Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 12 Final Prep
front 1 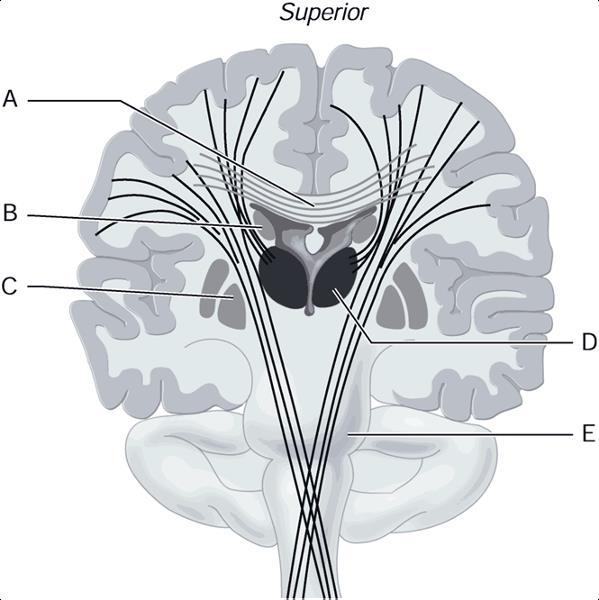 Using Figure, Match the following: 1) Pons 2) Corpus Callosum 3) Caudate Nucleus 4) Globus Pallidus 5) Thalamus | back 1 1) E 2) A 3) B 4) C 5) D |
front 2 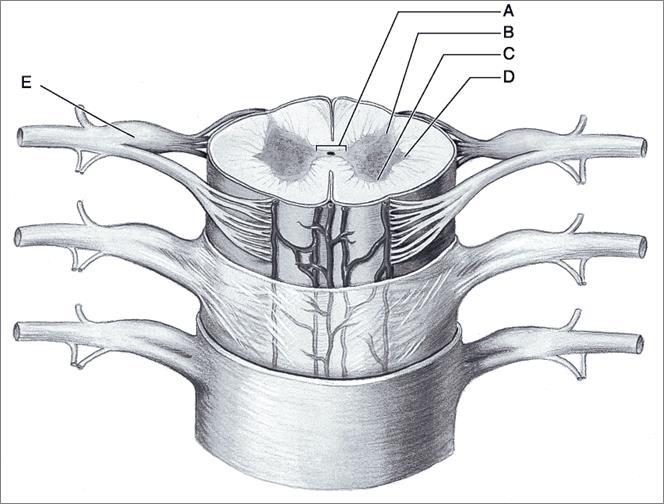 Using Figure, Match the following: 6) Site of efferent soma 7) Site of axons and afferent neurons 8) Site of sensory soma 9) Gray Commissure 10) Horn containing autonomic neurons 11) Site containing central canal 12) Multipolar neurons are common here | back 2 6) C 7) B 8) E 9) A 10) B 11) A 12) C |
front 3 Key: A) Occipital lobe B) Insula C) Temporal lobe D) Parietal lobe E) Frontal lobe 13) Auditory area 14) Primary sensory cortex 15) Somatic motor cortex 16) Motor speech area 17) Premotor area 18) Visual area 19) Taste (gustatory) area 20) Seat of intelligence, abstract reasoning | back 3 13) C 14) D 15) E 16) E 17) E 18) A 19) B 20) E |
front 4 Key: A) Primary motor cortex B) Hypothalamus C) Thalamus D) Prefrontal area 21) A major relay station for sensory information ascending to primary sensory areas of the cerebral cortex. Contains many specialized nuclei. 22) This brain area associates experiences necessary for the production of abstract ideas, judgement, and conscience. 23) The axons from this area form the major pyramidal tracts. 24) This area is the main visceral control center of the body. | back 4 21) C 22) D 23) A 24) B |
front 5 Match the following stages of sleep with their description: A) Stage 4 B) Stage 1 C) Stage 2 D) Stage 3 E) REM 25) The stage when vital signs (blood pressure, heart rate, and body temperature) reach their lowest normal levels. 26) Indicated by movement of the eyes under the lids; dreaming occurs. 27) Theta and delta waves begin to appear. 28) Very easy to awaken; EEG shows alpha waves; may even deny being asleep. 29) Typified by sleep spindles. 30) Begins about 90 minutes after the onset of sleep. 31) Necessary for emotional health, may be neural "debugging." | back 5 25) A 26) E 27) D 28) B 29) C 30) E 31) E |
front 6 Key: A) Thalamus B) Cerebrum C) Hypothalamus D) Brain stem E) Cerebellum 32) Gateway to the cerebrum 33) Motor command center 34) Survival center 35) Executive suite 36) Visceral command center | back 6 32) A 33) E 34) D 35) B 36) C |
front 7 Key: A) Cauda equine B) Conus medullaris C) Filum terminale D) Cervical enlargement 37) Where nerves serving the upper limbs arise. 38) Anchors the spinal cord in place. 39) Collection of nerve roots at the inferior end of the vertebral canal. 40) Point of termination of the spinal cord in an adult. | back 7 37) D 38) C 39) A 40) B |
front 8 True/False 41) NREM sleep normally exhibits four distinct stages, which appear to alternate. | back 8 True |
front 9 True/False 42) Missing | back 9 True |
front 10 True/False 43) Nuclei relating to the startle reflex are located in the corpora quadrigemina of the midbrain. | back 10 True |
front 11 True/False 44) Specific motor and sensory functions are localized in specific areas called domains, whereas memory and language have overlapping domains. | back 11 True |
front 12 True/False 45) A flat EEG is a good indication of deep sleep. | back 12 False |
front 13 True/False 46) The three basic regions of the cerebrum are the cerebral cortical gray matter, internal white matter, and the superior and inferior colliculi. | back 13 False |
front 14 True/False 47) Cell bodies of the somatic motor neurons of the spinal nerves are located in the ventral horn of the spinal cord. | back 14 True |
front 15 True/False 48) Meningitis is the most accurate term for inflammation of neurons. | back 15 False |
front 16 True/False 49) The adult spinal cord ends between L1 and L2 . | back 16 True |
front 17 True/False 50) Cerebrospinal fluid circulates within the ventricles of the brain and in the subarachnoid space. | back 17 True |
front 18 True/False 51) The terms fainting and syncope describe the same thing. | back 18 True |
front 19 True/False 52) The RAS is comprised of specific pathways primarily in the limbic system. | back 19 False |
front 20 True/False 53) Nondeclarative memories preserve the circumstances in which they are learned. | back 20 False |
front 21 True/False 54) The first obvious sign that the nervous system is forming in the embryo is the thickening of the surface ectoderm to form the neural plate. | back 21 True |
front 22 True/False 55) The left cerebral hemisphere is usually dominant. | back 22 True |
