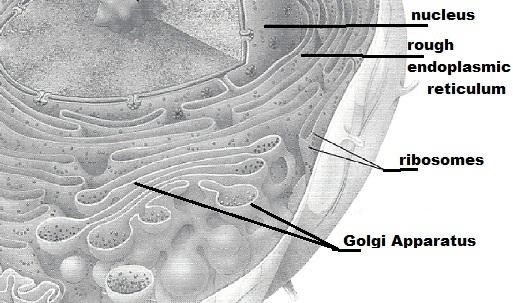 |
front 22 For each of the following cell types, list (a) one important
structural characteristic observed in the laboratory, and (b) the
function that the structure complements or ensures. | back 22 squamous epithelium tissue |
front 23 For each of the following cell types, list (a) one important
structural characteristic observed in the laboratory, and (b) the
function that the structure complements or ensures. | back 23 sperm |
front 24 For each of the following cell types, list (a) one important
structural characteristic observed in the laboratory, and (b) the
function that the structure complements or ensures. | back 24 smooth muscle |
front 25 For each of the following cell types, list (a) one important
structural characteristic observed in the laboratory, and (b) the
function that the structure complements or ensures. | back 25 red blood cells |
front 26 What is the significance of the red blood cell being anucleate (without a nucleus)? | back 26 The red blood cell(RBC) does not have a nucleus. The lack of a nucleus enables the RBC to have more room to contain hemoglobin which increases its efficiency to carrying oxygen. |
front 27 Red Blood Cell: | back 27 They did have a nucleus . When they are formed in the bone-marrow, they contain a nucleus, but when the become mature it is replaced by hemoglobin in order to carry more oxygen. |
front 28 Of the four cells observed microscopically (squamous epithelial cells, red blood cells, smooth muscle cells, and sperm) which has the smallest diameter? ________ Which is longest? _________ | back 28 smallest: RBC |
front 29 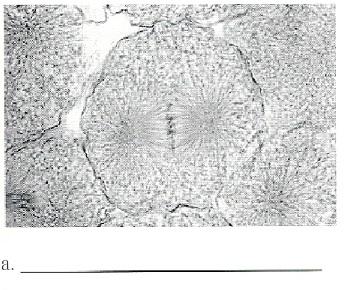 | back 29 Metaphase |
front 30 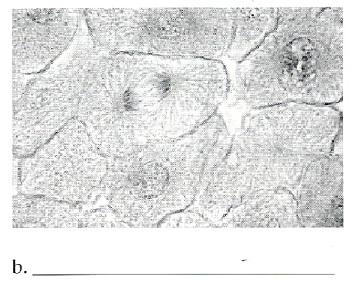 | back 30 Anaphase |
front 31 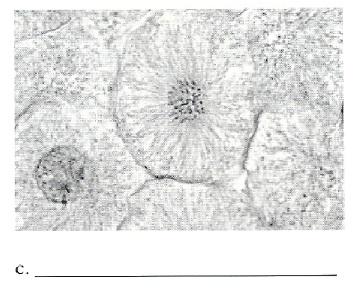 | back 31 Prophase |
front 32 What is the importance of mitotic cell division? | back 32 The importance of mitotic cell division is to make a greater amount of cells for repair and growth while maintaining the same genetic makeup. |
front 33 Division of the __1__ is referred to as mitosis. Cytokinesis is division of the __2__. The major structural difference between chromatin and chromosomes is that the latter are __3__. Chromosomes attach to the spindle fibers by undivided structures called __4__. | back 33 1. Nucleus |
front 34 If a cell undergoes mitosis but not cytokinesis, the product is __5__. The structure that acts as a scaffolding for chromosomal attachment and movement is called the __6__. __7__ is the period of cell life when the cell is not involved in division. Two cell populations in the body that do not routinely undergo cell division are __8__ and __9__. | back 34 5. A binucleate cell or multinucleated cell |
front 35 Interphase | back 35 - Centrioles replicate - DNA synthesis occurs |
front 36 Prophase | back 36 - Chromatin coils and condenses, forming chromosomes - The nuclear envelope fragments - The mitotic spindle forms - Chromosomes first appear to be duplex structures - Chromosomal centromeres are attached to the kinetochore fibers |
front 37 Metaphase | back 37 - Chromosomes line up in the center of the cell |
front 38 Anaphase | back 38 - The chromosomes are v-shaped |
front 39 Telophase | back 39 - Cleavage furrow forms - The nuclear envelope re-forms - Chromosomes stop moving toward the poles |
front 40 Anaphase and Metaphase | back 40 - The nuclear envelope is absent |
front 41 What is the physical advantage of the chromatin coiling and condensing to form short chromosomes at the onset of mitosis? | back 41 Short, compact bodies easier to manipulate during mitosis rather than long, thin chromatin threads. |