Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Cardiovascular System: The Heart
front 1 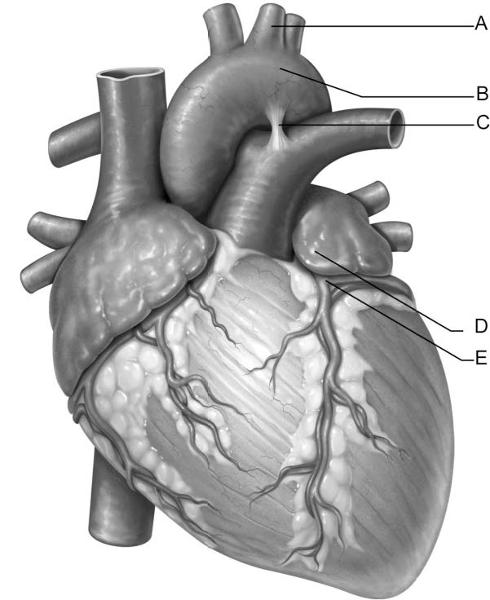 Identify the letter that indicates the left common carotid
artery. | back 1 A |
front 2 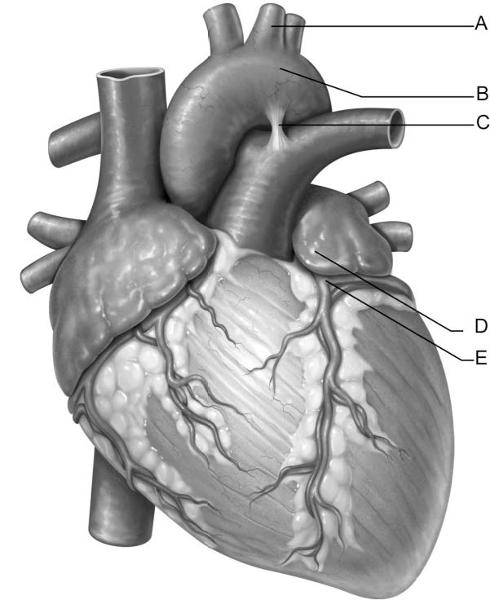 Identify the letter that indicates the left auricle. | back 2 D |
front 3 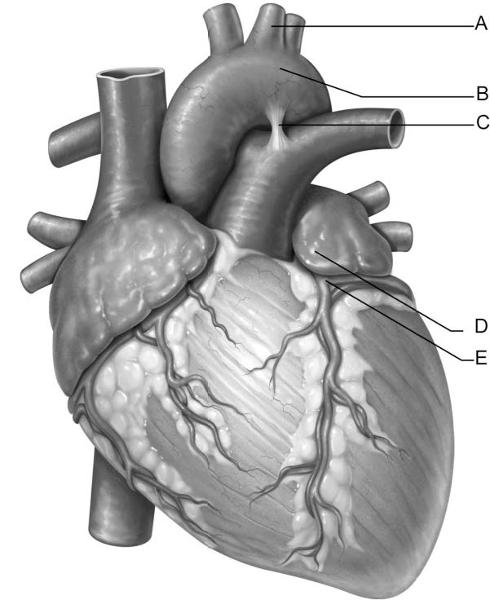 Identify the letter that indicates the ligamentum arteriosum. | back 3 C |
front 4 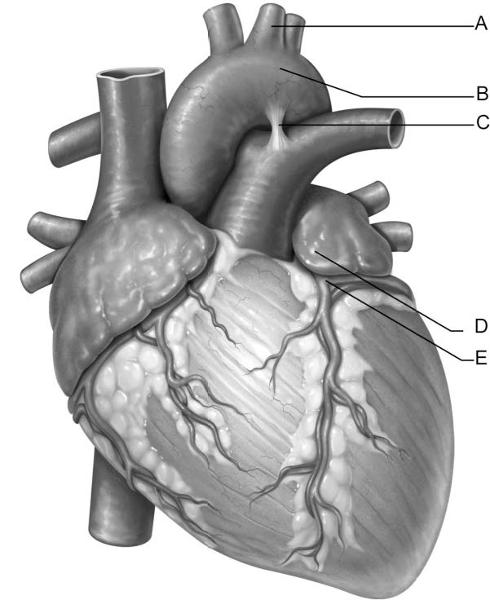 Identify the letter that indicates the left coronary artery. | back 4 E |
front 5  Identify the letter that indicates the aortic arch. | back 5 B |
front 6 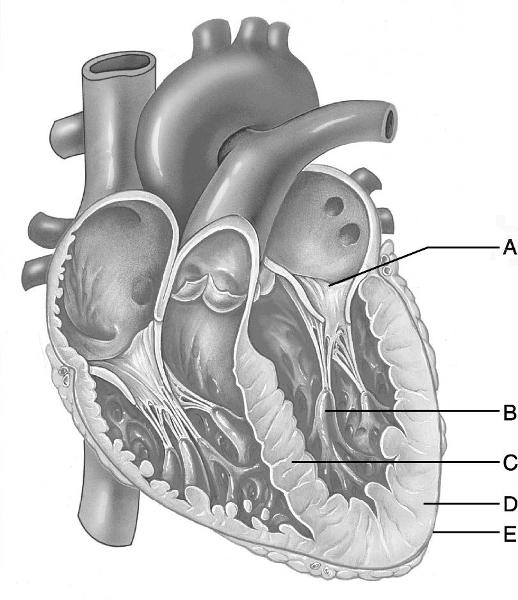 Identify the letter that indicates anchor points for chordae
tendineae, comprised of cells from | back 6 B |
front 7 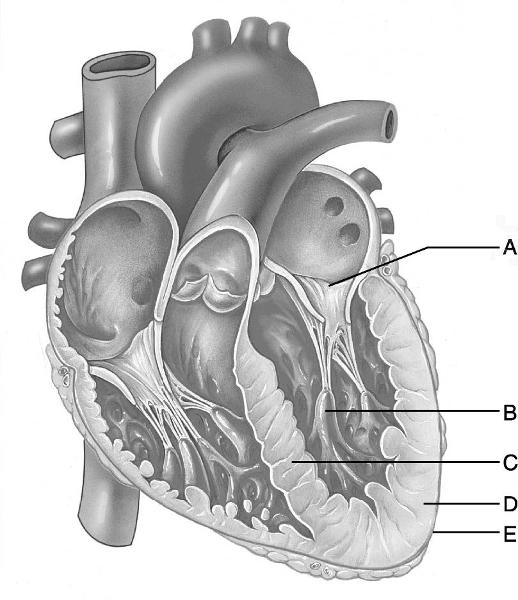 Identify the letter that indicates the tissue layer of the heart
known as the epicardium. | back 7 E |
front 8 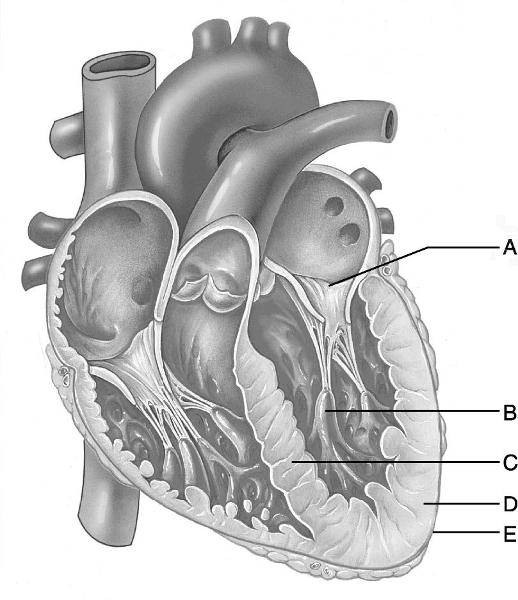 Identify the letter that indicates the left atrioventricular
valve. | back 8 A |
front 9 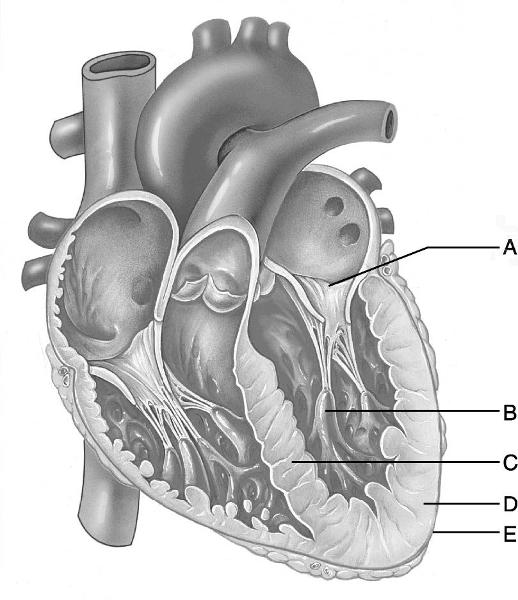 Identify the letter that indicates the location of the bundle
branches. | back 9 C |
front 10 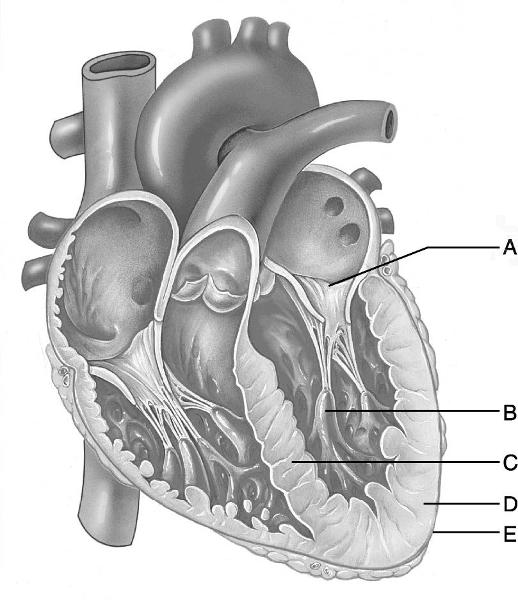 Identify the letter that indicates the thicker myocardial layer of
the left ventricle. | back 10 D |
front 11 The region between the right and left pleural cavities is the | back 11 E |
front 12 The accumulation of pericardial fluid due to inflammation or the
accumulation of blood in | back 12 C |
front 13 The heart chamber that receives oxygenated blood from the pulmonary
veins. | back 13 C |
front 14 The heart chamber that receives blood from the superior vena cava,
inferior vena cava, and | back 14 A |
front 15 The internal C-shaped crest of the right atrium which indicates the
openings for the Superior | back 15 B |
front 16 Threadlike structures of the endocardium that prevent prolapse of the
atrioventricular valves. | back 16 D |
front 17 The valve responsible for preventing backflow of blood from the lungs
into the heart. | back 17 D |
front 18 Heart valve with two cusps. | back 18 A |
front 19 Contraction of these structures tightens the chordae tendineae,
preventing valve prolapse. | back 19 D |
