Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels
front 1 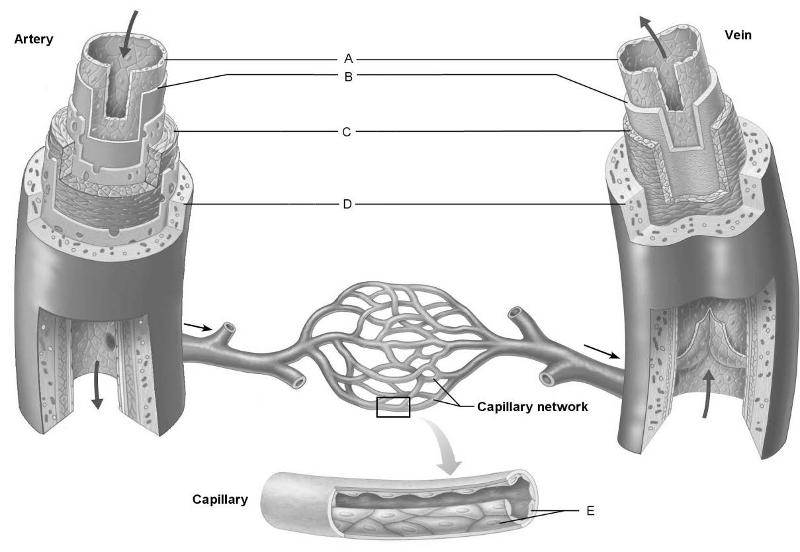 Identify the letter that indicates the layer common to all blood
vessels regardless of their size. | back 1 A |
front 2 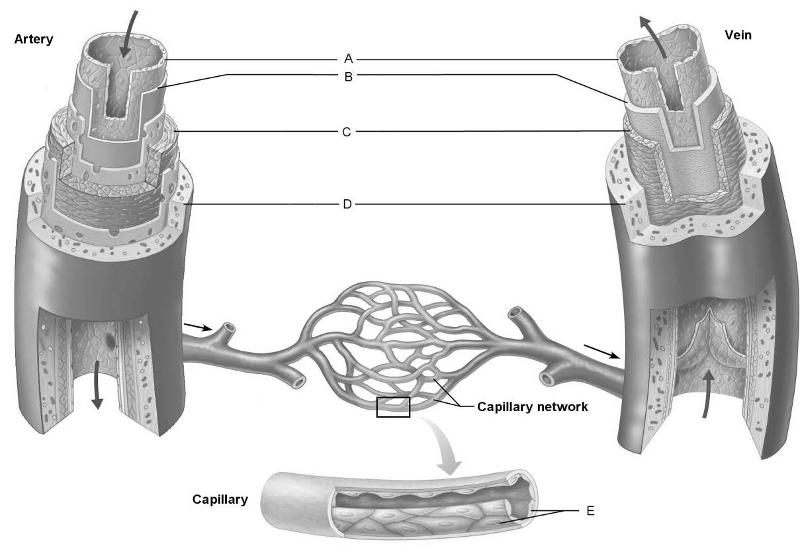 Identify the letter that is indicating endothelial cells. | back 2 E |
front 3 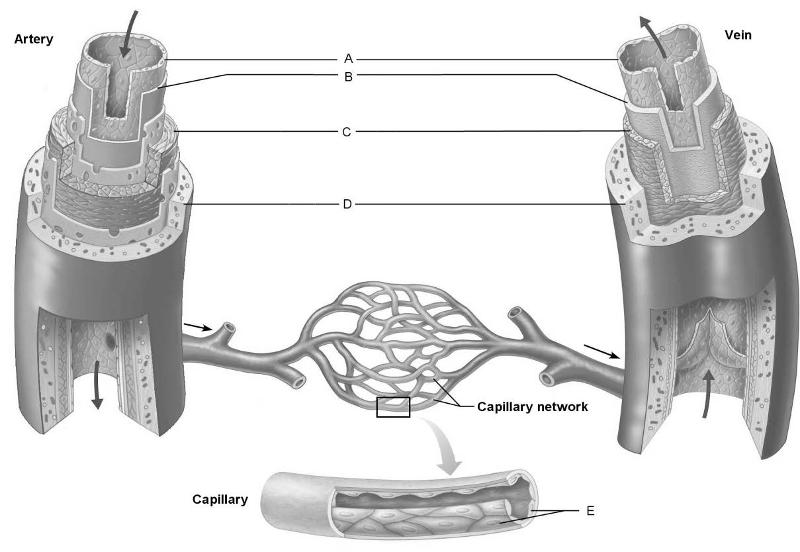 Identify the letter that indicates a connective tissue layer
consisting of longitudinal collagen | back 3 D |
front 4 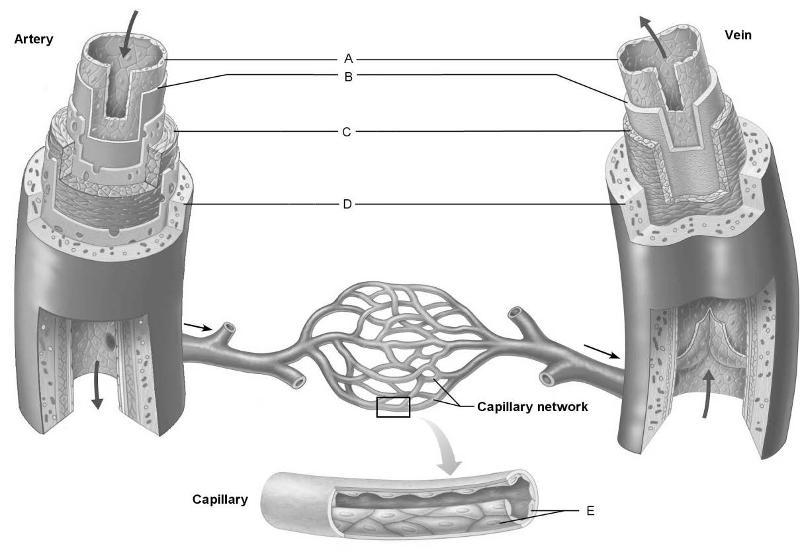 Identify the letter that indicates the blood vessel layer that is
comprised of circular and | back 4 C |
front 5 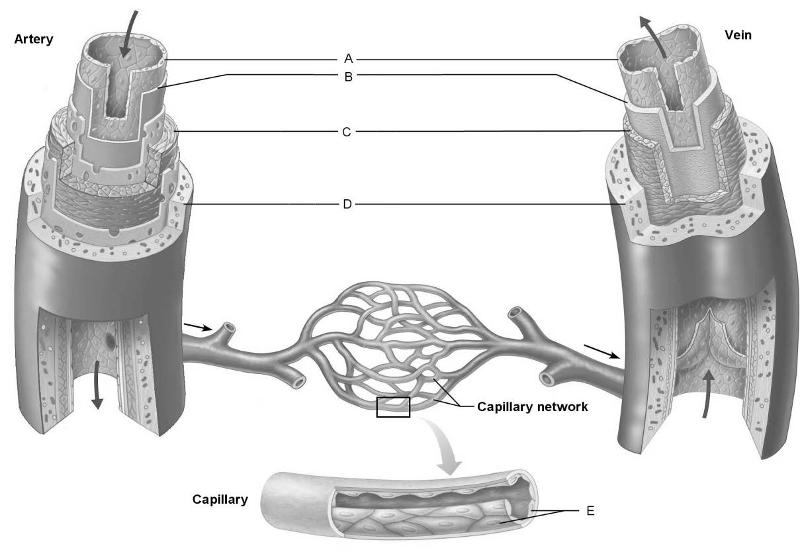 Identify the letter that indicates the subendothelial layer
associated with larger blood vessels. | back 5 B |
front 6 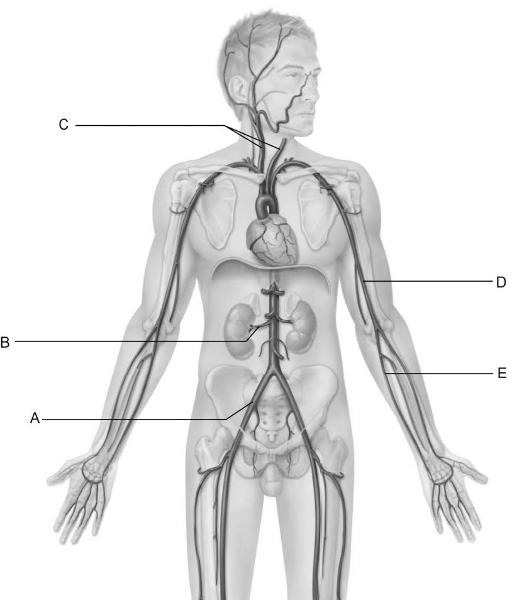 Identify the letter that indicates the common carotid
arteries. | back 6 C |
front 7 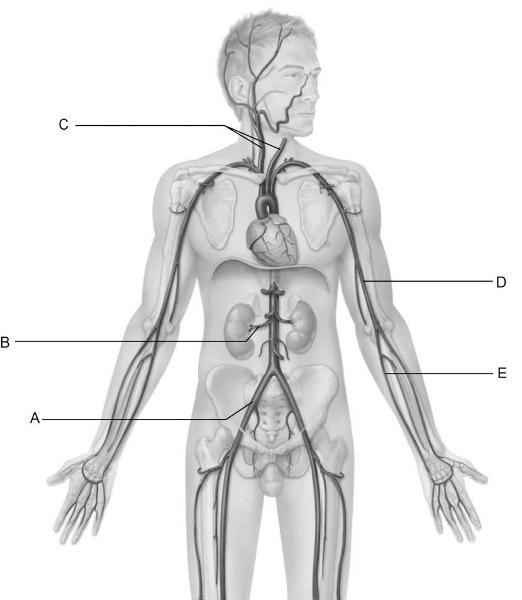 dentify the letter that indicates the common iliac artery. | back 7 A |
front 8 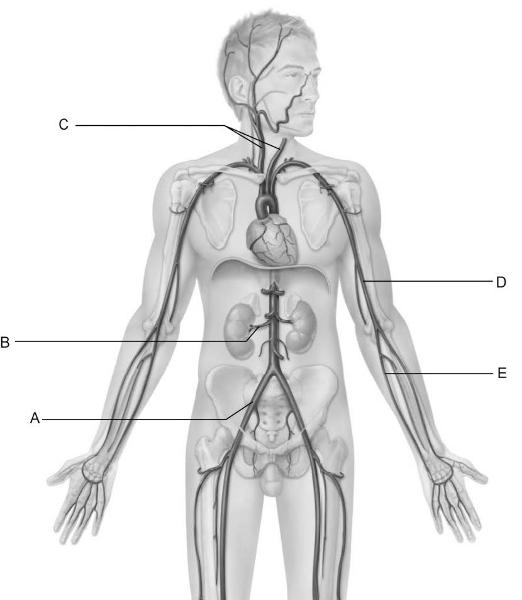 Identify the letter that indicates the brachial artery. | back 8 D |