front 23 True/False 56) The limbic system acts as our emotional, or affective, brain. | back 23 True |
front 24 True/False 57) The canal connecting the third and fourth ventricles and running through the midbrain is the foramen of Monro. | back 24 False |
front 25 True/False 58) Commissural fibers connect the cerebrum to the diencephalon. | back 25 False |
front 26 True/False 59) A disturbance of posture, muscle tremors at rest, and uncontrolled muscle contraction are all symptoms of damage to the basal nuclei. | back 26 True |
front 27 True/False 60) Projection fibers in the brain mainly connect the right and left hemispheres. | back 27 False |
front 28 True/False 61) Most of the ascending and descending pathways to and from the brain cross over from one side of the body to the other. | back 28 True |
front 29 True/False 62) The primary visual cortex contains a map of visual space. | back 29 True |
front 30 True/False 63) One functional center found within the medulla oblongata is a respiratory center involved in the control of the rate and depth of breathing. | back 30 True |
front 31 True/False 64) Sorting of sensory information and relaying it to the appropriate cerebral sensory area occurs in the hypothalamus. | back 31 False |
front 32 True/False 65) Embryonic damage to the mesencephalon could result in improper formation of the midbrain. | back 32 True |
front 33 66) Which statement about coma is true? A) Coma may be caused by widespread cerebral or brain stem trauma. B) During coma, brain oxygen consumption resembles that of a waking state. C) Coma is a form of deep sleep. D) Coma is neurologically identical to syncope. | back 33 A |
front 34 67) Which brain nucleus is the body's "biological clock"? A) Subthalamic nucleus B) Dorsomedical nucleus C) Lentiform nucleus D) Suprschiastmatic nucleus | back 34 D |
front 35 68) Nuclei of cranial nerves V, VI, and VII are found in the ___________. A) Pons B) Cerebrum C) Midbrain D) Medulla | back 35 A |
front 36 69) The arbor vitae refers to ___________. A) Flocculonodular nodes B) Cerebellar gray matter C) The pleatlike convolutions of the cerebellum D) Cerebellar white matter | back 36 D |
front 37 70) The brain stem consists of the ____________. A) cerebrum, pons, midbrain, and medulla B) pons, medulla, cerebellum, and midbrain C) midbrain, medulla, and pons D) midbrain only | back 37 C |
front 38 71) The primary auditory cortex is located in the ___________. A) Partietal lobe B) Prefrontal lobe C) Temporal lobe D) Frontal lobe | back 38 C |
front 39 72) Spinocerebellar tracts _______________. A) are found in the dorsal columns of the spinal cord. B) give rise to conscious experience of perception C) terminate in the spinal cord D) carry proprioceptive inputs to the cerebellum | back 39 D |
front 40 73) What cells line ventricles of the brain? A) ependymal cell B) astrocytes C) neurons D) epithelial cells | back 40 A |
front 41 74) The subarachnoid space lies between what two layers of meninges? A) arachnoid and dura B) arachnoid and pia C) arachnoid and epidura D) dura and epidura | back 41 B |
front 42 75) The vital centers for the control of heart rate, respiration, and blood pressure are located in the ____________. A) Medulla B) Cerebrum C) Midbrain D) Pons | back 42 A |
front 43 76) Cell bodies of the sensory neurons of the spinal nerves are located in ___________. A) the ventral root ganglia of the spinal cord B) sympathetic ganglia C) the dorsal root ganglia of the spinal cord D) the thalamus | back 43 C |
front 44 77) Which fissure separates the cerebral hemispheres? A) central fissure B) lateral fissure C) longitudinal fissure D) parieto-occipital fissure | back 44 C |
front 45 78) Which of the following best describes the cerebrum? A) decussation center B) executive suite C) motor command center D) visceral command center | back 45 B |
front 46 79) A shallow groove on the surface of the cortex is called a ________. A) gyrus B) furrow C) fissure D) sulcus | back 46 D |
front 47 80) Which of the following generalizations does not describe the cerebral cortex? A) Each hemisphere is chiefly concerned with sensory and motor functions of the contralateral side of the body. B) No functional area of the cortex works alone. C) The hemispheres are exactly equal in function. D) The cerebral cortex contains three kinds of functional areas. | back 47 C |