front 20 Cells of the conducting system located between the AV node and bundle
branches. | back 20 E |
front 21 Large cardiac cells of the conducting system embedded in the
ventricular walls between the | back 21 C |
front 22 Parasympathetic impulses to the SA node are transmitted on this
cranial nerve. | back 22 C |
front 23 Coronary artery that supplies the left atrium. | back 23 A |
front 24 Death of heart musculature due to lack of oxygen. | back 24 D |
front 25 The pericardial cavity lies between | back 25 B |
front 26 How did the sinoatrial (SA) node most likely get its name? | back 26 D |
front 27 The inner endothelial layer that lines the heart is the | back 27 D |
front 28 Which of the following vessels does not carry oxygen-poor blood to
the heart? | back 28 C |
front 29 The superior corner of the right atrium of the heart is located at
the | back 29 B |
front 30 The auricles are | back 30 B |
front 31 What structures anchor the chordae tendineae? | back 31 B |
front 32 Which structure develops from the embryological chamber called the
bulbus cordis? | back 32 B |
front 33 Which of the following structures is not found in the left
ventricle? | back 33 A |
front 34 The right ventricle pumps blood into which vessel? | back 34 C |
front 35 A drop of blood returning to the heart from the head region would
enter the heart through | back 35 C |
front 36 The cusps of the valves of the heart are covered by | back 36 C |
front 37 Semilunar valves are located | back 37 B |
front 38 A condition in which the ventricles are unable to pump blood
efficiently because of rapid, | back 38 B |
front 39 At which corner point of the heart does one listen for the sound of
the closing aortic | back 39 A |
front 40 What is the effect of the parasympathetic fibers carried by the vagus
nerve? | back 40 C |
front 41 The crista terminalis can be used to locate all of the following
structures except the | back 41 C |
front 42 Which vessel returns most of the venous blood from the heart to the
right atrium? | back 42 B |
front 43 During ventricular systole, blood is | back 43 C |
front 44 Blood within the pulmonary veins returns to the | back 44 B |
front 45 Blood is carried to capillaries in the myocardium by way of
the | back 45 C |
front 46 Which of the following veins does not deliver blood directly to the
right atrium? | back 46 D |
