Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 29/30 Cell Communication Mastering AP Biology
front 1 Which of the following traits was most important in enabling the first plants to move onto land? A. The development of sporopollenin to prevent the desiccation of zygotes B. Peroxisome enzymes that minimize losses from photorespiration C. Apical meristems D. Alternation of generations E. Rings of cellulose-synthesizing complexes | back 1 A. The development of sporopollenin to prevent the desiccation of zygotes |
front 2 Which term below is the proposed kingdom that would include embryophytes and charophytes? A. Streptophyta B. Pteridophyta C. Bryophyta D. Viridiplantae E. Plantae | back 2 A. Streptophyta |
front 3 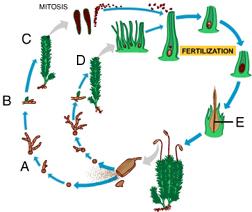 Which of these represents the sporophyte generation of the moss life cycle? A. B B. D C. C D. E E. A | back 3 D. E |
front 4 In moss, _____ produce sperm. A. Antheridia B. Sporangia C. Archegonia D. Protonemata E. Embryos | back 4 A. Antheridia |
front 5 The sperm produced by mosses require _____ to reach an archegonium. A. The development of a flower B. Wind C. Moisture D. Animals E. Eight | back 5 C. Moisture |
front 6 In mosses gametes are produced by _____; in ferns gametes are produced by _____. A. Mitosis ... mitosis B. Meiosis ... mitosis C. Binary fission ... mitosis D. Mitosis ... meiosis E. Meiosis ... meiosis | back 6 A. Mitosis ... mitosis |
front 7 The adaptation that made possible the colonization of dry land environments by seed plants is most likely the result of the evolution of _____. A. Pollen B. Cones C. Ovules D. Sporophylls E. Heterospory | back 7 A. Pollen |
front 8 All seed plants _____. A. Are heterosporous B. Exhibit a dominant gametophyte generation C. Are nonvascular D. Produce flowers E. Produce antheridia and archegonia on the same gametophyte | back 8 A. Are heterosporous |
front 9 Categories: 1. Cycads Only 2. Ginkgos Only 3. Gnetophytes Only 4. Conifers Only 5. All Gymnosperms Answers: - Redwoods - Pines - All species produce cones - Leaves have fanlike appearance - Includes three genera that vary greatly in appearance - Only one living species today - Have palmlike leaves - Undergo alternation of generations - Seeds do not form in an enclosed structure | back 9 Cycads Only: - Have palmlike leaves Ginkgos Only: - Leaves have fanlike appearance - Only have one living species today Gnetophytes Only: - Includes three genera that vary greatly in appearance Conifers Only: - Redwood - Pines - All species produce cones All Gymnosperms: - Undergo alternation of generations - Seeds do not form in an enclosed structure |
front 10 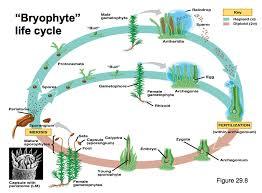 Label | back 10 a. Meiosis b. Mitosis c. Haploid d. Gametophyte e. Pollination f. Diploid g. Gametophyte h. Diploid i. Diploid j. Sporophyte Etc. Meiosis |
front 11 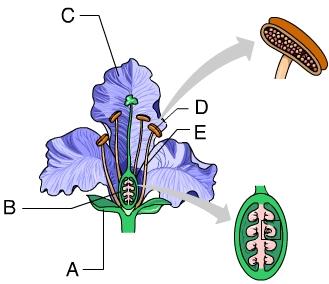 Ovules are found within structure _____. A. A B. B C. C D. D E. E | back 11 B. B |
front 12 Which of these is unique to flowering plants? A. An embryo surrounded by nutritive tissue B. Pollen production C. A dominant sporophyte generation D. Double fertilization E. Haploid gametophytes | back 12 D. Double fertilization |
front 13 The male gametophytes of flowering plants are also referred to as _____. A. Megaspores B. Endosperm C. Embryo sacs D. Male sporophytes E. Pollen grains | back 13 E. Pollen grains |