front 48 81) If the caudal portion of the neural tube failed to develop properly the ___________. A) hindbrain would not be present B) telencephalon would cease development C) cranial nerves would not form D) spinal cord may be affected | back 48 D |
front 49 82) The central sulcus separates which lobes? A) parietal from occipital B) frontal from parietal C) temporal from parietal D) frontal from temporal | back 49 B |
front 50 83) Neural tracts that convey life-saving information to the brain concerning burning pain would be ___________. A) lateral spinothalamic B) posterior spinothalamic C) anterior spinothalamic D) reticulospinal | back 50 A |
front 51 84) Which of these would you not find in the cerebral cortex? A) fiber tracts B) unmyelinated axons C) cell bodies D) dendrites | back 51 A |
front 52 85) The white matter of the spinal cord contains ____________. A) unmyelinated nerve fibers only B) myelinated nerve fibers only C) myelinated and unmyelinated nerve fibers D) soma that have both myelinated and unmyelinated nerve fibers | back 52 C |
front 53 86) Which of the following is not a role of the basal nuclei? A) controlling starting and stopping movements B) regulating attention and cognition C) inhibiting unnecessary or antagonistic movements D) initiating protective reflex actions | back 53 D |
front 54 87) An individual accidentally transected the spinal cord between T1 and L1. This would result in ___________. A) hemiplegia B) paraplegia C) quadriplegia D) spinal shock only | back 54 B |
front 55 88) Spastic paralysis suggests involvement of the _____________. A) neuromotor junction B) upper motor neurons C) lower motor neurons D) spinal nerve roots | back 55 B |
front 56 89) Ridges of tissue on the surface of the cerebral hemispheres are called ______________. A) sulci B) fissures C) ganglia D) gyri | back 56 D |
front 57 90) The frontal lobe is separated from the temporal lobe by the ________. A) cranial fossa B) longitudinal fissue C) central sulcus D) lateral sulcus | back 57 D |
front 58 91) Which of the following statements is a false or incorrect statement? A) Damage to the premotor cortex results in loss of motor skills programmed in that area but movement is still possible. B) Damage to the primary auditory cortex results in the inability to interpret pitch, loudness, and location. C) Damage to the primary motor cortex results only in the loss of both voluntary muscle control and reflexes. D) Damage to the visual association area can result in blindness. | back 58 C |
front 59 92) Two terms for the massive motor tracts serving voluntary movements are___________. A) segmental and nigrostriatal B) pyramidal and corticospinal C) extrapyramidal and rubrospinal D) supplementary and cerebellar-pontine | back 59 B |
front 60 93) An individual who could trace a picture of a bicycle with his or her finger but could not recognize it as a bicycle is most likely to have sustained damage to the ______________. A) calcarine cortex B) primary visual area C) lateral geniculate body D) visual association area | back 60 D |
front 61 94) Broca's area ___________. A) is usually found in the right hemisphere B) is considered a motor speech area C) serves the recognition of complex objects D) corresponds to Brodmann's area 8 | back 61 B |
front 62 95) Which part of the cerebral cortex in involved in intellect, cognition, recall, and personality? A) posterior association area B) combined primary somatomsensory cortex and somatosensory association cortex. C) prefrontal cortex D) limbic association area | back 62 C |
front 63 96) The blood-brain barrier is effective against _____________. A) nutrients such as glucose B) metabolic waste such as urea C) anesthetics D) alcohol | back 63 B |
front 64 97) All of the following are structures of the limbic system except the ___________. A) hippocampus B) caudate nucleus C) amygdaloid nucleus D) cingulate gyrus | back 64 B |
front 65 98) The process of linking new facts with old facts already stored in the memory bank is called _____________. A) association B) long-term memory C) rehearsal D) automatic memory | back 65 A |
front 66 99) Which category of memory is involved when playing a piano? A) motor B) declarative C) emotional D) procedural | back 66 D |
front 67 100) The brain area that regulates activities that control the state of wakefulness or alertness of the cerebral cortex is the ______________. A) thalamus B) limbic system C) reticular formation D) pyramids | back 67 C |
front 68 101) Which of the following would you not find in normal cerebrospinal fluid? A) protein B) potassium C) red blood cells D) glucose | back 68 C |