front 47 The desmosome-like structures that attach adjacent cardiac muscle
cells are called | back 47 A |
front 48 Oxygen-poor blood returns to the heart and enters the | back 48 A |
front 49 Which structure develops from the embryological chamber called the
sinus venosus? | back 49 A |
front 50 The small cardiac vein is present on the | back 50 A |
front 51 The epicardium is the same as the | back 51 A |
front 52 A specific coronary vessel that lies in the anterior interventricular
sulcus is the | back 52 A |
front 53 The artery that nourishes the walls of the left atrium is the | back 53 B |
front 54 The heart chamber with the thickest wall is the | back 54 D |
front 55 A specific coronary vessel that lies in the coronary sulcus is
the | back 55 B |
front 56 The heart chamber that pumps oxygenated blood around the systemic
circuit is the | back 56 D |
front 57 If the beating heart makes a "lub-dup" sound, the
"dup" sound is caused by | back 57 D |
front 58 The base of the aorta derives from which of these
"original" heart chambers in the embryo? | back 58 D |
front 59 Destruction of which structure will result in electrical signals
traveling to only one ventricle? | back 59 B |
front 60 Clinically, the posterior interventricular artery is referred to as
the | back 60 C |
front 61 Of the three layers of the heart wall, the layer that contains the
cardiac muscle is the | back 61 C |
front 62 Cells of the subendocardial conducting network | back 62 A |
front 63 There is a foramen ovale in the skull and another one in the heart.
The foramen ovale in the | back 63 C |
front 64 Insertion of a stent to treat coronary artery disease (CAD) | back 64 C |
front 65 Pericarditis can lead to all of the following except | back 65 D |
front 66 The "heartstrings" are | back 66 B |
front 67 The semilunar valves are closed when | back 67 B |
front 68 The atrioventricular node is located in the | back 68 B |
front 69 Of the following heart chambers, which is most affected by
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy? | back 69 C |
front 70 The left ventricular wall of the heart is thicker than the right
ventricular wall so that it can | back 70 C |
front 71 During left ventricular systole, blood exits the heart to enter
the | back 71 A |
front 72 To listen for the aortic semilunar valve on the chest wall, one would