front 14 In flowering plants the integuments of the ovule develop into a(n) _____. A. Endosperm B. Sporophyte C. Fruit D. Seed coat E. Cotyledon | back 14 D. Seed coat |
front 15 A carpel is composed of _____. A. Stigma, style, and ovary B. Zygote, anther, and endosperm C. Ovary, ovule, and anther D. Ovule, megasporocyte, and anther E. Petal, sepal, and stamen | back 15 A. Stigma, style, and ovary |
front 16 A stamen consists of _____. A. Stigma and style B. Ovary and sepal C. Anther and filament D. Stigma and filament E. Stigma and anther | back 16 C. Anther and filament |
front 17 In angiosperms, pollination is the transfer of pollen grain to the _____ of a flower on the same plant or another plant of the same species. A. Style B. Ovary C. Anther D. Ovulate cone E. Stigma | back 17 E. Stigma |
front 18 Angiosperms are most closely related to _____. A. Gymnosperms B. Green algae C. Charophyceans D. Seedless vascular plants E. Bryophytes | back 18 A. Gymnosperms |
front 19 Which of these was the dominant plant group at the time that dinosaurs were the dominant animals? A. Bryophytes B. Gymnosperms C. Angiosperms D. Seedless vascular plants E. Charophyceans | back 19 B. Gymnosperms |
front 20  This is an image of a(n) _____. A. Bryophyte B. Seedless vascular plant C. Angiosperm D. Charophycean E. Gymnosperm | back 20 D. Charophycean |
front 21 Plants evolved from green algae approximately _____ million years ago. A. 2,200 B. 130 C. 3,500 D. 400 E. 475 | back 21 E. 475 |
front 22 _____ are an example of seedless vascular plants. A. Lilacs B. Charophyceans C. Pine trees D. Ferns E. Mosses | back 22 D. Ferns |
front 23 The living plants that are most similar to the first plants to bear gametangia are the _____. A. Seedless vascular plants B. Angiosperms C. Charophyceans D. Bryophytes E. Gymnosperms | back 23 D. Bryophytes |
front 24 When you look at a pine or maple tree, the plant you see is a _____. A. Triploid endosperm B. Diploid gametophyte C. Haploid sporophyte D. Diploid sporophyte E. Haploid gametophyte | back 24 D. Diploid sporophyte |
front 25 In mosses gametes are produced by _____; in ferns gametes are produced by _____. A. Mitosis ... meiosis B. Binary fission ... mitosis C. Meiosis ... meiosis D. Meiosis ... mitosis E. Mitosis ... mitosis | back 25 E. Mitosis ... mitosis |
front 26 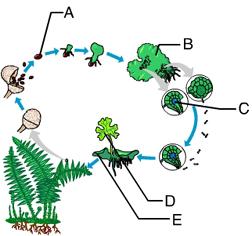 Which of these structures is diploid? A. E B. D C. B D. C E. A | back 26 B. D |
front 27 Where do fern antheridia develop? A. On the underside of the gametophyte B. On the tip of the haploid protonema C. On the tip of the sporophyte D. On the tip of the gametophyte E. On the underside of the sporophyte | back 27 A. On the underside of the gametophyte |
front 28 The conspicuous part of a fern plant is a _____. A. Haploid gametophyte B. Diploid gametophyte C. Diploid sorus D. Diploid sporophyte E. Haploid sporophyte | back 28 D. Diploid sporophyte |
front 29 Which of these characteristics is shared by algae and seed plants? A. Chloroplasts B. Embryo development within gametangia C. Vascular tissue D. Pollen E. Roots and shoots | back 29 A. Chloroplasts |
front 30 The closest algal relatives of land plants are _____. A. Chrysophytes B. Charophytes C. Rhodophytes D. Psilophytes E. Bacillariophytes | back 30 B. Charophytes |