front 9 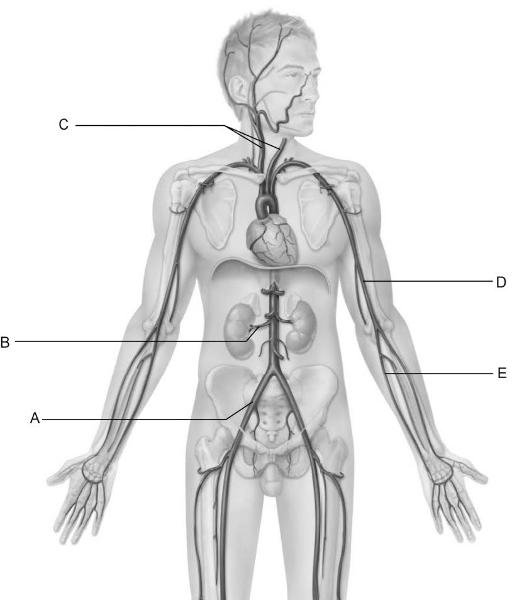 Identify the letter that indicates the renal artery as it branches
from the Abdominal aorta. | back 9 B |
front 10 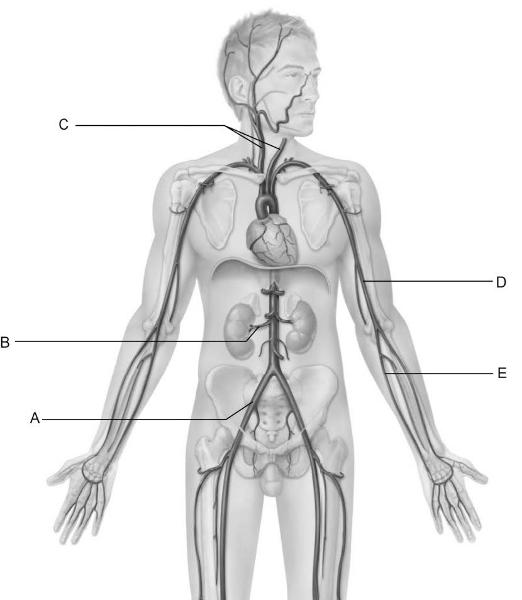 Identify the letter that indicates one of the primary arteries that
contributes to the superficial | back 10 E |
front 11 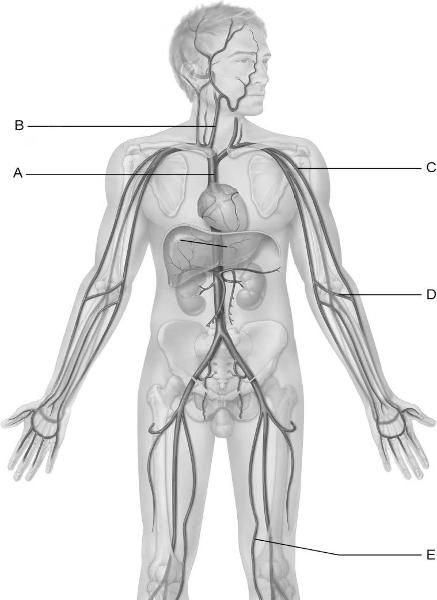 Identify the letter that indicates the vessel that is easy to find in
most people and is used to | back 11 D |
front 12 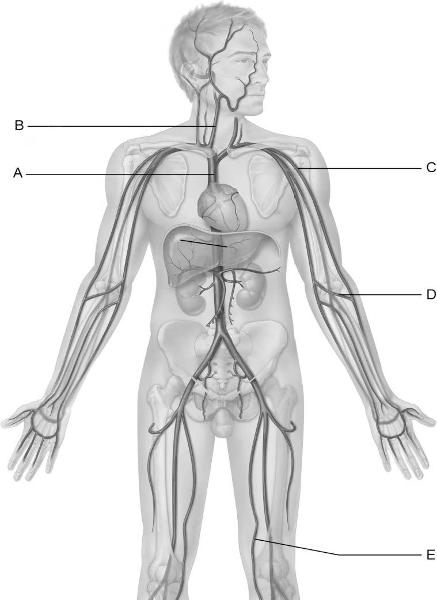 Identify the letter that indicates the longest vein in the
body. | back 12 E |
front 13 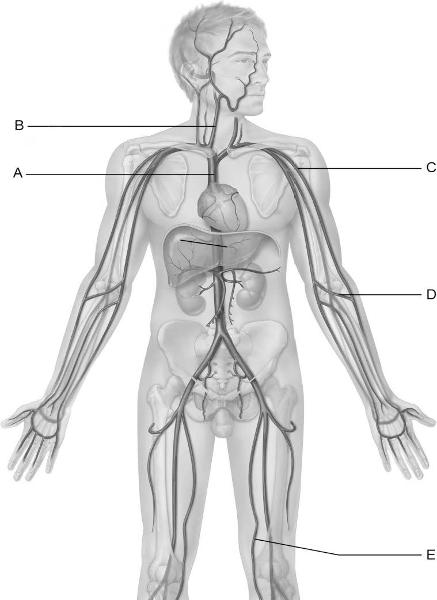 Identify the letter that indicates the vessel that arises from the
union of the left and right | back 13 A |
front 14 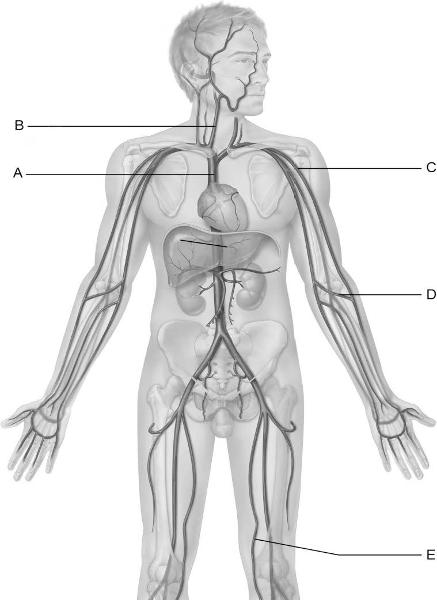 Identify the letter that indicates the cephalic vein. | back 14 C |
front 15 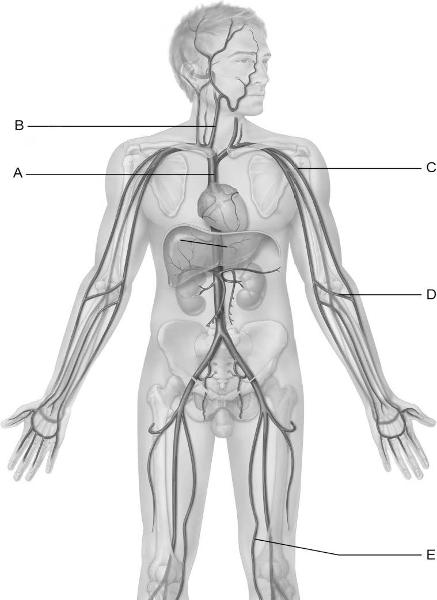 Identify the letter that indicates the internal jugular vein. | back 15 B |
front 16 Layer of blood vessels innervated by sympathetic vasomotor
fibers. | back 16 C |