front 69 102) REM sleep is associated with _____________. A) temporary skeletal muscle inhibition except for ocular muscles and diaphragm B) decreased oxygen use, especially in the cerebral cortex C) decreased vital signs, such as heart rate and blood pressure D) decreased activity of the brain, especially the cerebral cortex | back 69 A |
front 70 103) Which of the following is not a function of the CSF? A) reduction of brain weight B) nourishment of the brain C) protection from blows D) initiation of some nerve impulses | back 70 D |
front 71 104) Injury to the hypothalamus may result in all of the following except__________. A) loss of body temperature control B) loss of proprioception C) pathologic sleep D) production of excessive quantities of urine | back 71 B |
front 72 105) Important nuclei of the indirect (multineural) system that receive impulses from the equilibrium apparatus of the inner ear and help to maintain balance by varying muscle tone of postural muscles are the __________. A) reticular nuclei B) superior colliculi C) vestibular nuclei D) red nuclei | back 72 C |
front 73 106) Which of the following structures is probably not directly involved in memory? A) hippocampus B) thalamus C) prefrontal cortex D) medulla | back 73 D |
front 74 107) The area of the cortex that is responsible for sensations of the full bladder and the feeling that your lungs will burst when you hold your breath too long is the ____________. A) gustatory cortex B) visceral sensory area C) vestibule cortex D) olfactory cortex | back 74 B |
front 75 108) Which statement about coma is true? A) Coma may be caused by widespread cerebral or brain stem trauma B) Coma is a form of deep sleep C) Coma is neurologically identical to syncope D) During coma, brain oxygen consumption resembles that of a waking state. | back 75 A |
front 76 109) Tremor at rest, shuffling gait, stooped posture, and expressionless face are characteristics of ______________. A) spinal cord disease B) Parkinson's disease C) cerebellar disease D) Huntington's disease | back 76 B |
front 77 110) Which of the following is the mildest consequence of traumatic brain injury? A) swelling B) contusion C) hemorrhage D) concussion | back 77 D |
front 78 111) Declarative memory A) usually involves motor skills B) is hard to unlearn when learned once C) is best remembered in the doing D) is the ability to learn specific information | back 78 D |
front 79 112) Which of the following is (are) involved with motor activity (either initiation or coordination)? A) red nuclei B) Wernicke's area C) postcentral gyrus D) gustatory cortex | back 79 A |
front 80 113) Which statement is not true? A) Ten year olds are in REM sleep about 1.5-2 hours per night. B) Half of infant sleep is composed of REM sleep C) Stage 4 sleep increase in old age. D) Sleep requirements decline from infancy to early adulthood, level off, then decline again in old age. | back 80 C |
front 81 114) Which statement about epilepsy is most accurate? A) Absence seizures typically begin in adolescence and is often severely disabling. B) Epilepsy is often genetically induced but also frequently caused by head trauma, stroke, infection, and tumor. C) During seizures, sensory messages are precessed normally but responses are blocked. D) The aura in tonic-clonic seizures typically occurs as the patient regains consciousness. | back 81 B |
front 82 115) White matter is found in all of the following locations except the A) Outer portion of the spinal cord B) Corpus callosum C) Corticospinal tracts D) Cerebral cortex | back 82 D |
front 83 116) Second order neurons of both the specific and nonspecific ascending pathways terminate in the ____________. A) medulla B) thalamus C) somatosensory cortex D) spinal cord | back 83 B |
front 84 117) Loss of ability to perform skilled motor activities such as piano playing, with no paralysis or weakness in specific muscles, might suggest damage to the _______________________. A) Primary motor cortex B) rubrospinal tracts C) spinal cord D) premotor cortex | back 84 D |
front 85 118) Which brain waves are not normal for awake adults but are common for children? A) Theta B) Delta C) Alpha D) Beta | back 85 A |
front 86 119) The _________ includes the thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus. | back 86 Diencepalon |
front 87 120) Which ventricle is continuous with the central canal of the spinal cord? | back 87 4th |