place the stethoscope in | back 72 A |
front 73 Which of the following statements about fetal heart development is
false? | back 73 A |
front 74 The tricuspid valve is closed | back 74 D |
front 75 Which of the following is not an age-related change in the
heart? | back 75 A |
front 76 In the pericardial sac, the ________ lies directly deep to the
fibrous pericardium. | back 76 C |
front 77 This blood vessel is located in the anterior interventricular
sulcus. | back 77 B |
front 78 The cardiac centers that control heart rate are located in
the | back 78 B |
front 79 Sounds of the aortic valve are heard in the second intercostal space at the right sternal margin. A) True B) False | back 79 A |
front 80 The correct sequence of heart wall layers from superficial to deep is
epicardium, endocardium, A) True B) False | back 80 B |
front 81 Heart block interferes with the ability of the ventricles to receive
the pacing impulses of the A) True B) False | back 81 A |
front 82 Papillary muscles are horizontal ridges in the walls of the atrium. A) True B) False | back 82 B |
front 83 Formation of the interatrial and interventricular septa occurs during
the second month of A) True B) False | back 83 A |
front 84 Prolapse of the atrioventricular valves is prevented by the chordae tendineae. A) True B) False | back 84 A |
front 85 Oxygen-rich blood returning from the lungs enters the left atrium
through two right and two A) True B) False | back 85 A |
front 86 Contraction of the heart proceeds first on the right side of the heart and second on the left. A) True B) False | back 86 B |
front 87 The middle cardiac vein lies alongside the anterior interventricular artery. A) True B) False | back 87 B |
front 88 The electrical event that begins each heartbeat occurs at the sinoatrial (SA) node. A) True B) False | back 88 A |
front 89 Contraction of the ventricles begins at the apex and proceeds superiorly. A) True B) False | back 89 A |
front 90 Parasympathetic fibers innervate the SA node, AV node, and cardiac musculature. A) True B) False | back 90 B |
front 91 The right and left coronary arteries arise from the descending aorta. A) True B) False | back 91 B |
front 92 The fibrous skeleton of the heart forces the transmission of
electrical signals from the atria to A) True B) False | back 92 A |