front 17 Capillaries consist of only this layer. | back 17 A |
front 18 Structure that regulates blood flow into true capillaries. | back 18 C |
front 19 Wide leaky capillaries found in bone marrow and spleen. | back 19 A |
front 20 A "coming together" of alternate pathways of blood
vessels. | back 20 D |
front 21 Precapillary sphincters allow blood to leave this structure and enter
true capillaries. | back 21 D |
front 22 Collective name for the structures that drain the cranium. | back 22 B |
front 23 Present in most capillaries, these structures are absent in those of
the blood-brain barrier. | back 23 D |
front 24 Vessels of the small intestines, renal glomerulus, and synovial
membranes that allow passage | back 24 B |
front 25 Microvasculature that provides nourishment to the outer walls of the
aorta. | back 25 E |
front 26 Which layer of blood vessels contains smooth muscle tissue? | back 26 B |
front 27 Most small molecules pass through a capillary wall through which
route? | back 27 C |
front 28 Functionally, there are no valves in arteries (as opposed to in
veins) because | back 28 D |
front 29 29) Blood pressure is highest in the | back 29 A |
front 30 The hepatic portal system has two distinct capillary beds separated
by a portal vein. What are | back 30 A |
front 31 The pulse of the facial artery is palpated | back 31 B |
front 32 A blood vessel that ranges from 0.3 mm to about 1 cm in diameter and
has a large tunica | back 32 B |
front 33 In a capillary bed, relaxation of the precapillary sphincters causes
more blood to flow | back 33 C |
front 34 The dorsalis pedis artery is located by | back 34 B |
front 35 What artery enters the skull through the foramen spinosum and
supplies the inner surface of | back 35 C |
front 36 Two large (wide) arteries that have relatively superficial locations
and are often wounded are | back 36 D |
front 37 If a physician cannot feel a pulse in the popliteal fossa, the
________ artery is most likely | back 37 B |
front 38 Of the following, the only unpaired dural sinus is the | back 38 B |
front 39 Which vessel is missing in the following statement? "Tracing
venous blood from the inferior | back 39 A |
front 40 The foramen ovale in the heart normally closes | back 40 C |
front 41 Which vessel is most commonly used to bypass a damaged coronary
artery in coronary | back 41 B |
front 42 What vessel in the fetus connects the pulmonary trunk to the aortic
arch so that most of the | back 42 C |
front 43 Which of the following statements about arteries is false? | back 43 C |
front 44 Which branch (or branches) of the abdominal aorta supplies the
stomach? | back 44 A |
front 45 The cerebral arterial circle forms a loop around which
structures? | back 45 D |
front 46 The abdominal aorta divides at its distal end into which
arteries? | back 46 D |
front 47 Which of the following is most likely to become a varicose
vein? | back 47 B |
front 48 Fenestrated capillaries | back 48 B |
front 49 The correct proximal to distal sequence of the three vessels
branching from the aortic arch is | back 49 A |
front 50 What prevents the backflow of blood in veins? | back 50 A |
front 51 The largest molecules that pass through the walls of typical
capillaries are thought to use | back 51 B |
front 52 The internal carotid artery branches to form the | back 52 A |
front 53 Most systemic venous blood is both oxygen-poor and nutrient-poor.
However, systemic | back 53 C |
front 54 The ________ delivers arterial blood to the rotator cuff muscles and
thyroid gland. | back 54 C |
front 55 The diameter of a typical capillary is similar to that of | back 55 C |
front 56 Which of the following statements about arterioles is false? | back 56 D |
front 57 Systemic venous blood that is oxygen-poor but contains the lowest
concentration of | back 57 A |
front 58 A preferred site to insert intravenous catheters is into the | back 58 B |
front 59 Which artery arises from the inferior part of the abdominal aorta and
supplies the distal half | back 59 D |
front 60 The main arteries of the sole of the foot—the medial and lateral
plantar arteries—arise | back 60 A |
front 61 A dural sinus that contains a major artery and some cranial nerves
within it is the | back 61 C |
front 62 Which vessel is missing from the following statement? "Tracing
blood that drains from the | back 62 C |
front 63 In the adult, the hepatic portal system carries nutrients absorbed
from the digestive tract to | back 63 C |
front 64 The right suprarenal and gonadal veins drain into the inferior vena
cava, whereas the left | back 64 D |
front 65 By definition, veins are | back 65 A |
front 66 Which body tissues lack capillaries? | back 66 C |
front 67 Which arteries connect the basilar artery and the internal carotid
artery forming the posterior | back 67 B |
front 68 The extensor muscles of the forearm are supplied by which
artery? | back 68 B |
front 69 The lumbar veins drain the inferior posterior abdominal wall and
direct oxygen-poor blood | back 69 D |
front 70 Which of the following is not a branch of the celiac trunk? | back 70 C |
front 71 The right gonadal vein drains into the | back 71 A |
front 72 The circulatory route that runs from the digestive tract to the liver
is called | back 72 C |
front 73 Blood passing through the fetal ductus arteriosus bypasses
the | back 73 A |
front 74 All types of blood vessels contain a tunica intima. A) True B) False | back 74 A |
front 75 All arteries carry oxygen-rich blood, whereas veins carry oxygen-poor blood. A) True B) False | back 75 B |
front 76 Systemic blood pressure is regulated by adjusting the diameter of arterioles. A) True B) False | back 76 A |
front 77 In metabolically active tissues, blood is present in metarterioles,
and precapillary sphincters A) True B) False | back 77 B |
front 78 Postcapillary venules function much like true capillaries. A) True B) False | back 78 A |
front 79 The pulse of the posterior tibial artery is palpated behind the knee. A) True B) False | back 79 B |
front 80 Veins have less elastin in their walls than do arteries. A) True B) False | back 80 A |
front 81 Arterioles and venules have a vasa vasorum to provide nutrients to
their outer walls, whereas A) True B) False | back 81 B |
front 82 The middle and posterior cerebral arteries are connected by the
posterior communicating A) True B) False | back 82 A |
front 83 The internal iliac arteries supply blood both to the pelvic organs and to the lower limbs. A) True B) False | back 83 A |
front 84 The inferior vena cava ascends on the left side of the vertebral
bodies and to the left of the A) True B) False | back 84 B |
front 85 Muscular arteries regulate blood flow to organs and groups of organs. A) True B) False | back 85 A |
front 86 The elastic arteries are the largest arteries near the heart. A) True B) False | back 86 A |
front 87 The saphenous vein is not paired with an artery with the same name. A) True B) False | back 87 A |
front 88 Paired fetal umbilical veins carry blood from the fetus to the
placenta, whereas the unpaired A) True B) False | back 88 B |